Author of the article: Yachnaya Alina, oncologist surgeon, higher medical education with a degree in General Medicine.
Article publication date: 11/19/2013
Article updated date: 12/02/2018
The knee joints are one of the most heavily loaded joints in the body, and they are also highly susceptible to injury. Therefore, it is quite natural that inflammation of the meniscus is a fairly common pathology. The meniscus of the knee joint (in fact, there are two of them in the knee joint - internal and external) is cartilaginous tissue that performs shock-absorbing and stabilizing functions, and therefore in case of diseases or injuries of the meniscus, the entire joint suffers. At risk are:
- athletes, especially skiers, skaters, jumpers, runners;
- people doing heavy physical work;
- obese people;
- people with chronic diseases in which metabolism and normal blood circulation are impaired.
Causes of inflammation
Possible causes of inflammation of the knee menisci:
- meniscus damage caused by uncoordinated movements or injuries during unsuccessful jumps and squats;
- constant heavy stress on the legs and knees associated with heavy physical labor, sports or due to obesity;
- disruption of the blood supply to cartilage tissue, which causes degenerative changes in it.
The number 1 reason is still injuries. With any injury to the knee joint, it is the meniscus that is primarily affected.
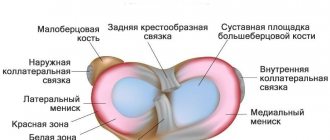
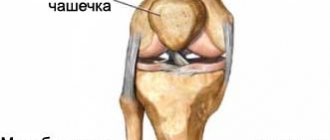
Anatomy and functions of the meniscus
The meniscus is a crescent-shaped cartilaginous formation. There are 2 menisci inside the knee joint - the outer (lateral) and the inner (medial). They form a layer between the bones of the thigh and lower leg. Menisci perform several functions in the body:
- cushions when jumping, walking and running;
- reduce friction of articular surfaces;
- reduce the load on the knee.
The inner meniscus is less mobile than the outer one, so injuries to it occur several times more often. Men between 18 and 40 years of age are most susceptible to problems with menisci.
Symptoms
When the meniscus is inflamed, the following symptoms are most often observed:
- The pain in the knee joint is sharp at first, but then it becomes habitual. Pain syndrome can also develop progressively if inflammation is caused by poor circulation or prolonged high stress.
- Limitation of movements.
- If the meniscus ruptures, the joint is blocked.
- An increase in the volume of the joint, with further development of inflammation - swelling of the adjacent soft tissues.
- The appearance of a click during movement and a symptom of rolling - the patient feels that the heads of the bones in the joint are “rolling”.
- Feeling of a foreign object in the knee.
In the acute period, the main symptoms (pain and limitation of movement) are clearly expressed, but they can be confused with a knee bruise or sprain. A few days after the injury, pain is localized in the projection of the meniscus (along the joint space). As a rule, during this period the patient can clearly indicate the most painful point.
When inflammation becomes chronic, the patient experiences mild pain in the joint when going up and down the stairs, a feeling of a foreign object inside the knee, and sometimes clicking sounds.
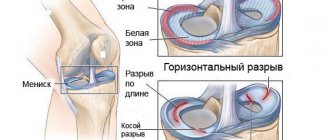
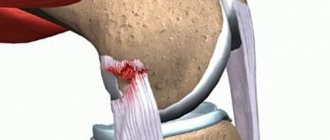
Pictured is a torn meniscus.
Meniscus injuries - causes and risk groups
There are 2 main types of meniscus damage - rupture of the body and separation from the place of attachment to the joint capsule. Causes of injury may include:
- sharp turn of the lower leg with a fixed foot;
- blow to the knee joint;
- falling to one's knee;
- sudden excessive extension of the knee.
People at risk for meniscus injury include:
- people with untreated knee injuries;
- professional athletes;
- patients with gout;
- patients with excessively mobile joints and weak connective tissue.
Diagnostic methods
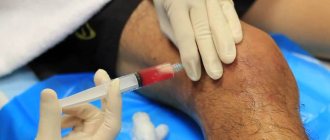
Since the symptoms of inflammation are nonspecific, it can be confused with other injuries and diseases of the knee, so a thorough examination is necessary to make a correct diagnosis . In addition to examination by an orthopedist, hardware and instrumental diagnostic methods are used:
- X-ray examination. It is worth saying that damage to the menisci is not visible on an x-ray - their cartilage tissue is transparent to x-rays. But x-rays can rule out other diseases or joint injuries.
- Ultrasound.
- Computed or magnetic resonance imaging.
Only after conducting appropriate research can we confidently say that the patient has inflammation of the meniscus.
Diagnostic measures
Symptoms indicating inflammation of the knee meniscus also accompany other diseases, for example, a tumor or cyst of the knee, the onset of arthrosis of the joint. The correct diagnosis is made faster if you seek medical help in a timely manner. Consultation with an orthopedist-traumatologist will help clarify the situation. After the initial survey, the doctor will select the necessary diagnostic methods that will give reliable results.
Initially, you should undergo tests and take an x-ray. If the need arises, the attending physician may choose other modern, effective methods to clarify the diagnosis: MRI of the knee joint, ultrasound.
The difficulty of X-ray examination lies in the insufficient degree of information content in the presence of minor pathological changes, so tomography is the method of choice today. Using magnetic waves, the smallest damage to the cartilage tissue of the meniscus, ligaments, muscles, and other structures of the knee joint is determined. The doctor receives the results of the study in the form of a three-dimensional 3D image, which allows a detailed study of the nature of the disorders with the possibility of increasing the size of the image.
When the x-ray shows nothing, but clinical manifestations are present, the patient is necessarily referred for a tomographic examination.
Treatment
Treatment for meniscus inflammation will depend on the cause of the disease (as well as on the nature and location of the injury, if inflammation developed as a consequence). What treatment options are there?
- First aid for injury consists of removing the blockade of the joint (if there is one) and eliminating the consequences of the injury (removing excess synovial fluid and blood from the joint capsule), pain relief, and immobilizing the limb for up to 4 weeks.
- With conservative therapy, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are prescribed in the form of ointment, cream or gel, sometimes NSAIDs are taken orally (by mouth). After removing the immobilizing bandage, physiotherapy and exercise therapy are prescribed.
- Surgery. Today, arthroscopy is most often used - a surgical operation (with a minimal incision and intervention in the body) to remove part of the meniscus or stitch the torn edges, if possible.
Folk remedies for this pathology are ineffective.
Timely diagnosis and treatment give good results, allowing the knee joint to fully function . Therefore, at the slightest suspicion of inflammation, you should consult a doctor. And people at risk need to carefully monitor their health, because any disease is much easier to prevent than to treat later.
Why is a meniscus needed?
The meniscus plays a vital role in the functioning of the musculoskeletal system. It is a kind of connecting link between the bones of the femur and the shin, while it separates them so that when moving they do not touch, which means they are not injured or destroyed. On the other hand, the meniscus limits bone movement, which prevents dislocation and reduces the rate of wear and tear on the joint.
First of all, the meniscus performs a stabilizing function. It promotes displacement of all components of the joint only in a certain direction. In addition, the meniscus protects the cartilage and bone at the junction from destruction. Thanks to him, the entire knee mechanism slides against each other without being subject to friction. At the same time, the meniscus provides a shock-absorbing function. Its fibrous structure can both stretch and compress, relieving stress on tendons and ligaments.
Gymnastics to restore knee function
Any gymnastics is indicated only if the acute period has already ended and you can work with the knee joint without pain. As a rule, gymnastics is prescribed after wearing a plaster cast or splint for a long time. To return the knee to working capacity, you need to begin to gradually warm it up according to a certain method.
Clinics offer physical therapy sessions where, under the supervision of a specialist, patients recover from serious injuries. If a doctor has diagnosed a meniscal tear, any exercise will be postponed until the tissue has completely healed.
Exercises begin with minimal loads. First, these will be exercises for flexion and extension of the sore knee. You need to do it while sitting on a high chair. 10 lifts twice a day is enough. Gradually, the load can be increased, in accordance with the doctor’s recommendations. If you experience any pain, you should immediately report it to a specialist to adjust your rehabilitation plan.
Types of meniscopathy
There are external (20%), internal (75%) and bilateral (5%) meniscopathies. A larger percentage of cases occur on the internal (medial) meniscus. Pathology manifests itself as:
- cyst formation;
- meniscus tear (marginal, transverse, flap or horizontal);
- detachment of cartilage tissue;
- instability or excessive mobility due to rupture.
Any unusual load can lead to one of the above symptoms.
Damage to nerves and blood vessels
They occur very rarely, in only 0.06-0.08% of cases. Neurological disorders may develop due to the use of a tourniquet or against the background of compartment syndrome. The cause of vascular damage is most often the careless handling of instruments by the surgeon. As you know, the popliteal artery is located very close to the posterior capsule of the knee joint. Consequently, dissection of the latter is often accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the vessel.
The structure of damage to various nerves during arthroscopy:
- subcutaneous – 84%;
- fibular – 10%;
- femoral – 6%;
- sciatic – 6%.
Fact! Ischemic and traction nerve injuries respond well to treatment. But if their anatomical integrity is violated, it is almost impossible to eliminate neurological disorders.
Complications after meniscus removal
Meniscus removal
incomplete and total can have consequences, like any surgical intervention, although the likelihood of negative reactions is low. According to statistics, about 90% of operations to remove the menisci of the knee joints predict a successful outcome without postoperative problems. Of course, with high precision of manipulation, compliance with asepsis and antisepsis during the procedure and proper postoperative care. But still, let’s announce possible complications:
- thrombotic formations in the operated limb;
- bleeding due to damage to blood vessels;
- injury to the nerve bundle;
- pathogenic infection inside a joint or in a surgical wound.
There is an opinion that it is common after removal of the meniscus
the consequence is arthrosis. We do not argue, but it is also important to take into account the fact that total surgery, namely, it threatens the appearance of degenerative pathogenesis in 15 years, is a rarely used tactic, used exclusively in particularly difficult cases, as a last resort. For example, if the scale and severity of the lesion are not subject to corrective plastic surgery or partial resection of the meniscus of the knee joint, which is very rare.
Specialists always try to leave as much of a functional unit as possible, understanding that the biomechanics of the bone joint of the knee rests on it. Therefore, being guided by the fact that removal of the meniscus will provoke consequences in the form of gonarthrosis of the knee joint, and not going to the doctor, is a huge mistake. Serious osteochondral degenerations, plus atrophy of the thigh muscles, will definitely not take long to occur. And even simple defects in the collagen structures of cartilage left to chance, which at one time could have been completely cured conservatively, promise a similar outcome.
Valuable information! First of all, the operation saves the meniscus, which means that the pathological source that interferes with the normal interaction of the articular bones will no longer act on the knee. By eliminating the damaging factor, the likelihood of the formation of a degenerative-dystrophic focus in the structures of the bone joint is also reduced.
Compartment syndrome
Occurs due to leakage of irrigation fluid in the presence of a defect in the joint capsule. The development of pathology is facilitated by an increase in irrigation pressure and blockage of drainage. Compartment syndrome is accompanied by soft tissue swelling and a sharp increase in intrafascial pressure. As a rule, it leads to necrosis of muscle tissue and the appearance of contractures in the postoperative period.
Compartment syndrome is treated conservatively. Patients are prescribed analgesics (Tramadol, Ketorolac), decongestants (Furosemide) and anti-ischemic drugs. They are also administered drugs that improve the rheological properties of the blood and relieve vascular spasm. If conservative therapy is ineffective, patients undergo surgery - decompressive fasciotomy.
Indications for surgery
Complete removal of the knee meniscus
inevitable if the diagnosis showed a rupture of most of the body or fragmentation of the cartilaginous layer. Fortunately, this happens extremely rarely. Organ-saving surgery, which is mainly performed, consists of partial removal of the meniscus of the knee joint, that is, resection of only the non-viable area. As for conservative medicine, it is used for minor fiber tears, microtraumas, structural degenerative-dystrophic changes, if they do not provoke pinching and joint instability.
Types of meniscal tears.
According to doctors, patients do not always go to the hospital immediately, but years after they have experienced the injury. And what previously seemed like an ordinary bruise, over time leads to serious complications. Since the shock-absorbing pad does not have a sufficient network of blood vessels, there are practically none, some tears in certain areas cannot heal on their own - they must either be resected or stitched. Meniscus surgery
, and it is reasonable to do it for fresh injuries, which increases the chances of full restoration of motor functions, has the following indications:
- the presence of a vertical break in the midline;
- transverse or longitudinal violation of integrity;
- flap (tongue-like) anterior tears;
- multiple bundles;
- separation of a fragment of cartilage from the main plate;
- pinched meniscus cartilage;
- highly fragmented structures;
- presence of cystic formations.
A removed meniscus in the hands of a traumatologist.
Loose meniscus pieces or torn pieces of cartilage that are constantly wedged between articulating bones are a real disaster for motor support functions and the health of the articular surfaces. Arthrosis is guaranteed if an operation to remove the meniscus of the knee joint, or rather its pathological fragments, was not performed in a timely manner. And advanced osteoarthritis is a direct road to disability. That’s why experts don’t advise tempting fate, but at least go to the emergency room first.
Attention! Internet sources often mention that they allegedly replace the meniscus of the knee joint, mind you, in passing and without any details. The scant information regarding the implantation of donor material or a meniscus implant simply means that such a technique has not yet received approval from orthopedic experts. Due to the insufficient clinical evidence base for its effectiveness, meniscal replacement, unlike knee arthroplasty, has not yet become widespread.
First aid to a patient
The victim may experience severe pain from a couple of days to a week. If the severity of pain is moderate, you can do without contacting a traumatologist. To relieve pain and reduce suffering, you need:
- Apply ice to the sore knee. This will relieve swelling. Cold during prolonged contact causes blood vessels to constrict, thereby reducing local hyperthermia.
- You can reduce the intensity of pain with the help of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, including ibuprofen, diclofenac, analgin.
- To reduce the risk of worsening the situation, it is important to ensure immobility of the injured limb using a splint. It is better if the knee is elevated in relation to the healthy leg.
When the acute period is over and the patient can see a traumatologist, the specialist will assess the extent of the damage and prescribe a course of treatment and care.
Ischemia of the muscles of the lower limb
To prevent bleeding during arthroscopy, doctors apply a tourniquet to the patient's leg. Unfortunately, long-term exposure can cause temporary paralysis of the lower limb. The pathology is characterized by a short-term impairment of muscle contractility and motor functions of the leg.
The leg is bandaged.
Table 2. The risk of developing paresis depending on the age of the patients and the time of application of the tourniquet.
| Short | Occurs in patients under 50 years of age who have had a tourniquet applied for less than 40 minutes. The predicted incidence of complications in such patients is 7.6%. |
| Average | Typical for persons under 50 years of age with an exposure time of 40-60 minutes and persons over 50 years of age with an exposure time of less than 40 minutes. Among this group of patients, paresis develops in 10-16% of cases. |
| High | Equal to 28% or more. Characteristic of all patients in whom a tourniquet was applied for more than 60 minutes. |
Thus, the likelihood of temporary paresis is much higher among older people. Those patients who have undergone complex long-term operations are also at greater risk. Undesirable complications can be avoided by reducing the time of application of the tourniquet.
Fact! Temporary paresis is usually harmless and responds well to treatment. To combat them, physical therapy, massage and physiotherapeutic procedures are used.
Types of Meniscus Damage
Although the meniscus can stretch, this does not mean that it is elastic like a ligament. When subjected to extreme tension, the tissue tears. Tears can be complete, incomplete, longitudinal, patch-like, transverse and fragmented. During an injury, rupture can occur with complications. This happens when torn fragments dislodge and damage nearby soft tissue.
There are several types of damage:
- Complete rupture, when the posterior or anterior horn completely detaches along with the body near the joint capsule.
- Rupture of only the internal fragment located away from the joint capsule.
- Damage to both the internal zone and the area located next to the joint capsule.
Cartilage tissue can be damaged both due to the constant negative impact of traumatic factors, and as a result of a progressive destructive process inside the joint.
Tool failure
In recent years, it has become less common due to the improvement of arthroscopic equipment. If an instrument breaks down, doctors immediately stop irrigation and aspiration. They then carefully remove the broken fragment using special equipment. If the piece is small and difficult to access, it may be left in the synovial cavity.
Tools.
Hemarthrosis - accumulation of blood in the knee
Usually develops due to damage to the ascending lateral femoral circumflex artery. Hemarthrosis is treated by arthroscopic lavage of the synovial cavity and intra-articular injection of a local anesthetic (Lidocaine, Novocaine) with adrenaline. After this, a pressure bandage must be applied to the patient’s knee.
Accumulation of blood in the capsule.