What are the most common elbow diseases?
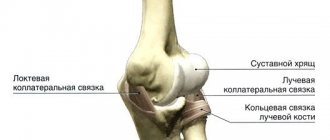
The elbow is a complex mechanism, which is represented by the connection of three bones (humerus, radius, ulna). Important blood vessels and nerve endings pass through it. Without realizing it, subjecting it to colossal stress in everyday life, people may increasingly encounter diseases of the elbow joint. Although the damage does not put the patient in mortal danger, it worsens the quality of life to a greater extent. Despite the periodic pain that bothers the elbow area, people attribute them to overwork, accidental bruises, the weather, and treat themselves by taking pills, applying compresses and using folk remedies. Unfortunately, in most cases, this leads to complications, loss of sensation and freedom of movement. Important! To determine the diagnosis, you need to consult a specialist.
Diseases of the elbow joints can be varied and the list of them is quite large:
- Various occupational injuries.
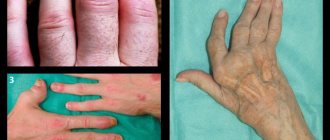
- Diseases caused by inflammation: tendonitis, epicondylitis, fasciitis, arthritis.
- Neurological diseases: nerve root lesions, carpal tunnel syndrome, neuritis, etc.
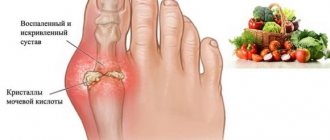
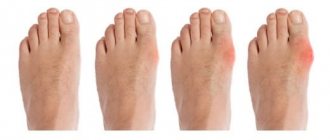
- Due to changes in tissues, both cartilage and bone: osteoarthritis, gout, chondrocalcinosis, osteochondrosis.
Methods for treating elbow pain
If there are no irreversible destructive processes in the cartilage and bone tissues, and the soft tissues are not damaged by malignant neoplasms, patients with pain in the elbows after exercise are prescribed complex treatment. It includes two areas - taking medications and various types of therapy. The list of medications, including ointments, is prescribed depending on the type of disease. For pinched nerves and inflammatory processes, the course of treatment includes anti-inflammatory drugs and anabolic steroids, including warming ointments. Additionally, warming baths and compresses with herbs or medications may be prescribed, which you will have to do yourself at home.
Physiotherapeutic measures may include massage, electrophoresis, and various types of hydrotherapy. A fairly effective aid in restoring the functions of the elbow joint is physical therapy, consisting of a set of exercises for the arms. However, it is not indicated for all joint diseases. On the contrary, in some cases, a fixing bandage is applied to the patient’s forearm, and special orthopedic products may be recommended to ensure complete immobility of the elbow.
Until recently, surgical intervention was the only option for relieving pain in cases of serious tissue destruction. However, today many clinics offer the use of chondoprotectors - medications that effectively restore cartilage tissue - before making a decision on prosthetics. If the course of treatment does not bring the expected results, surgery is prescribed.
Main diseases of the elbow joint and their treatment
What is Arthritis?
Arthritis is an inflammatory process that occurs in the joint and involves a disruption of immune processes in the body.
Symptoms of the disease are: pain, malaise, swelling due to excess synovial fluid, increased temperature in the affected area, vomiting, muscle aches, etc. There are two forms of arthritis: acute and chronic. The presence of this diagnosis can be confirmed by an orthopedic doctor
after examination with palpation, and then referred for hardware examination - radiography, magnetic resonance, or computed tomography to determine the presence and localization of the inflammatory process.
“Ten percent of elbow pain is due to arthritis.”
Basically, the patient is prescribed conservative therapy, which consists of taking medications, physical therapy, and physiotherapeutic procedures.
Surgery is used in severe cases when the disease is already too advanced. Ulnar epicondylitis
Epicondylitis is a disease that is quite common in the musculoskeletal system.
It often occurs due to the patient’s professional activity associated with overload. This problem affects musicians, surgeons and massage therapists, athletes, builders, as well as those professions where the emphasis is on the hands. Damage to muscle tissue and ligaments is a characteristic of epicondylitis, the appearance of which is provoked by constant overload of the elbow, trauma and microtrauma, and impaired local circulation. Treatment consists of eliminating pain, restoring full movement, and preventing muscle atrophy. Physiotherapy is an integral part of recovery. Magnetic therapy, dynamotherapy, and infrared radiation are beneficial with conservative treatment along with medication. Therapeutic exercises are also indicated to improve blood circulation and metabolic processes, which contributes to better absorption of medications and vitamins taken. Exercises should be performed daily, increasing the duration of exercise and load according to the schedule prescribed by the doctor. If conservative methods do not help within 3 months, then surgical intervention will be required. Advice.
To prevent the appearance and further development of epicondylitis, you need to have the right approach to physical activity, follow the rules of doing exercises, warm up before activity, avoid monotonous movements that load the joint, and also take complex vitamins regularly. Tunnel syndrome
Another problem of the elbow joint, which manifests itself as a pinched nerve, is tunnel syndrome. Compression of the nerve occurs due to inflammation of the ligamentous apparatus, incorrect positioning of the hand during physical activity, when working at a personal computer, playing sports, etc. The main signs of carpal tunnel syndrome are:
- numbness;
- tingling in fingers;
- shooting pain;
- muscle weakness and atrophy, cut.
Carpal tunnel syndrome can lead to loss of motor characteristics in the arm. Correct and timely consultation with a doctor is important here. The disease often requires surgical intervention, since conservative methods are possible only in the initial stages. During therapy, agents are used that increase blood circulation, reduce swelling and improve metabolic processes. An important part of non-surgical recovery is physical therapy aimed at strengthening muscles. Elbow arthrosis
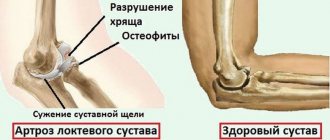
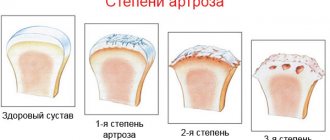
Arthrosis is a disease that occurs in people over 45 years of age. Tennis players, writers, violinists, pianists, drivers and women with hormonal changes are the main risk group. The causes of arthrosis are metabolic disorders, poor diet, chronic diseases (gastritis, tonsillitis, cholecystitis), inflammation due to infections entering the joint capsule, diseases of the endocrine system, etc.
Symptoms are divided into 4 groups: 1. pain when bending and straightening the arm; 2. crunching, which occurs as a result of bone friction; 3. restriction of movement in the joint; 4. modification of the shape of the elbow. To treat arthrosis, you must follow the following instructions:
- performing development exercises;
- refusal of loads on the sore arm;
- To reduce pain and inflammation, you need to take medications;
- in cases where the disease is advanced, surgery is required, but only in cases where conservative methods cannot help.
For arthrosis, it is advisable to adhere to a diet. It should be regular and varied.
The following should be removed from the patient’s diet:
- hot, spicy dishes;
- sparkling water, yeast dough, peas;
- rich broths;
- smoked fish and meat;
- strong teas and coffee.
Limit consumption:
- table salt (use sea salt);
- conservation;
- animal by-products (lungs, kidneys, tongue).
Be sure to include in your diet:
- jelly (no dyes);
- lean meats in gelatin, jellied fish;
- sufficient amount of water;
- vitamin and microelement complex;
- products containing calcium, phosphorus, manganese, magnesium, zinc, sulfur, vitamins B and C.
Injuries
Injuries are quite dangerous violations of the integrity of the elbow. They can be considered bruises, fractures and dislocations, and quite often they are accompanied by damage to blood vessels and nerves. After injury, before the regeneration period begins, the patient experiences severe pain, hematomas, ruptured tendons and deformities. As a result of the bruise, arthrosis or other problems may develop. The main injury to the elbow is a dislocation. It is necessarily accompanied by a bone fracture. A dislocation is accompanied by severe elbow pain, stiffness, and a person loses sensation in the wrist. Damage of this kind requires immediate consultation with a doctor and an x-ray of the elbow joint, which will show the extent of the damage, whether the muscles and nerve endings are affected. The doctor will restore the correct position by reduction, if possible, and apply a plaster splint. If the nerve has been damaged or the coronoid process is fractured, then treatment can only be surgical. Tissue bruising can occur due to a push, compression or blow to the elbow area. Symptoms of a bruise are pain when moving, bruises, increased skin temperature at the site of impact, and swelling. A bruise also requires consultation with a doctor.
Anatomy of the Human Ulnar Artery - information:
Ulnar artery, a. ulnaris , represents one of the two terminal branches (the larger one) of the brachial artery. From its origin in the ulnar fossa (opposite the neck of the radius), it fits under m. pronator teres, goes obliquely to the middle third of the forearm, deviating to the ulnar side.
In the lower two-thirds it runs parallel to the ulna, first in the space between m. flexor digitorum superficialis and m. flexor carpi ulnaris, in the lower third, due to the transition of muscles into tendons, its position becomes more superficial (sulcus ulnaris). At the radial side of the pisiform bone, the ulnar artery passes into the canalis carpi ulnaris (spatium interaponeuroticum) and, passing to the palm, is part of the arcus palmaris superficialis.
Branches of the ulnar artery:
- A. recurrens ulnaris, the recurrent ulnar artery, gives off two branches - rami anterior et posterior, which pass in front and behind the medial epicondyle, anastomosing with the aa. collaterales ulnares superior et inferior. Thanks to these anastomoses, as well as the above anastomoses between the branches of a. profunda brachii and a. radialis in the circumference of the elbow joint, an arterial network is obtained - rete articulare cubiti.
- A. interossea communis, the common interosseous artery, goes to the interosseous membrane, at the proximal edge, which is divided into two branches: a. interossea anterior along the anterior surface of the interosseous membrane reaches m. pronator quadratus, pierces the membrane and goes to the rear, where it ends in the rete carpi dorsale. At the beginning of your journey a. interossea anterior gives a. mediana (directed to the palm together with n. medianus), aa. diaphyseos radii et ulnae - to the bones of the forearm and rami musculares - to the surrounding muscles;
- a. interossea posterior passes through the upper opening of the interosseous membrane to the back side, gives off a. interossea recurrens, lies between the superficial and deep layers of the extensor muscles and in the wrist area anastomoses with a. interossea anterior.
Traditional methods of treating diseases of the elbow joint
We must not forget about the methods that our ancestors used to eliminate pain in bone joints. Attention! The use of these methods should be carried out as an aid to the main treatment, and not as a replacement for it. Let's look at the most effective treatment methods. 1. Rubbing the damaged area with tinctures of Kalanchoe and propolis; 2. Drink decoctions of chamomile, dandelion or St. John's wort; 3. Apply various compresses; blue clay is considered effective; 4. Baths with pine needles or sea salt; 5. Grind honey with apple cider vinegar. By following simple rules, eating right, without injuring or loading the limb, you can not only cure diseases that may appear in the elbow joint, but also completely prevent their reappearance.