A shoulder puncture is a surgical procedure in which the doctor inserts a needle into the joint. This procedure is carried out for diagnostic purposes or based on existing medical indications. The purpose of this procedure is to reduce the amount of synovial fluid in the joint. Puncture of the shoulder joint is performed when there is suspicion of inflammation (arthritis) with exudation and suspicion of hemarthrosis.
Content
- The essence of the procedure for puncture of the shoulder joint
- Who carries out the treatment?
- Why do they contact us?
- Expert opinion
- Reviews from our patients
- Sign up for treatment
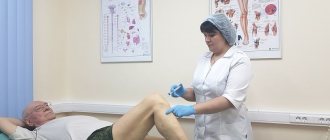
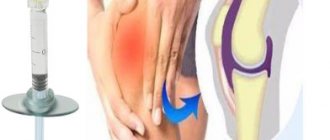
The essence of the procedure for puncturing the shoulder joint is to puncture the joint at a certain point, followed by removal of the pathological fluid. The whole process is absolutely painless and takes no more than 20-30 minutes.
After the procedure, medications are injected into the joint cavity in order to prevent further accumulation of pathological fluid. You can learn about how this procedure works from the reviews of other patients, as well as from the photo of the puncture (piercing) of the shoulder joint on the website.
Puncture of the shoulder joint is performed with a syringe with a volume of 10-20 ml. The skin and soft tissues are preliminarily anesthetized with lidocaine or novocaine. A large syringe is needed to pump out the maximum amount of fluid from the joint in a minimum number of manipulations.
|
|
Sign up for treatment
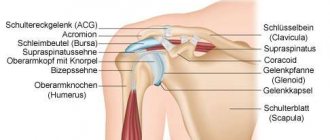
Joint anatomy
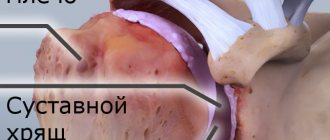
When performing a puncture of the shoulder joint, it is necessary to take into account its characteristic anatomical features. The synovial membrane is a membrane that differs in structure and origin from serous membranes (such as the pleural, abdominal, pericardial membrane). The main difference is that its inner side, facing the surface cavity, does not contain epithelial coating and endothelial tissue. The membrane thickness is not the same. In addition, it has increased sensitivity to thermal, infectious, traumatic and chemical influences.
Due to the fact that the sensitivity of the synovial membrane is significantly increased to various infectious lesions, strict adherence to all rules of asepsis is necessary before the puncture procedure, as well as before opening the joint cavity. In addition, mandatory sealing is required. The joint cavity contains synovial fluid in a small amount, approximately four milliliters.
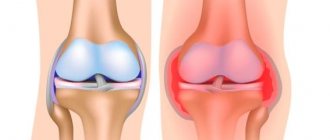
Synovial fluid is sterile, it is yellowish-straw in color and at the same time completely transparent. It is characterized by high viscosity, contains leukocytes and phagocytes, but still its bactericidal qualities are very insignificant. Since joint fluid contains mucopolysaccharides with a high specific gravity, it accumulates in the joint rather than dissipating from its cavity.
Puncture of the shoulder joint: indications
Main indications for puncture:
- Purulent arthritis is the appearance of pus in the shoulder joint.
- Hemarthrosis is the presence of blood in the joint capsule of the shoulder.
- Synovitis is an accumulation of inflamed synovial fluid inside a joint.
- For arthrosis and arthritis of the joint, special drugs are injected into the cavity to treat the disease.
- A puncture of the joint has to be done, and before the dislocation can be reduced, a painkiller is injected into the shoulder from the front, back and side. Without this, the procedure will be very painful and unpleasant for the patient.
Orthopedic surgeon Andrey Sergeevich Litvinenko, candidate of medical sciences, comments:
In cases where it is necessary to take fluid for examination, but its quantity is insufficient, a puncture of the shoulder joint under ultrasound guidance is used. This technique allows you to select at least 2 ml of joint effusion for analysis.
Medical specialists know all the indications for joint puncture. We also give injections into the shoulder with various drugs and blockade of the shoulder joint to relieve severe pain.
Sign up for treatment with us by phone +7 495 134 03 41
or leave a request on the website.
Author of the article:
Kholikov Timur Vyacheslavovich
Orthopedist
Make an appointment
Recent publications by the author:
- Ultrasound of the heel
- Plasmolifting: how many procedures are needed
- Hyaluronic acid: benefits
- Shock wave therapy for the shoulder joint
Indications for puncture
Before considering the technique and features of this medical procedure, you should dwell on the indications for performing a puncture:
- bleeding into the joint space (hemarthrosis);
- inflammatory processes in tissues;
- inflammatory diseases that lead to fluid accumulation - arthritis, synovitis, bursitis;
- anesthesia before reduction of a dislocation;
- injuries of various types - sprains, dislocations;
- suspicion of a tumor;
- the need to administer medications.
The extracted synovial fluid is sent to the laboratory for analysis for accurate diagnosis.
The shoulder joint connects the humerus to the shoulder blade. It allows a person to perform flexion, extension and circular movements.
Diseases or injuries of the shoulder joint are accompanied by acute pain, swelling of the tissues, the appearance of a characteristic crunch, increased body temperature, and general weakness.
After removal of the fluid, most patients note a decrease in pain and a general improvement in their condition.
Prices for joint puncture
| Services | Price | Sign up |
| Puncture of the hand | 2000 rub | Sign up |
| Knee joint puncture | 3000 rub | Sign up |
| Puncture of the elbow joint | 2000 rub | Sign up |
| Shoulder joint puncture | 3000 rub | Sign up |
| Ultrasound-guided hip puncture | 3000 rub | Sign up |
Joint fluid
It is very difficult to obtain a certain amount of joint fluid and not cause complications due to its small amount, increased viscosity and negative pressure of the fluid.
Healthy joints exert negative pressure:
- ankle – 270-210 mm water column;
- knee joint – 75-90 mm water column.
The presence of a factor such as negative pressure causes osmosis of fluid from the synovial and subchondral plates, from which the cartilage tissue of the joint comes. Puncture of the shoulder joint in people without complaints is performed in rare cases.
Our doctors
- LITVINENKO Andrey Sergeevich
Traumatologist orthopedist Sports medicine doctor Experience: 19 yearsSign up
- SKRYPOVA Irina Viktorovna
Physiotherapist rehabilitator Experience: 20 yearsSign up
- MOISEENKO Alexey Yurievich
Traumatologist orthopedist Sports medicine doctor Experience: 17 yearsSign up
- KHOLIKOV Timur Vyacheslavovich
Traumatologist orthopedist Sports medicine doctor Experience: 19 yearsSign up
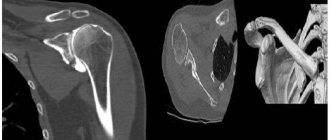
Impact points
There are three puncture points. For each patient, the doctor individually determines the most optimal access.
The shoulder joint is punctured in front by inserting a needle below the coracoid process of the scapula. The needle is advanced 2-3 cm deep so that it is between the coracoid process and the head of the humerus.
At the back, the puncture needle puncture point is in the depression formed by the deltoid and supraspinatus muscles. The needle is inserted to a depth of 3-4 cm, directing it from bottom to top.
On the outer surface of the shoulder, the landmark for performing a lateral puncture is the most convex part of the acromion of the scapula. The needle is advanced through the layer of the deltoid muscle, orienting it from the outside to the inside and slightly downward.
Why do they contact us?
- No queues
No need to wait, we work by appointment
- All in one day
Doctor's appointment, diagnosis and treatment on the day of treatment
- Let's relieve the pain
We will help you relieve pain in just 1-2 visits to us
- We guarantee
Professional approach, affordable prices and quality
- Doctor's appointment 0 RUB!
During course treatment all consultations are free
- Three treatment options
We will select several options and offer optimal treatment
Functions of synovial fluid
The main functions of synovial fluid are: locomotor, metabolic, trophic. In the first case, synovial fluid, together with articular cartilage, allows free movement of the articulated surfaces of the bone. In the second, synovial fluid participates in the metabolic processes that occur between the vascular layer and the articular fluid.
Trophic function means that synovial fluid performs a nutritional function for the avascular layers of cartilage. If inflammation occurs in the joint, the protein content in the synovial fluid increases. This is due to an increase in vascular permeability. The liquid subsequently becomes cloudy, the content of neutrophilic leukocytes increases, which occurs as a consequence of acute traumatic synovitis.
Joint puncture for therapeutic purposes
Joint puncture can also be prescribed as part of complex treatment of inflammatory diseases or joint injuries. In some cases, it is necessary to gain access directly into the joint cavity, and the only way to perform this procedure without the risk of bacterial infection is through a puncture.
With a simple needle you can perform various manipulations, including:
- removal of serous, purulent or hemorrhagic (blood) exudate for various types of joint inflammation;
- administration of antibacterial drugs, hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs, novocaine and anesthetic solutions;
- administration of oxygen is a method of treating adhesions due to the proliferation of fibrous tissue.
Non-steroidal and hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs are used to treat arthritis. If the former show sufficient effectiveness in the form of tablets and ointments, then steroids are used only for acute inflammation and severe pain. They can be administered intravenously or intramuscularly, and also taken in the form of tablets, and in advanced cases, intra-articular injections are indicated. Their effect is greatly enhanced by direct contact with the affected area.
Contraindications
Contraindications to the procedure may include general diseases of the patient, which may worsen as a result of manipulations, blood clotting disorders, long-term use of anticoagulants or antiplatelet agents, the development of a purulent-inflammatory process at the puncture site, gross deformation of the joint, changes in its shape or immobility, which can lead to complications.
In an anterior approach, the needle is inserted at the level of the coracoid process of the scapula
Recovery period
The patient’s rehabilitation period mainly depends on the severity of the pathology for which the puncture was performed.
If there was an accumulation of a large amount of fluid, then immediately after its evacuation, patients noted an improvement in their condition and a decrease in pain discomfort.
In the first days after the procedure, it is recommended to limit active movements in the affected joint. To reduce swelling and prevent the development of hematomas and hemorrhages, the application of a tight bandage and local cold to the joint area are indicated.
Therapeutic physical training will help speed up recovery. The physiotherapist selects the volume and type of exercises individually for each patient (the severity of the disease and the fitness of the body are taken into account).
Puncture of the shoulder joint is a valuable diagnostic and therapeutic method, which is often used in traumatology and rheumatology. This manipulation is well tolerated by patients and has a low risk of complications.
Risks and complications
The synovial membrane, which makes up the walls of the joint capsule, is a delicate tissue, damage to which will take a long time to recover and can cause pathological processes. It is also especially vulnerable to microbes, so strict antiseptic rules apply. So, the surface of the joint is disinfected in two ways: twice with iodine, then with alcohol. You need to be careful here: iodine, penetrating into the wound at the tip of the needle, can cause a chemical burn to the membrane. Instruments are sterilized chemically and thermally.
If a joint puncture is performed on a healthy joint for the purpose of sampling, it reduces the already small volume of synovial fluid. Excessive amounts of punctate can lead to the onset of inflammatory processes and cartilage destruction. Also, due to the negative pressure in the bag, osmosis of water and other foreign impurities from the synovial fluid occurs through its walls, and a decrease in its quantity will negatively affect this process.