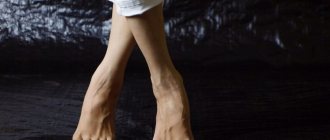
“Bumps” on your feet need to be treated!
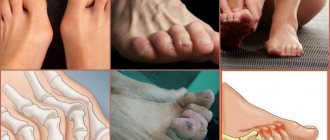
Hallux Valgus is an outward deviation of the big (first) toe
. The deformity develops with flat feet of 2-3 degrees. In this case, the first metatarsal bone of the foot deviates, its head protrudes under the skin in the form of a bump. Over time, the outward deviation of the finger increases, and it approaches the neighboring finger. Valgus curvature is accompanied by the development of arthrosis of the joint and is characterized by pain, which intensifies when walking. Inflammatory and dystrophic processes develop in a deformed joint. Subsequently, movements in the foot and throughout the lower limb are impaired. Over time, secondary pathological changes develop in the spine and hip joints.
Causes of hallux valgus
The pathology is most often observed in middle-aged women and is associated with wearing narrow, tight shoes with heels. However, incorrectly selected shoes are only one of the reasons. Women have weaker ligaments and muscles than men, and therefore hallux valgus occurs more often in them. There are several factors that predispose to hallux valgus:
- Obesity;
- Transverse flatfoot;
- Osteoporosis;
- Metabolic disorders accompanied by calcium deficiency;
- Heredity;
- Previous foot and ankle injuries;
- An occupation that requires standing for long periods of time.
If the finger has already begun to deviate, there is a chance that the deformity will progress. With the help of treatment in the clinic, you can get rid of this cosmetic defect and prevent complications associated with it.
What you need to know about correcting your feet
The following information is worth taking note:
1
. Foot surgery involves the correction of existing deformities, the predisposition to which remains;
2
. Hospitalization – after a preliminary examination (in a clinic);
3
. Anesthesia - at the discretion of the anesthesiologist, in most cases, spinal (plus sleep);
4
. During the operation, fixation of the bones with screws is necessary; it is possible to use conventional ones (they are removed during re-hospitalization after 3-4 months, available, provided free of charge) and special intraosseous ones (they are not removed, paid for through the bank);
5
. Sutures are removed 13-14 days after the operation;
6
. The described operations do not require a cast or crutches (with the exception of planovalgus foot).
7
. After the operation, dressings are performed as necessary, but no more than 2 times a week;
8
. Commercial patients stay in hospital for 5-14 days, non-commercial patients – 14-15 days;
9
. It is recommended to wear post-operative shoes (Baruk shoes) for 4-6 weeks from the date of surgery;
10
. The operated foot can be washed no earlier than 2 days after the surgical sutures are removed. Do not lubricate the postoperative scar with ointments!;
11
. 2 or 3 days after the removal of the surgical sutures, the development of the operated fingers begins - finger movements are made with the help of the hands and only up and down!;
12
. After the swelling has completely subsided (1.5-3 months), it will be necessary to make custom insoles (instep supports) - there is no point in buying ready-made ones. You need to wear them constantly.
13
. Any foot operation, regardless of complexity, entails some restrictions that have to be introduced into everyday life for a month and a half until the swelling subsides; in rare cases, swelling can last 3-4 months;
14
. The swelling will go away much faster if you carefully follow the regimen prescribed by your doctor, especially in the first 2-3 postoperative weeks. The main rule is to lower your legs down as little as possible and try not to walk;
15
. You can drive a car no earlier than after 1.5 months;
16
. It is not recommended to return to work earlier than a month after the operation (the period depends on the complexity and type of operation);
17
. In some cases, after surgery it is necessary to wear additional devices - an interdigital insert, a holder for 2-3 fingers, and others;
18
. You can wear heels 3-4 cm high 3 months after the operation, heels 6 cm high - after 6 months; however, it is worth remembering that the narrower the toe of the shoe and the higher the heel, the higher the likelihood that a recurrence of the deformity may occur;
19
. The resorption of scars is facilitated by the use of Contractubex ointment, but it requires constant use throughout the year. During the same period, scars, as a rule, decrease in size and fade in the vast majority of cases on their own;
20
. It is sometimes impossible to eliminate all deformities in one operation; the operation is often required in 2-3 stages;
21
. If the case is not too advanced, it is more logical to operate on both feet at one time;
22
. After surgery, heavy lifting, as well as excess weight, contribute to the development of flat feet and the further formation of new deformities;
23
. Moderate exercise can be continued 3 months after surgery; full physical activity is allowed only after 6 months;
24
. According to statistics, complications are possible in only 2% of cases. (The complications themselves are standard for surgical interventions);
25
. The feet will swell at first; after placing the toe in the correct position, the shoe size may increase.
A very important note - foot surgery is not cosmetic. The surgeon’s task is to try to make life easier for people with deformities that prevent them from wearing shoes and are accompanied by pain. You need to understand that after any surgical intervention, both complications and relapses are possible.
In most cases, something can be corrected or improved, but less often it is impossible.
The foot is a very complex mechanism that is used continuously throughout life (sometimes recklessly - I mean harmful shoes, excess weight, excessive physical or sports activities), and each person is individual, with his own characteristics of anatomy, biomechanics, physiology, lifestyle and etc. That is why it is not always possible to obtain a surgical result that satisfies both the patient and the surgeon. When deciding to undergo surgery, you need to be aware that as a result of treatment, the main problems will be solved, and there can be no talk of any guarantees in surgery. Not everything is in the hands of the doctor; there are many objective processes beyond the surgeon’s control that cannot be influenced.
Advantages of diagnosing and treating hallux valgus in our clinic
- Diagnostics
Thanks to modern X-ray machines, even small deviations of the toes are clearly visible on radiographs. To recognize secondary changes, we conduct x-ray examinations of other parts of the musculoskeletal system - the spine, joints of the lower extremities. - No pain
There is no pain either during or after the operation. All surgical interventions are performed under local anesthesia. In the postoperative period, to eliminate pain, we administer analgesic medications. We use only modern, effective and safe medicines. - Recovery
After operations performed in our clinic, recovery occurs very quickly. Already on the second day the patient can move without crutches, and after two weeks he can wear normal shoes.
If hallux valgus deformity of the first toe appears, do not wait for it to increase.
Modern surgical treatment of Hallux valgus
Hallux valgus is a disease that progresses rapidly and for many patients ends with surgery. Until recently, such operations were traumatic and painful. Today there are many gentle radical interventions that quickly return people to their usual way of life.
When is radical intervention indicated for hallux valgus?
- severely deformed finger;
- constant pain in the area of the first phalanx;
- inflammatory process;
- formed arthrosis or severe arthritis;
In children and at the initial stage of the disease, conservative therapy can still slow down the progression, but in severe cases, only surgery can help correct the problem. Surgical intervention reliably straightens the finger, symptoms disappear, and gait becomes painless and easy.
What operations are used for hallux valgus deformity?
Today, many surgical modifications (more than 400) have been developed that are effective at any stage of the pathology. The doctor chooses the technique, taking into account the degree of deformation, the patient’s age, concomitant diseases, and the condition of the foot.
Experts divide operations into 3 large groups:
- only soft tissues are involved;
- bone structures are affected;
- combined operations
- Operations on soft tissues.
This type of surgery is indicated for stages 1 and 2 of the disease. The operations are based on restoring the balance of the antagonist muscles of the big toe. The techniques are minimally invasive and are performed without the use of foreign attachments.
- Operations on bone structures.
- chevron osteotomy with small displacements - a small V- or L-shaped fragment is excised from the bone of the first finger;
- Scarf osteotomy - a Z-shaped excision is made along the entire first metatarsal bone, then the necessary axis is restored with titanium clamps; Patients do not feel these screws in the future, so they are not removed, organically fitting into the bone structure
For more complex pathologies, the following can be used:
- arthrodesis - with excision of articular surfaces and fixation of a fixed joint in a functionally advantageous position, immobilization is practiced in cases of severe arthrosis;
- arthroplasty – the joint is replaced with an artificial implant.
- Combined operations
These operations combine different modifications and are prescribed taking into account the characteristics of the patient’s deformity and foot.
How is the operation to get rid of Hallux valgus performed?
The intervention takes place in an orthopedic center as planned. After consulting the patient with the doctor, confirming the diagnosis through examination and radiographs, the patient is given a date for intervention. During the conversation, the doctor must tell you about all medications used and allergic manifestations. Before surgery, you should avoid visiting baths and saunas.
The surgical plan is developed for a specific patient, taking into account the characteristics of his disease and his body. You should not operate on both legs at the same time. As a rule, local or regional anesthesia is used. After two punctures, the bone growth is removed. Bone filing is carried out using micro-mills under X-ray control. The gentle operation takes from 30 to 60 minutes, the risk of complications is minimized. After the operation, the wound is sutured and the recovery period begins.
Rehabilitation period
On the first day after surgery, strict bed rest is indicated. After a day, the patient can carefully stand on the operated leg. Modern methods of surgical intervention make it possible not to resort to crutches or plaster splints during the recovery period, but for several weeks it is necessary to bandage the lower leg and foot to prevent severe swelling.
After a week, the patient can move around fully. Stitches are usually removed after 10-14 days.
Orthopedists advise listening to the following recommendations during the rehabilitation period:
- it will be useful for the leg to be in an elevated position, so at rest you should use a bolster under it;
- Before removing the sutures, it is necessary to protect the wound from moisture, so when taking a shower or bath, isolate the postoperative wound;
- after surgery, you can relieve swelling with cold compresses;
- during the first month, you cannot step on your foot completely; when walking, you must transfer your weight to the heel;
- at first it is necessary to avoid overload, long walking, and heavy lifting;
- after 2 months it is possible to visit the pool and do water aerobics;
- in the first 2-3 months it is advisable to use orthopedic shoes, and then give preference to wide and comfortable shoes with flat soles,
- do not forget to use devices prescribed by your doctor, be sure to use them to fix your thumb in the correct position;
- Do regular foot exercises
Specialists from the European Center for Orthopedics and Pain Therapy will write out an individual set of rehabilitation exercises for the foot, teach self-massage of the foot and conduct the necessary course of physiotherapy for better rehabilitation.
Full recovery ends in approximately 6 months. During this time, you cannot engage in active sports, running or jumping.
Complications and contraindications
Contraindications to surgery are the same as for other surgical interventions. This:
- Obliterating atherosclerosis;
- Diabetic foot;
- Skin purulent diseases;
- Cachexia;
- Acute fever.
Complications depend on the chosen operation, the condition of the body, and concomitant diseases.
These include:
- blood clot formation;
- infectious complications;
- disturbance of innervation;
- allergy
In order to minimize the risk of complications, it is important to entrust the operation to a highly qualified specialist.
Getting rid of Hallux valgus and excellent treatment results
The postoperative result is:
- minimal incisions;
- excellent aesthetic appearance;
- minimal risk of complications;
- desired effect.
Gentle surgical techniques reliably and painlessly return people to a light gait and healthy feet.
Hallux valgus - treatment and surgery
Hallux valgus is a painful bump on the joint of the big toe, which not only deforms the foot, but also interferes with normal movement. Can it be cured? Hallux valgus is often passed down from generation to generation from grandmothers to mothers, and from mothers to daughters. This disease also occurs in men, but is very rare.
However, it would be wrong to see the reasons for the appearance of a “bone” on the side of the thumb only in heredity: hallux valgus
- a direct consequence of incorrect pronation and excessive mobility of the first metatarsal bone.
Adding to the problem are dress shoes, which women love so much. Narrow, cramped high-heeled pumps constantly deform the big toe area, causing irritation, abrasions and calluses.
Pronation is a natural phenomenon; it occurs whenever a person walks or runs. At this time, the feet lie on the surface in a certain way, distributing the load differently. Normally, this happens evenly, but with hypo- and hyperpronation, the feet fall on the outer or inner side.
When the metatarsal bone is overly mobile and pronation is impaired, a lot of pressure is placed on the metatarsophalangeal joint, the tendons of the big toe are stretched more to relieve the tension and keep the joint immobile.
As a result, the thumb bends, bending the joint outward, and its tip turns towards the little finger. The metatarsal bone also bends outward. Together with the phalanx, it forms an arched curvature - soft at first, but over time beginning to ossify.
hallux valgus develops
: It is better to start treatment while the “bone” is still soft - this makes it easier to return the feet to their normal state without fear of relapses.
How does hallux valgus manifest?
The affected foot looks specific:
- Its upper part is flattened
- The joint of the thumb has a bulge - exostosis, the skin on it is thickened and often swollen, reddish
- The tip of the finger “looks” at the little finger
The patients themselves complain first of periodic and then constant aching pain in the feet, which is stronger after a long walk and weakens after rest. Over time, night pain appears. The more significantly the head of the first metatarsal bone is displaced, the stronger the pain: it becomes sharp, burning.
There are three stages of the disease, which are determined by the angle between the first and second metatarsal bones and the angle of inclination of the big toe to the first metatarsal bone:
| Stages | Angle between I-II metatarsal bones, degrees. | Angle between the big toe and the first metatarsal bone, degrees. |
| I | <15 | <25 |
| II | <20 | >25 |
| III | >20 | >35 |
Hallux valgus: treatment
Before starting treatment, a physical and hardware examination is required. The physical part includes examining the sore feet, palpating, and recording the patient’s complaints.
X-rays, MRI and CT scans provide important information regarding the severity of arthrosis changes and the condition of the soft and bone tissues of the foot.
In the initial stages, conservative treatment is possible and desirable in young patients, and if the third degree of hallux valgus has developed, surgery is inevitable. Conservative therapy is also recommended in old age.
Conservative therapy . It gives a good effect when movement in the first metatarsophalangeal joint is not yet very limited. Treatment of hallux valgus is aimed at relieving pain and preventing further worsening of the pathology:
- The use of warming ointments with anesthetics
- Physiotherapeutic sessions - courses of ozokerite, paraffin, phono- and electrophoresis, UHF and magnetic therapy
- Wearing orthopedic shoes with special inserts that correct the position of the big toe
- Exercise therapy classes
For overweight patients, it is recommended to reduce it to reduce the load on the feet.
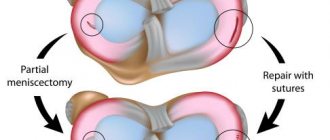
Surgery . It is effective at any of the stages that hallux valgus goes through: the operation can be performed only on the soft tissues of the foot, only on the bone (osteotomy) or in combination. The choice of treatment methods is based on the results of the examination and always takes into account the condition of the hallux valgus.
Surgery on soft tissues is recommended only at the very beginning of hallux valgus, when it is still possible to limit oneself to excision or relocation of the tendon of the adductor pollicis muscle to restore the uniformity of muscle tension. Sometimes, in addition to this, the exostosis and mucous bursa in the first metatarsophalangeal joint are removed.
Hallux valgus surgery is the only treatment measure in the second and third stages of the disease. Chevron and scarf osteotomies are performed in the traumatology or orthopedic department.
Chevron osteotomy - removal of part of the distal metatarsus. With scarf osteotomy, a zigzag cut is made of the first metatarsal bone, after which the fragments are connected and an angle is obtained between the bones. The operated area of the bone is fixed with titanium screws.
Hallux valgus: after surgery
There are a number of rules that will certainly have to be followed after hallux valgus has been removed: after surgery, patients are recommended to:
- Move in a special orthosis for at least six weeks
- The operated foot can be loaded immediately, but gentle loads must be chosen and alternated with rest
- When resting, keep your leg elevated - a low table or a small pad under the calf is good for this.
The stitches are removed after 10-12 days.
Hallux valgus: rehabilitation
The goal of the rehabilitation program is not only to restore the ability to walk normally, but also to prevent possible relapses, which often happen if you return to tight, high-heeled shoes.
It is important to spare the feet after hallux valgus surgery: rehabilitation lasts at least three months and, if all recommendations are followed conscientiously, ends with complete restoration of mobility of the joint of the first toe, improvement of motor functions, and disappearance of pain in the feet during and after walking.
Experts recommend:
- Wearing wide shoes with special insoles and liners
- Nightly contrast foot baths to restore normal blood circulation
- Performing exercises to improve the mobility of the foot joints (kinesitherapy)
- Foot massage
You can achieve complete recovery and insure yourself against the re-development of hallux valgus only through methodical exercises, revision of your “shoe” habits and careful treatment of your feet - measured loads, mandatory and sufficient rest after walking.
Preparing for surgery
If you decide to have surgery, then you need to undergo a full examination - blood and urine tests, a chest x-ray, and an ECG. Based on the results of these studies, the therapist will make a conclusion about the state of your health. Talk to your doctor about the medications you take regularly: some should be continued, while others should be stopped before surgery.
Special radiographs of the feet should be with you during the operation - this can help during the intervention.
Your home restoration
The success of your treatment largely depends on how closely you follow your doctor's instructions and recommendations in the first few weeks after surgery. You will meet with your doctor regularly to make sure your foot is healing properly.
Bandages: You will be discharged with bandages on your feet to keep your toes in the correct position. You will also have special post-operative shoes or a rigid splint to protect your foot. Sutures are usually removed 2 weeks after surgery, but the foot may require additional bandaging or rigid support for 6 to 8 weeks. To ensure successful healing, do not unbind or wet the bandages. This can lead to infection or return of the deformity. When you shower, it is advisable to cover the bandage with a plastic bag or cling film.
Weight-bearing: Your orthopedist may recommend using a walker or crutches for the first few days after surgery. Gradually, as the foot begins to heal, it will be possible to increase the load on it. Still, it is worth limiting walking in the first weeks after surgery.
Swelling and footwear after surgery: In the first days after surgery, try to keep your feet elevated as much as possible and apply ice to your feet to reduce swelling and inflammation.
Slight inflammation of the soft tissues of the foot in the first 6 weeks after surgery is normal. Once the cast and special shoes are removed, wear sneakers or soft leather boots for several months until the foot is completely healed. Do not wear high-heeled dress shoes for 6 months after surgery. Follow the tips for proper footwear above to help prevent the deformity from returning.
Operation
We perform almost all operations as a “one-day hospital” or even on an outpatient basis. This means that you enter the clinic a few hours before the operation, you are examined by a doctor again, medical documentation is filled out and you find yourself in the operating room.
Most operations are performed under general anesthesia: this means that the foot does not feel anything, and you are conscious and breathing on your own. General or spinal anesthesia is rarely used. A team of anesthesiologists is present nearby in case pain management needs to be adjusted.
After the operation, you will be taken to the ward. You will be discharged the same or the next day.