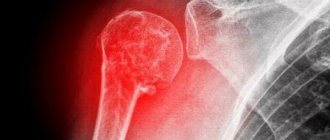
The humeral tuberosity is a prominence on the humerus and is the site of attachment for several rotator cuff muscles. The rotator cuff is made up of four muscles that surround the head of the humerus, and the rotator cuff is involved in the movement of the arm, holding the head of the humerus in the socket (socket). Falls directly on the shoulder often result in a fracture of the greater tuberosity of the humerus. Quite often, a fracture occurs in older people due to age-related changes such as osteoporosis and osteoarthritis.
Other injuries, such as a dislocated shoulder, can also result in a fracture of the humeral tuberosity. As a rule, isolated fractures of the humeral tuberosity can occur due to anterior dislocation of the shoulder or due to impact with the acromion or the upper part of the socket. A fracture of the humeral tuberosity may be accompanied by partial damage to the rotator cuff and tear of the labrum, which can cause persistent pain in the shoulder after consolidation of the fracture. In the absence of displacement, tuberosity fractures can be successfully treated using conservative treatment methods. If there is a displacement of more than 5 mm, surgical fixation of the fragments is necessary.
Symptoms
The main symptom of a humeral tuberosity fracture is pain at the top of the shoulder. Due to the fact that fractures are often accompanied by soft tissue trauma, there may be swelling in the shoulder area. In addition, the range of motion in the shoulder is significantly reduced. A fracture of the humeral tuberosity may also be accompanied by a partial or complete tear of the rotator cuff. Damage to the cartilage ring around the shoulder may also occur. In such cases, pain and weakness will persist after consolidation of the humeral bone tissue, and symptoms of shoulder instability may appear.
Is it possible to study on your own?
After healing the damaged bones and removing the plaster, the doctor must make individual recommendations for the development of the shoulder, elbow joint and the entire injured arm. Of course, we should not forget about the stress on a healthy limb.
It is better to entrust a massage to a competent specialist. If it is difficult to find one, ask someone close to you to master the necessary complex; in extreme cases, perform the elements of the massage yourself.
Of course, the last option is the most difficult; the main thing to remember is that recovery and the absence of problems in the future depend on the systematic nature of the exercises and their correctness.
The same can be said about the complex of physical therapy: of course, classes under the supervision of a competent specialist are preferable, but, if necessary, you can carry them out independently, the main thing is that the load is selected optimally. After a fracture, many people unnecessarily spare the injured arm, while others put unnecessary strain. Both cause a lot of harm.
Diagnostics
A history of injury and examination of the shoulder may lead the doctor to suspect a fracture of the humerus. First of all, radiography is performed, which allows you to diagnose changes in bone tissue and determine the presence of a fracture. But to diagnose possible injuries to soft tissues (rotator cuff), an MRI examination is required, which will allow a more differentiated approach to treatment tactics, since damage to the rotator cuff often requires surgical treatment.
Fracture of the greater tuberosity of the humerus
The humeral tuberosity is a raised area on the shoulder bone. The rotator cuff, which consists of four muscles surrounding the head of the humerus, attaches here. The rotator cuff itself secures the head of the humerus in the socket, thereby participating in the dynamics of the upper shoulder girdle. In case of traumatic positions of the shoulder, impacts, falls, it is the greater tuberosity that fractures. Such injuries can be observed in older people. They are at high risk of such damage due to certain age-related diseases.
But these are not the only reasons for such a fracture, since other injuries to the shoulder can lead to it, for example, a violation of the congruence of the articular surfaces of the bones. Fractures limited to one bone are caused by anterior movement of the shoulder. In addition, this effect is achieved by striking the lateral end of the scapula or the top of the glenoid cavity. Associated injuries with a fracture may include a tear of the labrum and certain injuries to the rotator cuff.
All of the above are the causes of stable pain in the shoulder joint after healing of the fracture. If there is a static arrangement of the damaged parts, the tuberosity can be cured using simple methods. If the shift is more than 5 mm, then it is necessary to secure it with a fragment through surgical intervention.
Symptoms
To identify an injury, you should pay closer attention to the injured shoulder. If there is a lighted fracture, pain will be observed in the upper part of the shoulder joint. You also need to pay attention to the skin. Swelling may occur throughout the joint. Active mobility of the shoulder will be greatly reduced, and passive mobility will be complicated. An absolute or incomplete tear of the rotator cuff is possible. Damage to the ligaments of the shoulder joint can also be expected. In this situation, pain and discomfort will remain after treatment of the fracture, and unpredictable displacement of the articular surfaces of the shoulder joint is expected.
Diagnostics
If there is a set of information about the patient and a timely examination of the injury, the attending physician may suspect a fracture of the humerus. The most accessible and fastest way to confirm this assumption is radiography of a part of the body, which allows you to accurately determine changes in the bone. But as for soft tissues, in particular, possible damage to the rotator cuff, the process is somewhat complicated by the need for magnetic resonance imaging, which will give the doctor the opportunity to consistently approach the treatment of the injury. This fracture is complicated by the fact that damage to the rotator cuff often requires surgery.
According to statistics, the vast majority of treatment for shoulder fractures occurs traditionally by fixing the damaged part of the body with bandages or a splint. At the same time, it is necessary to remember the importance of maintaining safely limited movements of the shoulder joint. Otherwise, prolonged immobility will lead to pathology of the shoulder joint, characterized by the term “frozen shoulder.”
When displacement is more than 5 mm, it is recommended to use surgical treatment methods. It is also required for a damaged rotator cuff. These methods consist in the fact that the ideal reposition of fragments is achieved in an open way by using plates and screws. To simplify things, let’s think about arthroscopy. The process of invasive surgical manipulation will significantly speed up and simplify the work of surgeons, nevertheless making it possible to restore the previous structure of the shoulder joint as accurately as possible.
Shoulder movements during treatment should be done carefully. 2–3 days after the start of observation by a specialist, you can begin to perform passive movements. As for full-fledged dynamics, the transition to it occurs only after a verification X-ray. Typically, the restoration of motor functions of the shoulder occurs in the seventh week after the fracture.
Remember the need for strength loads on the damaged joint and dynamic exercises.
This should be started no earlier than 3 months from the date of injury. Therapeutic exercise and physiotherapy conducted by clinic specialists makes it possible to restore the function of the shoulder joint to its required state within three to five months. The exception is particularly complex cases, which are very rare today. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Treatment
In most cases, humerus fractures are treated conservatively with immobilization using splints and bandages. But it is necessary to take into account that it is necessary to maintain a small range of motion in the shoulder, since prolonged immobilization can lead to frozen shoulder syndrome. Surgical treatment methods are indicated for displacements of more than 5 mm and, in such cases, comparison of bone fragments is carried out using osteosynthesis using plates and screws. In addition, surgical treatment is necessary in the presence of rotator cuff injuries. Modern arthroscopic treatment methods make it possible to restore the integrity of the structures of the shoulder and shoulder joint quite quickly and with minimal complications.
Passive movements in the shoulder can be carried out several days after the injury, and active movements are possible only after a control x-ray. As a rule, active movements and development of the joint begin 6 weeks after the injury. Strength training should begin no earlier than 3 months after the injury. A careful rehabilitation program (physical therapy, physiotherapy) allows, in most cases, to completely restore the function of the shoulder joint in a few months.
Fracture of the proximal humerus
Indications for surgical intervention for these fractures are determined by general and local concomitant injuries, the type and stability of the fracture, the quality of the bone tissue, and the age of the patient.
Conservative treatment is preferable in elderly patients with concomitant pathology and for fractures without displacement of the fragments.
Achieving the best results is possible with good reposition of the fragments and fixing them in the correct position until fusion occurs. For these purposes, methods of external osteosynthesis with plates and screws, intraosseous osteosynthesis with locking rods or endoprosthetics are used.
Clinical case:
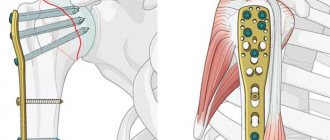
Fracture of the greater tuberosity of the humerus
Operation: Open reduction, anchor fixation of the greater tubercle of the humerus.
Clinical case:
Incorrectly healing comminuted fracture of the greater tubercle of the humerus.
Operation: Open reduction of the greater tubercle of the humerus with fixation with an anchor suture
Clinical case
Closed comminuted intra-articular displaced fracture of the proximal humerus.
Surgery: open reduction of fragments of the proximal humerus, external osteosynthesis with a plate and screws
Humeral shaft fracture
Humeral shaft fractures account for approximately 1% of all fractures. They usually result from direct trauma, but can also occur in sports where rotational forces are high, such as baseball and arm wrestling. Fractures of the third humerus can cause damage to the axillary nerve. Fractures of the middle and distal third may compromise the radial nerve.
Osteosynthesis with a plate allows the surgeon to perform a good reduction and create stable fixation of components with interfragmentary compression of bone fragments. The plate in such cases is the best means of correcting the deformity and remains the method of choice in the treatment of false joints of the humerus.
Another treatment option for shaft fractures is intramedullary osteosynthesis.
Clinical case
Closed fracture of the middle/3-n/3 humerus with displacement.
Surgery: open reduction of fragments of the middle/3-n/3 humerus, osteosynthesis with a plate and screws
Fracture of the distal humerus
Fractures of the distal humerus account for 2-6% of all elbow fractures in adults. There is a distribution of fractures relative to age and gender, with peak rates in young men and older women. Most fractures in the elderly are intra-articular injuries involving both columns.
Intra-articular injuries have a relatively favorable prognosis with open reduction and stable fixation.
Modern methods of plate and screw fixation provide the possibility of reliable reconstruction, so that the native elbow joint can be preserved in the vast majority of patients.
In patients with severe osteoporosis, achieving stable internal fixation of the distal articular end of the humerus may not be easy, so total elbow arthroplasty may be considered.
Clinical case
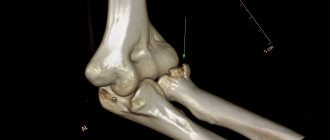
Closed intra-articular fracture of the head, trochlear condyle and lateral epicondyle of the humerus with displacement.
Operation: open reduction of fragments of the distal condyle of the humerus, external epicondyle, osteosynthesis with a plate and screws.
Clinical case
Closed intra-articular fracture of the head and part of the trochlea of the humerus with displacement.
Operation: open reduction of fragments of the head and part of the humerus trochlea, osteosynthesis with screws.
Fedotov Evgeniy Yuryevich, Traumatologist - Orthopedist, Candidate of Medical Sciences Conducts outpatient appointments at the CDC (consultative and diagnostic department) for adults
Physical therapy after a shoulder fracture
The functional stage of rehabilitation lasts 3-6 weeks. 3-4 weeks after a shoulder injury, the patient is recommended to undergo regular physical therapy exercises. Rehabilitation specialists at the Yusupov Hospital use modern devices from leading European manufacturers to restore limb function. The goal of rehabilitation at this stage is to restore the previous range of active and passive movements. The set of exercises is constantly expanding, but the starting position remains the same.
The patient should strive to gradually straighten the arm and perform exercises while standing without bending forward. He should perform the following physical exercises 4-6 times daily:
- raising a straight arm in front of you;
- swing your arms forward, backward and to the sides from the starting position “standing with a slight bend forward”;
- abducting the arms behind the back with the shoulder blades together (the arms bent at the elbows should first be in front of the chest).
At this stage of recovery, rehabilitation therapists use block simulators. Patients use them to lift and lower the injured limb, and spread their arms to the sides. Therapeutic exercise is complemented by water procedures. The patient is recommended to perform various movements of the limbs in the pool, crossing his arms in front of the chest, and exercises simulating freestyle and breaststroke swimming. Staying in water increases the effectiveness of training, puts additional stress on the muscles, and improves blood circulation in them. Physiotherapists include 10-12 magnetic therapy and balneological treatment procedures in the rehabilitation complex.
How long does it hurt to break the greater tuberosity of the humerus?
An injury to this part of the humerus, like most fractures, is painful. This disease worsens upon palpation, i.e. pressure on the sensitive area. An additional symptom that allows a preliminary diagnosis to be made before the patient is referred for imaging is limited mobility of the upper extremity - it is usually impossible to visit it above an angle of 70 degrees.
How long does it hurt to break the greater tuberosity of the humerus? It all depends on the scale of the injury, the rate of regeneration and rehabilitation, and the patient’s individual pain sensitivity. It can be assumed that the pain lasts from a few days to 4 weeks, and sometimes longer.
First aid
When a victim receives such an injury, first aid must be urgently provided in order to reduce pain and prevent possible displacement and movement of fragments.
First of all, it is necessary to fix the injured limb by tying the arm to the body and bending it at the elbow joint. To do this, it is possible to use a bandage, scarf, towel, or simply a torn piece of fabric.
To the place where the pain is most severe, it is necessary to apply ice or another source of cold , and also give the victim a remedy that can relieve pain.
It is necessary to take the patient to an emergency room or hospital as soon as possible to diagnose the damage and prescribe the necessary therapy.
An independent attempt to straighten the joint, as well as change the position of the arm, can lead to complications and worsening of the injury, as well as increased pain.
Damage classification
Several muscles are attached to the tubercle: teres minor, supraspinatus and infraspinatus. In case of injury, they lead to displacement of the fragment from above. Two main mechanisms lead to damage to the tubercle:
- Class A injuries. Type 1. Injuries included in this group are caused by a direct blow to the upper arm. This often happens when you fall. Such fractures often occur in older people, as they also experience weakening of the surrounding muscles.
- Class A injuries. Type 2. These can also be associated with the above mechanism, but are mainly caused by a fall on an outstretched arm.
- Class B injuries. These are injuries that occur as a result of a fall on an outstretched arm, but at the same time the outer rotor contracts, so displacement is observed.
Class A injuries can be compression injuries, belonging to the first type.
These can also be non-displaced type 2 fractures. Class B injuries may be type 1 if only the thin cortical fragment is displaced. The second type includes damage when the large tubercle is completely displaced and broken off.
Complications and prevention
The most common complications are:
- Biceps injuries . Can occur at the time of injury, leading to surgery to stitch the damaged muscle.
- Non-union of tubercle fragments . Occurs when there is poor fixation of the limb and entails surgical intervention.
- Calcium deposits and ossification of muscle fibers will also require surgical removal or laser therapy at the very initial stage.
- Arthrosis. Damage to cartilage tissue may be caused, which will then be treated conservatively.
Prevention of such disorders requires initial competent treatment and contacting specialists with any questions regarding pain that raise doubts.
Completing all necessary actions prescribed by the doctor during the period of treatment and rehabilitation will help avoid complications and promote a speedy recovery.
About the shoulder
Humerus, shoulder (lat. - Нumerus) - refers to the long bones. The humerus makes up the bone base of almost half of the free upper limb and is its initial section.
Like any long bone, the humerus consists of a body (diaphysis) and ends (epiphyses) - the proximal one, formed by the head of the humerus, connecting the shoulder to the scapula through the shoulder joint, and the distal one - forming the shoulder component of the elbow joint. Due to the large degree of freedom of movement of the shoulder in the shoulder joint (the ball and socket joint, the most mobile in the human body), the proximal part of the shoulder is the site of attachment of many muscles and ligaments, thanks to which an extremely complex and balanced process of movement of the shoulder is carried out in the shoulder joint, and with it and the entire free upper limb.
Moreover, during almost any movement, the head of the humerus is always strictly centered in the joint. The diaphysis of the humerus forms the lever of the shoulder and serves as the attachment point for part of the flexor and extensor muscles, providing the same movements of the shoulder in the shoulder joint, and the forearm in the elbow.
Due to the variety of functions of the shoulder and the complexity of the anatomical structure, damage to this area leads to significant dysfunction of the entire upper limb. Moreover, if we figuratively consider the free upper limb as a chain of successive links, and the shoulder is the initial link in the chain, then the higher the damage, the more significant the dysfunction of the entire chain.
The speedy restoration of the function of the upper limb plays a vital role in a person’s life: self-care, professional and creative activity, learning, tactile perception of the surrounding world.
Shoulder injuries are a fairly common pathology . There is a wide variety of injuries to both bones - bone fractures, fractures of hand bones, dislocation of the collarbone, and soft tissues (ruptures of muscles, tendons, ligaments, blood vessels and nerves), and various dislocations of the head of the humerus are also common.