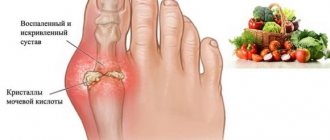
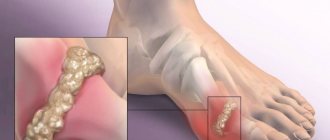
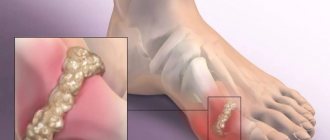
A type of inflammatory process in the joints is the presence of gouty arthritis. With this disease, uric acid accumulates in the joint structure. Under its influence, hyaline cartilage and periarticular tissues are destroyed. There is some order when pathological changes are sequential. First, the metabolism of uric acid is disrupted, its amount in the blood increases. Then crystals of this acid settle on the hyaline cartilage of the joint. After this, the joint structure is irritated and damaged, and an inflammatory process develops, that is, arthritis. Further, the consequences of such inflammation develop, and the periarticular tissue grows.
With gouty arthritis, the kidneys are affected, nephritis and urolithiasis develop. This is explained by the deposition of urate stones in the pelvis and ureters. Basically, this disease affects small joints (toes). In more rare cases, the ankle and knee joints, fingers, wrist and elbow joints are affected.
In most cases, the disease is observed in men whose age ranges from 30 to 55 years. However, gouty arthritis can appear before age 30. The inflammatory process continues over a long period of time, with constant relapses occurring. The appearance of true gout is observed in older people who confuse the disease with arthrosis.
Medical practice knows of cases where both small and large joints of the arms and legs are affected by a certain form of gouty arthritis. If the disease progresses slowly, only small joints are affected. The disease in rare cases is provoked by the presence of severe systemic reactions, although they are known in medical practice. It is necessary to take into account that with a long course of gouty arthritis, the function of the affected joints is impaired, as a result of which the patient may become disabled.
There are certain periods of development of the disease. During the latent period there are no clinical symptoms, so the presence of the disease can be determined based on elevated uric acid levels. During the acute recurrent period, the joints are severely affected, and the appearance of severe gouty attacks is noted. The chronic period of gouty arthritis is characterized by long periods of remission. Attacks can appear once every 10-20 days or every few months.
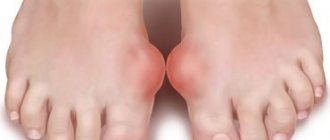
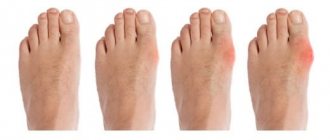
Gouty arthritis has a fairly typical clinical picture, so it is possible to detect the disease in a person in a timely manner. The first manifestations are pain in the joint of the big toe, reddened skin over the inflamed joint. In addition, the person responds that the pain intensifies during movement, and the body temperature rises to 39 degrees.
Some manifestations of gouty arthritis need to be considered in more detail. The thumb is primarily affected. In the absence of adequate therapeutic and diagnostic measures, the disease will necessarily begin to progress. As a result of this, the inflammatory process will affect small joints.
High activity of gouty arthritis causes redness of the skin over the affected joint. An addition is the general temperature reaction. If the inflammatory process continues for a long time, tophi will begin to form. These are subcutaneous nodules around the joint. Tophi consist of elements of articular tissue and uric acid. There is a gradual destruction of the articular cartilage, and cavities form in the bone adjacent to the joint. Such cavities are filled with monosodium urate crystals. In addition, uric acid is deposited in the tissue that surrounds the affected joint and under the skin above it. Such deposits are whitish dense nodules. As a result of the appearance of such nodular deposits and bone growths, the appearance of the leg changes greatly. If a person does not seek qualified treatment during this period, he may become completely disabled and lose the ability to care for himself.
Why is gout dangerous?
Without adequate treatment, gout progresses rapidly, especially in mature and elderly patients. Without appropriate therapy, serious complications are possible.
Major complications
Gouty arthritis Uric acid, in the form of crystals (tophi) is deposited in all parts of the body. When such deposits become lodged in joints or periarticular tissues, severe inflammation occurs. This leads to severe pain and fever
Urolithiasis Crystals that occur with gout often form in the kidneys. They become the main cause of kidney failure and ultimately lead to the death of the patient.
With gout, kidney stones can form at all stages of the disease, excluding the first
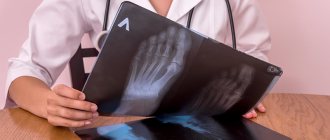
Where to get an x-ray
When prescribing a referral for an X-ray examination to a patient with suspected gouty arthritis of the joint, the doctor will immediately inform him where exactly this diagnosis can be carried out. As a rule, x-rays are taken in the same clinic where the appointment took place. Such diagnostics are carried out by public and private medical institutions that have the necessary equipment.
The cost of an x-ray of a joint for gout depends on where exactly the diagnosis is carried out. Usually the price of the procedure is in the range of 800-2500 rubles.
Related Articles
X-ray for arthritis: radiological signs of arthritis and principles of treatment
Berries for gout: which ones are useful, which ones are prohibited, how to eat them
Gout of the elbow joint: symptoms and clinical picture, diagnosis and treatment methods
Ayurveda for arthritis: clinical picture and types of disease, treatment features
Gout of the ankle joint: how does gouty arthritis manifest and how to treat it?
Gout in women: clinical features, symptoms and diagnosis, treatment and prognosis
Stages of the disease
Asymptomatic hyperuricemia As the name suggests, it occurs without symptoms. But at this time, uric acid accumulates in the body. This period ends with the first attacks of gout.
Acute gouty arthritis First attack of gout. It occurs due to a sharp jump in the level of uric acid in the patient’s body. As a rule, exacerbation occurs at night. The attack worsens over the course of a day and only goes away after a few days.
Intercritical period This is the time period between exacerbations of gouty arthritis. There is usually no pain during this period, but the joint continues to deteriorate. This period is considered the most suitable for effective treatment of gout.
Chronic gouty deposits in the joints Appear when there is a high level of uric acid in the blood, which persists for several years. At this time, gout attacks become stronger, and the intervals between them become shorter.
The progression of the disease leads to the fact that people eventually cannot move without the help of crutches or a wheelchair
What does an x-ray show for gout?
The manifestations of such arthritis are clearly visible on x-rays. On x-rays, the specialist recognizes places where there is an accumulation of salt crystals. Therefore, when symptoms of this disease appear, the doctor first of all sends the patient to undergo such an examination. It makes it clear whether signs of gout are really present, and not of another joint pathology.
The main essence of the diagnostic procedure is the absorption of rays by the tissues of the affected area. This area is subsequently projected on film or a computer monitor. The information received is processed by the doctor. Based on the conclusions made, he can judge the patient’s current condition and select the optimal treatment for him.
X-rays help determine the extent of destruction of bone structures due to gout.
X-ray signs of gout
X-rays help to accurately determine the type of disease; this type of diagnosis is one of the most accurate
The swelling of soft tissues characteristic of the disease helps identify arthritis in the early stages of development. The development of bone inflammation cannot be ruled out. Due to the active course of the disease, bone destruction occurs. Destructive processes can occur both inside and outside the joint.
X-ray manifestations of joint disease are primarily observed at the edges of bone structures. They take on the appearance of a kind of shell or shell. There is a whole classification of stages according to the signs of gout, which can be seen on x-rays:
- First stage. Cysts and accumulations of urates form in the affected area. Soft tissue compaction is observed.
- Second stage. Large cysts characteristic of the pathology form in the joint area. Erosive processes also begin on the surface of the joint.
- Third stage. Tissues are subject to severe erosion. It can occupy about a third of the entire joint. As a result, partial destruction of the bone occurs and salt crystals are deposited in the empty cavities.
X-ray changes are usually observed during the 1st and 2nd stages of gouty arthritis. They are formed over 9 years. After about 10-15 years, irreversible destruction occurs in the joint area. If the patient begins to properly treat his disease in a timely manner, he will be able to avoid negative consequences and serious complications that can even lead to disability.
Timely recognition of the pathological process in the joint helps to quickly defeat the disease and prevent its transition to a chronic form.
Having learned your diagnosis, it is strictly forbidden to try to cope with it using alternative medicine methods. Gout requires well-chosen drug treatment.
Treatment methods for gout
Doctors at the DaliMed clinic have developed unique methods to relieve patients from this serious illness. An acute gouty attack resolves within three visits. After this, the main treatment occurs.
After completing the full course and restoring normal uric acid levels, the patient can even allow himself to deviate somewhat from the prescribed diet.
A course of treatment
Diet for the period of treatment: Avoid consumption of fatty animal products, offal (canned food, sausages), carbonated drinks, and alcohol.
It is necessary to consume enough water and plant products.
Drug therapy for gout is aimed at reducing the level of uric acid in the patient’s body, stopping the acute inflammatory process and relieving pain.
Treatment methods are selected individually
- Innovative drugs aimed at reducing uric acid in the patient's blood.
- Medicines developed in Europe that promote the resorption of crystals in the body (tophi).
- Specialized medications that relieve inflammation and restore tissue.
- Laser therapy.
- Ozone therapy.
- Reflexology.
- Physical activity prescribed by the doctor.
Gout
Gout is a disease of the joints caused by the deposition of uric acid salts in them. The patient experiences attacks of intense joint pain, the joints become swollen, the skin over them turns red, most often the big toe.
English synonyms
Gout, Podagra.
Symptoms
Symptoms of gout appear suddenly, often at night.
- Severe joint pain. Typically first in the big toes, but sometimes in the feet, ankles, knees, arms, wrists. The most intense pain persists during the first 12-24 hours from the onset of the attack.
- Prolonged aching pain in the joints. After severe pain passes, some discomfort remains in the joints - from several days to several weeks. Over time, pain attacks become more intense and last longer as more and more joints are affected.
- Inflammation and redness of the joints. The affected joints swell, turn red, and become very sensitive.
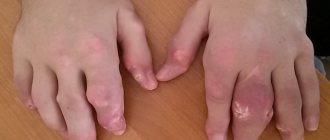
- Lumps under the skin (tophi). With a long course of gout, tubercles may form under the skin, most often in the area of the fingers and toes, on the elbows, knees, and the skin of the ears.
general information
Gout occurs when the level of uric acid in the blood rises. Uric acid salts begin to settle in the joints and surrounding tissues, causing inflammation and severe pain. The concentration of uric acid in the blood may increase as a result of impaired excretion from the body, as well as increased formation, which is associated with excessive consumption of purines.
Purines are substances from which uric acid is formed. Some foods contain purines and, accordingly, increase the amount of uric acid in the body:
- alcohol (especially beer, wine),
- honey, coffee, strong tea, chocolate, cocoa,
- cheeses,
- broths (meat, chicken, fish),
- raw smoked products,
- by-products from internal organs (heart, kidneys, liver, brain, tongue),
- fish, canned meat,
- legumes (peas, beans, eggplants, beans, nuts, seeds, soybeans),
- sorrel, spinach,
- cauliflower,
- mushrooms, mushroom broths,
- raspberries, figs
Since uric acid is excreted in the urine through the kidneys, in case of kidney disease the process of its excretion may be impaired, which predisposes to gout.
For some people, gout flares up frequently, while for others it only flares up a few times a year. Taking medications will help prevent recurrence of gout attacks.
With gout, nodules (tophi) consisting of deposits of uric acid salts sometimes appear under the skin on the fingers, arms, legs, and elbows. They usually do not cause pain, but during gout attacks they become very tender and swollen.
Crystals of uric acid salts can deposit in the urinary tract of people with gout, forming stones. In such cases, medications help reduce the risk of kidney stones.
Who is at risk?
The risk group includes people with high levels of uric acid in the body.
Uric acid levels increase:
- regular consumption of alcohol (especially beer),
- chronic diseases (diabetes, hyperlipidemia, atherosclerosis),
- high blood pressure,
- taking certain medications, such as those used to treat hypertension, heart failure, or prescribed after organ transplantation,
- hereditary predisposition,
- age and gender - gout is more common in men, since their normal uric acid levels are higher than in women (however, after menopause, women's uric acid levels increase; in both women and men, gout most often develops at the age of 40- 50 years.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of gout is most often made taking into account the characteristic symptoms and history of the disease.
Laboratory diagnostics
- Serum uric acid. Elevated levels of uric acid are an argument in favor of the diagnosis of gout. However, not all people who have elevated uric acid levels suffer from gout. At the same time, in a small number of patients with severe manifestations of this disease, the level of uric acid in the blood may be within normal limits.
- During the acute period of the disease, the level of uric acid in the serum is not so important, since uric acid is released into the tissues and its concentration in the blood may decrease.
- Complete blood count (without leukocyte count and ESR) (CBC). During an acute attack of gout, your white blood cell count may rise moderately and your erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) may increase significantly.
Other studies
- Study of synovial (joint) fluid. The detection of uric acid crystals in it is specific for gout.
- X-rays of joints and bones for gout are of auxiliary value. In the later stages of the disease, large tubercles may be visible on bone radiographs - signs of deposition of uric acid salts in them.
Treatment
Treatment for gout usually involves taking medications.
Depending on the characteristics of the patient’s body, the doctor determines the most suitable medications for him. There are medications to treat acute attacks, to prevent recurrent attacks, and to reduce the risk of complications from gout.
In addition to taking medications, you can relieve a gout attack by:
- drinking large amounts of water during an attack (2-4 liters per day),
- complete rest (it is recommended to place the affected limb higher, for example, place a pillow under the foot),
- a diet primarily consisting of liquid foods (milk, milk soups, lactic acid products, jelly, compote, vegetable and fruit juices, liquid porridges).
During an attack, it is necessary to avoid alcohol and foods that increase the level of uric acid in the blood.
Prevention
- Drinking enough fluid (2-4 liters per day).
- Quitting alcohol. Alcoholic drinks, especially beer, increase uric acid levels in the blood.
- Healthy eating. It is necessary to consume more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, low-fat or low-fat dairy products. You should limit your consumption of meat, poultry, and fish.
- Maintaining normal weight. If you are overweight, gradual, smooth weight loss through exercise and a healthy diet is recommended.
Recommended tests
- Serum uric acid
- Clinical blood test (with leukocyte formula)
Advice from a doctor
- Do not put stress on the sore joint. It is necessary to periodically fix it in an elevated position and apply ice for 15-30 minutes 2-3 times a day until the pain subsides.
- Eliminate aspirin. It can cause spikes in uric acid levels in the blood and worsen attacks.
- Regularly measure your uric acid level - it should not exceed 60 mg/l.
- Do exercises. Dedicate at least half an hour to physical education every day.
- Drink at least two liters of clean water per day.
- Get a blood test to determine your levels of essential minerals and vitamins.
- If necessary, supplement your diet with a good vitamin and mineral complex . It is especially important for gout patients to provide themselves with vitamin C.
- Avoid carbonated drinks and juice powders containing fructose.
- Avoid alcohol.
- Review your diet in favor of vegetables, fruits and cereals.
- Consume no more than 120 grams of animal protein per day , avoid offal and fatty sausages.
After our course of treatment, the pain will go away, your former mobility will return, and if you follow the doctor’s recommendations, you can forget about gout forever.
Why does the disease appear?
If we talk about the etiology of the disease, it has not been fully studied. However, there are major risk factors. These include:
- The presence of a hereditary predisposition.
- A person does not adhere to proper nutrition, excessively abuses meat, sausage, coffee, and alcoholic beverages.
- Concomitant diseases are present. Such diseases include heart failure, hemoblastosis, kidney disease, and hormonal abnormalities.
- If a person is using certain medications that lower blood pressure. Also, such medications include diuretics, cytostatics, etc.
Gouty arthritis can be primary or secondary. The development of primary gout occurs due to the combination of genetic predisposition and high consumption of purines with those foods that were listed earlier. The development of secondary gout is associated with the presence of the above diseases and the use of medications.
Microcrystals of sodium urate accumulate in the joints slowly, and there are no symptoms for a long time. The disease manifests itself after being provoked by a certain factor (physical fatigue, injury, infection, stress, after hypothermia, fasting, consumption of harmful foods along with alcoholic beverages).
Diet for gout
Considering that gouty arthritis is a consequence of not following the correct diet, a complete cure for the disease will not occur unless you strictly follow the necessary dietary recommendations. Therefore, gout often has a progressive nature. A person with such a diagnosis must conscientiously approach such a therapeutic measure as a diet.
The most important principle is to avoid foods that contain large amounts of purine. The breakdown of such substances provokes a powerful release of uric acid. At the same time, it does not have time to be eliminated from the body. The patient is allowed to eat wheat and rye bread, borscht, okroshka, milk noodles, boiled beef, chicken, turkey, low-fat fish, eggs, cottage cheese, and milk. And also potatoes, beets, carrots, tomatoes, cucumbers, pumpkins, cabbage, berries, jam, nuts, weak tea, vegetable and fruit juices, vegetable and butter.
It is not recommended for consumption of meat, fish, mushroom rich broth, pork, lamb, sausage, fatty fish, canned food, pickles, spicy foods. In addition, dietary nutrition should exclude the consumption of porcini mushrooms, champignons, baked goods, herbs, raspberries, chocolate, strong coffee, alcohol, pepper, mustard, feta cheese, and seafood.
A patient with gouty arthritis must remember that an excess of certain foods is not allowed. If a situation arises where prohibited food is eaten, it is necessary to immediately take the appropriate medication. The effect of such a drug is aimed at removing or binding metabolic products of uric acid.
At the end of a year of treatment, if the person feels satisfactorily, there are no relapses, the strict dietary restriction is lifted. After which, the person can choose whether to adhere to a dietary diet, while the dosage of the drug taken is reduced or it is completely canceled, or continue to take medications and allow the intake of prohibited foods.