Detailed description of the study
B vitamins are biologically active substances vital for the human body, which are involved in metabolic processes and energy production. They belong to the category of water-soluble vitamins. This study is comprehensive, as it evaluates the level of the most important representatives of B vitamins.
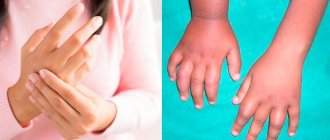
Vitamin B1, or thiamine, is an important component of muscle and nerve cell function. It is also involved in carbohydrate metabolism. Severe thiamine deficiency can lead to severe heart failure, peripheral neuropathy (a feeling of numbness, burning in the arms or legs), and Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome - brain damage, memory disorders and dementia in patients who abuse alcohol.
Vitamin B2, or riboflavin, supports cellular metabolism and is part of coenzymes in many redox reactions. B2 deficiency (ariboflavinosis) manifests itself in the form of inflammatory lesions of the lips, corners of the mouth, tongue, skin of the nose, ears and eyelids; and also in the form of anemia, normocytic and normochromic.
Vitamin B3, or niacin, nicotinic acid, is involved in the metabolism of proteins, fats, carbohydrates and in the formation of erythrocytes - red blood cells. Optimal levels of niacin reduce the risk of developing diabetes and also lead to lower cholesterol levels in patients with diabetes. Vitamin B3 deficiency is associated with the development of pellagra, a disease of the three “Ds”: dementia (dementia), dermatitis (skin inflammation), diarrhea.
Vitamin B5, or pantothenic acid, is part of coenzyme A, which is involved in one of the main processes of cellular metabolism - the Krebs cycle, thanks to which energy is produced in the body. Vitamin B5 deficiency is most often associated with neuromuscular dysfunction, such as restless leg syndrome.
Vitamin B6 consists of a group of vitamins: pyridoxine, pyridoxal, pyridoxamine and their esters. They are part of many coenzymes. B6 deficiency is manifested by burning of the lips, tongue (cheilitis, glossitis), gum damage (gingivitis), peeling of the skin (dermatitis), numbness, burning and sometimes cramps in the arms or legs (peripheral neuropathy).
Vitamin B9, or folic acid, contributes to the normal synthesis of red blood cell DNA in the red bone marrow. With a deficiency of folic acid, the maturation of red blood cells is disrupted, immature red blood cells (megaloblasts) appear in the blood, which leads to the development of megaloblastic anemia. Insufficient levels of vitamin B9 are especially dangerous in pregnant women, as this can lead to malformations of the brain and spinal cord in the fetus. In general, folic acid deficiency is often associated with a lack of vitamin B12.
Vitamin B12, or cyanocobalamin, like folic acid, is involved in the physiological maturation of red blood cells, as well as in the formation of the myelin sheath of nerve pathways. Diseases associated with vitamin B12 deficiency develop against the background of atrophic gastritis with a deficiency of internal Castle factor - without this factor, vitamin B12 supplied with food is practically not absorbed in the intestines. Cyanocobalamin deficiency leads to anemia, glossitis, peripheral neuropathy, as well as loss of sensitivity, poor coordination and behavioral disorders. Also, a specific pathology associated with B12 deficiency is a disorder of the structure of the spinal cord (funicular myelosis).
In clinical practice, it is sometimes difficult to assess which vitamin deficiency is associated with certain symptoms. Excessive levels of B vitamins are usually not detected due to the fact that they are eliminated from the body quite quickly.
A comprehensive analysis of B vitamins in the Hemotest laboratory allows you to assess the level of each vitamin studied. The results of this test will help the attending physician determine the need and tactics for subsequent treatment.
How important is nutrition for osteochondrosis?
Experts have not reached a consensus on the appropriateness of a certain diet to alleviate the symptoms of osteochondrosis. Some people believe that eating certain foods slows down degenerative changes in the vertebrae. Others talk about the futility of diets. Let's try to figure this out.
What is recommended to eat?
The most important is the consumption of products involved in the production of spinal cartilage tissue. These are the so-called chondroprotectors. An impressive amount of these substances is found in cartilage, the skin of fish and animals, and collagen hydrolysis products (gelatin). In addition, these same foods contain a lot of protein, which is important for connective tissue. People who consume these foods are more likely to have a healthy spine.
As a dessert, it is recommended to use fruit and berry jellies, rich not only in gelatin, but also in various vitamins.
Equally important is drinking enough water, since the internal nucleus pulposus (which makes up the intervertebral disc) mainly consists of fluid and, if there is a lack of it, contracts and undergoes deformation, leading to an exacerbation of the disease.
Rescue products for osteochondrosis
- Proteins – more than 30% of the total daily diet. These are meat, fish, eggs, nuts, legumes, and some vegetables.
- Minerals:
- Calcium. Namely milk and its derivatives, poppy seeds, sesame seeds, cabbage, dill, almonds, garlic, peanuts and others.
- Vitamin D: red caviar, beef liver, soy milk, sardines, eel, tuna, salmon, herring.
- Magnesium: bran, cashews, buckwheat, soy, almonds, spinach.
- Phosphorus: Peanut butter, broccoli, chia seeds, pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds and sesame seeds.
- Manganese. These are wheat, rye, buckwheat, millet, rice, oatmeal, legumes, berries, greens, nuts, green tea.
- Vitamin A: cod liver, pork liver, fish liver oil, butter.
- B vitamins: seafood, red meat, mushrooms, cereals, milk.
- Ascorbic acid: bell pepper, rose hips, barberry, sea buckthorn, berries, fruits.
- Polyunsaturated fats: vegetable oils (linseed, soybean, nut), fish oil, shellfish.
Foods that aggravate spinal diseases
With osteochondrosis, it is often recommended to avoid salty foods. And not without reason, salt retains water in the tissues, thereby increasing pressure on the spine. Therefore, foods containing large amounts of salt should be excluded from the diet. These are semi-finished products, pickles, smoked foods, canned foods, where you cannot control the amount of salt added.
Sweets, especially sugar, are also not healthy, as they slow down metabolism and impair blood circulation throughout the body, including in the intervertebral discs.
Products known to wash away calcium, magnesium, and potassium should also be excluded. These include coffee and carbonated drinks.
With osteochondrosis, an important condition for a mild course of the disease is the absence of excess weight - as an unnecessary and dangerous load on the spine. Therefore, meals should be fractional, balanced and low-calorie, especially if you already have excess body weight.
Rice is the best absorbent
Many doctors recommend the rice diet to their patients. Rice, entering the body, collects all harmful substances and salts and removes them from the body.
But there are some subtleties in such a diet.
For example, all starch must be removed from rice by soaking it in water: in the proportion of 0.5 liters of water + two tablespoons of rice. Rinse and fill with fresh water every day for 6 days; for convenience, you can have several containers. The greatest effect will be achieved if you consume the cereal raw, but you can also cook it. After rice, you should refrain from eating and drinking for 4 hours. Such a diet will help not only with osteochondrosis, but also generally improve the functioning of the entire body. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
References
- Clinical oncohematology. Practical guide / ed. M.A. Volkova, 2001. - 576 p.
- Guyton, C., Hall, E. Textbook of Medical Physiology. 13th Edition, 2015. - P. 1075-1093
- Kumar, V., Abbas, A., Fausto, N. et al. Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease, 2014. - 1464 p.
- Xiang, D., Zhang, Q., Wang, Y. Effectiveness of niacin supplementation for patients with type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Medicine (Baltimore), 2021. - Vol. 99(29).
- Kennedy, D. B Vitamins and the Brain: Mechanisms, Dose and Efficacy - A Review. Nutrients, 2021. - Vol. 8(2). - P. 68.
B vitamins and back pain
Back pain is born with a person. Unfortunately, sometimes babies receive spinal injuries at birth. Children grow and mature, their workload increases, and a sedentary lifestyle contributes to the further development of the disease. Backache
getting younger every year. Girls and boys have stopped walking and spend a lot of time on their phones or at computers. Adults gain weight and spend their free time watching TV.
Causes of spinal diseases
Every tenth resident of industrialized countries consults a neurologist once a year with back pain. Mostly, diseases arise from muscle strain, sprained ligaments, and joint damage. There can be several causes of back pain. There are acute neuralgic pains from thirty to forty days or chronic pains up to six months. People suffer, material losses are associated with partial or complete loss of ability to work.
The first group includes patients in whom pain occurs suddenly, lasts a short time, and the pain syndrome can be relieved. The second group of patients has chronic spinal diseases. Doctors classify some as patients with “age-related changes,” while others are mercilessly called “victims of lifestyle.” As a result, a diagnosis of osteochondrosis is made, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory injections of group B are prescribed to restore nerve endings, and a back massage
and physical therapy.
When did wizards appear who make life easier? In Poland at the beginning of the twentieth century, scientist Casimir Funk discovered B vitamins, which enhance metabolism.
Today, an in-depth analysis is being carried out on the use of drugs for pain in the spine. Whether vitamin complexes will become a serious competitor to analgesics, time and new scientific research will tell. Based on practice, it can be argued that B vitamins have analgesic properties. It has been clinically proven and it is important to note that if sharp, sudden back pain occurs, using B vitamins with NSAIDs is safer than just NSAIDs.
Vitamins B1, B6, B12
Their properties:
- The drug B1 (thiamine) calms the nervous system, affects brain function, and transmits genetic information during cell division. Found in plants: apricots, dried apricots, potatoes, spinach, grains and bran. In dairy products in smaller quantities.
- The drug B6 (pyridoxine) affects metabolic processes in the body and the cardiovascular system. Pyridoxine is found in nuts, tomatoes, meat, poultry, etc.
- The drug B12 (cyanocobalamin) is involved in hematopoiesis in the sheath of nerve fibers. Found in products of animal origin.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) provide significant benefits in the treatment of back problems. If B1, B6, B12 are used separately, the result will be modest. When NSAIDs are combined with B vitamins, they reduce side effects. Such drugs alleviate suffering from back diseases; they are combined and used in medical practice for acute back pain. Some patients refuse analgesics for their own individual reasons, so doctors turn to group B.
Purpose of vitamins
Neurotropic drugs treat the nervous system:
- B1 acts as a pain reliever and relieves numbness in the limbs.
- B6 is used to treat tunnel neuropathy (nerve compression).
- B12 dulls pain and affects the treatment of motor functions.
Vitamins of this group affect the nervous system. The drug Milgamma, which includes vitamins B1, B6, B12, Diclofenac and a separate complex of group B, was used in an experiment on patients with acute pain. At the end of the check, it turned out that the first to refuse treatment with diclofenac began to have side symptoms (gastrointestinal tract). Then they stopped taking Milgamma, but completed the course of combined B vitamin preparations.
Everything, of course, is very individual, but among doctors it is believed that the use of vitamin B is simply vitamin therapy to strengthen the nervous system. But pharmacology is moving, scientists are working. In the future, group B drugs will be studied for the treatment of back and will lead to recovery.
Vitamins B1, B6, B12 play a role in therapy for nonspecific back pain for pain relief and repair. They reduce the dose of analgesics and non-steroidal drugs, reduce side effects in gastrointestinal disorders, headaches, pressure surges, and back pain gradually goes away.
The future lies with the complex
In modern medicine, back pain ranks second after colds. The treatment algorithm in our time is incredibly wide. Various methods are used to relieve pain. There are more and more specialists, the knowledge of doctors is expanding. Chiropractors and osteopaths, neurologists, neurosurgeons, and pharmacologists work to alleviate spinal diseases.
In practice, the effectiveness of the combined action of NSAIDs and B vitamins has been proven. Patients with back diseases are usually prescribed NSAIDs, since they are considered the main pharmacological agent of therapy. Injections with B vitamins have established themselves as an important component in the treatment of osteochondrosis.
Thoroughly studied risks of using NSAIDs set the rules for drug treatment.
When prescribing NSAIDs, patients should use gentle doses and reduce the duration of use as much as possible, and use more B complex vitamins. As time passes, humanity will reveal all the secrets and capabilities of these drugs. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr