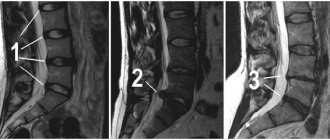
Foraminal disc herniation is one of the types of hernia, which occurs in 10% of the total number of this pathology. It is characterized by bulging of the intervertebral disc into the space where the nerve roots extending from the spinal cord are located.
Foraminal disc herniation is characterized by severe pain that cannot be relieved with conventional painkillers.
If you suffer from this disease, immediately contact the neurosurgery department of the CELT clinic. We have everything you need to help you!
Depending on the type of operation and category of complexity from 100,000 - 250,000 rubles.
Included in the price:
surgery, anesthesia, dressings, medications, food and hospital stay, observation by a surgeon in the postoperative period.
40-60 minutes
(duration of operation)
2-3 days in hospital
Indications
- persistent and severe symptoms of compression of the spinal nerves by a herniated disc, not amenable to conservative therapy
- the patient's desire to get rid of pain
Contraindications
- chronic diseases in the stage of decompensation
- acute inflammatory processes in the body
What it is
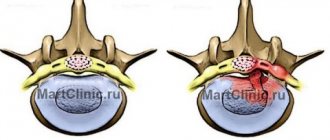
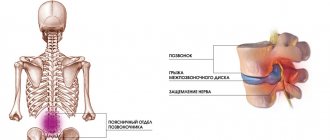
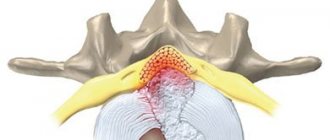
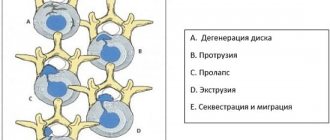
A foraminal hernia is a protrusion of the intervertebral disc into the opening where the nerve roots are located . It is called foraminal. With a paraforaminal hernia, the intervertebral disc is displaced and partially extends beyond the established boundaries of the physiological space.
Foraminal hernia is characterized by protrusion of the disc towards the nerve roots
The foraminal space is the area between the vertebrae that are connected to each other. The spinal roots pass through it, like through a canal. When discs protrude into it, patients immediately begin to experience severe pain, because the disc begins to put pressure on the nerve endings. Considering that the foraminal opening is only 1.5 cm long, the resulting hernia immediately affects the nerve fibers, they have nowhere to move.
Clinical picture
The disease progresses quite quickly . When a foraminal hernia occurs, pronounced symptoms immediately appear. It is almost impossible to get rid of the pathology with the help of medications. The pain becomes constant.
Narcotic analgesics can help relieve the pain a little. But doctors recommend not to waste time trying drug treatment, physiotherapy and other methods, but to undergo surgery immediately after the diagnosis is established.
Classification
Depending on the location of the foraminal hernia between the L4 and L5 vertebrae, several types of displacement are distinguished.
When the hernia is located:
- at the entrance to the intervertebral foramen - medial;
- in the cavity itself - intraforaminal;
- at the exit from the opening of the intervertebral canal - lateral;
- outside the vertebrae - extraforaminal.
Left-sided and right-sided foraminal hernias are also distinguished depending on which direction the displacement occurs.
Prevalence and significance
Foraminal hernias of the spine, fortunately, are not very common. Among all people who have been diagnosed with intervertebral hernias, 4-10% of patients are diagnosed with foraminal protusion. This is considered the least successful option for the location of the hernia .
Such hernias are dangerous for patients. They affect life. In the initial stages, the severity of symptoms depends on the size of the hernia and the size of the foraminal space. But as the disease progresses, the quality of life changes significantly.
Video: “Formation of protrusions and hernias of the spine”
Possible complications
Ignoring the problem, reluctance to go to the doctor and self-medication for a hernia L5–S1 is fraught with the development of severe complications, including:
- hernia sequestration;
- spinal canal stenosis;
- complete paralysis of the legs;
- loss of control over urination and bowel movements;
- persistent impotence.
Therefore, at the first signs of deviations from the norm, you should contact a chiropractor, neurologist or vertebrologist. The doctor will be able to select the most effective therapy for a given patient, which will help not only eliminate the unpleasant manifestations of the disease, but also affect the condition of the disc itself.
Thus, a hernia of the L5–S1 spine can pose a serious danger, but if you seek medical help in a timely manner, it can be effectively dealt with and a high quality of life can be maintained.
0 0 votes
Article rating
Risk factors, causes
Hernias between the L4 and L5 vertebrae, in which the intervertebral disc partially extends beyond the established physiological space, may occur due to:
Pay attention to the reasons for the formation of intervertebral herniation, unsuccessful falls, impacts, which resulted in displacement of the lumbar vertebrae;- intense physical activity, during which the patient lifted and carried heavy objects, sharply bent over, bent, jumped, turned;
- dystrophic processes developing in the tissues of intervertebral discs;
- a sedentary lifestyle, in which the spinal column is bent, skeletal muscles atrophy, and osteochondrosis develops;
- inflammatory processes that have developed as a result of the activation of viral and bacterial infections.
Very often, the exit of the intervertebral disc into the foraminal opening is provoked by lifting heavy objects . The space between the lumbar vertebrae L4 and L5 suffers mainly, since they bear the greatest load.
Risk factors for the development of pathology include:
- inadequate living conditions;
- hard work;
- low mobility;
- overweight;
- professional sports.
Under the influence of these factors, protrusion of the intervertebral disc into the foraminal opening may begin.
Preventive measures for intervertebral hernia
Four simple tips will help prevent disease:
- Play sports. Exercise will help strengthen your back muscles. A well-developed muscle corset will support the spine. If you have a chronic medical condition, consult your doctor before starting exercise.
- Keep your back straight. Watch your posture, especially when you sit for long periods of time.
- Lift weights correctly. Don't bend your lower back. While bending, the hip joints should work.
- Maintain a normal weight. Extra pounds are bad for more than just your back. Because of them, the cardiovascular system and other organs suffer.
And the most important advice: if you have back problems, do not hope that it will “go away on its own” and do not self-medicate. Visit a doctor. Our rehabilitation neurology clinic employs excellent specialists who are ready to examine and advise you. Make an appointment, call +7 (495) 230-00-01
Take care of yourself, book a consultation now
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
An advanced intervertebral hernia can lead to disability, when a person is unable to cope with household chores and constantly needs outside help. Therefore, when the first symptoms appear, it is important to immediately undergo an examination and begin treatment for a disc herniation. If measures are taken on time, most patients can manage with medication and physical therapy. The more pathological changes in the spine increase, the higher the likelihood that you will have to resort to surgery.
Consequences
When diagnosing a foraminal hernia, doctors exclusively recommend surgery . If the patient refuses, he will be prescribed a course of drug therapy. As practice shows, after treatment with pills and injections, people still come for surgery.
For dorsal foraminal hernia, delaying treatment is not recommended . It progresses quickly, noticeably worsening the state of health. Lack of adequate therapy can cause deterioration in the functioning of the lower extremities. Depending on whether the patient has a left- or right-sided protusion, atrophy of the patient’s left or right leg is possible.
There is no point in delaying the treatment of foraminal hernia, as it progresses quite quickly
In some cases, it is even possible that a paraforaminal hernia may compress the anterior artery running in the spinal canal. This leads to poor blood circulation and lack of oxygen. As a result, the patient may have a heart attack, which will cause paralysis.
Rehabilitation
After surgery, the rehabilitation period begins. Its severity and duration depend on the type of hernia surgery performed. Therefore, after nucleoplasty, patients can return to their normal routine on the same day and only give up heavy physical work and bending. After endoscopic removal and microdiscectomy, rehabilitation is more complex and requires a hospital stay of about a week.
Patient 15 years old with disc herniation L4-L5: left
After discharge, the patient receives detailed recommendations. During the rehabilitation period, drug therapy, wearing an orthopedic corset, exercise therapy, and physiotherapy are indicated. Sometimes patients are recommended sessions of manual therapy, kinesitherapy, swimming, and yoga.
Patient 15 years old the day after removal of a herniated disc L4-L5.
Symptoms and diagnostic methods
Most often, patients who, during the diagnostic process, are diagnosed with foraminal hernias between the L4 and L5 vertebrae, come with complaints of severe back pain. But this is not the only symptom of pathology.
Signs of the development of a paraforaminal hernia include:
- lack of tendon reflexes;
- weakness of the foot flexors/extensors;
- sudden increased pain that temporarily blocks physical activity, the patient may take an unnatural body position;
- impaired sensitivity of the skin of the legs;
- deterioration in motor function: the patient cannot step on his foot normally;
- disruptions in the functioning of the pelvic organs;
- the beginning of the process of soft tissue necrosis.
Delaying a visit to the doctor or trying to self-medicate can lead to paralysis of the limbs.
After a preliminary interview and examination of the patient, the doctor may assume the presence of a hernia. The preliminary diagnosis can be confirmed and the location of the hernia can be determined using magnetic resonance or computed tomography. These examination methods make it possible to determine the size of the protrusion and determine exactly how it affects the nerve endings.
To confirm or exclude the presence of concomitant pathologies of the spine, ultrasound and x-ray examination are prescribed.
Video: “Intervertebral disc herniation”
Want to know more about herniated discs? Read the following articles :
- You will learn how to treat a herniated cervical disc on the page pozvonochnik/drugie-zabolevaniya/mezhpozvonochnaya-gryzha/gryzha-diskov-shejnogo-otdela-pozvonochnika-s4-s5-s5-s6-s6-s7.html
- Read more about risk factors for thoracic hernia in the next article.
- What is a sequestered hernia of the spine and how is it treated?
Which doctor treats protrusions
First of all, one can never say that a patient has a foraminal protrusion or hernia until the doctor sees it with his own eyes, examining MRI scans of the corresponding part of the spine, performed with a sufficiently high resolution (1.5 Tesla).
Accordingly, the patient must first be examined by a neurologist and prescribed magnetic resonance imaging. CT, or X-ray computed tomography, is less informative. No other diagnostic methods allow an accurate diagnosis.
Perhaps, in the case of a prolonged course of the disease, a significant decrease in strength in the legs and in the presence of sensitivity disorders, it is still possible to conduct electroneuromyography, which will show how severe the disorders are in the corresponding nerve roots of their peripheral nerves. This study can determine prognosis, for example, in determining the degree of disability. But ENMG is an auxiliary diagnostic method; it does not show the actual presence of hernias.
Treatment
Did you know that...
Next fact
The doctor evaluates the anatomical features of the hernia, established using CT or MRI, neurological manifestations and the patient’s subjective sensations. Based on the results obtained, treatment tactics are determined.
If the hernia is small and the patient says that the pain is of moderate intensity, then you can try conservative treatment methods in combination with physiotherapy. But most often they resort to surgical intervention.
Conservative treatment is intended for:
- reducing pain;
- eliminating external factors that aggravate the problem;
- relieving inflammation;
- improving tissue trophism in the affected area;
- strengthening the muscles that support the spinal column in the correct position;
- reducing swelling and the size of the formed hernia.
Sometimes it is possible to alleviate the condition using conservative methods. But more often with their help you can simply delay the time when surgery becomes necessary.
Drugs
When an intervertebral disc bulges, a complex of several groups of drugs is prescribed. Conservative treatment is aimed primarily at reducing pain.
The doctor may prescribe:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- analgesics (including narcotics);
- glucocorticosteroids;
- medications needed to reduce muscle tension;
- medications that improve tissue trophism.
Sometimes doctors give local injections of medications into the affected area (blockades). They can temporarily reduce pain. Chondoprotectors and B vitamins are also prescribed. The standard treatment regimen includes recommendations for injections of Milgamma and Diclofenac.
Surgery
In case of foranominal herniation of the intervertebral disc between the L4 and L5 vertebrae, surgery is most often prescribed immediately.
It is recommended if the patient has:
- paralyzed limbs or sphincter;
- pronounced pain syndrome that cannot be controlled with medication;
- the size of the protrusion is more than 8-10 mm.
Operations are performed only in special neurosurgical departments of hospitals. Depending on the condition, they can carry out :
- laminectomy;
- microdiscectomy;
- installation of interaxial spacers.
During a laminectomy, the intervertebral discs and bony structures located above the problem area are partially removed. With microdiscectomy, the entire disc that is compressing the nerve endings is removed. Interaxial spacers are installed to reduce the intensity of compression of the spinal cord.
If a patient has a lateral hernia, it is often necessary to remove the entire facet joint. Alternative methods of surgical intervention include endoscopic operations, in which the disc is partially removed.
Exercises, exercise therapy, massage
Drug treatment is always combined with physiotherapeutic procedures, massage, acupuncture, manual therapy, water procedures and therapeutic exercises . But only a doctor should prescribe massage and exercise therapy, taking into account the patient’s condition. Often these methods of therapy for foraminal hernias are strictly prohibited due to the increased likelihood of pinched nerve endings or prolapse of the core of the intervertebral disc into the canal . In the initial stages of the disease, you can try to reduce the size of the hernia using electrophoresis with special medications .
Treatment at home
At home, you can slow down the development of a hernia with the help of a bandage. Patients should understand that it is almost impossible to get rid of a foraminal hernia without surgery .
But if they have chosen this method of therapy, then it is necessary to slightly adjust their lifestyle.
At home, you can increase the likelihood of success from conservative treatment methods by wearing a bandage and using an orthopedic mattress for sleeping.
It is important to be able to keep the spinal column straight: it is necessary to minimize the amount of bending and twisting.
It is prohibited to stretch the spine during hernias . This can cause an increase in the distance between the vertebrae and even greater prolapse of the intervertebral disc.
As a result, pressure on the nerve roots will increase.
If the vertebrae return to their place, the hernia may be compressed and the nucleus pulposus of the disc may fall out into the area where the spinal nerve endings pass.
Prevention
The development of a foraminal hernia between the L4 L5 vertebrae can be prevented if all risk factors leading to its occurrence are minimized . It is necessary to avoid excessive physical activity and be careful to prevent injuries.
In patients who lead a healthy lifestyle and do not forget about the importance of moderate physical activity, the likelihood of developing this pathology is minimal.
FAQ
How to relieve pain?
It is recommended to lie on your back on a flat surface and take an anesthetic or NSAID. For acute pain, a blockade will help.
Is there a chance to be cured without surgery?
Yes, if you seek qualified help early, it is possible to use only conservative treatment.
How long does the rehabilitation period take?
Recovery after surgery ranges from 1 to 2 months.
Bibliography:
- Kalantarov, T.K. General issues of propaedeutics of surgical diseases [Text]: educational manual / T.K. Kalantarov, E.M. Mokhov - Tver: Triada, 2012.
- Bubnovsky, S.M. A herniated spine is not a death sentence! / CM. Bubnovsky. - M.: Publishing house "Eksmo" LLC, 2011
- Handbook of Spine Surgery. Ali A Baaj, Praveen V. Mummaneni, Juan S. Uribe, Alexander R. Vaccaro, Mark S. Greenberg.–Thieme, New York—Stuttgart.–2011.
- European Manual of Medicine. Neurosurgery. W. Arnold, U. Ganzer, Christianto B. Lumenta, Concezio Di Rocco, Jens Haase, Jan Jakob A. Mooij. 2009.
- Amosov, V. N. Hernia. Early diagnosis, treatment, prevention / V.N. Amosov. — M.: Vector, 2013
Themes
Intervertebral hernia, Spine, Pain, Treatment without surgery Date of publication: 12/01/2020 Date of update: 03/16/2021
Reader rating
Rating: 5 / 5 (1)