Causes of increased uric acid
In normal concentrations, the organic substance stimulates the nervous system, the action of norepinephrine and adrenaline, and resists the malignant degeneration of cells.
Getting into the blood from the liver, after combining with carbon dioxide, it leaves the body naturally. Orthopedic doctor Andrey Sergeevich Litvinenko comments:
Depending on diet and physical activity, the level of uric acid in the blood varies. The norm for men is 419 µmol/l, for women – 349 µmol/l. Under certain factors, its excess occurs - hyperuricemia. Uric acid salts can settle in joint tissues, such as the knee joint, and provoke gouty gonarthrosis.
Pathology occurs against the background of concomitant diseases and poor nutrition. Provoking factors:
- pathologies of the liver and gall bladder - hepatitis, cholecystitis;
- impaired filtration function of the kidneys;
- problems with enzyme production;
- vitamin B 12 deficiency;
- diabetes and obesity;
- toxicosis in pregnant women;
- disturbances in alkaline balance due to infatuation with protein foods;
- dermatological abnormalities;
- taking diuretics, NSAIDs.
The accumulation of salts for a long time occurs asymptomatically, until injuries, overeating or infection activate the inflammatory process, causing gouty arthritis, etc.
What is gout on women's legs?
Under the influence of provoking factors in women, the natural processes of uric acid secretion and entry into the body are disrupted, and the level of urea in the blood increases significantly. This is due to insufficient production of estrogen, which in the female body begins during menopause. Therefore, gout most often affects women over 50 years of age with acute deficiency of the sex hormone and pathologies of the endocrine system. The main symptoms are:
- Formation of tophi (accumulation of urates in articular tissues);
- Nephrolithiasis (accumulation of urea in the kidneys with subsequent formation of stones);
- Gouty (urate) nephropathy.
Signs of gout of the knee joint
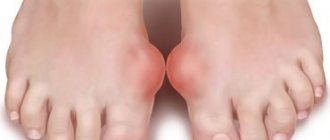
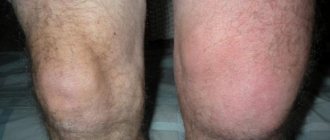
The first painful attacks are short-term. Sudden attacks often occur at night. The affected joint swells, the skin acquires a purplish hue. One of the main signs is a local increase in temperature up to 40 degrees and inflammation of the thumb. The slightest touch to the inflamed area causes unbearable pain. After a few days, the pain disappears without a trace.
Over the course of 1-8 months, everything repeats itself: pain in the knees due to gout increases, attacks last longer, and the time between them decreases. Their occurrence is often caused by the consumption of fatty foods and alcoholic beverages. In the absence of therapeutic and diagnostic measures, the symptoms of knee gout progress. There comes a time when they take on a chronic form and affect small joints.
Basic principles of treatment of gouty arthritis of the joints
Treatment of gout in men and women should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor and with periodic urine and blood tests. It must be comprehensive and aimed at suppressing the level of uric acid, accelerating its removal from the body, and must include:
You can find out more about the symptoms and treatment methods for joint arthritis, prices, and make an appointment with our specialists by calling the numbers in the Contacts section Call! We will be happy to assist you!
- during an exacerbation of gout, rest is necessary, especially for the affected limb, dry heat, vodka compresses, but warming compresses, visiting the bathhouse and sauna are not recommended;
- a diet with a decrease in protein in the diet to 0.8-1 g / kg of the patient’s weight, drinking plenty of fluids;
- drug therapy:
- painkillers and drugs - NSAIDs in combination with colchicine, are prescribed as early as possible at the first signs of an acute attack of arthritis;
- taking medications that normalize salt metabolism, as well as for the prevention and/or treatment of kidney damage;
- urate-lowering drugs are indicated for persistent hyperuricemia and acute attacks of arthritis, chronic arthritis and the presence of tophi. And also to prevent the formation and dissolution of existing uric acid crystals. Allopurinol is usually the drug of first choice in urate-lowering therapy;
- local therapy - in the presence of inflammatory fluid in the joint, a joint puncture is performed to remove it and followed by intra-articular administration of glucocorticosteroids;
- a necessary condition is weight control, as well as limiting the intake of certain medications (at the discretion of the attending physician) that adversely affect protein metabolism in the body;
- During the period of remission, in addition to nutritional therapy, physical therapy, physiotherapeutic procedures, light physical labor and exercise, long walks, osteopathic, acupuncture, and massage are recommended.
You can find out more about the symptoms and treatment methods for joint arthritis, prices, and make an appointment with our specialists by calling us in the Contacts section.
Call! We will be happy to assist you!
In medicine, there are 3 phases of the disease:
- With latent symptoms, the symptoms are erased. Doctors determine the development of primary inflammation by urine analysis.
- In the acute stage, severe pain occurs.
- The chronic course is due to alternating exacerbations and short remissions.
The frequency of attacks varies from 2 times a month to once a year. Can my knees hurt with gout? The anomaly provokes thinning of the cartilage, the formation of punctures in nearby bones - voids filled with microcrystals of sodium urate, lumps under the skin. Nodular formations and bone growths lead to the development of acute sensations. If measures are not taken, inaction will lead to loss of ability to work.
Symptoms and treatment of gouty arthritis of the knee joint in women, other acute attacks are rare, fewer tophi occur - dense chalky granulosa lumps, punctures. They are usually bothered by aching pains, which can easily be confused with arthritic pain. The pathology is recognized visually by a rheumatologist or arthrologist by severe swelling.
Gout, gouty arthritis: symptoms, signs and treatment
Gout, or gouty arthritis, is a disease in which metabolic disorders occur in the body and uric acid salts are deposited in the joints. This is a very unpleasant but easily treatable disease.
Gout is relatively uncommon. Although I hear the word “gout” almost every day. For example, most grandmothers call arthrosis of the big toe “gout.” This is what they usually say: “Gout has grown on my leg.” In fact, gout, although it affects the same big toes, most often affects men. In women, gout (real, true gout) is several times less common.
Previously, some 100 years ago, gout was generally considered an exclusively male disease. But in our time, due to the fact that women began to eat better, eat more meat and sausages, gout began to occur much more often among them than, for example, a century ago.
In addition, gout in women has become more common due to the use of certain medications, primarily medications for high blood pressure. Some drugs to reduce high blood pressure, when used for a long time, lead to an increase in the concentration of uric acid in the body.
But still, in men, gout manifests itself much more acutely and “aggressively”, since the concentration of uric acid is significantly influenced by male sex hormones.
Below I will tell you about the symptoms, signs and treatment of gout, as well as what diet you should follow for this disease.
Signs of gout
“Classical” gout belongs to the group of arthritis. It develops in people who have a hereditary predisposition to this disease. Moreover, the potential patient may not even be aware of his heredity.
For example, if his parents or relatives lead a healthy lifestyle, do not abuse alcohol and eat properly, then the disease may not manifest itself in them and will exist all their lives only in a latent, hidden form. And our potential patient, who has a predisposition to this disease, will provoke the disease in himself only if he leads a not entirely healthy (from the point of view of a tendency to gout) lifestyle.
Thus, a typical gout is often (but not always) an overweight man who abuses either alcohol or so-called “purine foods”: meat, meat soups, smoked meats, fish and salted foods, offal (liver, kidneys), beans, beans , chocolate, grape wine.
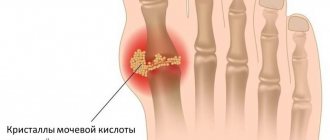
When these products are abused, there is an increased formation of uric acid in the blood , which, in turn, forms a poorly soluble salt of sodium urate. When the concentration of uric acid in the blood reaches a maximum level, its salts in the form of microcrystals are deposited in the joint cavity, forming a kind of “depot” there.
The presence of microcrystals of sodium urate in the joint cavity is a serious irritant for it. But nevertheless, crystals can remain in the joint for a long time asymptomatically - until some provocation (physical overload, stress, prolonged fasting or, conversely, too much “purine foods” and alcohol) provokes an acute gouty attack, that is attack of gout. Regular acute attacks of gout are the main symptom of this disease.
Gout symptoms
The first attacks of gouty arthritis are almost always short-lived. The attack usually begins suddenly, most often at night. In most cases, the joint of the big toe becomes inflamed (sometimes one, sometimes both). Less commonly, the thumbs, knee, ankle, elbow joints, heel tendons, and very rarely the wrist joints become inflamed.
The pain is such that, according to my patients, it makes you want to literally “climb the wall.” The affected joint swells, turns red, and the skin over it becomes bright red or purplish and hot to the touch. Even a light touch to the inflamed joint or the slightest movement in it causes unbearable pain. The patient suffers for 3-4 days, when suddenly the attack passes, as if nothing had happened.
However, after some time, the pain just as suddenly recurs. Moreover, if at the beginning of the disease the intervals between attacks are quite long, from one to eight months, and the attacks themselves are short-lived, then over time everything changes. The attacks are becoming longer and longer, and the intervals between them are becoming shorter.
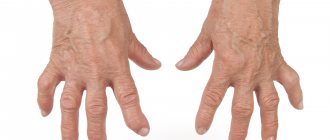
Eventually, there comes a time when the pain in the joints becomes constant, and there are practically no intervals between attacks. This condition is called "status gouty", or chronic gouty arthritis. In chronic gouty arthritis, articular cartilage is destroyed , and special defects are formed in the bones adjacent to the joint - “punches”, which are a cavity filled with microcrystals of sodium urate.
In addition, sodium urate crystals can be deposited even under the skin, forming whitish, hard nodules filled with a pasty mass. Such nodules are called tophi, and most often they are located on the ears or near the joints. Sometimes tophi break through and uric acid crystals are released through the resulting fistula. Fortunately, usually within a few days after the tophi breaks through, the wound heals without consequences.
In addition to the above troubles, gout, especially advanced ones, is almost always accompanied by the deposition of urate in the kidneys, which leads to urolithiasis , and sometimes to inflammation of the kidneys (pyelonephritis).
It is important to know!
Female variants of gout are usually much milder. Women very rarely have acute gouty attacks, and tophi and punctures in the bones are much less likely to form. Most often, female gout manifests itself as mild chronic pain in the knee or ankle joint. And an experienced doctor can guess that this is not arthrosis only by the severe swelling of the inflamed joint, which is uncharacteristic of arthrosis.
Diagnosis of gout
Having assumed that the patient has gouty arthritis (and in classic cases this is quite easy), a competent rheumatologist or arthrologist will refer the patient for an x-ray of the hands and feet, as well as a biochemical blood test.
With advanced gout, the doctor can easily detect characteristic gouty “punches” in the periarticular bones on x-rays of the hands and feet. A blood test will show an increase in uric acid levels. If such an increase is clearly expressed and is combined with the presence of “punches” in the bones and characteristic gouty symptoms, then the diagnosis is considered reliable, and then we only need to select the correct treatment.
The problem, however, is that if you do a uric acid test at the very moment of the attack (and usually it is at this time that the patient goes to the doctor), then such an analysis may not record any abnormalities. That is, at the time of an attack, the level of uric acid in the blood may turn out to be normal (after all, at the time of an attack, the maximum amount of uric acid goes into the inflamed joint).
Therefore, it is necessary to measure the level of uric acid in the blood several times, including between attacks. But gout patients often don’t have the patience for this. As soon as the next attack “subsides,” they often completely stop thinking about their health again.
Meanwhile, without correct diagnosis and without proper treatment, gout can lead to very undesirable consequences not only for the joints, but also for the kidneys.
Continuing the topic, I would like to note that, despite the frequent mention of the term “gout” in the literature and in conversations, in reality it turns out that the correct diagnosis of gout patients is not always made and is often very late. Sometimes you have to deal with monstrous diagnostic errors.
For example, at the time of an attack, surgeons managed to diagnose one of my patients with “gangrene of the big toe” and amputated the toe inflamed by gout. Literally 3 weeks later, his big toe on his other foot became inflamed, and the patient was about to amputate that too! Fortunately, the man realized that this time he should consult another doctor, and turned to me for help. Upon examination, it immediately became clear that the patient did not have gangrene, but classic gout. I prescribed the anti-gout drug colchicine to the patient, and the attack was eliminated literally in one day! The next day there was no trace left of the imaginary gangrene.
Another patient was treated for arthrosis for seven years, despite the fact that his joints became inflamed in attacks, alternately, about once a month, and the inflammation never lasted longer than 5-7 days. The most surprising thing in this story was that in numerous tests of blood taken from a vein, the patient’s uric acid simply went off scale. She was more than 2 times higher than normal! But doctors managed to ignore this over and over again. And they continued to stick to their line. During one of the attacks, the man even had time to have his knee operated on and a completely healthy meniscus was removed. But the operation, naturally, did not bring any relief to the patient. The knee periodically continued to become inflamed along with other joints.
Only after the man came to see me and laid out a pile of tests in front of me, which clearly showed a constant increase in uric acid levels, was the patient finally given adequate anti-gout treatment. And just a month after the start of treatment, gout attacks, for the first time in all the past years, began to disappear. And then they stopped altogether. Treatment of gout
After diagnosing a patient, I usually say, without any irony, “Congratulations, you have gout.” I’m really not being ironic, because of all the possible diagnoses, this is one of the most favorable. Gout is very easy to treat and is not particularly difficult for a competent specialist.
Although here, as often happens, there is a “fly in the ointment.” Yes, gout is very treatable, but many gout patients do not want to accept the conditions that are necessary for recovery - since the “conditions” are the refusal of those foods (and alcohol) that caused metabolic disorders. And when I tell patients that to get rid of the disease they need to give up their favorite foods and alcohol, they often simply don’t want to hear me.
That’s why every time I have to patiently explain that without a diet there can be no talk of recovery, no matter what “cool” medications are used. Another thing is that in many cases the diet is a temporary measure, and if certain conditions are met, after a year or two the strict restrictions can be lifted.
The classic but outdated version of the gout diet is here >>
The diet for gout updated and corrected by Dr. Evdokimenko is here >>
***
Drug therapy for gouty arthritis consists of two components: treatment of an acute attack and therapy of the gout itself.
To relieve an acute gout attack, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Voltaren, ibuprofen, Movalis, Nimulide, etc.) or a special short-acting anti-gout drug - colchicine - are successfully used. A vodka compress can be applied locally to the sore joint.
Drugs to relieve an acute attack are used for a short period of time, in a short course of three to seven days. And directly for the treatment of gout, in the absence of contraindications, for several months or years a drug is used that reduces the formation of uric acid in the body - purinol, also known as allopurinol .
Following a diet and using purinol (allopurinol) leads to normalization of the patients' condition within the first month of therapy. Although during the first week, during therapy with purinol or allopurinol, an exacerbation of the disease may even occur. But then the attacks become weaker and occur less and less often, and over time they stop altogether.
And after about a year, if my ward is feeling well, I allow some relaxations in his regime. I ask the patient what he would like to stop - diet or medication, since we can limit ourselves to one thing or the other. If the patient is already accustomed to the diet, then there is no point in breaking it. In this case, it is better to reduce the dose of medications taken or stop them altogether.
If the patient finds it difficult to tolerate dietary restrictions, then you can abandon the diet, but continue taking medications. However, the medications will have to be used for several years - which, in general, is not scary, since purinol (allopurinol) rarely causes any side effects and is generally well tolerated by patients.
Article by Dr. Evdokimenko© for the book “Arthritis”, published in 2004. Edited in 2011 All rights reserved.
READ MORE:
- Diet for gout: nutrition, products and menu
- No more medications needed?
- All articles by Dr. Evdokimenko
Diagnostics
Doctors do not consider hyperuricemia and periodic swelling of the finger to be the main signs of gout of the knees. They are considered as evidence of a violation of purine metabolism. Some people with high uric acid levels do not show signs of gout. The patient is sent for x-rays of bones, blood biochemistry and urine analysis. Synovium is also tested for sodium urate. In acute and chronic forms, the image shows characteristic deposits in the voids. A series of tests confirms a high concentration of uric acid. Since liver and kidney pathology is considered one of the reasons, the patient undergoes an ultrasound examination.
| Injection into the knee joint for gout |
Sign up for treatment
Causes and mechanism of development of gouty arthritis
It has now been established that this disease is caused by metabolic disorders, and a diet high in meat only aggravates this disease, but is not the cause of its occurrence.
Predisposing factors:
- sedentary lifestyle, systematic overeating, obesity;
- unbalanced diet (predominance of protein (meat) foods, regular consumption of alcoholic beverages, absence or very little consumption of fresh vegetables and fruits);
- hereditary predisposition, diabetes mellitus;
- kidney diseases of various nature, taking certain medications (aspirin, riboxin, etc.);
- occupational hazards (for example, lead intoxication).
Gout can also be secondary, for example, in diseases of the cardiovascular system (hypertension, congenital and acquired heart defects), blood diseases (myeloid leukemia), etc.
With gouty arthritis, purine compounds and uric acid salts accumulate in the blood in large quantities, which are formed in excess, but are slowly eliminated. This leads to their deposition in the form of crystals - urates in joints, tendons, under the skin in the form of nodules (tophi), surrounded by a connective tissue capsule, as well as in the kidneys.
Most often the process is localized in one or two joints of the big toes, sometimes in the joints of the hands, and less often in the ankle, elbow and knee joints. The hip and shoulder joints are rarely involved in the process during gout.