Osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine is the main cause of lower back pain in 3 out of 4 cases. If left untreated, it often leads to a herniated disc, causing patients to have difficulty walking and significant limitations in mobility. The disease is widespread - more than 50% of people complain of its manifestations in various stages. And no wonder, the entire lower back is the lower part of the spine, and it bears the heaviest load.
Is it possible to avoid the “price for upright walking,” what is needed for its early diagnosis, and how to stop or slow down the course of the disease? Let's look at it in the article.
Reasons for development
During a person’s life, due to upright posture, the lumbar region experiences a colossal vertical load, which even the large size of the vertebrae cannot fully compensate for. Therefore, the slightest changes in the human body, a decrease in the muscular corset of the lower back, excess weight, injuries, incorrect movements and much more can lead to the development of the disease. You should also always remember about age-related changes in the spine that affect each person.
Summarizing the above, we can identify the most common risk factors, the combination of which leads to osteochondrosis of the lumbar region:
- Uneven and incorrect loads on the spine (lifting weights from an inclined position, etc.).
- Excess weight (almost every kilogram is important).
- Lower back injuries, including sports.
- Weakening of the muscle corset (long-term work in a monotonous position, etc.).
- Poor diet, poor in minerals and vitamins.
Osteochondrosis: is it dangerous?
Spine
Throughout our lives, the spine is subject to a lot of stress, and it is not surprising that injury can be caused by many factors, for example, heavy lifting, poor posture, accidents and even stress. Hoping that the pain will go away on its own is pointless. It is necessary to contact professionals in the following fields: neurology, orthopedics, ultrasound diagnostic doctors, physiotherapy, osteopathy, manual therapy, rehabilitation.
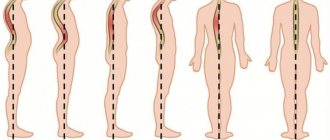
Varieties
The type of this disease is determined by its location on the spine. There are three main types of osteochondrosis. This:
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- chest;
- lumbar.
About pathogenesis
The initial cause of osteochondrosis is a sedentary and sedentary lifestyle. This lifestyle leads to the development of a destructive process in articular cartilage. Over the years, people experience a physiological reduction of the vascular bed in the intervertebral discs. This makes the recovery process in the intervertebral discs more difficult due to injury and excessive stress. Osteochondrosis develops from a lack of a nutritious diet. Articular cartilage loses flexibility and strength, and changes its shape and composition.
Unfavorable factors
An unfavorable factor for the intervertebral discs is the activity of the spinal muscles in an irrational and asymmetrical position. These are: incorrect postures, lack of movement, carrying bags on the shoulder, a soft pillow and mattress. Flat feet may also be the root cause. When the feet do not provide the necessary shock absorption from the support, the spine itself takes on the support.
Obesity
Obesity can also be the cause of the development of osteochondrosis. Excess fat deposits, which are located in various locations, make it more difficult to maintain balance and overload the intervertebral articular cartilage.
What does osteochondrosis lead to?
Complications that occur with osteochondrosis can be of the following types: protrusion, disc herniation (intervertebral hernia, spinal hernia), kyphosis, radiculitis.
What causes complications?
Science has not yet fully figured out the reasons that cause changes in the joints. Most often, a person first experiences osteochondriacal symptoms at the age of 35 or older. This disease develops and worsens from all kinds of spinal injuries, from an immobile or overly active lifestyle, as well as from vibrations. With age, manifestations of osteochondrosis appear more and more. Today, it has been noticed that people aged 18 to 30 are increasingly beginning to notice osteochondriacal symptoms.
Main causes of osteochondrosis
Here we highlight the main causes of this disease:
- heredity;
- metabolic disorders, infectious diseases, intoxication;
- obesity;
- lack of nutrients in the form of microelements and fluids;
- aging;
- vertebral injury;
- incorrect posture, curvature, flat feet;
- bad ecology;
- passive lifestyle;
- excessive loads;
- when constantly in uncomfortable positions;
- from spinal overloads that occur when wearing high-heeled shoes, as well as during pregnancy in women;
- when suddenly stopping sports activities;
- from stress;
- from smoking.
Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Symptoms
The symptoms of the disease can vary quite widely, but the totality of the main signs of osteochondrosis develops, as a rule, into three syndromes:
- Vertebrogenic lumbodynia (synonymous with lumbago).
- Vertebrogenic lumboischialgia.
- Vertebrogenic sciatica (inflammation of the sciatic nerve).
However, in addition to pain in the lumbar region (with or without irradiation to the legs, gluteal, groin areas), tension in the lower back muscles, weakness in the legs, crunching when moving in the lower back and difficulty moving in the lumbar region, a number of other important symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis should be highlighted:
- Numbness in the legs and a crawling sensation in the legs.
- Leg cramps.
- Pelvic disorders (urinary retention or incontinence, constipation or diarrhea).
- Weakness in certain muscle groups in the legs.
These complaints can guide a neurologist to the level of spinal damage and make a differential diagnosis with other spinal diseases.
Prevention
In order to prevent lumbar osteochondrosis, you should accustom yourself to follow the following recommendations:
- When working at a desktop computer, try to maintain an even posture and take breaks to stretch your body;
- whiten the time for swimming and hardening;
- when choosing a chair, give preference to models with a flat back;
- get an orthopedic massage;
- when lifting weights, first squat down, and only then, from this position, lift the heavy thing;
- When carrying loads, distribute them in both hands;
- wear high-heeled shoes as little as possible;
- Avoid sudden and prolonged drops in air temperature.
Diagnostics and x-ray signs
Osteochondrosis should be diagnosed using only one type of instrumental methods - x-ray. In modern medicine, the best way to visualize the entire structure of the spine is MSCT or MRI, however, simple radiography has not lost its indicative value (as a screening study). It is important to remember that the main stage in diagnosing problems with the spine will be a medical examination, which sometimes makes it possible to make a diagnosis without any examination at all.
The neurological status reveals pain on palpation of the spinous processes of the vertebrae, tension in the lumbar muscles, and if there is only osteochondrosis, then there should be no symptoms such as: decreased tendon reflexes, impaired sensitivity, tension symptoms (signs of compression of the spinal cord roots), muscle disorders joint sensation, weakness of the leg muscles, limitation of movements in the legs. If these symptoms are present, differential diagnosis should be made with disc herniation and other, more serious diseases of the spine.
Spinal tumors
Spinal tumors are quite rare. Tumors can be benign or malignant. Primary malignant tumors of the spinal cord are very rare. Malignant spinal tumors are usually metastatic in nature and have a primary focus in other organs and tissues.
From a clinical and anatomical point of view, tumors can be classified as epidural, intradural extramedullary and intramedullary tumors.
Metastatic tumors of the spine are the most common for bone metastases.
The most common solid tumors secondary to the spine are breast, prostate, and renal carcinoma, which account for almost 80% of spinal metastases. Tumors of unknown primary origin account for about 5% -10% of cases. Metastases of neoplasms of the hematopoietic system account for about 4% -10%.
Treatment
Treatment of the disease involves long-term, comprehensive therapy. There are several directions in treatment - drug relief of exacerbation, non-drug auxiliary methods, as well as a preventive method of physical therapy, partially used in the acute period, and which does not lose its relevance to this day.
✓ medication
It is a combination of muscle relaxation therapy, anti-inflammatory pathogenetic therapy, as well as the use of neuroprotective drugs. The choice of drugs and dosage calculations are based on the person’s weight, gender, and the presence of concomitant diseases.
In the acute period, it is advisable to inject drugs such as diclofenac, meloxicam; often, when acute pain occurs, Boyko’s mixture is used. Also, in parallel, they begin to carry out therapy to relieve muscle spasm and protect the nerve fiber from damage.
✓ non-drug
Represented by physiotherapy and manual influences. Considering the massiveness of the muscle groups and the fairly extensive level of the anatomical zone, physiotherapy can only be an auxiliary method. DDT, electrophoresis, and magnetotherapy are used, which enhance the effect of medications. However, massage and manual therapy are sometimes able to completely relieve the symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis, even without the support of medications. This is due to the fact that muscle spasms can be relieved quite well, and pain is not always provoked by an inflammatory process; sometimes only careless movement leads to pain, the consequences of which are removed effectively in the first hours after the development of pain.
Gymnastics for lumbar osteochondrosis is aimed at stretching the back muscles and strengthening them. If you have an established diagnosis of lumbar osteochondrosis, you should engage in physical therapy daily. If you follow the general rules (limiting excessive physical activity, hypothermia), controlling body weight and doing exercises for lumbar osteochondrosis, you can sometimes forget about the disease for many years.
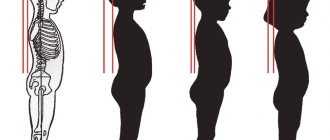
How does osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine occur?
The lumbar region is located in the lower part of the spinal column. This area takes the maximum load, since most of the body is supported by the pelvic bone. This is why lumbar osteochondrosis is so common.
Various back diseases are a person’s price for walking upright. The lower back experiences the heaviest stress during physical activity. Degenerative processes in this hotel are always accompanied by severe pain and stiffness of movement of the entire spine.
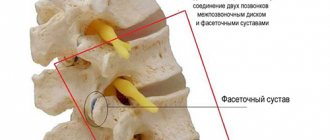
The spine is a chain of vertebrae separated by intervertebral discs. The lumbar region consists of 5 vertebrae. Discs allow the spine to be flexible.
With the development of osteochondrosis, blood circulation and metabolic processes are disrupted. The structure of the intervertebral discs changes. The internal gelatinous substance protrudes. The fibrous ring may not withstand such a load and crack. Compression of the nerve endings occurs, manifested by acute pain radiating to the lower extremities. If left untreated, tissue degeneration will continue. A dangerous complication is loss of sensation in the legs.
Possible consequences
In the absence of proper treatment for a long time, osteochondrosis continues to progress, leading to serious complications. Thus, damage to the lumbar region can cause the formation of intervertebral hernias, the development of sciatica and lumbar syndrome. With sciatica, the sciatic nerve is pinched or inflamed, and the person experiences a burning, stabbing or shooting pain, usually radiating to the buttocks, thigh or lower leg. Lumbago syndrome is characterized by “lumbago” - powerful spasms in the lumbar area, during which a person is often not even able to move.
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic region is dangerous due to the risk of developing intercostal neuralgia (tokaralgia). Chest pain can be constant or intermittent, occurring only during physical activity or at rest. Sometimes the pain radiates to the arm and neighboring areas of the body. In addition, the patient may be bothered by muscle tension, which causes difficulty breathing and discomfort when coughing. With cervical osteochondrosis, neurological complications such as cervicago (“lumbago in the neck”) and cervicalgia (rather intense chronic pain, accompanied by muscle tightness) develop.
One of the most dangerous consequences of osteochondrosis is spinal stroke. Even with timely medical intervention, acute circulatory disorders in the spinal cord can lead to dangerous complications in the future. With extensive damage, there may be a complete loss of pain and temperature sensitivity in the areas innervated by the damaged area, lameness, partial or complete paralysis of the body. In some cases, pelvic function disorders develop (urinary and fecal incontinence, impotence). Due to the massive death of neurons, even after rehabilitation, lost functions may not be fully restored. Often, a spinal stroke causes disability: for example, musicians or massage therapists who have lost tactile sensitivity can no longer work normally. Movement disorders are characterized by paresis (significant decrease in muscle strength, lethargy) and over time lead to muscle atrophy.