Joint arthroscopy > Knee arthroscopy
It is possible to receive a quota
Make an appointment
Ask a Question
Prices for arthroscopy
Various joint diseases and injuries are very common in people who lead a fairly active lifestyle. In this case, arthroscopy is often used.
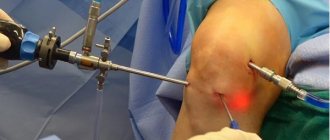
Knee arthroscopy is deservedly considered one of the most modern, minimally invasive and extremely effective manipulations currently used in the treatment of injuries and joint diseases. For diagnostic purposes, this procedure is the most reliable manipulation. To carry out this operation on the joints, a variety of special instruments are used, the main one being the arthroscope.
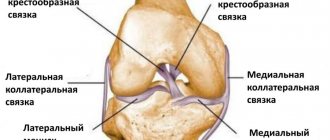
An arthroscope is a fiber-optic telescope inserted into a joint (shoulder, hip, knee, ankle) in order to be able to evaluate and treat certain pathologies. A video camera is attached to the arthroscope , after which the image is displayed on a specially designed monitor. This procedure is considered the most common orthopedic surgery performed worldwide.
Knee arthroscopy
However, now, in the age of victorious technological progress, there is such a medical intervention as arthroscopy of the knee joint, which makes the examination much simpler and non-traumatic.
Arthroscopy has its advantages:
- It keeps healthy tissues intact and does not interfere with their normal development.
- It does not require subsequent long-term rehabilitation with strict restrictions.
- It allows not only to examine the joint from the inside, but also to perform operations on it.
- It allows you to make a 100% correct diagnosis and examine the joint thoroughly.
- It allows the patient to be discharged within a few days.
- If you put in the effort, recovery will be quick, knee arthroscopy will be forgotten, and your leg will function fully.
Knee arthroscopy is the best solution known to modern medicine.
Advantages of osteosynthesis
Fractures of the tibia involving the knee joint are always a difficult situation. For such injuries, it is necessary to use knee osteosynthesis surgery, selecting a type of intervention that avoids the use of a large number of metal fixators, and also helps to restore motor function after surgery as soon as possible, while ensuring the highest possible biomechanical performance in the area of the affected joint.
Most often, doctors resort to using wire tying or using thin, strong knitting needles. This method allows the fragments to be fixed, allowing the metal structure to work in synergy with the parts of the skeleton. Moreover, after the operation, the tensile force acting on the fragments is transformed into compression, which enhances the fusion process.
Most often, osteosynthesis is indicated for fractures of the patella to fix bone fragments in complex fractures with displacement of bone fragments. Sometimes the operation requires additional immobilization for up to one and a half months.
Diagnostics
With injuries to the knee joint, the clinical picture can be very vague - often it is simply pain that occurs when trying to bend the leg. If x-rays and palpation are not able to give a 100% accurate result, arthroscopy of the knee joint is used. It is usually used to diagnose:
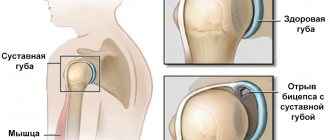
- Damage to the menisci.
- The fact of rupture of tendons and ligaments.
- Arthritis and arthrosis.
- Patella dislocation.
- Joint fracture.
All of these diseases are extremely serious. In many cases, treatment can begin immediately after diagnosis - with arthroscopy, the necessary tools are at hand. All of these diseases are extremely serious. In many cases, treatment can begin immediately after diagnosis - with arthroscopy, the necessary tools are at hand.
FEATURES OF OPERATIONS ON THE PATELLA IN TOTAL KNEE ENDOPROSTHETICS
Patellar instability is one of the main postoperative complications, which can worsen the results in the form of pain and functional limitations. This may require revision surgery. Considering these circumstances, we consider it necessary to substantiate the indications and tactics of intervention on the patella depending on its various anatomical and functional features in patients with gonarthrosis. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the violation of the normal tracking (amplitude of movement) of the patella in the frontal plane, manifested by its subluxation or outward dislocation.
Our patients had two options for intervention on the patella: preservation of their own patella after its specific treatment or replacement of its articular surface with a polyethylene implant.
Indications for safe surgery were young age, low weight and small stature of the patient, intraoperatively identified normal articular surface of the patella and congruent gliding, in cases where the size and thickness of the patella were insufficient for replacement, and the presence of a pronounced intercondylar groove of the femur.
Indications for replacement of the articular surface of the patella were old age, obesity, the presence of so-called anterior pain or other patellofemoral symptoms and radiological changes in the patellofemoral joint, a history of subluxation or dislocation of the patella, intraoperative pathological sliding of the patella or severe destruction of the patellofemoral joint. joint, the need to improve the ability to climb stairs and the presence of a non-anatomic femoral intercondylar groove.
Important additional factors in determining the indications for various options for surgery on the patella are the assessment of the position and sliding of the patella using specific indicators (TT-TGindex, Install-Salvatti index, Blumensaat index, Merchant classification of patellofemoral arthrosis, etc.). However, in our opinion, they do not provide clear indications for the tactics of operations on the patella during endoprosthetics.
Taking into account the above data on the pathology of the patella, a classification was proposed, assessed, among other things, visually during the operation, which determined further tactics for its treatment.
The following 4 degrees of patellar damage were identified:
Grade 1 includes the presence of all three facets, a carina with diffuse chondromalacia, and the absence of exostoses - 90 patients (22.6%):
2nd degree - the same changes with marginal exostoses - 158 patients (39.7%):
Grade 3 – deep diffuse damage to the articular surface of the patella, facets and carina are not identified, the patella is flat with marginal exostoses – 107 patients (27%).
Grade 4 – concave patella with marginal exostoses, displaced, as a rule, laterally, with valgus deformation of more than 15 degrees – in 43 (10.7%) patients.
Depending on the severity of the patellar pathology, various types of treatment were carried out, including elements of heat treatment, removal of exostoses, deinnervation, etc., and indications for various surgical tactics were determined.
Endoprosthetics of the knee joint without implantation with a polyethylene coating after specific treatment of its articular surface was performed in 356 (89.4%) patients with damage to the patella of the first three degrees. The reason for such a high frequency is that, according to our observations, the incidence of pain in the patellofemoral region after replacing the patella with an implant reaches 40–50%. In this case, the question of the peculiarities of treating the surface of the patella in order to prevent anterior pain syndrome becomes especially relevant. These features depend on the degree of damage to the patellofemoral joint. Thus, in the first degree of damage to the patella, only removal of foci of chondronecrosis is indicated. Denervation is not indicated due to the increased risk of osteonecrosis of the patella. In the second degree , resection of exostoses, excision of the inflamed synovium and peripheral denervation are indicated. In the third degree, contour plasty with the formation of a keel and denervation around the patella is indicated.
In the fourth degree, replacement of the articular surface of the patella with an implant is indicated , which was performed in 42 (10.6%) patients.
It must be taken into account that subluxation of the patella is more common than complete dislocation, and the frequency of instability leading to revision interventions was, according to our data, 8%. The etiology of patellofemoral instability may be related to imbalance of the extensor mechanism, errors in surgical technique and positioning of endoprosthetic and patellar components.
One of the most common causes of patellar instability is improper positioning of components during surgery. This trend is associated with an increase in the Q angle of the knee joint, which is defined as the angle between the vector of action of the quadriceps muscle and the line passing through the head of the femur and the center of the patella [1]. The Q angle is closely related to the axis of the lower limb. During primary knee arthroplasty, errors in positioning of both the femoral and tibial joints and the patella can affect the Q angle values.
It must be remembered that there is always a resultant shear force tending to subluxate the patella. Due to the presence of the Q angle, the intercondylar groove of the femur becomes of great importance. Most prostheses have less restricted block flanges than a natural knee. Consequently, as the Q angle increases, the patella will tend to move more laterally, which can lead to patellar tilt, subluxation and dislocation. In addition, changes in the mobility of the patella can cause chronic pain in the anterior part of the joint. Taking this into account, we must use surgical methods that allow us to achieve sufficient function of the endoprosthesis and its stability without increasing the Q angle.
The positioning of the femoral and tibial components for the occurrence of complications in the patellofemoral joint is associated with their incorrect installation, in particular, with the obligatory absence of internal rotation. If this parameter is not observed, the inwardly rotated femoral component creates the appearance of an inclination of the patella. This causes excessive pressure on the patella. When installing the femoral component in the frontal plane, lateralization of the femoral component is preferable to restore normal mobility of the patella. The location of the tibial component is similar to the femoral one. In this case, it is necessary to prevent excessive medial placement of the tibial component. Otherwise, the tibial tuberosity is displaced antiphysiologically laterally.
Compliance with these recommendations allowed us to avoid, in most cases, complications in the patellofemoral joint and subsequent pain in the anterior part of the knee joint.
Literature.
- Hungerford D., Barry M. Biomechanics of the patellofemoral joint // Clin. Orthop. 1979. Vol. 144, p. 9–15.
Treatment
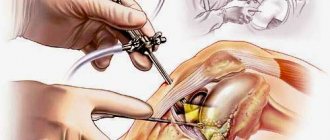
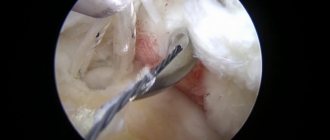
Arthroscopy allows you to get rid of the cause of the disease: stitch the gap, remove the foreign body, reduce the fracture. In addition, with its help, medications can be introduced into the joint cavity to promote recovery.
Arthroscopy of the knee joint, reviews of which are mostly positive, as an operation is used in the following cases:
- If the menisci or cartilage are damaged.
- If the ligaments are torn.
- If there is a chronic inflammatory process inside the joint.
- If the knee has been crushed and bone or cartilage fragments need to be removed.
Treatment is carried out in two options: medication or surgery.
Indications may be:
- damage (and rupture) of the meniscus of the knee joint;
- damage to articular cartilage (the damaged area is smoothed or treated using high-frequency cold ablation; large areas of damage are usually treated with microfracture (formation of many holes in the subchondral bone);
- removal of the free intra-articular body (cartilage, bone) on the joints;
- resection of inflamed synovial tissue (synovectomy);
- reconstruction (restoration or plastic surgery) of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee joint.
Operation
If you type “knee arthroscopy surgery” into a search engine, you can see that the operation takes place in several stages and, despite its low morbidity, requires careful preparation.
- Collection of information. Before surgery, the patient must:
- Donate blood.
- Get an ECG.
- To make an X-ray.
- He should also visit an orthopedist and an anesthesiologist. The latter will determine how ready the patient is for anesthesia and which method will be optimal for him. As a rule, local anesthesia is used during arthroscopy.
- Direct preparation. When all the tests have been completed and the doctors have determined that the operation will not harm the patient, he must prepare: acquire crutches that will be needed while the leg is being restored; buy painkillers that will be used during treatment; refrain from drinking and eating twelve hours before surgery.
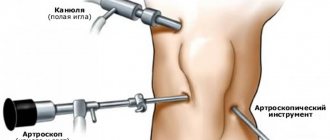
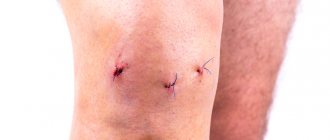
- Operation. Knee arthroscopy is performed on the same day the patient arrives at the hospital. He is placed in a sterile room, and the leg is tied at hip level with a tourniquet so that the blood does not flow into the joint cavity in full. After this, anesthesia is administered and three incisions are made, seven millimeters each. Through them the following are introduced into the joint:
- A light source and camera that allows the doctor performing the operation to see his own actions.
- Hollow Fluid Tube - A sterile solution allows the joint to be flushed and inflated, providing better visibility and more room for instruments.
- An arthroscope, with the help of which all necessary procedures are performed.
When the tears are stitched up, the fracture is reduced, the joint is no longer in danger and the operation, arthroscopy of the knee joint, is completed, the instruments are removed, the sterile liquid is pumped out. The cavity, if necessary, is filled with medications: antibiotics, which fight possible infection, and anti-inflammatory drugs, which will prevent fever. The incisions are covered with a sterile cloth and the knee is bandaged to form a pressure bandage. After this, the patient is escorted to the ward, where:
- After a period of time, the bandage is replaced with an elastic one, which reduces pain and prevents swelling.
- An ice pack is applied to the knee, which also reduces pain and prevents swelling.
The patient is discharged as soon as he can move independently on crutches - usually this happens on the day of the operation, but sometimes it is necessary to stay for a couple of days so that doctors can observe the dynamics.
Contraindications
Although the operation is performed quite often and quickly, there are a number of contraindications for its implementation that must be taken into account before the intervention. These include a large volume of affected tissue around the wound, torn, crushed and infected surfaces. In this situation, primary wound treatment (surgical) is first performed, and the osteosynthesis procedure is performed after healing. Surgical intervention is also contraindicated in case of acute infection or exacerbation of chronic pathologies, local inflammatory process with suppuration, severe combined injuries and shock, large blood loss, when the operation is associated with a high risk.
Instrumental research methods
During preoperative preparation, patients undergo an ECG, radiography of two joints (knee or hip) in 2 projections, MRI and densitometry. Let's look at why research data is needed.
Table 1. The purpose of instrumental diagnostics before endoprosthetics.
| Method | Information content, results | Purpose of the study |
| Radiography | Gives an idea of the anatomical features of the structure of bones. Allows you to assess the severity of osteoarthritis. Unfortunately, soft tissues are not visualized on radiographs. | Radiography is needed to select the most suitable endoprosthesis design, as well as the optimal method of its fixation. |
| Magnetic resonance imaging | Makes it possible to obtain a three-dimensional image of articular cartilage, capsule, ligaments, periarticular tissues, nerves, and vessels. | Helps the doctor to correctly plan the operation and select the least traumatic surgical approach to the joint. |
| Densitometry | Measuring bone density makes it possible to determine the degree of osteopenia or osteoporosis. | Densitometry helps surgeons in choosing a method of fixing a prosthesis and allows them to assess the risk of periprosthetic fractures. |
| ECG | Necessary for identifying heart failure and serious diseases of the cardiovascular system. | Anesthesiologists take into account the results of electrocardiography when choosing an anesthesia method. |
Arthrosis of the left hip joint.
Efficiency of the technique
Arthroscopy today is used more and more often, gaining ground from other methods of treating diseases of the knee joint. The advantages of the method are:
- short rehabilitation period;
- low risk of complications;
- high efficiency, good treatment results;
- the ability to use the method for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Arthroscopy surgery in Moscow can be performed in most medical centers. The average price is 20 thousand rubles. The cost depends on the type and purpose of the intervention, and the level of the clinic. It is necessary to clarify how much the operation itself, the stay in the ward, and the prices for the necessary studies will cost.
How is the operation performed?
Endoprosthesis replacement is performed early in the morning. First, compression bandages are applied to the legs to prevent the expansion of deep veins and blood clots. Next, spinal anesthesia or general anesthesia is performed (the method of pain relief is selected taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient). After this, the catheter is slowly inserted into the bladder to take control of the kidneys. Surgery is performed with or without a tourniquet, depending on the complexity. As soon as the equilibrium concentration of the anesthetic drug in the blood is reached and it begins to act, the surgeon begins the operation:
- An incision is made down the center of the knee.
- The fabrics are moved apart and fixed.
- The kneecap is displaced.
- The tension of the ligaments fixing the joint is reduced.
- Damaged bone tissue is removed.
- The cut edges are polished.
- The lower part of the femur is replaced with a metal prosthesis.
- A titanium plate is fixed to the upper part of the tibia.
- A polyethylene liner is installed on the plate.
- A test prosthesis is attached to check its functionality.
- After successful testing, the endoprosthesis is attached.
- Surgical sutures are placed and drainage is created.
- The bandage and splint are attached.
All procedures take no more than 3 hours. After the anesthesia wears off, additional pain relief will be required after 5 hours to avoid acute pain.
Risks and complications
Total knee replacement surgeries have a low complication rate.
Possible complications include:
- An infection that affects less than 2 percent of patients
- Blood clot in the legs, known as deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
- Blood clot in the lungs or pulmonary embolism
- Fracture during or after surgery
- Nerve damage leading to numbness or weakness
- Continued pain or stiffness
If the patient has signs of infection or blood clots, medical attention should be sought immediately.
Signs of infection include fever, redness, swelling, bleeding, exhaustion, or increased pain in the surgical area. If redness, tenderness, or swelling occurs below the knee or in the lower leg, ankle, or foot area, it may indicate a blood clot in the leg. Shortness of breath or chest pain may indicate a blood clot in the lungs.
Other common complications include:
- Allergic reaction to bone cement
- Excess bone forms around the artificial knee joint, resulting in limited movement of the knee.
- Excess scar tissue limits knee movement
- Patellar instability resulting in painful dislocation to the outside of the knee
- Damage to the ligaments, arteries, or nerves around the knee joint
- Patella dislocation
- Bleeding in the knee joint
- Wear of implant surfaces causing loose components
Advantages of endoprosthetics
Knee replacement surgery is considered technically complex. To carry out the intervention, you need a surgeon with a narrow specialization - a professional who specializes in endoprosthetics.
There are two main options for the operation:
- Unipolar prosthetics This is the name for installing an implant in only one damaged area. It often happens that the pathology does not affect the entire joint and unipolar prosthetics are enough to restore functional mobility.
- Total arthroplasty is the replacement of a complete joint.
The prosthesis is developed after an X-ray examination, taking into account the patient's anatomy. The essence of the operation is that the surgeon removes the damaged fragments and instead installs a biocompatible endoprosthesis that takes over the functions of the removed tissue. After completing the main part of the operation, drainage is installed on the wound. This is necessary in order to avoid blood accumulation in the joint area. In addition, they prevent infections and, if necessary, replace blood loss.
The operation is complex, but safe when performed in a modern clinic. And an endoprosthesis allows you to live an active and fulfilling life, forgetting about joint pain.
Postoperative treatment.
If you do not require any special post-operative care, you will be introduced to the physical therapy plan and treatments will begin the day after surgery. This means that each patient with a certain picture of the disease receives his own postoperative treatment program, which contains accurate information about the necessary measures for certain periods of rehabilitation. Of course, the doctor who will see you on an outpatient basis will receive all the necessary information for the best postoperative management. This is how the success of your postoperative treatment is achieved outside the walls of the clinic.
Consultations with other specialists
Before surgery, a person needs to be examined by an orthopedic traumatologist, therapist, otorhinolaryngologist (ENT), neurologist, gynecologist or urologist. If during the examination the patient is diagnosed with any infections or chronic diseases, he may need to consult other doctors (infectious diseases specialist, vascular surgeon, cardiologist, endocrinologist). The therapist's conclusion should state that the operation is not contraindicated:
- fluorography (not earlier than 3 months before the proposed operation
- dentist (about a month before the proposed operation)
- gynecologist (about a month before the proposed operation): smear for flora, cytology, doctor’s conclusion that the operation is not contraindicated.
Rehabilitation period
After surgery, you may need a temporary cast or splint for 5-6 weeks. Sometimes bandages are not applied, but walking is allowed only with crutches until the stitches are removed at 10-12 days. Then walking with a cane is acceptable until complete healing.
In our clinic you can get a preliminary consultation with a doctor with an estimate of the cost of knee osteosynthesis. In addition, it is important to take into account the cost of the examination and the preparatory stage, the features of the metal structures, the type of operation and the rehabilitation period. Our doctors perform all types of interventions, have extensive experience and can help restore the joy of movement.