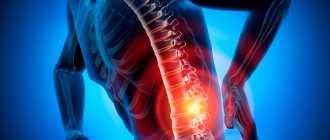
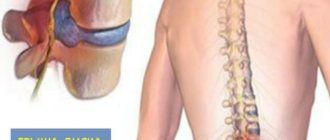
A herniated disc, or, as it is often called, a herniated disc, is a very common pathology that affects several aspects of the patient’s health at the same time. First of all, this disease causes severe pain to the patient. In addition, it can lead to the development of numerous complications, among which are:
- decreased sensitivity of the muscles of the buttocks, thighs, and legs;
- paresis and complete paralysis of the muscles of the lower extremities;
- various dysfunctions of the pelvic organs.
At risk of developing this pathology are primarily patients with scoliosis and other postural disorders, obesity, lack of certain vitamins and nutrients in the body, as well as elderly people whose intervertebral cartilage may undergo age-related changes.
Prices for manual therapy treatment
| SERVICES LIST | PRICE, RUB. |
| Soft manual techniques (45-60 min.) | 7 500 |
| Osteopathic techniques (30-75 min.) | 7 500 |
| Magnetic Vacuum Acupuncture | 1 600 |
| Intra-articular administration of a drug (excluding the cost of the drug) | 4 400 |
| Intra-articular injection (diprospan) | 5 500 |
| Orthoplasma into the joint | 7 000 |
| Intra-Articular PRP Injection | 6 500 |
| PRP therapy for tendonitis, ligamentitis, contractures | 6 500 |
Contact us
Call now
8 (495) 803-27-45
Make an appointment through our service
Make an appointment
Our prices
30% DISCOUNT ON ALL SERVICES FROM PRICE LIST
| Service name | Prices | -30% |
| Appointment with a neurologist-chiropractor | 1000 | 700 |
| Appointment with examination by a neurologist-chiropractor | 1500 | 1050 |
| Manual therapy classic 1 zone | 1000 | 700 |
| Classical manual therapy 2 zones | 1800 | 1260 |
| Multicomponent manual therapy (1 session) | 2600 | 1820 |
| Manual therapy using osteopathy (I level of complexity) | 2300 | 1610 |
| Manual therapy using osteopathy (II level of complexity) | 2600 | 1610 |
| Manual therapy with osteopathy (5 sessions) | 10500 | 7350 |
| Manual therapy with osteopathy (10 sessions) | 20000 | 14000 |
| Joint manual therapy session (one joint) | 600 | 420 |
| Paravertebral blockade | 1500 | 1050 |
| Ultrasound-guided paravertebral blockade | 2000 | 1400 |
| Osteopathy (1 session) | 3800 | 2660 |
| Kinesio taping | 800 | 560 |
| Postisometric muscle relaxation | 1500 | 1050 |
| Acupuncture | 1600 | 1120 |
| Electro-reflexotherapy (device ray-1) | 1550 | 1085 |
Symptoms of lumbar disc herniation
The treatment program for intervertebral hernia includes manual massage, which must be performed by a qualified specialist. When developing treatment, the doctor takes into account the patient’s physical condition, existing medical indications and contraindications to the procedures.
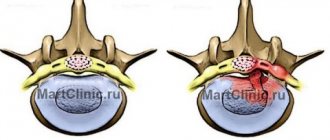
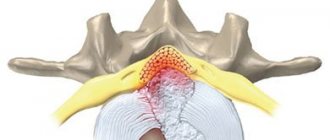
The main symptom of the disease is displacement or damage to the fibrous membrane of the intervertebral cartilage, which leads to the leakage of a jelly-like secretion that fills the disc ring.
The pathological process develops gradually, in several stages:
- Prolapse. The intervertebral disc is displaced a short distance and falls into place without outside intervention.
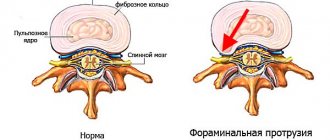
- Protrusion. The displacement becomes more noticeable, but the disc is still located between the vertebrae, remaining within the limits of natural mobility.
- Extrusion and sequestration. The core of the disc bulges and comes out, gets pinched between the vertebrae and ruptures, causing the internal contents to spill out.
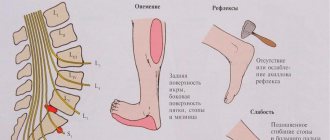
Symptoms depend on the stage of development of the disease and may include: deterioration of the reflexes of the lower extremities, numbness of the feet, lameness, burning sensation, hypertonicity of the back muscles, impaired bladder function, increased sweating, decreased potency in men.
Causes of hernia
- Progressive osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine.
- Poor posture, physical inactivity, weakness of the back muscles.
- Heredity.
- Previous spinal injuries.
- Prolonged hypothermia, sudden climate change.
- Increased physical activity.
- Sudden movements, sports activities with insufficient warming up of muscles, errors in position and pace of exercises.
- Prolonged stay in a sitting position.
- Exceeding normal body weight.
Intervertebral disc herniation: Causes of occurrence
Over many millennia, humans have anatomically adapted to the effects of gravity. Thus, the main power axis of our body, the spine, has acquired a shape reminiscent of a spring with a double S-shaped curvature. The elasticity and firmness of the spine is provided by the intervertebral discs. Thanks to their elastic properties (virtually non-compressible liquid), shocks and tremors experienced by the brain or spinal cord during any movement are significantly softened. But being very fragile, vulnerable formations, they unfortunately suffer from constant gravitational influence.
The appearance of a hernia is most often the result of gradual aging or wear of the intervertebral disc (degeneration). As we age, our spinal discs lose some of their water content. This makes them less flexible and more prone to tearing.
Loss of fluid is the main reason.
During the day, due to the resulting loads on the spinal column, fluid with waste products leaves the intervertebral disc, which leads to a decrease in its size. If loads prevail, then fluid consumption prevails over replenishment of its reserves. Thus, the disc loses water, increasing degeneration (degeneration, destruction) of its tissues develops, which is also accompanied by loosening of the fibrous part, the appearance of cracks (“dry soil”), and a decrease in height (it seems to “shrink”). This leads to a relative increase in the length of the intervertebral ligaments, and all together to an increase in the mobility of the vertebrae relative to each other. The next stage marks the exit of the inner part of the intervertebral disc beyond its limits, which can be facilitated by heavy lifting, unsuccessful turns of the torso, neck, etc. .
But at the same time, there are also many other reasons leading to the appearance of intervertebral hernias, among them:
- general underdevelopment of the muscular corset of the spine,
- heavy physical activity,
- consequences of past injuries,
- incorrect posture,
- the presence of significant psycho-emotional overloads,
- hereditary factor, some others.
All these reasons affect the disruption of water-salt metabolism in the spine and can ultimately lead to the formation of hernias.
Physiology of the spine: age-related changes.
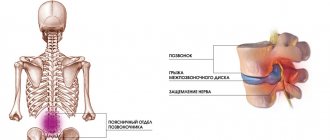
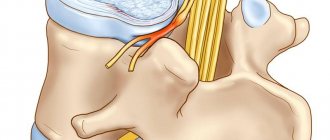
When forming the shock-absorbing and biomechanical properties of the intervertebral disc, the nature of water exchange is of particular importance, which is influenced by the so-called pump mechanism (for more details, see the section Detensor therapy ), as well as hormones of the pituitary gland, adrenal glands, thyroid gland, and individual characteristics of loads on the spine. At the age of 18 to 23 years, the tissue of the discs is most saturated with water and minerals and, as a result, they are strong and flexible. Over time, the content of mineral salts and water decreases, and, as a rule, this process occurs more intensively after 40 years, their depreciation function decreases. Under the influence of loads, they can even flatten, and sometimes the annulus fibrosus and nucleus pulposus protrude (without rupture of the annulus fibrosus) beyond the endplates, which is called protrusion. Over time, degenerative changes in the ring and core intensify and lead to the appearance of cracks and radial tears. With sudden movements: coughing, lifting heavy objects, sneezing, etc., rupture of the fibrous ring may occur. The contents of the intervertebral disc often protrude into the spinal canal in the form of a drop. A hernia can put pressure on a nerve root, causing irritation or compression.
Clinical picture of the cervical spine
>Intervertebral discs begin from the 3rd intervertebral space and provide flexion, extension of the neck and lateral bending with a significant amplitude. The posterior longitudinal ligament is wide, and the height of the intervertebral discs is relatively small. These anatomical and physiological features of the structure of the cervical spine make it very mobile. However, in the cervical region, the posterior longitudinal ligament is weaker, so disc protrusion can occur not only in the posterior, but also in the posterolateral direction. The transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae have openings. Located one above the other, they form a canal through which the vertebral artery, vein and sympathetic nerve pass, therefore, with a hernia of the cervical spine, cerebral circulation may be disrupted and vertebobasilar insufficiency (VBI) may occur.
This often leads to dizziness, headaches, hearing loss, memory loss, and uneven gait.
Read more about vertebobasilar insufficiency..
Autonomic disorders are also additional confirmation of the diagnosis
The following symptoms are also characteristic of a cervical hernia: pain in the neck, shoulder blade, shoulder or arm, numbness of the fingers, pressure surges.
Clinical picture of the lumbosacral region
Herniation of the intervertebral disc in this part of the spine is the most common. Its occurrence is facilitated primarily by the special operating conditions of the lumbar region - higher loads compared to other parts of the spine, since the discs of the lumbar region bear almost the entire weight of the body. The high incidence of hernias in this part of the spine is also associated with the anatomical features of the lower back, primarily with the significant height of the intervertebral discs. Also, in the formation of lumbar hernias, an important role is played by the weak and narrow longitudinal ligament; its width between the lower lumbar vertebrae is only 1-4 mm, so it cannot serve as sufficient resistance to hernial formation. Your spinal cord does not extend into the lower part of the spinal canal. At your waist, the spinal cord divides into a group of long nerve roots (cauda equina) that resemble a horse's tail. All these structural features of the lower lumbar spine make it especially vulnerable.
When a lumbar intervertebral disc herniation occurs, severe pain appears in the lower back. The patient loses the ability to move independently. Later, the pain in the lower back decreases, but shooting pain appears in the buttock, along the back or side of the leg, radiating to the toes.
Knee and Achilles reflexes decrease or disappear. In some cases, the symptoms of an intervertebral hernia are accompanied by a disorder in the pelvic organs in the form of delayed urination or stool. The patient is characterized by an antalgic posture; more often he prefers to stand rather than sit.
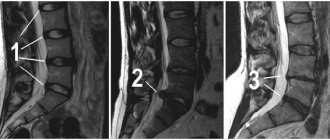
Intervertebral hernia: Diagnosis
Magnetic resonance imaging is used to diagnose intervertebral hernia. Due to the relative softness of the intervertebral disc, the most objective method of examination is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the spine. For the same reason, many parts of it are not visible on an x-ray. After receiving an MRI, your doctor will ask you many questions during your appointment to make a correct diagnosis and develop a treatment plan. These questions will likely include the following:
- When did you start experiencing symptoms?
- Does pain prevent you from doing normal activities?
- Do you feel any pain, weakness or numbness in your arms or legs?
- Do you notice any changes when urinating or bowel movements?
- Does coughing, sneezing or straining to have a bowel movement worsen your leg pain?
- What, if anything, improves your symptoms?
- Is the pain related to sleep or work?
- What medications or nutritional supplements do you take?
To determine the true cause of the pain, the doctor will check your neurological status during the examination:
- Reflexes
- Muscle Strength
- Sensitivity (Ability to sense soft touch, pinpricks, or vibration)
Indications for hernia treatment
Manual therapy is prescribed in the complex treatment of intervertebral hernia in the presence of the following medical indications:
- The occurrence of pain in the first stages of development of the pathological process, when the protrusion of the disc is still small, and restrictions on the mobility of the lumbar spine are observed.
- Significant pain in the final stages preceding a herniated disc.
- Disc displacement between the vertebrae, neurological pain, numbness and tingling of the limbs, spasms of the lower back muscles.
- Osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine.
- Acute pain, long lasting (several months).
Make an appointment
Surgeries to remove a hernia in the lumbar spine
In some cases, in order to avoid disability and get rid of back pain once and for all, the patient may be indicated for spinal surgery. Emergency medical attention is required if:
- the patient has difficulty urinating and defecating;
- with unbearable pain;
- with significant loss of sensation in the legs and arms.
Surgeons of the clinic named after. N.I. Pirogov are fluent in the most modern and minimally traumatic methods of surgical treatment, with proven clinical effectiveness.
Advantages and disadvantages of this treatment method
The demand for manual therapy in the treatment of intervertebral hernia is due to a number of important advantages:
- Effective reduction of pain until it disappears completely.
- Restoring blood flow, enhancing tissue metabolism in the affected area.
- Reducing swelling, relieving muscle spasms in the area of the spinal segment with an intervertebral hernia.
It is impossible to ensure complete recovery of a patient with a hernia using manual therapy methods, which requires the appointment of additional treatment procedures. This area of medical practice can be used as an alternative to surgery. Treatment is effective provided that the pain is moderate in severity and the pathology does not progress beyond protrusion or slight protrusion of the nucleus.
On the day of your initial appointment with any doctor in our Neurology clinic, you can undergo manual therapy or massage with a 25% discount. This way you can form an objective opinion about the services of our clinic and the quality of work of our specialists. And if after this you decide to pay for the full course of further procedures, you will receive a 10% discount on the course of treatment.
How is manual therapy performed for a herniated disc?
Before starting work with an intervertebral hernia, the chiropractor examines the patient in order to localize the pathological protrusion. The examination may require CT or MRI procedures. The treatment program is drawn up taking into account the patient’s condition, the stage of development of the disease, and is aimed at both eliminating the main symptoms and preventing the development of complications.
If manual therapy is carried out in an acute period, the specialist chooses softer techniques to relieve the pain symptom. An improvement in the patient's condition is noted after the first procedure. The treatment uses shock-pulse techniques and decompression techniques, while the efforts applied by the therapist are increased gradually.
The actions of a manual therapy specialist are aimed at creating negative pressure in the spinal column, due to which the hernia will be reduced into place. Further procedures are necessary to prevent the consequences of pathological changes, restore the location of the nucleus of the intervertebral disc, reduce pain, and eliminate the causes that led to the development of a hernia (spinal osteochondrosis).
Diagnostics
The basis of any treatment is a comprehensive diagnosis. Only after a diagnosis of osteopathy has been made, manual therapy brings real benefits without negative side effects. At the appointment, the doctor talks with the patient, learns about his complaints, chronic diseases in order to identify contraindications, and collects anamnesis. The specialist evaluates the flexibility of the spine, range of motion in the joints, the presence of functional blocks, and examines the discomfort zone and associated zones.
Based on the results of the conversation, the doctor prescribes tests and books the patient for the next appointment. The following research is carried out:
- general blood/urinalysis;
- X-ray;
- CT scan;
- MRI;
- Ultrasound.
At the next appointment, the specialist will analyze the information received and select a treatment method. The selection of an individual treatment plan will be based on diagnosis + research data.
How is the session going?
At the appointment, the doctor finds out the patient’s condition, and if it is repeated, he assesses the dynamics of changes, for example, the degree of scoliosis leveling. In the process of work, hard + soft techniques are used.
During the treatment, the doctor uses
Manual therapy techniques:
- myofascial release, effects on muscles, ligaments;
- abdominal therapy, effects on internal organs;
- traction techniques, for example, traction traction of the spine, impact on the cervical, thoracic, lumbar spine separately;
- post-isometric muscle relaxation;
- autorelaxation methods;
The therapist has a lot of techniques that he directs to certain parts of the patient’s body. Manipulation techniques involve the use of short jerky movements in the area of the sacrum or spine. Mobilization techniques are aimed at slight traction of the vertebrae and tilting of the spine. Soft techniques are beneficial in relieving pain, improving muscle tone, and relieving tension.
A few more techniques:
- stretching of shortened ligaments and muscles - suitable for rehabilitation of damaged tissues;
- pressure (pressure) or acupressure, used to influence compaction in the muscles;
- relaxation - tensing the muscles in a certain way for their subsequent complete relaxation.
The benefit of the procedure is to restore the mobility of joints and the spine, reduce muscle spasms, correct organic disorders, and eliminate blockade of the vascular and nerve plexuses.
In his work, the doctor uses manual muscle testing (MMT)
MMT is a method of biological feedback with the body. MMT assesses the activity of the stretch reflex (stretch reflex) under conditions of isometric contraction.
Manual therapy methods
Manual therapy demonstrates high effectiveness in the treatment of hernias that arise as a result of displacement of the vertebrae or intervertebral discs, deformation and dysfunction of the spinal column. Pressure on localized points and stretching of muscle fibers allows the structures to return to their natural position.
Achieving results is ensured by using several methods of manual therapy:
- Muscle-energy method.
This technique is the mildest in impact, and therefore has a minimum of contraindications. The treatment eliminates sudden shocks, active movement, and is aimed at relaxing muscle fibers and smoothly stretching them to increase elasticity and increase blood circulation. This allows you to gently return the spinal segments to their place. The method is suitable for use in cases of severe pain. - Musculofascial release.
A mild impact most often does not cause any discomfort in the patient. Smooth and slow movements aimed at stretching and stretching muscle fibers gradually restore flexibility to the spinal column. The technique relieves swelling in tissues and relieves pain. Despite the softness of the impact, it has significant power. - Pulse technology.
A more traumatic technique should only be performed by a qualified specialist, as it can aggravate the displacement of the intervertebral disc or lead to pinched nerve fibers. Impulse effects involve sharp jolts, rapid tapping, and high intensity movements. The procedure is aimed at restoring the position of displaced vertebrae along the vertical axis. The force of impact is usually moderate, but the movements are sharp, so the accuracy of the actions performed is important. - Craniosacral osteopathy.
The technique covers all segments of the spinal column. Using techniques of stretching, pressing, twisting and turning, the doctor restores the correct position of the vertebrae along the entire length, correcting postural disorders. During treatment, the clearance between the vertebrae increases and the blood supply to tissues improves.
Localization of intervertebral hernia
The methods used in manual therapy for intervertebral herniation are selected based on the location of the disc protrusion.
- Cervical spine
Treatment in this case is aimed at reducing the mobility of spinal structures using automobilization techniques. With one hand, the doctor tilts the patient's head forward, while with the other he holds the chin. The patient slowly turns his head, shaking it slightly. When performing the procedure, it is important to take into account contraindications: manipulation of the neck in the later stages of the disease is excluded; Do not make sudden movements or twisting; If the affected area is painful, massage is not performed. - Thoracic department.
This pathology is characterized by acute pain in the chest area, which is similar to the symptoms of intercostal neuralgia. Manual treatment uses techniques of force on the processes of the vertebral segments and techniques for relaxing the muscles of the damaged area. The procedure is performed on the patient in a lying or sitting position; in addition, triangular prisms can be used, which are inserted between the vertebrae, after which tapping is performed with a hammer. This allows you to remove compression from the disk. A thoracic hernia is treated using transverse massage and stretching of the muscle fibers. - Lumbar region.
Manual therapy for intervertebral hernia in this case involves the use of a wide range of techniques. This is due to the need for maximum relaxation of the muscles, which are the strongest in this area of the spine. The main technique of influence is traction (traction). If the hernia is localized in the posterolateral part, then traction is performed by the legs with the patient lying on his stomach.
The manipulation is performed with caution, in a uniform rhythm of movements. After a break, stretching is repeated with greater force. When a crunching sound appears, we can talk about the positive dynamics of manual therapy. The procedures are carried out every other day; as the course of treatment is completed, the pain decreases and the crunching goes away.
For a hernia in the lumbar region, a directed push is used, which is necessary if softer techniques do not allow the vertebrae to return to their place. This technique can only be used by experienced specialists if there are no results from using more gentle methods.
The essence of the method and the difference from conventional massage
Manual therapy is a set of specific movements used to correct the spinal column . The main goal of this method is to restore the structure of discs and vertebrae. Special techniques help achieve the effect.
Manual therapy and therapeutic massage are different methods of therapy. This therapy is a whole system, so the chiropractor must have extensive knowledge in this area. The technique resembles a regular massage, but there is a big difference between these methods .
The effect of traditional massage extends to a wide area of the body, while manual therapy involves targeted impact with a certain force. Regular massage acts superficially, that is, on the skin, muscles and ligaments, but with manual therapy the effect occurs much deeper.
With the help of manual therapy, you can return the hernia to its original place , and the tissues and organs will not be affected. This method avoids surgery, and the amount of medications is significantly reduced. The manipulations are carried out gently and are highly effective.
Certain movements create negative pressure in the spine, which will push the hernia back to the place where it came from. After exposure, blood flow accelerates, which improves nutrient absorption. This is simply necessary to eliminate the disease.
During manual treatment, the muscles stop showing a defensive reaction, as they are deeply relaxed. In this state, weights and additional devices are not needed to stretch the spinal column.
Results of manual hernia treatment
- Treatment involves performing procedures to restore the functionality of the spine, thereby eliminating the underlying cause of the disease.
- With a spinal hernia, compression of the nerve roots and narrowing of the space between the vertebrae is observed. The use of manual therapy methods can reduce compression of the structures of the spinal column, which reduces pain in the affected area and leads to remission of the disease.
- The pathological process of destruction of the intervertebral disc is triggered as a result of impaired blood circulation and metabolism in the lumbar region. During a course of manual therapy, blood flow is completely restored along the entire length of the spinal column.
- When using medications and physical therapy, the symptoms of the disease are eliminated, but only biomechanical effects using manual therapy methods can free pinched vessels and nerves and improve the patient’s condition.
Intervertebral hernia is difficult to treat and often causes serious suffering to the patient. Manual therapy is one of the most effective treatments that can eliminate the need for surgery, restoring the natural functionality of the spine, eliminating pain and restoring freedom of movement. A full course of treatment allows you to achieve significant improvements; at the initial stage of the disease, the chances of a complete cure are high.
A course of manual therapy is carried out in combination with other procedures to enhance the effect of treatment. Depending on the diagnosis, this may be acupuncture, physiotherapy, osteopathy, etc. These procedures complement each other and can be completed in our center.
Symptoms of a spinal hernia
Signs common to all forms of the disease can be recognized without specialized equipment:
- pain in the neck, chest, lower back, legs or buttocks - depending on the area of the spine in which the hernia has formed (“disc prolapse”);
- numbness of the neck, arms, feet;
- limited mobility of the spine;
- weakness.
Under certain conditions, pain can intensify - with deep breaths, overwork, sudden movements, and strong physical exertion. If you notice one or more of the described signs, consult a doctor. Otherwise, the consequences of lack of treatment will not be long in coming:
- impotence;
- headache;
- poor coordination of movements;
- absent-mindedness;
- spinal cord injury;
- blood pressure problems.
Disability is an undesirable but probable result of neglecting the achievements of traditional or oriental medicine.
Who will treat you?
In our center, we have assembled an excellent team of doctors who can not only professionally diagnose and formulate a course of treatment, but also carry out all the necessary procedures. You can get to know our doctors and the level of their work better in the video on the website and from the video reviews of our patients below.
Dremin Evgeniy Vitalievich
neurologist, reflexologist, chiropractor.
6 years of experience. more
Learn more about manual therapy
Contraindications to manual therapy for hernia
Absolute contraindications to manual therapy for intervertebral hernia are malignant neoplasms, infectious diseases in the acute stage, and the rehabilitation period after surgery. The possibility of treatment for relative contraindications is determined by the doctor individually for each patient.
The list of restrictions includes:
- Acute stage of osteochondrosis or intervertebral hernia.
- Anomalies in the development of the spinal column (congenital or acquired as a result of injury).
- Arthrosis in the last stages.
- Pregnancy.
- Hypermobility of the vertebrae in extreme form.
Before prescribing a course of manual therapy, the patient must undergo a series of examinations that will allow him to formulate an overall picture of the disease. For these purposes, ultrasound, MRI, X-ray, ECG, CT procedures are performed, a general blood test and densitometry are taken.