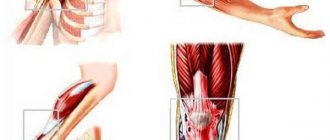
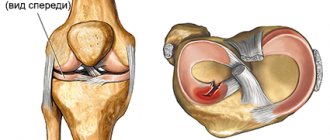
Arthritis of the lower extremities is an inflammatory disease that affects the joints. Its occurrence can be an independent process or as a consequence of existing infectious foci in the human body, as well as autoimmune and metabolic changes.
The inflammatory process in the joints has common features with similar processes occurring in any other parts of the body. Redness and swelling develop in the tissues surrounding the affected joint. In addition, symptoms appear that indicate the development of a destructive process in the joint. If not properly treated, such disorders can cause disability.
1.What is inflammation and its causes?
Inflammation
is the process by which the body's white blood cells and certain chemicals protect us from infection and foreign microorganisms - bacteria and viruses.
In general, it turns out that inflammation is a useful protective reaction of the body. But in some diseases, such as arthritis, for example, the immune system causes an inflammatory reaction even in the case when there are simply no foreign substances whose attack needs to be repelled. Such diseases are called autoimmune diseases. As a result, the body's defense system causes damage to its own tissues. And the body perceives them as if there is an infection or some kind of pathology in healthy tissues.
Causes of inflammation and its consequences
During inflammation, chemicals from the body's white blood cells are released into the blood or affected tissues to protect the body from foreign invaders. This release of chemicals increases blood flow to the area of injury or infection and can cause redness and heat production. Some chemicals cause fluid to leak into the tissue, causing swelling. The protective process can also stimulate nerves and cause pain.
Can inflammation affect internal organs?
Yes, inflammation can affect organs as part of an autoimmune disorder. The type of accompanying symptoms depends on which organs are affected. For example:
- Inflammation of the heart (myocarditis) can cause shortness of breath or fluid buildup in the body;
- Inflammation of the small tubes that carry air into the lungs can also cause shortness of breath.
- Inflammation of the kidneys (nephritis) can cause high blood pressure or kidney failure.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
3. Treatment of pain in the legs (ankles, feet, toes)
Treating leg pain at home often helps to cope not only with pain, but also with other symptoms - swelling of the legs, cramps, and discomfort. Treatment, as a rule, begins with eliminating the factors that caused pain in the legs.
and other unpleasant sensations.
For example, you should stop exercising at least temporarily if you experience pain in your legs (feet, ankles, or toes) during exercise. Physical activity “through pain” is contraindicated. It is important to wear high-quality and comfortable shoes. Arch supports and other orthopedic devices
will help make walking more comfortable.
Cold application, rest, foot massage, gentle and gentle exercises
(for example, for stretching tendons) will help cope with leg pain, leg swelling or cramps. To relieve leg pain, you can take over-the-counter pain medications.
For swelling of the legs, swelling of the feet and ankles
You can raise your swollen legs just above the level of your heart and sit like that for a while. If you have a sedentary job, get up and walk around for a few minutes every hour. Reduce your salt intake.
If your home treatments for leg pain (feet, ankles, toes), leg swelling, and other problems do not have the desired effect, consult your doctor. Consultation with a specialist is required
and when the pain and swelling intensify, signs of infection appear, the skin turns pale, tingling and numbness appear.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Symptoms of joint inflammation
Symptoms of joint inflammation may include:
- Redness;
- Joint swelling, warm to the touch;
- Joint pain;
- Loss of joint function.
Symptoms of joint inflammation can also include those sensations that are often associated with a cold - high fever, chills, fatigue, headaches, loss of appetite, muscle stiffness.
Pain is not the main symptom of an inflammatory disease
, since many organs do not have many pain-sensing nerves. And treatment of organ inflammation is aimed at addressing the cause of inflammation, whenever possible.
Visit our Rheumatology page
Diagnostics
Rheumatologists are involved in determining the cause of joint swelling. According to indications, patients are referred to orthopedic traumatologists, infectious disease specialists, endocrinologists, and other specialists. The doctor interviews the patient, carries out an external examination: studies the configuration of the joint, color, temperature of the skin, palpates, and evaluates the range of movements. Depending on the results of the initial objective examination, the following diagnostic procedures may be prescribed:
- Radiography.
It is a basic research method and is performed in two projections. The images visualize changes in the contours of the articular ends of the bones, narrowing of the joint space, marginal defects, areas of destruction and osteolysis. - Sonography.
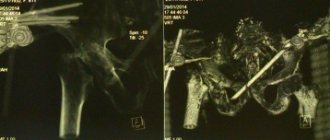
Used to study the condition of soft tissues. Detects effusion, hemorrhages, foci of calcification in periarticular structures. Allows you to quickly determine the cause of swelling. - CT and MRI
. They are carried out at the final stage of the examination if the results of radiography and ultrasound are ambiguous. They make it possible to detail and differentiate inflammatory, tumor, traumatic lesions, to clearly determine the volume and localization of the pathological process. - Joint puncture.
Indicated for synovitis, hemarthrosis. The resulting liquid is sent for bacteriological, cytological, and immunological examination to clarify the nature of the disease. - Arthroscopy.
Recommended for detailed visual examination of the joint and biopsy sampling. A biopsy is performed if arthritis of autoimmune origin, tuberculosis, or neoplasm is suspected. Sometimes diagnostic arthroscopy is complemented by therapeutic measures. - Lab tests
. A general blood test confirms the presence of inflammatory changes, eosinophilia in allergies. Based on the results of biochemical and serological tests (presence of rheumatoid factor, CRP, CEC), autoimmune diseases are confirmed.
Joint puncture
4. Treatment of joint inflammation
There are different methods of treating inflammatory diseases (including arthritis) - medications, rest, exercise and surgical treatment of damaged joints. The specific joint treatment regimen depends on several factors, including the type of disease, the person's age, whether the patient is taking any other medications, medical history, and the severity of symptoms.
The goal of treating inflammation may be:
- Avoiding activities that increase pain;
- Reducing pain with painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Maintaining muscle strength through physical therapy;
- Reducing stress on joints using canes, support devices, etc.;
- Control and slow down the development of the underlying disease.
Medicines to treat joint inflammation
can be very different. They help reduce swelling and pain in the joints and slow or stop the progression of inflammatory disease. The group of drugs prescribed by a doctor may include:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (aspirin, ibuprofen, naprxen);
- Corticosteroids;
- Antimalarial drugs;
- Other drugs, for example - methotrexate, sulfasalazine, penicillamine, cyclophosphamide, etc.;
- Biological drugs.
Some of these drugs are traditionally used to treat other diseases. For example, cancer or inflammatory bowel disease, or to reduce the risk of transplanted organ rejection. But in this case the dosage will be much less. This means the likelihood of side effects is reduced.
In any case, no medications should be taken without first consulting a doctor. Moreover, potent medications for the treatment of joint inflammation.
Reasons for development
In medical practice, the number of all inflammatory joint diseases is large - about 100. True, most of them are not associated with serious pathologies and arise due to overwork, climate change and other factors. When these causes are eliminated, the person quickly recovers.
But not all prerequisites for the development of inflammatory processes in the joints are harmless. Many of them, without treatment, risk arthritis, polyarthritis, arthrosis, bursitis, and other serious health problems. If the inflammatory process is started, the pathology quickly becomes chronic and severe.
Causes of inflammation:
- any infection (viruses or bacteria);
- excessive systematic loads in athletes and people whose profession involves heavy physical labor;
- frequent hypothermia of the legs;
- prolonged stay in conditions of high humidity;
- autoimmune disorders and diseases;
- lupus, rheumatism of the legs, history of arthritis;
- metabolic and endocrine system disorders;
- injuries of the lower extremities involving bone joints;
- wearing uncomfortable or tight shoes;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- age-related changes in the structures of bones and cartilage;
- excess weight.
Inflammatory processes in the joints of the legs can be avoided by limiting stress, avoiding excess weight, and avoiding hypothermia and colds.
How to understand what the reason is
A doctor should carry out the diagnosis, so if you have pain or discomfort in your foot, you should not put off visiting a specialist. But already at the initial stage you can independently navigate the symptoms:
- With arthritis, the joint becomes inflamed suddenly, without provoking factors such as injury. The pain occurs mainly at night and disappears when walking.
- When the ankle bones are fractured, the bone structures of the ankle are also damaged. Swelling is visible, you experience pain at the slightest step on the foot.
- With tunnel syndrome, compression of the walls of blood vessels and nerve roots occurs (for example, this happens with diabetes, after an injury, or against the background of arthrosis). Extensive edema forms, a cooling of the limb is observed, which is replaced by a local increase in temperature.
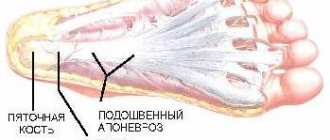
- With tendinitis, the tendons become inflamed and swelling occurs. Pain occurs when putting weight on the leg. If left untreated, there is a risk of infection and rupture of tendon fibers.
- With gout, severe pain occurs mainly during sleep. The pain is acute, spreads to the entire foot and radiates to the big toe. Gout and salt deposition have nothing in common with arthrosis in nature, with the exception of pain.
- When the heel bone is fractured, extensive swelling, hematomas are noticeable, the foot hurts, and motor activity decreases. This problem is relevant for runners and can lead to chronic pain.
- With partial or complete dislocation, the bone tissue of the ankle thickens and the heel turns inward. The joint becomes deformed, causing extensive swelling and prolonged pain.
Unlike problems of a traumatic nature, arthrosis does not have such pronounced symptoms. With degenerative changes in the cartilage, the ankle hurts and is somewhat limited in mobility. Symptoms are often vague, so a person does not rush to consult an orthopedist, but experiments with gels, ointments, local remedies, traditional medicine and wastes precious time.
With arthrosis, there are no visible signs - swelling, hematomas
How to quickly help yourself in case of an ankle injury
If you feel severe pain in your foot due to injury or severe mechanical stress, do the following:
- place your foot on a small hill;
- remain in this position until the pain becomes less intense;
- apply a cold compress of ice wrapped in thick cloth for 20 minutes;
- eliminate the load on the leg, swaddle the injured foot tightly with a bandage (relevant during the first two days);
- As soon as possible, go to the doctor.
A cold compress of ice helps in the first hours after injury