Published: 06/17/2021 12:50:00 Updated: 06/17/2021
Gout is a systemic disease characterized by impaired purine metabolism in the body and the deposition of urate crystals in the joints. The main manifestation of the disorder is considered to be repeated attacks of arthritis with intense pain in the joints and the appearance of tophi - gouty nodules. Also, with this disease, accumulation of salts in the kidneys is possible with the development of urolithiasis and renal failure.
The prevalence of the disease among adults in Europe ranges from 0.9 to 2.5%, and in the United States reaches 3.9%. Gout is most often diagnosed in men over 40 years of age. Among women, the pathology occurs 6-7 times less often.
Detailed description of the study
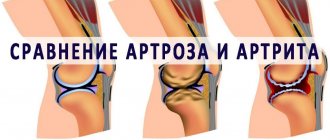
There are a large number of different joint diseases. Among them are often found: rheumatoid arthritis, gout, post-infectious joint damage. Inflammation in the joints is manifested by swelling, tenderness, redness and a local increase in temperature in the affected area. Patients often experience pain and impaired joint mobility. In the future, their deformation, destruction of cartilage tissue, and narrowing of the joint space may occur. Some diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, also have systemic manifestations: a person notices pathological weakness, fatigue, weight loss, and fever.
It can be difficult to make a differential diagnosis of joint diseases due to similar symptoms. Laboratory tests help establish the correct diagnosis.
This study contains two tests necessary to identify the cause of joint inflammation:
- C-reactive protein;
- Uric acid.
C-reactive protein (CRP) is one of many molecules involved in immune responses. CRP is detected in the blood of patients during various inflammatory processes and is considered a marker of the acute phase of their course. An increase in CRP levels is observed within the first four hours after tissue damage and reaches a peak after 24–72 hours.
The content of CRP during inflammation can be increased by 20 times or more. The most common joint diseases that are accompanied by increased CRP are:
- Rheumatoid arthritis;
- Gout;
- Reactive arthritis.
CRP is also a marker of disease activity.
It should be noted that determining the level of CRP plays an important role in assessing joint inflammation, but is not a specific marker for this group of diseases. The indicator may reflect inflammation of another localization, including against the background of acute infections, injuries, and others.
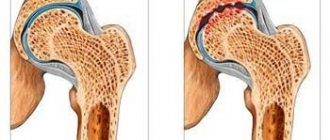
Uric acid is one of the main products of protein metabolism in the human body. This substance is mainly excreted in the urine. When there is an excessive level of uric acid in the blood (hyperuricemia), deposition of its salts (urates) is observed with the formation of crystals. The latter are deposited in joints, subcutaneous tissue, and kidneys (where urates can form stones).
Gout is a systemic pathology, which is characterized by the accumulation of monosodium urate crystals in the joints, as well as other organs and tissues. An increase in uric acid levels suggests that joint inflammation is associated with the development of this disease.
Thus, this comprehensive study will help the doctor in differential diagnosis of the causes of joint damage and selection of therapy.
It is necessary to donate venous blood for analysis. Often the complex is prescribed in conjunction with other studies, such as general analysis and blood biochemistry, to check other organs and systems.
A detailed description of the studies and reference values are presented on the pages with descriptions of individual studies.
The nature of joint disease in men and women
Elena is a Doctor of Medical Sciences, a professor at the Department of Internal Medicine at the Medical Institute of Tula State University, supervises postgraduate education of doctors in the field of Rheumatology and heads the journal Clinical Medicine and Pharmacology. Elena told the Myslo portal how “male” and “female” joint diseases differ.
Gout has always been considered a typical “male” rheumatic disease. In the Middle Ages, gout was called “the disease of gluttons and kings,” meaning that people with good incomes usually suffered from it, having the opportunity to eat plenty of meat and drink large quantities of wine. A portrait of a gouty man from those times is a well-fed, cheerful middle-aged man with a duck leg in one hand and a glass of wine in the other.
However, today we understand that medieval ideas about gout are outdated and not all facts should be perceived so unambiguously.
Among men aged 40 to 65, gout is indeed statistically the most common cause of arthritis. But this disease can occur in young people and women. True, women begin to get sick later, in typical cases of primary gout - after menopause.
about possible contraindications, consult a specialist
What is gout?
Gout is a disease that develops as a result of a disorder in the metabolism of uric acid. Unlike animals, the human body does not have the enzyme uricase that can destroy uric acid, so when uric acid accumulates, crystallizes and causes various pathological processes. Inflammation occurs in the joints, conglomerates can form in the kidneys, leading to the development of urolithiasis or impaired renal filtration. Kidney damage leads to increased blood pressure and an increased risk of strokes. With a high level of uric acid in the blood, the inner wall of blood vessels is damaged and the risk of vascular accidents increases.
Joint damage is often the first, but not the only sign of this serious disease, which affects the entire body, so it is very important to promptly recognize the disease and begin treatment.
Where does uric acid come from and why does it accumulate?
The source of uric acid is protein compounds, so-called purine bases. During their transformations in the body, uric acid is formed. Approximately 1/3 of uric acid is formed from the breakdown of proteins in food, and 2/3 of it is formed in the tissues of our body (mainly in the liver and small intestine).
There are two reasons for the accumulation of uric acid:
- a lot of it is formed as a result of excess nutrition or disease,
- it is poorly excreted from the body by the kidneys.
about possible contraindications, consult a specialist
Who is at risk for developing gout?
These are obese people who regularly drink large quantities of alcohol, especially beer.
There are also some diseases in which secondary gout often occurs:
- chronic kidney disease with renal failure,
- dysfunction of the thyroid and parathyroid glands,
- psoriasis,
- some blood diseases, etc.
How to recognize gout?
The first sign of the disease is sudden severe pain, swelling and redness of the joint, and impaired movement in it. An attack can be triggered by alcohol consumption, overeating, fasting, dehydration, physical activity, injury, blood loss, etc.
Traditionally, at the onset of the disease, those joints in which the temperature is lower are affected, that is, the joints of the feet (more often in men) or hands (more often in women). This happens because uric acid crystallizes faster at low temperatures. But sometimes inflammation may first appear in the elbow, knee, ankle or wrist joint. Body temperature may rise and chills may appear. In these situations, you should consult a doctor.
Why, with such severe symptoms, can people remain unaware of their illness for years and not receive treatment?
Gout is a special disease. Inflammation in the joints in this disease is paroxysmal in nature. This means that the attack can be interrupted spontaneously, while inflammation and pain in the joint at the beginning of the disease disappear without treatment. And when it gets better, the patient forgets about visiting the doctor until the next attack. The insidiousness of the disease is that each new attack will be more severe and longer, affecting more and more new joints.
In addition, we must not forget that gouty arthritis is the tip of the iceberg, and its huge underwater part is problems associated with damage to the kidneys, blood vessels, heart and other organs and systems.
about possible contraindications, consult a specialist
How can you prevent the disease?
If this is hereditary gout that occurs in young men and women, there is no way to prevent it, it is necessary to make a timely diagnosis and begin treatment, which lasts a lifetime and helps keep uric acid levels under control.
With secondary gout, which is a consequence of other diseases, it is important to treat the underlying disease. For example, restoring the function of the thyroid gland when it decreases allows the level of uric acid to be normalized.
Traditionally, the doctor recommends monitoring body weight, not abusing alcohol, and regularly conducting medical examinations.
Can gout be cured with diet?
The doctor will definitely recommend a patient with gout to change his diet.
Today we are talking not only about limiting high-purine products*: red meat (pork, lamb, beef), processed meat products (sausages, smoked meats, canned food), offal (liver, kidneys, lung, heart), seafood (squid, shrimp , oysters, lobsters, etc.), broths and products made from them (jelly, aspic). It turned out that high levels of fat and yeast-containing foods in the daily diet also contribute to increased uric acid levels.
about possible contraindications, consult a specialist
Not only ethanol in alcoholic drinks, but also fructose in sweet carbonated drinks are contraindicated for gout, since they negatively affect the metabolism of uric acid and cause an increase in its content in the blood.
General principles of nutrition for gout:
- avoid overeating,
- eat small meals 4-5 times a day (3 main meals + 1-2 snacks),
- ensure optimal drinking regimen: 30 mg per kg of ideal body weight (in the absence of cardiac, renal failure and edema syndrome of other origin),
- reduce salt intake to 5-8 g per day.
It is recommended to include dairy products, eggs, vegetables, fruits, pasta, cereals, fresh fish, poultry and rabbit meat, and veal in the daily diet of gout patients. The recommended serving of fish and meat is 120 g per day.
The excretion of uric acid salts - urates - in urine is promoted by: cranberries, lingonberries, cherries, citrus fruits, alkaline mineral waters.
Complete fasting is contraindicated for patients with gout, as it can provoke the development of acute arthritis.
It is believed that legumes, asparagus, cauliflower, mushrooms, oatmeal, and wheat bran contain a lot of purines, but it is known that plant foods do not cause hyperuricemia - an increase in uric acid in the blood.
about possible contraindications, consult a specialist
Diet for gout is important, but it is not the only treatment. In most cases, diet alone cannot control the level of uric acid, because only 1/3 of the precursors of uric acid - purines - enter the body with food.
Some patients are treated by a doctor for a long time and without success. With what it can be connected?
Most often, this happens, unfortunately, due to either undisciplined adherence to the doctor’s recommendations, or to the patient’s deliberate refusal to take medications. At the same time, the treatment of such a chronic disease as gout requires long-term use of individually selected drugs that allow you to preserve not only health, but in the long term life, since high uncontrolled levels of uric acid in the blood are a risk factor for the development of not only kidney failure, but also heart attacks and strokes .
Many of our patients are not always ready to give up alcohol and change their eating habits. And this is a very important aspect of an integrated approach to treatment, which cannot be underestimated.
Who treats gout?
In our country, rheumatologists and general practitioners treat gout. In order to establish a diagnosis and prescribe treatment, additional research will be required. The doctor will prescribe a blood test, urine test, and, if indicated, instrumental examinations. This is necessary so that the treatment is individualized, tailored to the characteristics of each patient and ensures the achievement of maximum results.
What results can be expected when treating gout? After all, this is a chronic disease
As with any chronic disease, treatment is mainly aimed at maintaining quality of life, preventing the development of the disease and the risk of complications. It is believed that the disease is well controlled if acute attacks of joint inflammation are absent or rarely occur, the target level of uric acid in the blood is maintained, and the functioning of internal organs does not deteriorate.
Address
Medical city Tula, Lenin Ave. 66 A, room 158. tel. 8-(4872)-52-60-70 tel. 8-967-431-77-41 sozvezdie-tula.ru
* Products containing many protein bases - precursors of purines, from which uric acid is formed
about possible contraindications, consult a specialist
References
- Rheumatoid arthritis. Clinical recommendations. Association of Rheumatologists of Russia, 2021. - 102 p.
- Rheumatology: National Guide / ed. E.L. Nasonova, V.A. Nasonova. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2008. - 720 p.
- Kishkun, A.A. Guide to laboratory diagnostic methods. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2007. - 800 p.
- Internal diseases in 2 volumes: textbook / ed. ON THE. Mukhina, V.S. Moiseeva, A.I. Martynova, 2010. - 1264 p.
- Kasper, D., Fauci, A., Hauseret, S. Harrison`s Principles of Internal Medicine 19/E (Vol.1). McGraw-Hill Education, 2015.
Diagnosis of gout
The diagnosis and treatment of gout is carried out by a rheumatologist, internist or general practitioner (family doctor). Most often, the patient comes not at the onset of the disease, since the symptoms of acute gouty arthritis quickly disappear, which can be regarded by a person as recovery, but during one of the subsequent exacerbations. The doctor conducts a conversation with the patient, during which the fact of an acute joint attack in the past, the presence of characteristic complaints, as well as risk factors for the development of pathology are established. The phenomena of bursitis and tophi - the main objective manifestations of gout - are more often found on the leg. The diagnosis can be confirmed by a comprehensive examination of the body using laboratory and instrumental methods. If gout is suspected, the following tests are performed:
- Clinical blood test. During an attack of gouty arthritis, an acceleration of the COE, an increase in the number of leukocytes and a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left are possible.
- Determination of urate in blood serum. About 70% of patients with an exacerbation of gout have a high level of uric acid - more than 0.42 mmol/l in men and 0.36 mmol/l in women.
- Determination of uric acid in daily urine. The method is used to assess the risk of kidney stones.
- General urine analysis. It is carried out for the purpose of diagnosing diseases of the urinary system that contribute to the development of gout or are its complication.
- Examination of synovial fluid. Biomaterial is collected for analysis using puncture of the affected joint. The presence of monosodium urate crystals in the joint fluid makes it possible to confirm gout, and its sterility during bacterial culture excludes infectious causes of arthritis.
- Microscopic examination of a biopsy sample from tophi. When viewed through a polarizing microscope, urates appear as needle-shaped crystals with a pointed end. This method is also highly specific in diagnosing gout, like the previous one.
Instrumental diagnosis of gout may include research methods such as:
- Ultrasound of affected joints;
- MRI and CT;
- X-ray diagnostics.
X-rays at the onset of the disease are carried out for the purpose of differential diagnosis with other arthropathies, but there are no specific signs of gout. Only when the pathology becomes chronic can one see intraosseous tophi and marginal bone erosions in the photographs.
Ultrasound examination of joints before the development of chronic gout is effective only during exacerbations.
MRI makes it possible to detect tophi inside the joints even before they appear under the skin, making it possible to begin specific therapy for hyperuricemia earlier. The method is used in differential diagnosis with other diseases, as well as to monitor the effectiveness of treatment. CT, in comparison with other imaging methods, allows for more accurate differentiation of tophi masses.