Video
Sequestered disc herniation. Question answer.
Topic: Questions and Answers
Sequestered disc herniation
Topic: Encyclopedia of diseases
Title
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment methods
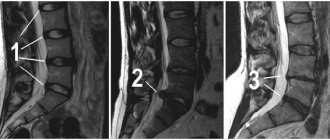
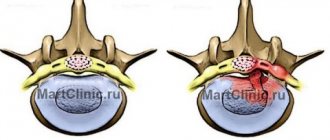
Sequestrated disc herniation (disc herniation with sequestration) is the most severe degree of disruption of the integrity of the intervertebral disc, in which the substance of the disc core falls out and is completely separated from the disc. A herniated disc, which performs a shock-absorbing function, is a rupture of the fibrous ring of the disc and bulging of the nucleus pulposus. Symptoms of a ruptured disc can vary depending on the severity of the rupture and the location of the ruptured disc.
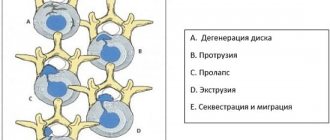
Disc herniations are classified based on the extent of the tear and location in relation to the posterior longitudinal ligament. The posterior longitudinal ligament runs vertically along the spine and runs near each disc along the back. The posterior longitudinal ligament separates the posterior part of the disc from the epidural space, which surrounds some of the spinal nerve roots. Violation of the integrity of the annulus fibrosus is divided into protrusion, extrusion and sequestration.
With protrusion, the annulus fibrosus protrudes, but without damaging or affecting the longitudinal ligament and maintaining the nucleus pulposus within the annulus fibrosus. Protrusion can be without pain or accompanied by pain, depending on the effect on the nerves. Disc extrusion (disc herniation) is a complete rupture of the annulus fibrosus, allowing substance from the nucleus pulposus to leak into the epidural space. Symptoms of disc extrusion also depend on the effect on nerve structures.
Disc sequestration means that the nucleus pulposus has fallen out of the disc entirely and separated from the disc due to contact with the longitudinal ligament. Nucleus pulposus material may enter the epidural space and is considered a free fragment. Disc sequestration is often accompanied by severe pain in the back and legs. In severe cases, the patient may develop cauda equina syndrome, which is manifested by disruption of the bladder and intestines and impaired sensitivity in the lower extremities. Cauda equina syndrome is an indication for emergency surgical treatment, since without surgery there can be irreversible damage to the nerve structures. In most cases, sequestration of a disc herniation occurs against the background of pronounced degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs. But sequestration of a disc herniation can occur both from systematic intense loads and from excessive one-time loads. Although most patients with a herniated disc do not require surgical treatment, when the disc herniation is sequestered, the likelihood of surgical intervention increases significantly, especially in cases where there are significant neurological symptoms.
What is a dorsal hernia
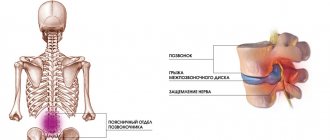
A dorsal hernia is a protrusion of an intervertebral disc into the lumen of the spinal canal. Each vertebra consists of a body, an arch and several processes. The anterior wall of the vertebral foramen is the vertebral body, and the posterior and lateral walls are the vertebral arch. Located one on top of the other, the holes form the spinal canal. It contains the spinal cord and the initial parts of its roots, which then become the spinal nerves.
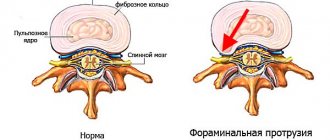
Intervertebral discs are located between the bodies of two adjacent vertebrae along the entire length of the spinal column from the cervical region to the coccygeal region. They consist of the nucleus pulposus and the fibrous ring around it. A dorsal hernia is formed when part of the disc breaks through the fibrous ring and rushes back towards the vertebral arch. Thus, the core ends up in the spinal canal, compressing its structures.
Reasons for development
A dorsal hernia does not occur on its own. The exact reason why this particular type of pathology develops has not yet been found. There are a number of factors that contribute to its appearance. These include:
- Genetic factor.
- Impaired metabolism or nutrition of the disc.
- Mechanical impact.
As for the genetic factor, a family predisposition of people to the occurrence of hernias has been proven. If one or both parents had this disease, there is a high chance that their children will also develop it as they grow older. This is due to individual characteristics of the structure of the spine, ligamentous apparatus and predisposition to degenerative processes in general. In some people, the body ages faster, in others - more slowly. This is a genetically determined process. As well as the occurrence of osteochondrosis and spinal hernias.
Metabolic disorders are one of the main factors. On average, obliteration of the vessels supplying the intervertebral disc ends at 27 years of age. After this, the disc is not supplied with blood, but receives nutrients from the surrounding tissues. Metabolism occurs during movement. The higher the physical activity, the less chance of metabolic disorders in the intervertebral discs. In people with low physical activity, hernial protrusions occur more often.
Mechanical impacts mean not only injuries, but also excess weight. Dorsal hernias most often occur when the injury does not occur on the spine itself, but lies in an axis parallel to it. For example, when jumping from a height or hitting the parietal part of the head. Excess weight is also a mechanical impact on the spine. Lifting heavy objects is also dangerous.
Rehabilitation
The complexity and duration of rehabilitation depend on the type of surgery performed. With hydroplasty or another method of puncture therapy, the patient can leave the clinic on his own legs on the same day. In the future, it is enough for him to give up increased physical activity and bending.
After other types of interventions the following are indicated:
- drug therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- exercise therapy;
- gentle regime of physical activity.
How long the body will take to recover depends on the extent of the operation performed and individual characteristics. Sometimes wearing a rigid or semi-rigid corset or Chance collar is indicated.
Thus, it is always easier to cope with a dorsal hernia in the initial stages of its development. Sometimes conservative methods are sufficient, in other cases surgery is indicated. But even in such situations there is no need to be afraid; modern neurosurgeons have high-tech equipment, which allows them to reduce intraoperative risks and the likelihood of complications to a minimum.
What is the danger
The danger of dorsal hernias is that they often compress the structures of the spinal canal. This protrusion forms a stenosis - a narrowing. The larger the size of the hernia, the greater the stenosis.
In the cervical spine, the discs are usually small. Here they compress the roots that form the brachial plexus, which affects the functions of the upper limbs. In rare cases, paresis is possible.
Hernias rarely form in the thoracic region. They can also compress the roots, causing impaired chest excursion and pain. In rare cases, protrusions in the cervical and thoracic regions compress the spinal cord. This causes disruption of innervation in the underlying parts of the body.
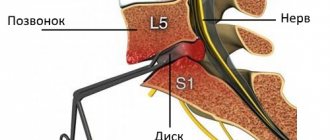
The most dangerous is a dorsal hernia of L5-S1 or L4-L5. There is no longer a spinal cord in the lumbar region; only the roots remain here. The spinal cord is surrounded by several membranes and can withstand pressure for a long time. The roots are more mobile and delicate structures. One hernia in the lumbosacral region can affect several roots at once. In this case, the innervation of the lower extremities, perineum and pelvic organs suffers.
Each type of intervertebral hernia has serious complications, so you should not delay treatment.
See how easy it is to get rid of a hernia in 10 sessions
Localization of dorsal hernia
Dorsal hernias occur in different parts of the spine.
Dorsal cervical hernia
Dorsal cervical hernia most often occurs in the interval C5-C6, C6-C7. Less often - in the interval C4-C5. In a more proximal direction, this pathology practically does not occur. In the cervical region, protrusions are often post-traumatic in nature. For example, this happens in car accidents involving belted passengers.
The cervical region has small vertebrae and a narrow spinal canal. Small hernias of this section affect the roots, which affects the innervation of the arms and shoulder girdle. Medium-sized protrusions can compress the substance of the spinal cord, causing disruption of the innervation of the body, internal organs and even legs.
Find out more about the symptoms and treatment of cervical hernia, read our article.
With a dorsal hernia, protrusion of the intervertebral disc occurs into the lumen of the spinal canal
Dorsal hernia of the lumbar and sacral region
Dorsal lumbar disc herniations most often occur in the L4-L5 space, less often in the L3-L4 space, and almost never in the more proximal regions. The sacrum itself does not have vertebral discs - it is a solid bone structure. But between the last lumbar and first sacral vertebrae a lumbosacral hernia often occurs.
Dorsal hernias of the lumbar and sacrum occur most often during destructive processes in the vertebral bodies, in people with obesity and a sedentary lifestyle. Injuries to this section are rare; the vertebrae here are the most massive.
At this level there is no longer any spinal cord substance; what remains is the so-called “cauda equina” - a bundle of spinal roots. Hernias of the lower back and sacrum are dangerous because they can affect several nerve roots at once. In this case, the innervation of the lower extremities and pelvic organs suffers.
Read more about lumbar hernias in this article.
Dorsal thoracic hernia
Dorsal hernias of the thoracic spine are rare. They most often occur as a result of traumatic injury (a car accident or falling flat on your back). In this case, a hernia can appear between any two thoracic vertebrae.
Here, roots emerge from the spinal cord and innervate the chest and internal organs. If the protrusion affects one of them, pain and disruption of innervation occurs exactly along the affected root. The size of the hernial contents determines how deep the structures will be damaged. Large bulges can cause compression of the spinal cord. This leads to disruption of the innervation of the lower extremities and perineum.
More information about thoracic hernias here.
A dorsal hernia of the thoracic region can appear between any two vertebrae of this region
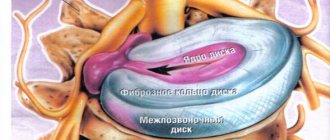
What is an intervertebral disc
Intervertebral discs are cartilaginous formations of a close to round shape, located between the bodies of adjacent vertebrae. Like the vertebrae of different parts of the spine, they have different sizes. Therefore, in the lumbar region the discs are the largest and strongest, which has developed evolutionarily. This allows the spine to withstand daily stress.
Each intervertebral disc has its own internal nucleus, called the pulpous nucleus. It is a viscous, gelatinous mass with high elasticity, which ensures the main shock-absorbing function of the spine.
The nucleus pulposus is surrounded by a special, fairly dense membrane - the fibrous ring. It has a fibrous structure, and the fibers are intertwined in 3 different directions. The last element of the intervertebral disc is the endplates that protect it.
Unlike most other anatomical structures of the human body, discs have a diffuse type of nutrition. In other words, nutrients are not supplied to it directly with the blood through the vessels, but penetrate through the membranes. This is one of the reasons for their gradual destruction over the years, since with age the intensity of blood flow decreases, chronic diseases affect it, and eating habits often leave much to be desired.
The intervertebral discs of the lumbar spine, particularly L4–L5, have a significantly larger diameter than they are tall.
Types of dorsal hernia
Dorsal hernias differ in types depending on their location in relation to the spinal canal. Thus, foraminal, median-paramedian, diffuse, median, left-sided and right-sided, as well as sequestering hernia are distinguished.
Foraminal
A foraminal hernia is a hernia that protrudes far into the lumen of the spinal canal (from the Latin foramen - hole). This is the most dangerous type. Such protrusions of the nucleus pulposus affect the radicular structures and the spinal cord. This type is quite common and always has many symptoms.
Median-paramedian, medial-paramedian
This type is characterized by displacement of the disc centrally and sideways. This protrusion causes damage to the nerve roots. As a rule, it is precisely such hernias that lead to the development of movement disorders.
Paramedian, paramedian
Paramedian hernia is a displacement of the intervertebral disc to the side (to the left or to the right). In this case, the nerve root is slightly affected. As a rule, this type leads to tension in the back muscles on the affected side and poor posture.
Diffuse
Dorsal diffuse disc herniation is characterized by destruction of the nucleus pulposus while the annulus fibrosus is preserved. In this case, the disc can bulge from any side. This type leads to stenosis of the spinal canal and the rapid development of radicular syndrome.
Medial/median
The dorsal median hernia will stand in the lumen of the spinal canal exactly in the middle. It does not affect the radicular structures, but can compress the spinal cord. This type occurs infrequently and is characterized by a discrepancy between the localization of symptoms and the location of the lesion.
Left/right
Most often, the hernia is located only on one side or affects mostly one side. Right-sided ones are more common. All symptoms are located on the same side. Large and median hernias can cause disturbances on both sides at once.
Sequestering
A sequestrum is a necrotic area of tissue lying among living, functioning tissues. A sequestered form of dorsal hernia is said to occur when part of the intervertebral disc is separated from its main mass. In this case, the sequester lies in the spinal canal.
Read about other types of spinal protrusions in the article “Types of hernias.”
Intervertebral hernia - specialists in Moscow
Choose among the best specialists based on reviews and the best price and make an appointment with
an Orthopedic Surgeon
Dubinsky Artyom Igorevich
Moscow, st.
Sretenka, 9 (Capital Medical Clinic) +7 0 Write your review
VertebrologistOrthopedistSurgeon
Sychenikov Boris Anatolievich
Moscow, st. Avtozavodskaya, 16, bldg. 2 (Clinic “Medicine 24/7”)
+7
0 Write your review
VertebrologistOrthopedistSurgeon
Symptoms of a dorsal hernia
There are a number of common manifestations that are characteristic of an intervertebral hernia of any part. These include:
- Pain
is the first and most common symptom; - Spasm of striated muscles
is a painful muscle tension corresponding to the localization of the pathology; - Radicular syndrome
is a disturbance of innervation due to damage to the roots of the spinal cord (loss of sensitivity, changes in reflexes, motor disorders, dysfunction of internal organs).
The specific features of the manifestation of each of these syndromes depend on the localization of the pathology.
What types of intervertebral hernias are most difficult to treat?
4 stages of treatment for intervertebral hernia
Symptoms of lumbar dorsal hernia
Manifestations of a dorsal hernia in the lumbar region range from low back pain to disorders of the pelvic organs and paresis of the lower extremities. Symptoms largely depend on the size of the hernia and the number of damaged roots. Pain from a spinal hernia can be localized in the lumbar region, buttocks, and along the back of the thigh. Particularly intense pain is observed when the sciatic nerve is pinched.
Sensory disturbances occur along the front surface of the lower leg and in the foot. There may also be a feeling of tingling, burning, or numbness. Movement disorders in the form of paresis and paralysis are observed in severe cases. They affect the toes and ankle joints, and rarely the knee joints.
Dorsal herniation of the L5-S1 intervertebral disc can lead to dysfunction of the pelvic organs. In this case, constipation or incontinence of feces and urine is observed. Erectile dysfunction and infections of the urogenital tract are possible.
Symptoms of thoracic dorsal hernia
The most common symptom of a hernia is aching pain.
This species is rare. The difficulty in diagnosing it is that the pathology occurs under the guise of other diseases. Pain along the nerve (clearly on the affected half of the chest between the ribs) can be mistaken for intercostal neuralgia, myalgia, or herpes zoster.
Disruption of innervation at this level affects internal organs more than superficial structures. Respiratory disturbances and cardiac arrhythmias may occur. Sensory impairment is very rare and often goes unnoticed.
Symptoms of cervical dorsal hernia
Cervical dorsal hernia most often manifests itself as a radicular syndrome in the innervation zones of the spinal nerves C6, C7 and C8. They are responsible for the motor and sensory function of the arms and shoulder girdle. In this case, numbness and tingling “crawling” are felt in one or more fingers or both hands. Such symptoms are called paresthesia - they are the main evidence of a violation of innervation. Pain occurs most often in the neck or along the nerve - from the shoulder girdle to the fingertips.
There may be impairment of motor function of the arm or both arms. Most often, the lesion is one-sided and movements are impaired in one or two fingers of the hand. With deeper injuries, paresis in the shoulder joint is possible.
Changing the position of the nerve roots
Most often, the roots in the zone of conflict with the disc are poorly visualized, which is especially typical for sequestered hernias or protrusions. In such cases, the expected location of its location can be determined by an imaginary trajectory connecting the “pre-hernial” and “post-hernial” images of the root. In other cases, a herniated disc displaces the root asymmetrically. With large sequestered hernias or protrusions and a pronounced adhesive process, the hernia and paradiscal tissues are not differentiated and look like a single conglomerate.
The following CT changes in the extrasaccal portion of the root are also identified:
- dislocation
- aggregation
- compression
- conglomeration
Diagnostics
Diagnosis and treatment of dorsal hernia is carried out by doctors such as neurologists, vertebrologists, and neurosurgeons. First of all, you should contact a neurologist or vertebrologist. These specialists diagnose the condition of the spine, evaluate symptoms, and identify the location and depth of the lesion. It is impossible to establish a diagnosis without additional research methods. These include:
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
This is the gold standard for diagnosing intervertebral hernias. Tomography allows you to see both bone structures and soft tissues. In this way, it is possible to diagnose pathology, determine its type and location, and assess damage to spinal cord structures. - CT scan.
This type of study is used when it is not possible to do an MRI. To a greater extent, it is aimed at assessing bone structures, and to a lesser extent – soft tissues. - X-ray of the spinal column.
This type of examination does not show soft tissue. The presence of a hernia is not visible on x-ray. But this type of study allows us to evaluate the bone structures, location and integrity of the vertebral bodies. Used with CT or MRI. - Lab tests.
A general blood test and clinical urine test are performed. In some cases, a number of additional tests are performed at the discretion of the doctor.
How to treat spinal diseases?
Step 1. It is recommended to contact a trainer involved in physical therapy. Sometimes this type of physical activity helps not only to heal, but also to prevent the development of back diseases altogether. Working with a trainer is necessary at first - it is important to learn how to perform the exercises correctly. Then you can study at home on your own.
Contact a trainer
Step 2. You can take medications prescribed by your doctor. It is important to remember that you cannot prescribe medications yourself - they may have contraindications.
Take medications if necessary
Step 3. In some cases, it is necessary to wear a back support corset. However, before purchasing this device, it is also important to consult a specialist.
Use a corset
Supportive corset for the spine
Step 4. Massage therapy is also a good therapy option. You should find a good massage therapist and take a course.
Massotherapy
Step 5. In case of severe pain, you can ask your doctor for an appointment for a blockade.
Blockade
Step 6. In any case, it is important to visit a specialist’s office, get advice on treatment, and discuss any concerns regarding back health.
Talk to your doctor
Step 7. It is important to monitor your body weight and, if necessary, reduce it. Excessive weight negatively affects the condition of the spine and increases the already heavy load on it.
Watch your weight
Treatment of dorsal hernia without surgery
Drugs for the treatment of dorsal hernia
Medication
Treatment of dorsal hernia with conservative methods is aimed at reducing the severity of symptoms. For this use:
- Paravertebral blockades
- the introduction of local anesthetics (Novocaine or Lidocaine) into the projection of the hernial protrusion, allows you to get rid of pain; - Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
(Diclofenac, Nimesulide, Ketanov) - not only relieve inflammation, but also reduce pain, used in tablet or injection form; - Muscle relaxants
(Sirdalud, Meloxicam) – relieve muscle tension, relieve spasm and associated pain; - B vitamins
are prescribed if the patient has radicular syndrome.
Read about the most effective method of relieving pain from a hernia in the article “Spinal block”.
Folk remedies
Of all the folk remedies, ointments and ointment applications help the most. You should choose an ointment with an anti-inflammatory effect (Voltaren, Fastum, Diclofenac). It is recommended to use them according to the instructions and in combination with traditional medicine methods. Applications can be carried out by applying the ointment to gauze and applying it to the sore area for half an hour to an hour.
Bubnovsky method
Treatment according to the Bubnovsky method is therapy using physical exercises. The equipment used is a multifunctional simulator developed by Bubnovsky. If it is not available, your own body weight is sufficient for exercise. Bubnovsky himself claims that this type of treatment can replace traditional therapy. But it is recommended to use physical exercises in conjunction with the main treatment.
Physiotherapy
The use of physiotherapeutic methods is also an additional method of treatment and rehabilitation. Most often used:
- Magnetic therapy is the use of magnetic radiation to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Acupuncture is a traditional method of Chinese medicine, performed by trained professionals, aimed at reducing pain, treating paresis and organ dysfunction.
- Electrophoresis is the directed movement of drug particles in an electric field, most often used with cariprazyme to reduce inflammation and with novocaine to reduce pain.
Exercise therapy
Exercise therapy should begin under the supervision of an instructor. The most commonly performed exercises are:
- From a standing position, slowly turn and tilt your head.
- From a standing position, swing your legs forward, backward, left, right.
- From a supine position, raise your arms and stretch your torso along the floor.
- From a supine position, lift and bend alternately the right and left legs at the knee joint.
- From a lying position on your stomach, lift and bend your legs at the knee joints, try to touch your buttocks alternately with your right and left leg.
Massage and manual therapy
Massage and manual therapy are often used for back problems. They help reduce pain and muscle tension. Most often, soft, gentle techniques are used in combination with basic drug treatment. Massages are not recommended in cases where the hernia is complicated by paresis.
Conservative treatment methods
It is possible to do without surgical intervention only in the early stages of the development of pathology. On average, conservative treatment is effective if a dorsal herniation of the L5–S1 or other intervertebral disc up to 0.5–0.7 cm in size is detected. In other cases, it is also prescribed, but the likelihood of reducing pain and improving the patient’s condition is sharply reduced.
As part of conservative therapy, the vertebrologist prescribes a set of measures, each of which will potentiate the effect of the other. Therefore, its components are:
- drug therapy;
- traction therapy;
- exercise therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- use of orthopedic corsets, bandages or collars.
Semi-rigid lumbar corset
At first, patients are advised to adhere to strict bed rest in order to minimize the load on the spine. The doctor decides individually how long you will need to stay at home in bed. In the future, short walking and sitting are allowed, but lifting weights and performing heavy physical work is strictly prohibited. Otherwise, the dorsal hernia will increase and the patient’s condition will worsen. As a result, the only way to get rid of pain will be surgery.
Drug therapy
The objectives of drug treatment are to eliminate pain, eliminate muscle spasms, improve the conduction of nerve impulses, and create better conditions for the regeneration of the intervertebral disc. Therefore, patients are prescribed:
- NSAIDs;
- muscle relaxants;
- B vitamins;
- chondroprotectors.
Drugs to relieve pain from disc herniation
Sometimes a dorsal diffuse disc herniation L5–S1 measuring 0.5 cm or more provokes severe pain, the relief of which requires blockades. The procedure is carried out only in a medical facility and involves injections of solutions with painkillers and anti-inflammatory substances at precisely defined points around the affected area.
Traction therapy
Spinal traction in the early stages of dorsal hernia development can be very effective. Thanks to the course of procedures, the pressure on the intervertebral disc is reduced, which quickly leads to an improvement in the patient’s condition.
Traction traction of the cervical spine
Exercise therapy
The basis of conservative therapy is physical therapy. A properly selected set of exercises relieves spasms from overstrained muscles and tones relaxed ones. Exercise therapy also helps reduce pain.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed outside the acute period of the inflammatory process and are aimed at accelerating tissue repair processes. Therefore, patients may be advised to:
Magnetic therapy of the lumbar spine
- electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- massotherapy.
Alternative Methods
In order to increase the effectiveness of conservative therapy, patients can take courses:
- acupuncture;
- reflexology;
- osteopathy;
- kinesitherapy.
Points for acupuncture
Removal of dorsal hernia
Removal is not the primary treatment method. Surgical intervention is resorted to if there are indications.
Indications for surgical treatment:
- Large size hernia (more than 10mm).
- The presence of paresis or paralysis.
- Lack of sensitivity due to compression of the nerve roots.
- Disorder of the function of the pelvic organs.
- Failure of conservative treatment for three months.
We use non-surgical hernia treatment techniques
Read more about our unique technique
Types of surgical interventions
- Microdiscectomy
is the removal of the disc along with the hernia through a paravertebral incision 2-3 cm long, used for relapse. - Laminectomy –
resection of part of the intervertebral disc along with the hernia through a small incision, used for relatively large protrusions. - Endoscopic discectomy
is the removal of a hernia or disc using special endoscopic instruments, performed through a puncture in the skin and minimal incisions. - Nucleoplasty
is also a minimally invasive technique that allows you to destroy hernias by introducing various substances into the disc, and is used for small sizes.
Rehabilitation after surgery
Therapeutic exercises and swimming help to recover faster after removal of a dorsal hernia
During the rehabilitation period, it is recommended to continue treatment. Preference should be given to the same physiotherapeutic interventions that were used before surgery. For example, in case of severe pain, electrophoresis with Novocaine is used.
Read more about electrophoresis here.
It is important to start physical therapy on time. Light gymnastic exercises under the supervision of an instructor are suitable for this. In the late rehabilitation period, when postoperative wounds have healed, it is recommended to go swimming in the pool.
Prevention and prognosis
There is no specific prevention of dorsal hernia, but there are a number of nonspecific ways to prevent the development of hernial protrusion. People with a genetic predisposition are prescribed chondroprotectors - drugs that improve the nutrition of intervertebral discs.
It is also important to adjust your lifestyle - give preference to moderate physical activity, walking, swimming, yoga. Lifting heavy objects should be avoided. In addition, it is important to adjust your diet to avoid gaining excess weight.
As for the prognosis, with early diagnosis and timely treatment it is favorable. The larger the hernia, the less favorable the prognosis.
How to diagnose
The main diagnostic methods that can confirm extrusion of intervertebral discs are magnetic resonance imaging and computer scanning. An MRI will show the exact cause of back pain: lumbar radiculopathy can accompany not only intervertebral hernias, but also foraminal (lateral) lumbar stenosis against the background of compression of the sciatic nerve by a cyst, tumor, etc. CT better demonstrates damage to bone tissue.
Early in-depth diagnosis is necessary if neurological disorders increase, persistent pain syndrome occurs, or if treatment of intervertebral disc extrusion involves epidural administration of drugs.
Approach to treating the disease in our clinic
The Paramita clinic has developed a unique approach to the treatment of dorsal hernias. This:
- thorough preliminary examination of the patient using instrumental studies and oriental methods;
- development of an individual treatment plan for each patient, taking into account the characteristics of the disease;
- using a treatment complex that includes advanced European techniques and traditional Eastern methods, which allows you to get rid of a hernia and improve the health of the body as a whole.
We eliminate pain during the first visits to the doctor.
FAQ
How to relieve pain from a dorsal hernia?
The most effective method is paravertebral blockades, which are performed only in medical institutions. At home, you can use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Is there a chance to cure a dorsal hernia without surgery?
In some cases, it is possible to avoid surgery for a dorsal hernia. Timely initiation of conservative therapy can delay surgery or help avoid it. In advanced cases, if complications occur, surgical intervention is mandatory.
How long does the recovery period take after surgery?
The early postoperative period is one to two weeks. In favorable cases, complete recovery requires 4-6 weeks. With a less favorable outcome, rehabilitation may take up to six months.
Themes
Intervertebral hernia, Spine, Pain, Treatment without surgery Date of publication: 11/12/2020 Date of update: 12/23/2020
Reader rating
Rating: 5 / 5 (2)