Lumbosacral radiculitis is an inflammation of the nerve roots extending from the spinal cord at the level of the lumbar and sacrum (radix in Greek - “root”). The main causes of lumbosacral radiculitis are dystrophic changes in vertebral structures due to osteochondrosis.
This disease can be provoked by birth defects (sacralization), infectious lesions (tuberculosis, influenza), as well as injuries and hypothermia. Sometimes it develops as a complication of meningitis and encephalitis.
Lumbosacral radiculitis: symptoms
The leading symptom is pain of varying intensity. It can be aching and chronic, or it can be burning and sharp. Sometimes a painful attack occurs suddenly when a person tries to straighten his back, but it is not possible to do this completely, and new attempts only intensify the pain. An attack can begin after hypothermia, heavy physical labor, or staying in one position for a long time. The pain often radiates to the leg. In severe cases, the function of the pelvic organs is impaired.
Development mechanism
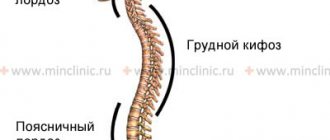
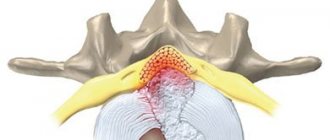
The spine is formed by vertebrae separated by intervertebral discs. In the middle is the spinal canal with the spinal cord inside: spinal nerves extend from it on opposite sides.
Some of them are responsible for motor functions, others for sensitivity. All of them pass through the foraminal openings and innervate different parts of the body and internal organs. If one or another nerve is compressed by pathological structures, a whole set of motor and sensory disturbances arise, which are typical signs of radiculitis.
Possible complications of pathology
If lumbar radiculitis is treated incorrectly, serious complications can occur. For example, if the chronic form of the disease is not treated for a long time, the risk of pathological changes in the radiculomedullary arteries increases (they are gradually compressed, resulting in impaired blood flow). The radicular veins can also be compressed in the absence of medication.
Complications of radiculitis
In rare cases, lumbar radiculitis can lead to spinal cord infarction (with the development of ischemia due to impaired blood flow). Such a serious condition can lead to paralysis of the body or result in death, therefore, in order to avoid serious complications, sciatica must be treated as its first symptoms appear.
Which doctor should I contact?
Neurologists are involved in the diagnosis and treatment of radiculitis; if necessary, other specialized specialists are involved - vertebrologists, orthopedic traumatologists, and neurosurgeons. Complex therapy can be carried out with the participation of a chiropractor, physical therapist and reflexologist.
Baths
How to treat radiculitis at home? If you regularly take medicinal baths during remission, you will forget about the disease for a long time. The classic recipe is with an infusion of pine branches. They are poured with boiling water in a ratio of 1 kg per 3 liters, boiled for 10 minutes and allowed to brew. The infusion time is from 3 to 5 hours, after which the infusion is poured into a bath with warm water. The course of treatment is 10-14 sessions.
Baths with pine branches are good for radiculitis
In addition to coniferous crops, you can use medicinal herbs:
- calamus;
- chestnuts;
- chamomile
For variety, add sea salt or essential oils to warm water.
How to recognize lumbosacral radiculitis
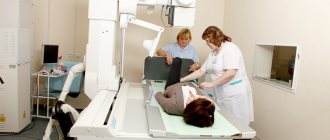
If a pinched nerve root is suspected, the doctor will order an x-ray, which is performed in frontal and lateral projections. With its help, intervertebral hernias, dislocations, fractures, defects and displacements of the vertebrae are identified. In order to exclude degenerative disorders in the spine, a spondylogram is performed. To confirm the infectious nature of the inflammation, a lumbar puncture is indicated, the results of which determine pathologies such as meningitis and encephalitis. Diagnostics may include MRI, CT scan of the spine, myelography, and laboratory blood tests.
Types of massage at home
If you have simple massage skills, try to use the basic techniques of its classical variety:
- stroking;
- rubbing;
- shaking;
- kneading.
All movements must be performed strictly according to the flow of lymph, in a certain sequence. They stroke the back and lower back with varying intensity, gradually warming up and relaxing the muscles. Rubbing also effectively relieves spasms and improves blood circulation. However, you should not do massage yourself if you do not know the basic rules of its implementation. In this case, it is better to invite an experienced specialist for a home massage.
Interesting article in continuation:
EVERYTHING about massage for lumbosacral radiculitis: is it possible to do it, massage technique at home
Drug treatment
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are prescribed to relieve acute pain, inflammation and muscle spasms. These are drugs based on diclofenac, nimesulide, ibuprofen, meloxicam. The choice of dosage form depends on the intensity of the symptoms: severe pain is eliminated with intramuscular injections, moderate pain can be relieved with tablets. In the acute period, local agents - ointments, gels and creams - can additionally be used. The second choice drugs are steroids - Hydrocortisone, Dexamethasone, Diprospan. They have a powerful anti-inflammatory effect. If NSAIDs with hormones are ineffective, then therapeutic blockades with Lidocaine and Novocaine are performed.
Antispasmodics and muscle relaxants (Mydocalm) help relax spasmodic muscles. If swelling is present, diuretics and magnesium sulfate are prescribed. Swollen tissues put additional pressure on the nerve, so removing excess fluid greatly alleviates the condition. To enhance the effect of analgesics and normalize the functioning of the nervous system, sedatives are added. Treatment of lumbar radiculitis also includes B vitamins, which improve nerve conduction. The most commonly used are Milgamma and Neuromultivit. If the disease is of non-infectious origin, then ointments with a warming effect can be prescribed - based on turpentine, snake and bee venoms, camphor. They relieve pain due to local irritant action.
Rubbing and warming
Rubbing your back is an effective way to relieve pain. To carry out the procedure, you can use both pharmaceutical ointments and folk remedies. They need to be rubbed with massage movements throughout the lumbar region where pain is felt. This usually takes 5-7 minutes, during which time the back has time to warm up and becomes receptive to the absorption of drugs.
Important! In order for rubbing to be effective, immediately after it you need to wrap your back in warmth, it is advisable to remain in a horizontal position. It is best to use woolen clothing that retains heat for a long time.
The following rubbing and heating products are popular:
- Black radish . The root vegetable available in our area has many medicinal properties. Radish juice is used for grinding. It can also be used for heating by grating it. This compress stays on the lower back for at least half an hour.
- Potato . Take 5-6 tubers, cook until tender, crush together with the peel. Lubricate the sacral area with sunflower oil, rubbing it for several minutes, which will make this area susceptible to treatment. We make a compress from potatoes and apply it on top of the rubbed back until it cools.
- Ointments based on bee or snake venoms . These products are sold in most pharmacies and are effective for rubbing against radiculitis. For example, Apisatron is popular; this ointment contains bee venom, mustard oil, and auxiliary components.
- Fir cream-balm Massage with a warming effect . Contains Siberian fir oil, gum turpentine, red pepper extract. Fir cream-balm successfully fights radiculitis pain, activates metabolism, and improves blood circulation in the area of application.
In order for rubbing and warming to bring results, they must be performed regularly. It is best to use potato and radish compresses before bedtime, and ointments several times a day. Providing warmth to your back is necessary in every case.
Non-drug treatment
Non-drug methods are used after the acute symptoms have subsided, when there is no longer severe pain. Their task is to strengthen the muscle corset, improve blood supply to the lumbosacral region and stimulate recovery processes. Help speed up recovery:
- physiotherapy – laser, ultraviolet, magnet, electrophoresis with painkillers, hormones, therapeutic mud;
- massage sessions using soft techniques to avoid re-pinching the nerve;
- special exercises that the physical therapy instructor will show help relieve excess stress from the spine and improve posture;
- reflexology;
- manual therapy;
- traction traction using dry or underwater methods.
The benefits of a radiculitis belt
The term “sciatica belt” refers to belts that can be made from different materials. Elastic models that support the lumbar region in a fixed position are popular among patients. This helps reduce pain and relax muscles.
If you do not have allergies and can tolerate products made from natural materials, buy a belt made of dog or camel hair. It perfectly retains heat, protects against drafts, and also has a warming massage effect.
Be sure to read: Lower back pain after sex: 20 causes, 5 treatments, positions and exercises
Great article on the topic:
TOP 12 types of belts for sciatica: which is better, prices + reviews
It is advisable to use belts after acute pain has been relieved.
Prevention
Preventive measures to prevent radiculitis are simple:
- competent organization of sleeping space. A comfortable bed is an elastic mattress of medium hardness and a small pillow of medium thickness. The ideal choice is orthopedic bedding;
- a complete and balanced diet will not only provide the body with healthy vitamins and minerals, but will also help maintain normal weight;
- adequate physical activity. Hard work is bad for your back, so if possible, you should reduce the load. Physical inactivity also threatens with negative consequences for the spine, and you should exercise at least once a week.
Doctors at our center have been working with patients suffering from radiculitis for many years. With timely treatment, the prognosis is always favorable. With us you will receive complete treatment, starting from examination and diagnosis, and ending with advice on lifestyle correction.
Exercises outside the acute stage
- Lie on your back, stretch your arms forward and begin to lift your upper body. Your legs should be on the floor with your knees bent. Stay in this position for 5-10 seconds, return to the starting position, rest and repeat the movement 10-15 times;
- The starting position is the same. Bend your left leg at the knee, and rest the palm of your right hand on your left knee. Pull your leg forward, resting your hand on it and creating an obstacle. Do this movement for 5-10 seconds, then rest and repeat the same with your right leg and left arm. The total number of approaches for each side is 10-12 times;
- Hanging on a horizontal bar or on a door frame. If you don’t have a horizontal bar, use the door, first placing something hard under it to support it so as not to tear off the hinges. The door must be open. Grab the door frame with both hands, bend your knees and hang on straight arms for 10-15 seconds. If necessary, use a small chair for safety. First do 5 such hangs in a row, gradually increasing their number to 20.