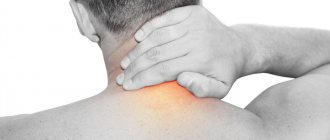
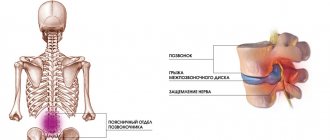
Cervical radiculitis is a range of symptoms that occur when the nerve endings of the cervical spine are compressed. Pain, loss of sensitivity, or muscle weakness can be localized on the right or left side, depending on which side the affected root is located on.
Painful symptoms are usually very severe and require immediate relief. You can undergo a course of treatment for cervical radiculitis at the CELT Clinic! Our neurologists, pain clinic specialists, and neurosurgeons have extensive and successful experience in this area and have modern methods and means to quickly and effectively relieve our patients from suffering.
At CELT you can get advice from a neurosurgeon.
- Initial consultation – 3,000
- Repeated consultation – 2,000
Make an appointment
Causes
Symptoms of cervical radiculitis can appear as a result of a number of spinal diseases that are accompanied by pinched nerve endings:
- osteochondrosis in advanced stages;
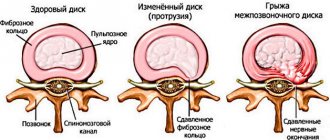
- intervertebral disc herniation;
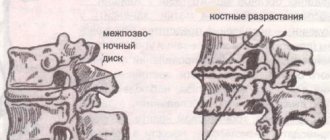
- osteoarthritis;
- spondylosis;
- spinal canal stenosis;
- spinal injuries, with displacement of the vertebrae.
Prevention
An excellent prevention of radiculitis is therapeutic exercises, which are recommended to be performed daily, except during periods of exacerbation. Avoid hypothermia and stress, watch your weight, engage in swimming or other sports, try not to stand in a bent position for a long time and watch your posture. Throughout your life, adhere to the principles of a healthy diet, stop drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking tobacco. These simple measures can protect you from developing dangerous diseases and radicular syndrome.
Classification
The classification of cervical radiculitis is based on the etiology of the disease, its form and location. Depending on the cause of cervical radiculitis, there are:
- primary - develops as a result of inflammatory processes;
- secondary - develops due to chronic changes in the spine.
As for the localization of the disease, according to it, the following types of radiculitis are distinguished:
- cervical - characterized by pain in the back of the head and neck, dizziness, nausea, blurred vision and hearing, and impaired coordination of movement;
- cervical-brachial - accompanied by pain and numbness of the arms, shoulder blades, dizziness, nausea, and impaired coordination of movement;
- cervicothoracic - pain in the upper chest is added to the above clinical manifestations.
Depending on the development of the disease, there are two forms of cervical radiculitis:
- acute - accompanied by intense pain and rapid development;
- chronic - characterized by exacerbations due to hypothermia or unsuccessful sudden movements.
Development of radiculitis in childhood
Children are at risk of developing sciatica due to constant use of computers and reduced time for physical activity. The modern rhythm of life and the stress of studying lead to the inability to fully move during the day, which leads to weakening of the back muscles. In children, cervical and thoracic forms of radiculitis are diagnosed due to the development of scoliosis. It is necessary to instill in your child a love of sports and monitor posture from an early age. At the first signs of spinal curvature, you should contact a pediatric orthopedist, who will prescribe the necessary set of therapeutic measures. Due to their age, children manage to overcome the disease forever.
Clinical manifestations
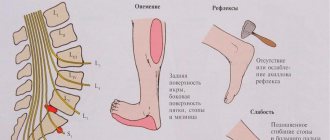
One of the most striking clinical manifestations of cervical radiculitis is pain. They are localized in the neck area, radiate to the back of the head, shoulder blades, shoulders, forearms, hands and have a cutting, piercing, searing nature. When trying to make movements, they intensify. In addition, symptoms of radiculitis include the following:
- pain in the cervical spine spreading to the scapula area. shoulder, forearm in the form of a strip, stripe, along the nerve; is persistent and intense in nature and can intensify with movement in the cervical spine; The pain is especially alarming at night; the pain exhausts the patient, bringing severe physical and moral suffering, sleep is disturbed;
- weakness in the hand, the patient has difficulty holding a bag, spoon, pen, fine movements in the fingers, handwriting are impaired; difficulty using the computer keyboard;
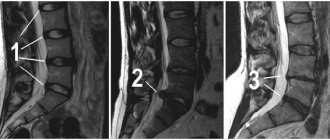
MRI of the spine
- Cost: 16,000 rub.
More details
- There is numbness in the fingers of the hands, for example, the little finger and half of the ring finger or in the II, III and half of the ring finger, a feeling of decreased sensitivity in the forearm, elbow, shoulder;
- curvature in the cervical spine, the head is tilted to the side, it hurts less;
First aid
An acute attack of radiculitis limits the patient's ability to move, so the person needs outside help. The algorithm of actions is as follows:
1. Give the patient a painkiller in the form of a tablet or give an analgesic injection. Neuropathic pain cannot be tolerated.
2. Additionally, give a sedative to drink. Preference should be given to natural remedies (valerian, peony, motherwort). This will partially relieve the pain.
3. Place the patient on a chair in a position comfortable for him if it is impossible to ensure bed rest, otherwise, put him to bed.
4. Immobilize the painful part of your back with a tight belt (you can use a sheet, bath towel or corset).
5. Apply ointment or gel from the NSAID group to the sore area to relieve inflammation.
6. Hold the patient if necessary.
After the ambulance arrives, provide the patient with peace, and then help him visit a neurologist for further treatment.
Diagnostics
Treatment of the symptoms of cervical radiculitis is possible only after making a correct diagnosis. It is this area that receives special attention. The patient is examined by a neurologist, pain clinic specialists, and neurosurgeons who check reflexes and motor and sensory disorders. In addition, diagnostic studies are carried out, which include:
- radiography;
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- computed tomography;
- radiography;
- electrodiagnostics of peripheral nerves;
Consequences
If left untreated, radiculitis becomes chronic and can bother a person throughout his life, worsening his quality of life and reducing his productivity. Possible complications:
1. Ischemic spinal cord infarction.
2. Blockage of veins and vessels located in the pathological area.
3. Development of paralysis of the upper and lower extremities.
4. Disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, heart, kidneys and others.
5. Paresis.
6. Disability.
7. Psychological personality disorders.
To avoid negative consequences, consult a neurologist in a timely manner.
Reviews of doctors providing the service – Cervical radiculitis
In 2000, Andrei Arkadyevich performed spinal surgery on me.
Four days in the clinic and I have been living a full life for 20 years without restrictions on movement and I remember with gratitude Dr. A.A. Khodnevich. God bless him. And in 2000 he could walk no more than 10 meters. Read full review Viktor Alexandrovich
20.05.2020
Low bow to Alexander Semenovich Bronstein and Andrei Arkadyevich Khodnevich. I arrived at CELT on July 2, 2021 with extreme pain that I endured for 10 days. Hernia C6-C-7. I was given two blockades in Ivanovo, about 9 complex IVs, I lost 6 kg in a week and was in a panic, I didn’t see a way out and nothing happened to me... Read full review
Elena Nikolaevna L.
20.10.2019
Treatment
Complex conservative treatment, which has been practiced by CELT doctors for several years, invariably gives positive results. It allows you to release pinched nerve endings and relieve pain, weakness and numbness of the upper extremities, eliminate inflammation and muscle spasms. Treatment is carried out using a number of modern techniques:
| Methodology | Description |
| Drug treatment |
|
| Limitation of physical activity |
|
| Physiotherapeutic treatment |
|
| Surgical techniques |
|
Operations for diseases of the spine
- Cost: 100,000 - 250,000 rubles.
- Duration: 40-60 minutes
- Hospitalization: 2-3 days in hospital
More details
It is worth noting that we resort to surgical intervention in extreme cases, if there are appropriate indications:
- lack of improvement with conservative treatment;
- intense pain symptoms;
- feeling of weakness in the hand;
- decreased hand sensitivity.
CELT neurosurgeons use minimally invasive techniques that involve small incisions or punctures. Before the operation begins, it is planned and a three-dimensional model is created. The process uses microsurgical and endoscopic techniques, ultrasound equipment and laser. The use of modern techniques makes it possible to make surgical intervention minimally traumatic and minimize the rehabilitation period. Our patients can go home the very next day and return to work two to three weeks after surgery.
How to treat
Therapy for osteochondrosis begins with relieving acute pain. For this purpose, injections of painkillers are made into the passage of nerves in the vertebrae - blockades. Next, with the help of massage, muscles relax. And for prevention, physical activity is prescribed. It should be without serious effort. It is best to start with regular walks, then you can switch to swimming and stretching. If the pain is tolerable, then drug treatment is used as a last resort. In order to avoid the appearance of osteochondrosis, you need to adhere to a healthy lifestyle, a properly balanced diet and avoid gaining excess weight.
To treat a hernia, surgical intervention by a neurosurgeon is sometimes required. Invasive treatment methods are used when the size of the hernia is too large and neurological symptoms are observed (pins and needles, severe numbness of the limbs). These methods solve the issue radically, but do not exclude relapses and postoperative complications, which can even lead to disability. Conservative treatment methods include massage, diet, physiotherapy, and the use of analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs. They are more preferable. An integral element is therapeutic exercises. The exercises included in the complex should be aimed at stretching the spine and strengthening the back muscles. The full composition and volume of therapy should be prescribed by a neurologist.
Attacks of radiculitis are usually well relieved by intravenous and intramuscular injections of painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs and the use of compresses with the same drugs. A massage course is also sometimes prescribed. Radiculitis is a temporary condition and goes away quickly if osteochondrosis and hernia are properly treated.
Preventive measures
The best treatment for any disease is its prevention, and sciatica is no exception. You can minimize the risk of developing this disease by:
- to live an active lifestyle;
- regularly engage in sports and swimming;
- eliminate hypothermia and intense stress;
- correctly distribute loads when lifting and carrying heavy objects;
- Healthy food;
- organize the workplace taking into account all the rules and recommendations of ergonomics;
- promptly seek professional medical help for diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Our specialists know how to return you to your normal lifestyle, relieving you of pain and inflammation.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
What is an intervertebral hernia
If a tear forms on the spinal disc, and it itself shifts away from the spinal column, resulting in inflammation and swelling, this is an intervertebral hernia. It is often a consequence of osteochondrosis. It can be identified by the following symptoms:
- the pain is pinpoint, the location of the lesion is clearly defined, and is poorly relieved by painkillers;
- movements are constrained (for example, a turn cannot be performed in the usual volume);
- with physical activity the pain increases sharply;
- atypical reflexes when trying to stand up.
There are several stages of this disease: disc prolapse, protrusion, extrusion, sequestration.