An L4-L5 hernia means the following: The letter “L” stands for the lumbar spine. Those. The herniated disc is located between the fourth and fifth lumbar vertebrae.
Clinically, a L4-L5 hernia can manifest itself:
- Pain in the lower back and leg.
- Numbness in the leg.
- Weakness in the extensor of the foot.
1.According to the location, pain from a hernia L4-L5 can start from the lumbar or gluteal region, spread to the sacrum, along the lateral surface of the thigh, lower leg to the first toe. The spread of pain below the knee indicates the presence of the so-called. “radicular syndrome”, i.e. The hernia has reached a certain size and affects the spinal root.
Pain in the leg can be of a different nature: from pulling, twisting, chewing pain to shooting, electric shock, tugging pain. Intensity ranges from insignificant, appearing sometimes, only in certain positions, under load, to very strong, not allowing any movement, forcing one to remain in one “comfortable” position.
2. Numbness in the leg with a hernia of L4-L5 is located in the same area as the pain. Numbness may be manifested by a decrease in pain and temperature sensitivity in this area. Sometimes patients note crawling in this area. In addition, dry skin, impaired sweating, and cold skin may be observed in this area.
3. A typical neurological sign for L4-L5 disc herniation is weakness of foot extension. Those. the patient cannot stand on his heels independently or when in this position one toe is located lower than the other.
It is difficult for a non-physician to objectively assess all these symptoms.
An accurate diagnosis of L4-L5 hernia can be confirmed or rejected after magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the lumbar spine (using a 1.5 Tesla machine) and consultation with a neurosurgeon.
The size of the detected disc herniation does not determine the choice of treatment. In addition, the width of the spinal canal and the location of the hernia in relation to the spinal root, as well as many other factors, are taken into account.
What is a lumbar disc herniation?
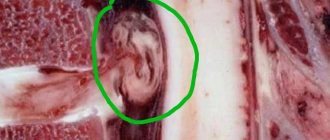
Intervertebral hernia is a disease that occurs due to a violation of the integrity of the fibrous ring and displacement of the central part of the intervertebral disc. As a result, the spinal nerve endings are compressed and the surrounding soft tissues become inflamed.
A hernia is formed due to the progression of degenerative-dystrophic processes in the spine itself, which affected any of the elements between 2 (two) adjacent vertebrae.
To treat a hernia of the lumbar spine, you can contact our clinic “Aspect of Health” in Ufa.
Types of intervertebral hernia
The general classification of intervertebral hernias includes the division of pathology depending on the location of the lesion in a specific part of the spine:
- neck;
- chest;
- lumbar
Locations within the spinal cord canal:
- near-median;
- posteromedial;
- posterolateral.
By size:
- 1-3 mm – protrusion;
- 3-6 mm – prolapse;
- 6-15 mm – developed hernia.
Anatomical feature:
- free;
- wandering;
- moving.
Particularly notable is Schmorl's hernia, which is the insertion of parts of the nucleus at the level of the spongy tissues of the vertebra, which does not cause compression of the spinal structures and nerve endings. Lumbar disc herniation is most often diagnosed at the level of the L4-L5 and L5-S1 vertebrae.
Sequestered hernia L5-L4
Posterior hernia L5-L4 undergoes sequestration more often than other localizations. This is due to anatomical features. This sector is subject to maximum pressure from neighboring vertebral bodies.
A herniated intervertebral disc L5-L4 with separation of part of the nucleus pulposus gives a pronounced inflammatory reaction. Inflammation involves muscles, ligaments, tendons, subcutaneous tissue and radicular nerves. The variety of clinical symptoms that arise does not allow a quick diagnosis to be made. Therefore, if a sequestered hernia of L5-L4 is suspected, surgery is often prescribed. In fact, you can completely do without it if you don’t let your condition get worse until part of the nucleus pulposus is torn off.
L4-L5
Lumbar hernia accounts for more than 50% of all cases of damage to this pathology of the spine, and in 46% it is at the level of the L4-L5 segment. The division occurs into the following types:
- median - located epidurally and often reaches large sizes. Can penetrate through the nerve sheath into the subarachnoid space;
- anterolateral - located outside the anterior circumference of the vertebral body. It is characterized by detachment of the longitudinal anterior ligaments, leading to the formation of sympathetic syndrome;
- posterolateral - passes through the back of the fibrous ring and from the side of the midline it passes in the place where median hernias appear, on the side (lateral), as well as next to the midline (paramedian).
Forms and symptoms of the disease
L4 L5 disc herniation has several forms of manifestation, and each has its own symptoms.
There are also symptoms characteristic of any type of this hernia:
- increased pain when moving, defecating, eating;
- pain subsides when standing;
- autonomic disorders (increased sweating, increased dry skin, swelling of the ankles);
- severe pain in the lower back when trying to lift a straight leg while lying on your back, and immediate subsidence of pain when bending the knee of the raised leg.
(if the table is not completely visible, scroll to the right)
| Title and description | Symptoms |
| Foraminal hernia - the rupture of the fibrous ring is directed to the anterior part of the spine. |
|
| Paramedian hernia - a hernial protrusion protrudes from the left or right side, compressing the roots of the spinal cord. |
|
| Dorsal hernia - rupture of the fibrous ring occurs on the back side. The hernial protrusion is directed back towards the spinal cord. This is the most dangerous type of L4 L5 disc herniation due to its close proximity to the spinal cord. It not only compresses and injures the body of the spinal cord, but also causes many difficulties in treatment |
|
| Medial hernia (Schmorl's hernia) - the development of a hernia occurs inside the vertebrae. | It is asymptomatic. |
L5-S1
Such a lumbar intervertebral hernia is formed between the 5th lumbar and 1st sacral vertebrae. In the direction of displacement it happens:
- dorsal or posterior - towards the spinal canal;
- circular - uniform protrusion of the disc;
- foraminal - protrusion towards the lateral openings of the column, from where the nerve roots emerge;
- diffuse - uneven distribution of displacements in several places of the disk;
- paramedian or median - protrusion slightly from the center or directly to the center of the spinal cord canal.
The most dangerous are the posterior and foraminal variants. In the first case, the displaced disc and damaged nucleus come into contact with the cauda equina; in the second, it infringes on the nerve roots extending away from the spine.
Stages of development
Any stage of development of a lumbar hernia is accompanied by certain symptoms. The following stages are distinguished:
- Prolapse is a slight displacement of the disc, which falls into place if the provoking factors cease to act.
- Protrusion is a pronounced displacement, but within the boundaries of the spine.
- Extrusion - the nucleus emerges from the disc space.
- Sequestration - rupture and cracking of tissue occurs.
- Symptoms and signs of pathology
At the early stage of development of a hernia in the lumbar region, symptoms do not appear for a long time. Over time, the following clinical picture occurs:
- pain in the lower spine, buttock and leg (pain in the lower limb is generally more pronounced);
- restrictive mobility of the lumbar region;
- weakening of the leg muscles, up to paralysis;
- sharp shootings in the lower back;
- numbness and tingling in the buttocks, legs, or thigh;
- inability to move your toes or lift them;
- stoop due to poor posture;
- dysfunction of the pelvic organs (uncontrolled urination and defecation);
- asymmetrical body position;
- lameness;
- improper functioning of the sebaceous glands of the limb in which the nerves are affected.
Advantages of surgical treatment:
- The speed of onset of the analgesic effect. The next day the patient feels a significant reduction in pain in the leg, only minor pain in the postoperative wound remains. With conservative therapy, achieving this effect requires time from 1-2 months to 1 year.
- Radicality of treatment. Removal of an intervertebral hernia relieves the patient of pain for many years, unlike patients treated conservatively. The latter have to relieve attacks of exacerbation of back and leg pain several times a year, which become stronger and longer lasting every year.
Diagnostics
If unpleasant symptoms occur, you should contact a neurosurgeon to diagnose and identify the stage of development of a lumbar hernia. At the Aspect Health clinic, doctors will examine the patient and prescribe a CT or MRI examination (disc damage is visualized).
We remind you that the results of the images will not tell you about all the symptoms of the disease. In our clinic, we treat each patient individually, not based on the image, but based on the presence of certain symptoms.
There are several recommendations to follow:
- do not stay in one body position for a long time, it needs to be changed periodically;
- do more swimming, which has a positive effect on the spine;
- lie down more often, in this state the load is removed from the vertebrae;
- do not carry heavy objects;
- do not make sudden movements;
- Do not heat or overcool the affected area.
Causes of L5-L4 disc herniation
Potential causes of the development of L5-L4 disc herniation are factors leading to degenerative dystrophic changes in the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral disc. Osteochondrosis is the most common reason why hernial protrusions occur. In second place is osteoporosis and cicatricial deformation of the ligamentous tendon apparatus.
The following risk factors should be excluded:
- excess body weight, which greatly increases the shock-absorbing load on the intervertebral discs;
- poor posture and curvature of the spinal column;
- unstable position of the vertebral bodies against the background of deformation of the ligamentous and tendon apparatus;
- violation of the tone and atony of the muscular frame of the back, often caused by leading a sedentary lifestyle with a complete lack of regular sufficient physical activity on the muscles;
- a decrease in the intensity of microcirculation of blood and lymphatic fluid in the spinal column, which sharply reduces the percentage of fluid absorption during diffuse exchange;
- incorrect placement of the feet and curvature of the lower extremities lead to incorrect distribution of the shock-absorbing load along the spine during movements;
- hard physical labor;
- diseases of the uncovertebral, facet, and facet joints of the spine;
- diabetic angiopathy, smoking and alcohol consumption;
- numerous pregnancies carried out without following the recommendations given by the attending physician.
Also, this type of hernia can be caused by ankylosing spondylitis, injuries, or the spread of certain infections that have a destructive effect on cartilage tissue in the human body.
Hernia treatment
There are two treatment methods: conservative and surgical.
Conservative treatment is divided into the following types:
- medicinal – based on taking various medications;
- non-medicinal.
Non-drug therapy, which consists of the following procedures:
- physiotherapy (laser therapy, electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, acupuncture, acupressure therapy, hirudotherapy, etc.);
- massage technique (used only during periods of no exacerbation);
- Exercise therapy (exercises designed to strengthen the muscles of the spine: careful rotations, turns, bending of the body).
Surgical intervention to remove a lumbar hernia involves the use of the following methods:
- discectomy (only part of the spinal disc is removed);
- laser reconstruction (excess moisture is removed from the damaged pulp);
- in advanced cases, the entire disc is removed and a prosthesis is placed.
Acute period
It lasts up to 1 week, and at this time a hernia of the lumbar spine is manifested by exudative inflammation. Here the doctor must decide whether surgery is required or not. Absolute indications for it are spinal stroke, pelvic disorders, reactive epiduritis, cauda equina syndrome. In other cases, conservative therapy is prescribed.
The patient requires pastel mode and the use of a fixation belt. It is important to minimize pain using analgesics. NSAIDs are also used, among which preference is given to Diclofenac and its analogues due to their speed of action. The complex necessarily contains decongestants, for example, Furosemide, Acetazolamide. Vascular medications and Novocaine-Dexon intradermal blockades are added.
Additional methods, the use of which is still controversial, include warming procedures, reflexology, magnetic laser therapy, electrophoresis
Subacute period
A lumbar hernia enters the subacute period at 2-3 weeks. Adhesions form around it, deforming the epidural space and compressing the nerve roots. If treatment for a lumbar disc herniation proceeds correctly, the pain will subside. Then pain relief and decongestant medications can no longer be used. The issue of manual therapy is resolved individually. Electrophoresis with lidocaine, lidase, sodium hydroxybutyrate and other medications is prescribed. If there are sensory disturbances, dorsanvalization, autonomic deviations, and magnetic therapy are added.
Recovery period
The recovery stage for a hernia of the lumbar spine begins at 4-6 weeks and can last up to six months. All medications are discontinued and exercise therapy is prescribed with exercises without turning, lifting heavy objects or bending. For paresis, electrical stimulation is added. The main goal is to eliminate pain.
Doctors do not recommend abandoning the fixation belt for lumbar hernia, even at the recovery stage. Positive changes are caused by balneotherapy, patients go to sanatoriums where various therapeutic baths are actively used, among which radon, sulfide, and hydrogen sulfide have the best effectiveness for lumbar intervertebral hernia. Turpentine baths will help relax muscles and relieve pain. Elderly people and patients with cardiovascular diseases are recommended to visit sodium chloride baths.
Features of surgical treatment
Modern medicine, in the fight against lumbar spinal hernias, increasingly places emphasis on minimally invasive surgical methods. In any case, operations are resorted to only in situations where all other methods have failed and in the presence of absolute indications that were listed earlier.
Complications and consequences
If you do not take action to treat a lumbar disc herniation, there is a risk of developing lumbomyalgic crises. These are localized, wave-like pains that last for several days. The crises are then replaced by sciatica syndrome, where pain occurs in a specific location, such as the leg. Over time, it migrates to the distal zone of innervation of the sciatic nerve - the groin or thigh.
Paresthesia in the lower parts of the legs should alert you, which may indicate a risk of deterioration in motor activity, including muscle atrophy.
Serious complications of a lumbar hernia can affect the genitourinary system, which in men can be accompanied by impaired potency and gynecological pathology in women. And the most dangerous consequence is paralysis of the lower limbs.
Paramedian disc herniation L5-L4
An uncomplicated paramedian hernia L5-L4 is a protrusion of the nucleus pulposus in the area of the lower or upper surface of the fibrous ring. It is located on the left or right. Symptoms corresponding to:
- numbness and muscle weakness in only one limb;
- pain syndrome is localized mainly in the area of the affected disc;
- paresthesia is quickly replaced by a decrease in skin sensitivity;
- on the lower limb on the affected side, tendon reflexes quickly fade away;
- gait changes, lameness appears;
- overstrain of the muscular frame of the back on the affected side is visible.
Paramedian L5-L4 disc herniation can be treated using manual therapy methods. Surgery may only be required if sequestration occurs.