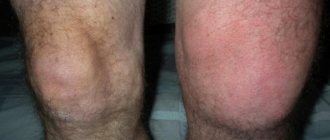
If arthrosis progresses, doctors often prescribe surgery - arthroscopy. A special endoscopic instrument equipped with a video camera is inserted into the joint and displays an image with multiple magnification on the monitor. The procedure is performed under anesthesia, gives the patient a good prognosis, but requires a serious, very responsible attitude during the recovery period. What recommendations must be followed to avoid complications in the form of adhesions, contractures and relapses?
Knee arthroscopy is not as scary as rehabilitation after it
PERIOD OF INPATIENT TREATMENT:
- Intraoperative antibiotic prophylaxis is a single intravenous administration of a broad-spectrum antibiotic, if necessary, repeated administration after 24 hours.
- Prevention of thromboembolic complications - compression hosiery, or elastic bandaging of the limbs during surgery and in the postoperative period (up to 3-5 days), administration of low molecular weight heparin (up to 5-10 days), tableted anticoagulants.
- Cryotherapy in the postoperative period - local cold, 30-40 minutes, 3-4 times a day, during the first 3 days.
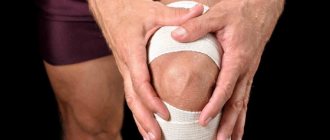
- Ensuring joint rest in the early postoperative period. If necessary, the joint is fixed with an orthotic bandage. Usually the limb is in a straight position. When plasticizing the cruciate ligaments, the joint is fixed with a hinged orthosis in a closed position, or with a flexion angle of 20-30 degrees.
- Pain therapy, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- Lymphatic drainage.
- Physical therapy for the first period 1 day - isometric tension of the thigh muscles, movements of the foot in the ankle joint. Day 2 - passive movements in the knee joint are added, in a painless range, flexion of 20-30 degrees and full extension of the joint. The patient is activated and walking is allowed with a measured load on the leg.
- When activated, additional support/cane or crutches are used, depending on the degree of permitted load on the leg
Physiotherapy after arthroscopy
Most patients undergo physical therapy while recovering from surgery. Various methods are used, among which the most common are massage, ultrasound therapy, UHF therapy, magnetic laser treatment, lidase electrophoresis, and magnetotherapy.
But physiotherapy has contraindications, including pregnancy, fever, exacerbation of chronic diseases, bleeding, and neoplasms.
When preparing for knee arthroscopy, you need to remember the need for rehabilitation, which will take some time. If you strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations and prescriptions, then each stage will pass without complications, after which you will be able to quickly return to your normal life.
OUTPATIENT TREATMENT PERIOD, 1-3 WEEKS:
- Dressings. Typically, examination by a traumatologist and dressings are carried out on day 1 after surgery, days 3-4, and days 7-12. Aseptic dressings are changed and, if necessary, a joint is punctured to evacuate fluid. Sutures are removed within 7-12 days.
- Use of anti-inflammatory and vascular drugs.
- Elastic bandaging of the limb for up to 3-7 days.
- Cryotherapy up to 3-5 days.
- Lymphatic drainage.
- Depending on the type of operation performed, one or another degree of activity is allowed. After meniscectomy, walking with a dosed load on the leg is allowed from the first day after the operation.
It is recommended to limit the load, use a cane or crutches with support under the elbow until 5-7 days after surgery. When performing a meniscus suture, it is recommended to walk with crutches without supporting the leg for up to 4 weeks. When performing ACL plastic surgery in the early postoperative period, walking with crutches is also recommended (it is possible to use crutches with support under the elbow) for up to 3 weeks. First, you walk without putting any weight on your leg. Then, when walking, the foot (not the toe) is placed on the floor, but without transferring weight to the operated limb. In the absence of pain, a gradual increase in the axial load on the straight leg is carried out.
- Additional fixation of the knee joint. During operations on the meniscus, elastic bandaging of the joint area is used, or wearing a soft (or semi-rigid) knee pad. When ACL plastic surgery is performed, the joint is fixed with a postoperative hinge orthosis, with a gradual increase in the allowed flexion angle. Movements can begin within 3-5 days after surgery; the angle of allowed flexion is gradually increased to 90 degrees within 2-3 weeks after surgery. At night, the orthosis can be locked in the extension position.
- Electrical stimulation of the thigh muscles (optional).
- Physiotherapy.
- Light massage, mobilization of the patella by passively moving it up and down and to the sides.
- Full extension of the knee joint in a supine position (without hyperextension of the joint!).
- Passive movements in the knee joint. The use of the Arthromot apparatus for developing passive movements in the joint has a good effect.
- Therapeutic physical education by periods. Isometric tension of the muscles of the hip flexors and extensors, gluteal muscles, and foot movements continue. Active movements in the knee joint, flexion and extension in a painless range are added. Movements are carried out in a “closed loop”, that is, in such a way that the heel is in contact with the surface all the time during movements. For example, lying on your back, bend the knee joint so that the heel slides along the surface of the couch; you can help bend with your hands, grabbing the lower third of the thigh. Exercises are added to gradually strengthen the muscles of the limb, but without significant loads and taking into account the pain syndrome: slowly raising a straight leg, in a lying position (toes towards you), and holding the weight for 5-7 seconds. Standing straight leg raise. Exercises with a tourniquet for the calf muscle. Possible exercises in the pool. Classes are conducted 2-3 times a day, 10-15 repetitions.
Arthrotherapy
To restore patients after meniscus removal, drug treatment methods can also be used. The use of arthrotherapy allows:
- reduce pain and prevent damage to hyaline cartilage by reducing friction of articular surfaces;
- accelerate the regeneration of tissues that have been damaged as a result of injury and during surgery;
- form a better scar in place of damaged tissue.
The procedure uses platelet-rich plasma and hyaluronic acid. This combination has a more pronounced effect compared to using these drugs separately.
WEEK 4-6:
- It is possible to walk with full support on the leg (in an orthosis), walking with one crutch, or without additional support.
- Development of range of motion in the joint. The allowed range of flexion is more than 90 degrees (up to full range of motion). By this time, full extension should be achieved and preferably 90 degrees of pain-free flexion.
- Formation of correct gait. You need to walk slowly, not with long steps, trying not to limp on your operated leg.
- Physical therapy aimed at strengthening the thigh muscles. It is advisable to conduct classes under the supervision of a physical therapy doctor and taking into account the reaction of the joint to the load.
Classes are held 2-3 times a day, 10-15 repetitions. Raising and holding a straight leg (toes towards you). Not deep slow spring squats (flexion 30-40 degrees), exercises with light resistance (rubber band), an exercise bike with minimal load and a small angle of flexion in the joint, strengthening the adductor and abductor portions of the quadriceps femoris muscle, exercises in the pool - swinging leg movements, walking in the water.
If the joint swells, pain in the joint increases after exercise, and the joint does not recover by morning, the load should be reduced and consult with your doctor.
rehabilitation
rehabilitation
- anatomical type of rupture;
- rupture zone (the closer to the capsule, the faster the recovery);
- extent of damage;
- duration of injury;
- the patient’s age and state of physical health;
- associated damage to intraknee structures.
The quality of medical care provided is of no small importance. In different clinics, after arthroscopic removal of the meniscus, complications develop in 0.2-10% of patients. As you can see, the spread is quite significant. Relatively speaking, in the worst clinic complications occur 50 times more often than in the best.
WEEK 6-8:
- It is possible to walk and exercise in a functional orthosis, with full range of motion.
- Continue strength training. Exercise bike, active flexion and extension, abduction and abduction with elastic resistance (rubber band), not deep slow squats (flexion up to 60 degrees), exercises in the pool, walking and running in the water, breaststroke swimming is possible. It is possible to exercise on block simulators, without using a simulator that loads the muscles of the anterior thigh.
- Training aimed at coordination of movements. Swaying the body on half-bent legs, stepping onto a step, exercises on a platform, with a safety net, holding onto a support.
It is necessary to avoid sharp extensions and hyperextensions of the legs, swing movements, jumping, and twisting loads. Despite the reduction in pain, the ligament at this time is in the process of restructuring, its strength is reduced and the joint needs protection.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
You will be prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures:
- laser treatment;
- electromyostimulation;
- UHF treatment;
- extracorporeal shockwave therapy (shock wave therapy);
- ion-galvanization;
- magnetic therapy;
- hot paraffin treatment (only in the later stages!).
Electrical stimulation is one of the options for physiotherapy.
Exercise therapy and physiotherapy will help:
- relieving spasms from tense muscle structures and increasing the tone of weakened and atrophied muscles;
- activation of microcirculation and blood flow in the lower limb;
- stimulating metabolism in joint structures;
- relief of painful manifestations and swelling.
4-6 MONTH:
- Continuation of activities aimed at strengthening muscles and coordination of movements.
- Jogging on a flat surface is possible.
- Using a knee brace during loads, the danger of awkward movements (transport, travel) and exercise therapy.
It is necessary to avoid premature increased loads, early return to sports, sudden leg extensions, especially straight leg movements, jumping, running on hard or uneven surfaces, twisting loads, falls, and uncontrolled movements during sports exercises.
Limiting sports activities after ACL surgery is necessary for up to 4-6 months. Limiting contact or team sports to 9-12 months.
I would also like to emphasize that the selection of a rehabilitation program should be carried out individually and take into account many factors. This is a fairly long and important stage of treatment, without which it is unlikely that good functional treatment results will be achieved.
Elastic bandaging
For 6 weeks after surgery, there is a risk of blood clots and swelling. Therefore, a specialist prescribes elastic bandaging in the early period, and compression stockings in the later period. The degree of compression of these medical devices is selected by the orthopedist, taking into account the volume of intervention and the predisposition factor to thrombosis. Applying an elastic bandage and wearing compression garments prevents the development of deep vein thrombosis.
Bandages are used less and less; they hold up very poorly when moving. This type of compression knitwear is most often used.
The technique of how to bandage a leg will be taught to you in the hospital. First, the bandaging is carried out by a doctor, and when you return home you will have to do it yourself. Be attentive to everything the medical staff says and teaches you while you are still in the clinic or rehabilitation center.
Knee replacement in the Czech Republic: guarantees, prices, rehabilitation, reviews and statistics.
Find out more
Preparatory stage
Before undergoing arthroscopy, the patient must be properly prepared. First of all, a general examination is carried out to assess the patient's condition. It includes general urine and blood tests, ECG, fluorography, coagulogram. Tests are also carried out to identify possible severe infections (viral hepatitis, HIV, syphilis).
Preparation for surgery includes compliance with the following rules:
- stop taking any medications for two weeks (except for vital ones, but you must inform your doctor about this);
- the last meal should occur no later than 8-12 hours;
- Before the procedure, the patient needs to buy crutches, since it will be impossible to walk without them at first (doctors recommend learning how to use these devices in advance and understanding the principle of their operation).
The day before the operation, the doctor conducts a conversation with the patient, explaining what the intervention is, how it will happen, and enlightens about the possible consequences. The specialist also gives recommendations on rules of conduct during the recovery period.
Indications
For diagnosis, arthroscopy is done if other research methods do not provide a clear picture. Most often today, MRI is used for diagnostic purposes. Using this technique, the following pathological conditions can be identified:
- ligament ruptures;
- meniscus injuries;
- cracks and fractures;
- inflammatory and degenerative processes affecting the joint;
- synovitis;
- damage to the cartilage tissue of the joint.
The following reasons are indicated:
- popliteal fossa cyst;
- synovitis;
- ruptures of the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments;
- meniscus lesions;
- cartilage diseases;
- deforming arthrosis;
- arthritis;
- Hoffa's disease (inflammatory process of fatty tissue of the joint);
- Koenig's disease (osteochondritis dissecans);
- post-traumatic proliferation of bone tissue.
Reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee joint
The anterior cruciate ligament is one of the most sensitive muscles that contributes to the activity of the knee. Thanks to it, the upper part of the articular surface of the tibia and the posterior part of the intercondylar surface of the lateral condyle of the femur are connected. It also protects against strong displacement of the lower leg during active movement, dislocations, and sprains.
A torn cruciate ligament cannot be restored without surgery. It can be left without medical intervention, but naturally, it will no longer work normally and will cause constant pain. In this case, it is worth remembering that you cannot play sports or dance with such a knee. If left untreated, it will provoke the development of arthrosis.
People who are elderly and have an inactive lifestyle can avoid having surgery, but simply avoid placing heavy loads on the sore leg and do a light set of exercises. Younger people who want to live actively and not feel pain cannot do without surgery.
Anterior cruciate surgery involves replacing the ligament with a substitute (graft). Nowadays, modern medicine allows us to take part of the patient’s own patella for a ligament transplant. If this cannot be done, donor tendons are taken. The operation can be performed under various types of anesthesia, which is prescribed by the doctor. Medication-induced sleep may also be used for your comfort. During the operation, the surgeon makes small incisions of 0.5 in diameter to replace the ligament. The duration of such an operation is no more than two hours.