Spinal cord injury is characterized by:
- transient paresis or paralysis
- mild sensory disturbances
- pelvic dysfunction
These symptoms occur at the time of injury and disappear within a few hours or days.
With a SPINAL CORD CONTUSATION, softening of the brain substance, hemorrhage, and tissue necrosis are noted.
Symptoms:
- paralysis
- loss of sensation below the level of the lesion
- dysfunction of the pelvic organs (retention of urination and defecation).
Recovery time ranges from 4 to 8-10 or more weeks.
SPINAL CORD COMPRESSION can occur acutely at the time of injury, hours or days after the injury (early compression), or months and years after the injury (late compression).
Compression of the spinal column occurs from a hematoma, a displaced vertebral body or disc, or a bone fragment. Clinical symptoms:
When the spinal cord is damaged at the C1 – C4 level, victims experience:
- paralysis of arms and legs
- loss of sensation from the level of the lesion
- pelvic disorders (urinary retention and defecation)
- impairment of breathing, cardiovascular activity, and swallowing due to edema and swelling of the brain stem
Causes
The main cause of spinal injuries is excessive stress on it. Violations arise due to the following factors:
- degenerative processes;
- age-related changes;
- sudden external impact as a result of an accident, fall;
- sudden movements;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- lifting weights;
- improper exercise;
- presence of tumors;
- formation of metastases;
- autoimmune disorders;
- blow with a blunt object to the spine;
- posture disorders.
Spinal injuries are possible when jumping, diving, sports, or exposure to electric current.
Medical assistance at the scene
- The victim should not be seated, raised to his feet, or turned from side to side. It is necessary to lift and shift the patient with three people (“Dutch bridge”) and very carefully, on command.
- The stretcher is hard; if they are not there, then on a soft stretcher with a shield. We place the patient on his back.
- If there is a soft stretcher and there is no shield, then we place the patient on his stomach (unless there is a cervical injury!).
- If the cervical vertebrae are damaged, we put a thick cotton collar or a special collar on the neck (you can use splints or sandbags). Lie only on your back! Call "03". It is better not to touch the patient until the ambulance arrives.
- At the same time, antishock therapy is carried out.
Symptoms
At the site of damage to the vertebrae, hematoma and swelling are observed. The more pronounced they are, the stronger the pain in the victim. The symptoms resemble diseases of the internal organs; when making a diagnosis, they must be excluded.
Injuries of this kind are always accompanied by a decrease in muscle tone, their atrophy is observed, especially with loss of motor activity.
If the injury is caused by infection, the patient is at high risk of developing osteomyelitis.
Caring for patients with spinal cord injury
- The patient should lie on a backboard.
- Rational position:
- For fractures of the thoracic and lumbar spine, lying on the stomach is advisable; cervical - only on the back.
- For fractures and dislocations of the cervical spine, skeletal traction (Gleason loop, cervical corset) is usually used.
- Regular toileting of the respiratory tract (mucus suction, postural drainage, vibration massage, breathing exercises, oxygen, inhalation) - prevention of pneumonia.
- Prevention of bedsores:
- clean, dry, wrinkle-free bed linen
- rubbing the skin 3-4 times a day with 3% camphor alcohol, salicylic, menthol alcohol or a mixture (5 ml of shampoo + 250 ml of distilled water + 250 ml of 96% alcohol).
- rubber circles, cotton-gauze “donuts”, anti-decubitus mattress
- change the patient's position every 2-3 hours, in consultation with the doctor
- To prevent limb contractures:
- correct physiological alignment
- passive movements
- massage, therapeutic exercises
- use of stops, loops, special splints
- Prevention of deep vein thrombosis of the leg and thromboembolism:
- lower limb bandaging or stockings
- prevention of dehydration
- low doses of heparin
- For atony of the stomach and intestines:
- periodic evacuation of stomach contents (nasogastric tube)
- cleansing enema, gas outlet tube
- when peristalsis occurs, use laxatives (no strong laxatives)
In some cases, they resort to mechanical removal of feces.
- Prevention of urinary infection:
- in the acute stage - permanent catheter
- periodic catheterization with simultaneous lavage of the bladder, antispastic solutions - acidification of urine (drink water with ascorbic acid - 1 t. in the first 3 days x 4 times a day, lemon)
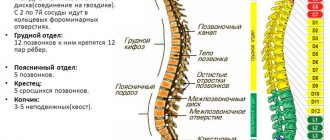
Classification
Doctors distinguish bruises, fractures, dislocations of various parts, as well as compression, dislocation, paraplegia, quadriplegia.
When fractures occur in the neck area, the integrity of the bone is disrupted; in other parts, the vertebrae are displaced relative to the axis. When this happens, the spinal cord is compressed. This type of injury is called compression.
Bruises affect soft tissues without affecting the vertebrae. However, the hematoma formed in the victim affects the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid. Dislocations are characterized by stretching or tearing of ligaments. Due to this pathology, the vertebrae may become displaced.
When the lower part of the thoracic region is affected, paraplegia is observed. Damage to the upper part and neck is called quadriplegia. As a result of this injury, the function of the limbs is impaired.
There are stable and unstable injuries. The former do not pose a particular threat to the patient's health. Unstable injuries leave severe consequences and aggravate the deformity.
Injuries where the spinal cord remains unaffected are called uncomplicated. Organ damage always leaves complications. Complicated injuries are divided into reversible and irreversible. When the spinal cord is compressed by a hematoma, compression myelopathy is diagnosed.
According to the classification of spinal injuries, closed and open injuries are also distinguished.
Remember!
An overfilled bladder, overstretching of the rectum with feces, bedsores, and cystitis provoke and intensify muscle spasms.
- When transporting patients to diagnostic rooms, turning over in bed should be very gentle and careful, excluding flexion/extension, rotation and lateral displacement of the spine
- Psychological support for patients:
goodwill, empathy, confidence and optimism in the actions of a nurse greatly influence the psyche of the patient
Rehabilitation is carried out in specialized centers
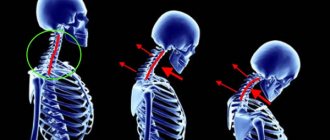
Neck injuries
The cervical spine is damaged in 20% of cases, and 35% of patients die. The cause of injury to this area is the sharp impact that is typical for victims of car accidents. This type of injury is called whiplash. Its symptoms are dizziness, sharp pain, loss of consciousness, and deterioration of neck mobility. Neck injuries also occur after diving head first in shallow waters.
The cervical spine, due to its mobility, is more susceptible to dislocations. The reason for this is a sharp turn of the head. The pathology is accompanied by pain in the neck, shoulder blades, and shoulders. Patients have difficulty swallowing and a feeling of constriction in the back of the head. Treatment of spinal injuries must begin immediately after they occur, otherwise it will be difficult to realign the cervical vertebra.
Bruises of the cervical spine lead to deterioration in the functioning of the limbs, as a result of which paralysis can develop. The patient has dry skin and his pupils become very narrow.
The most severe lesions are the atlas and epistrophy vertebrae, which are the uppermost ones. In most cases they lead to the death of the victim. Such damage provokes compression of the medulla oblongata, causing deterioration in the patient’s respiratory and cardiac systems.
Diagnostic features
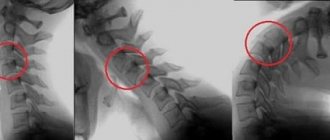
The nature and location of the victim’s injuries are determined after a neurological examination. The victim's metacarpal, knee and Achilles reflexes are checked. After a visual examination, the patient is sent for an x-ray, which shows the dislocation of the vertebrae and depicts fractures.
The study is carried out in lateral and posterior projections. However, this method does not always determine pathology. CT gives a more accurate result. The procedure is recommended if the patient is in critical condition and requires emergency care. This technique is effective because it shows damage to soft tissue and bones.
The integrity of bone tissue and the condition of the spinal cord is reflected by MRI. The procedure reveals abnormalities that may not be visible on x-rays.
If osteoporosis is suspected, densitometry is required. This technique shows the level of calcium in the blood. The examination lasts about 30 minutes, while the patient must remain motionless.
EMG is used to assess the extent of nerve damage. Since spinal injuries cause disturbances in the functioning of internal organs, the patient undergoes an ultrasound and ECG.
The results of instrumental diagnostic methods must be confirmed by a blood test, which displays the concentration of calcium and C-reactive protein.
Spinal injuries in children
It is common for children to experience neck injuries during childbirth. In this case, a traumatic brain injury is also diagnosed. The main causes of pathology are:
- high fetal weight;
- malposition;
- oligohydramnios;
- premature birth;
- large fetal head with a narrow maternal pelvis.
Children who have received such damage develop problems with memory, academic performance, and attention.
In children, spina bifida also occurs, accompanied by incomplete coverage of the nerve structures. This injury is most often observed in the lumbosacral region. After diagnosing this pathology, it is very important to monitor the child’s weight, since as he grows, the pressure on unformed vertebrae increases. The disease is accompanied by muscle weakness, paralysis, and orthopedic disorders.
Treatment
Conservative:
- Taking analgesics, muscle relaxants
- Local and case medicinal blockades
- Orthotics (hyperextension corsets, “Schanza” or “Philadelphia” type orthoses) for 6 months
- Limiting physical activity for the entire treatment period
- Physiotherapy
Operational:
- Transpedicular fixation of the vertebrae
- Percutaneous transpedicular fixation of vertebrae
- Percutaneous transpedicular vertebral stenting
- Percutaneous transpedicular vertebroplasty of the vertebra
- Reconstructive operations on the spinal cord, transpedicular fixation of the vertebrae
- Anterior decompression, corpectomy, installation of body replacement allograft, vertebral fixation
Clinical example No. 1
Patient A., 37 years old, injured as a result of a fall while skiing. Complains of pain in the thoracolumbar junction. CT revealed a compression fracture of the Th12 vertebral body
The patient underwent minimally invasive surgery: Reclination of the Th12 vertebral body, percutaneous transpedicular fixation of the Th11, L1 vertebral bodies with the Viper 2 system
The patient was activated the next day after surgery. Moves independently without additional support. The sutures were removed on the 12th day after surgery. At the time of discharge he had no complaints.
Prevention
You can prevent spinal injury during sports by using protective equipment. When driving a car, you must wear a seat belt.
To keep your spine strong, you need to exercise regularly and watch your posture. Sudden movements are not allowed. Strength training should be carried out under the supervision of a trainer, observing the biomechanics of movements. Loads on the spine are symmetrical.
It is necessary to monitor your weight and avoid overeating, as this puts increased stress on the spine. Athletes should be careful during training and if they experience back pain of various locations, consult a doctor.
Lesions of the spine cause a number of disturbances in the functioning of internal organs. Recovery directly depends on the timeliness of therapeutic measures and completion of the rehabilitation course. If there is no result from conservative treatment methods, surgery is recommended to the patient. In most cases, if the injury does not affect the spinal cord, treatment of spinal injuries will be successful.
Clinical example No. 3
Patient S., 72 years old, felt a sharp pain in the thoracic spine while lifting heavy objects. The examination revealed a fracture of the Th7 vertebral body with a decrease in the height of the body in the anterior section by more than 50%.
The patient underwent surgery: percutaneous transpedicular stenting of the Th7 vertebral body