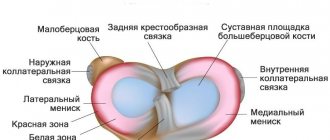
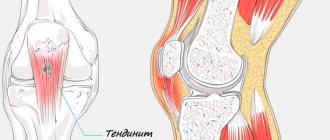
Often the cause of pain and limited mobility in the knee joint is a disease called gonitis. In scientific articles and medical reference books it may be listed as arthritis of the knee joint or gonarthritis. These are alternative names for this pathology that occurs with damage to the knee joint. Like arthritis of any other localization, arthritis is the result of an inflammatory process in the joint.
The disease is heterogeneous in etiology, clinical course and outcome. It can develop slowly and gradually or rapidly, accompanied by pronounced symptoms. In some cases, the result is complete loss of function of the lower limb and disability. Knowledge of the symptoms, basic patterns, early detection and properly selected treatment will help slow down the rate of development of gonitis and make life easier for the patient.
What is this - driving?
If a person’s kneecap swells and reaches a significant size, and he takes a forced position with his knee bent, we can talk about drive. What it is? Gonit (arthritis, monoarthritis or osteoarthritis) is an inflammation of the knee joint. A large amount of fluid collects in the knee during inflammation, causing it to swell. It can occur with clear symptoms (when fever, weakness, malaise appears), or it can be asymptomatic. In this case, the process of destruction of cartilage and tissue constantly occurs, immobilizing the patient partially or completely.
Clinical forms:
- Acute – develops rapidly and exhibits vivid symptoms;
- Chronic – asymptomatic.
For reasons:
- Primary - occurs as an independent disease as a result of bruises, injuries, infection in an open wound on the knee;
- Secondary – occurs as a consequence of diseases already raging in the body:
- Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammation of the joint;
- Ankylosing spondylitis is a chronic inflammation of the spine and joints;
- Tuberculosis is damage to the body by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Accordingly, a type of gonitis develops - tuberculosis;
- Syphilis is a lesion of Treponema pallidum. Accordingly, a type of gonitis develops - syphilitic;
- Gonorrheal drives - defeat by gonorrhea;
- Brucellosis drives;
- Dysenteric drives;
- Pneumococcal drives;
- Septic drives;
- Rheumatic drives;
- Phlegmonous drives;
- Other diseases: polyarthritis, psoriasis, Reiter's syndrome, etc.
Based on the nature of the accumulated exudate, the following types are distinguished:
- Serous - formed from blood serum, without pus;
- Purulent - damage by staphylococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, salmonella, E. coli, etc.;
- Serous-purulent.
go to top
Symptoms and signs
Common symptoms and signs of knee gonitis are:
- Pain that gets worse with movement;
- Increase in volume;
- Puffiness, swelling;
- Redness, fever;
- Limited movement;
- The acute purulent form is characterized by weakness, deterioration, chills, and fever.
With a long course of the disease, significant changes occur not only in the knee joint, but also in the muscles of the affected leg, for example, atrophy.
Signs of gonorrheal gonorrhea:
- Unbearable pain;
- Heat;
- Intoxication.
The syphilitic form rarely affects one joint. It affects two joints on both legs at once. In this case, there is a local increase in temperature, rounding of joints that do not lose their mobility, and painful sensations, especially at night.
The tuberculosis form has the following symptoms:
- Minor pain;
- Slight swelling;
- Local temperature;
- Moderate limitation in movements, flexion;
- Rapid muscle atrophy.
Of particular interest is acute purulent drive, which is expressed in the following symptoms:
- Pain;
- Increase in local temperature;
- Redness of the skin;
- Edema;
- Fluid accumulation;
- Limited mobility;
- Chills;
- Weakness;
- If left untreated, osteomyelitis, stiffness, and muscle atrophy develop.
go to top
Manifestations of persecution
With this pathology, the joint can become very swollen and red.
Inflammation of the joint has the following symptoms:
- Painful sensations. Severe pain during physical activity, but may be slightly dull at rest.
- Swelling. Suppuration or serous deposits cause swelling that extends above the knee.
- High skin temperature and hyperemia at the site of the inflammatory process.
- The joint is painful on palpation.
- Limited mobility due to swelling and pain.
Tuberculosis or other types of pathology caused by infectious diseases have the following additional symptoms:
- fever or severe chills;
- high body temperature or constant low-grade fever;
- weakness;
- lethargy;
- dizziness;
- pre-fainting states.
Causes of inflammation of the knee joint
Depending on the causes of inflammation of the knee joint, primary and secondary forms of the disease are distinguished:
- In the primary form, the disease develops against the background of injuries, bruises, abrasions, infection penetration directly into the knee joint through a laceration;
- In the secondary form, the disease develops as a consequence of other infectious diseases already raging in the body:
- affecting the knee joints, such as rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis,
- in the presence of infections in the body that enter the knee joint through the blood or adjacent organs - tuberculosis, syphilis.
go to top
What can gonarthrosis be like?
1. Depending on the pathogenesis, the following types of gonarthrosis are distinguished:
- Primary (ideopathic). The reason for its development still remains unknown. Usually occurs in older people. As a rule, with this type, bilateral joint damage occurs.
- Secondary, arising against the background or as a result of a previous pathology of the knee joint (trauma, developmental disorders, infectious or systemic disease, and so on). Can be found in people of any age. This is usually a one-way process (left-sided only or right-sided only).
2. Depending on the clinical manifestations of the disease and the degree of impairment of joint mobility, three degrees of gonarthrosis are distinguished:
- 1st degree, with initial manifestations of the disease. Patients at this stage are periodically bothered by pain that appears deep in the knee and intensifies during long walking or other stress on the legs. May be accompanied by swelling of the knees with spontaneous disappearance of symptoms. Deformation of the knee joints is not observed at this stage.
- 2 degrees, with an increase in symptoms of 1 degree gonarthrosis. Characterized by more intense and prolonged pain. During movement, there is a crunch in the knee; stiffness is possible in the morning, which goes away during the day. Leg flexion and extension are slightly limited.
- 3 degrees, with the most severe symptoms characteristic of this type of disease. Signs: pain from periodic to constant, not only while walking, but also at rest, often appears with weather changes. This stage is characterized by a sharp disturbance in gait and limitations in mobility. There is a visual enlargement of the knee joint and its deformation. An X-shaped (valgus) or O-shaped (varus) deformity is possible.
Drives in adults
Drivenitis in adults can develop in both primary and secondary forms. Often patients with the gonorrheal form of gonitis are men. In women, driving develops against the background of untreatable infectious diseases, as well as bruises and injuries that they receive from falls while walking in heels or during pregnancy.
Here it should be noted the development of this disease as a result of physical violence. It develops more often in men than in women, since it is the stronger sex who are often subjected to physical beatings on the street or in gyms. In women, inflammation of the knee joint develops against the background of physical violence in the family by the spouse.
go to top
Preventive measures
In order to prevent gonarthritis, the above etiological factors of the disease and risk factors should be limited or avoided. That is, weight control, regular physical activity, especially with prolonged passive position of the lower extremities, moderation of vertical loads on the skeletal frame, and proper diet are necessary.
What is it - gonarthrosis is a disease of the knee joint of a non-inflammatory nature, in which the blood supply to the cartilage covering the articular surfaces of the femur and/or tibia is disrupted.
As a result, the cartilage is destroyed, sections of the bones begin to rub against each other, as a result of which they become denser and grow. This is often accompanied by inflammatory phenomena.
Symptoms of the disease are caused only by the above processes; Calcium salts, even if deposited in the joints, are not the cause of pathology. The pathology most often develops in people 40 years of age and older; it mainly affects women and people involved in professional sports or who have injuries to the knee joints.
Articular cartilage does not regenerate, so the disease must be detected and treated in the early stages.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of an inflamed knee joint is carried out using the following procedures:
- General examination and collection of complaints: joint swelling, pain are checked, general condition is checked;
- Taking an anamnesis: how it all started and how it proceeded before the patient arrived at the hospital;
- Joint puncture to analyze the fluid for the pathogen and sensitivity to antibacterial therapy;
- X-ray of the affected joint;
- Blood analysis;
- Consultations with a rheumatologist and surgeon.
go to top
Reviews about
Irina Vasilievna
03.11.2020
I liked the fact that the center treated my problem with understanding. It seems like you can give up on age and just take medications. But it turned out that there is a way out and treatment of knee arthritis is possible without surgery.
You can live without pain.
Thanks to the doctors, staff and managers.
Igor
09.09.2020
I express my gratitude to the doctors of Dr. Bubnovsky’s center for their attention and professionalism. For curing the long-standing problem of knee arthritis without surgery.
The pain is gone, and now I won’t give up gymnastics because it really works.
Sergey
02.03.2020
My knee has been bothering me for a very long time. They diagnosed arthritis of the knee joint, I took medications, my body got used to them and everything went round and round.
At Dr. Bubnovsky’s center they offered an integrated approach to treatment and I felt much better.
Thanks to the doctors and staff.
Treatment
It is better not to treat persecution at home. You can’t do this without the help of doctors. How do doctors treat inflammation of the knee joint?
- Provide bed rest by applying a fixing plaster splint to the affected area;
- Medicines are prescribed in the form of antibiotics for both external and internal use;
- In the secondary form of the disease, intensive treatment of the root cause - the underlying disease - begins;
- Physiotherapeutic procedures are carried out only when the inflammation subsides. During the period of exacerbation they are contraindicated;
- Blood transfusion is possible;
- Surgical intervention is performed only when necessary, when significant changes occur in tissues, joints, and the patient loses the ability to walk.
For gonorrheal gonorrhea, exudate is surgically removed and antibiotics are administered intramuscularly and intraarticularly. As you recover, physiotherapeutic procedures are carried out and sanatorium treatment is prescribed.
For tuberculosis and syphilitic forms of the disease, specific procedures are prescribed under the supervision of a doctor.
Acute purulent form of gonitis is treated by puncture - removing purulent contents, administering antibiotics and ensuring rest.
The diet for the treatment of this disease consists only of eating foods rich in proteins and vitamins to strengthen the immune system.
go to top
How to treat gonarthrosis
Diagnosis and treatment of this type of joint pathology such as gonarthrosis involves a medical examination and further X-ray examination. This will allow you to determine the extent of the disease and make an accurate diagnosis, as well as track the dynamics of its development.
Gonarthrosis is an incurable disease, but this does not mean that it does not need to be treated at all. The earlier treatment is started, the longer the progression of the disease can be delayed.
The main treatment methods are:
- Medication: analgesics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, chondroprotective drugs, corticosteroid anti-inflammatory hormones.
- Physiotherapeutic, using the following procedures: UHF, diathermy on the area of the diseased joint, hydrocortisone phonophoresis. In addition, paraffin baths and balneotherapy (radon and sulfide baths), as well as compresses with bischofite, are effective.
- A method of therapeutic exercises, with an individual development of a set of exercises based on the patient’s medical history and diagnostic results, aimed at reducing pain, relaxing muscles, increasing joint space and improving blood circulation in the joint.
- Treatment with folk remedies, using compresses, tinctures, baths, rubbing, and so on. Examples of folk recipes:
- Apply a compress using blue clay to the knee area, for the preparation of which you need to dilute the clay with water until a creamy mixture is obtained. Keep on your knee for two hours.
- Prepare a dandelion infusion: fill a dark glass bottle with yellow dandelion heads and pour vodka over them. Place in a dark place for one month. Strain. Rub the infusion on your knees every day before bed.
- For two weeks, apply a compress of horseradish to the sore knee, for which the crushed roots of the plant should be boiled in a water bath, and then the mixture should be placed on gauze.
- Orthopedic, using a cane or crutches while walking to unload the affected joint. Sometimes special orthoses are used, with which you can relieve certain parts of it. Custom insoles are also used.
- Surgical, which is used if all other methods are ineffective. Indications for surgery are determined jointly by the doctor and the patient. The doctor must inform the patient about alternative options.
Possible surgical procedures:
- Puncture of the knee joint. Prescribed for excessive accumulation of joint fluid in order to remove it and, if necessary, subsequent intra-articular administration of hormonal drugs.
- Arthroscopy. It is a diagnostic procedure necessary to clarify the diagnosis. Can be combined with pneumoarthrography.
- Transcondylar osteotomy of the tibia. With its help, the deviation of the limb axis is corrected in the case of formed articular deformities.
- Arthrodesis is an economical resection of the joint with further fusion of the resected bone surfaces, resulting in the formation of a stable “straightened” limb. Lately it has been extremely rare. Prescribed for grade 3 gonarthrosis.
- Arthrolysis. This operation is mobilizing in nature and is prescribed for the 2nd and 3rd degrees of the disease. An arthrotomy is performed from a parapatellar incision, after which the altered (thickened) synovial membrane, osteophytes and adhesions are removed to restore joint mobility.
- Arthroplasty is the resection of remnants of articular cartilage and the subsequent formation of articular surfaces with a “simplified form”. This operation carries a risk of developing instability in the joint, so it is performed quite rarely.
- Endoprosthetics. Prescribed in case of severe damage to the knee joint, characterized by destruction of the articular surfaces, persistent pain and limited mobility.
As you can see, deforming gonarthrosis is a serious disease that requires treatment for quite a long time, so any of the treatment methods described above must be prescribed by a specialist!
loading…
Life forecast
The prognosis for life during persecution depends entirely on the causes and course of the disease. How long do people live with inflammation of the knee joint? All life. If the defeat occurred due to other diseases, then they are the ones that shorten the patient’s life. In the primary form of the disease, only complications are possible that do not affect life expectancy, but significantly reduce its quality. You can remain disabled if you do not undergo treatment.
If left untreated, the following complications are possible:
- Complete immobilization of the patient due to the destruction of tissue, cartilage, and changes in the structure of the joint;
- A breakthrough of purulent contents in the tissue of the leg and thigh, which will lead to the spread of the disease to nearby tissues.
- Sepsis.
Therefore, it is necessary not only to treat inflammation of the knee joint, but also to carry out preventive procedures that will prevent its reoccurrence:
- Treatment of other diseases of the body, especially infectious and musculoskeletal diseases;
Avoiding injuries, bruises, abrasions, lacerations. Treat them in a timely manner and bring them to full recovery.