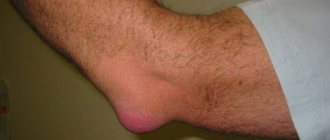
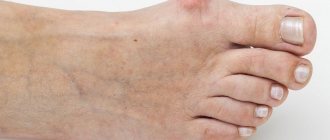
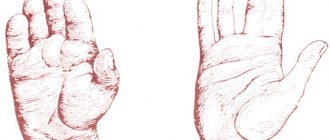
Arthritis is an inflammatory disease of the joints. With arthritis, a person experiences pain during active movements, flexion and extension, as well as when walking if the joints of the legs are inflamed. Sometimes the skin over the sore joint begins to turn red, and a local increase in temperature or general fever is observed.
Clinical picture
The disease is caused by metabolic disorders inside the joint, which results in an increase in the synovial membrane, leading to tissue proliferation and destruction of cartilage. Excess fluid in the joint leads to inflammation and pain and fever.
Signs of arthritis can appear gradually, starting with just a slight swelling and discomfort in the crook of the joint or phalanges of the fingers, followed by severe pain and other symptoms.
Kinds
Arthritis is divided according to localization:
- monoarthritis - arthritis of one joint;
- oligoarthritis (two or three affected areas);
- polyarthritis - arthritis of more than 3 joints.
Based on the nature of the changes that occur, arthritis is divided into:
- inflammatory, which is characterized by the presence of inflammation,
- degenerative, when first there is a malnutrition of the cartilage, dystrophy, a change in the appearance of the affected joint, followed by its deformation.
Arthritis can be acute or chronic:
- Acute arthritis develops rapidly, accompanied by severe pain and inflammation in the tissues, which disappear after 2-3 days.
- Chronic arthritis progresses gradually, slowly becoming a serious disease.
Due to the origin of the disease:
- Infectious or purulent arthritis. Manifests itself under the influence of a certain infection.
- Rheumatoid arthritis. It is formed due to the predominance of infectious and allergic diseases. This type is more dangerous than the first, as it often develops into chronic inflammation. If rheumatoid arthritis is left untreated, the patient may experience difficulty walking.
- Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. This type predominantly occurs in children under 16 years of age. Unfortunately, the etiology of the disease is unknown to date, but has serious consequences: difficulty walking and disability in children.
- Reactive. Reactive arthritis manifests itself mainly due to changes in immunity in people who have a hereditary disposition to insufficient utilization of antigen complexes. Reactive arthritis sometimes occurs as a consequence of many infections. Most often it is a consequence of previous enterocolitis.
- Gouty arthritis. Usually one joint is affected, an attack of pain usually develops at night or in the early morning hours, if left untreated, attacks are repeated more often and last longer, and the level of uric acid in the blood is elevated.
- Osteoarthritis. Joints fail within a few years. A characteristic symptom is a crunching sound in the fingers or toes. It is dangerous because it can hit the spine. They may begin to swell and hurt.
- Traumatic. It appears in the presence of open and closed joint injuries and in the case of regularly occurring minor injuries.
- Rheumatism is a chronic connective tissue disease primarily affecting the heart and joints. Its etiology is also unclear, as are the causes of the development of rheumatoid arthritis;
- Arthrosis is a form of arthritis that affects only the joints and periarticular tissues, without affecting other organs.
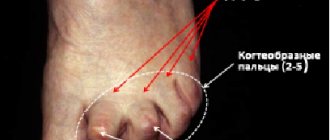
Inflammation of the joints on the toes in children
Features of thumb arthritis in children are as follows:
- more often rheumatoid and reactive variant;
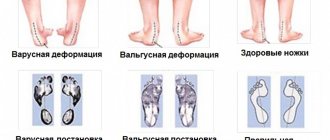
- the cause of 60% is flatfoot placement;
- pronounced clinical symptoms from the first days (imperfect immunity and rapid generalization);
- favorable outcome in 70% (which is significantly higher than in adults).
The pathology can manifest itself in children, but most often has a favorable outcome.
Correction using orthopedic shoes, insoles, prostheses (special for the first toe).
Causes
The clear and exact cause of arthritis has not yet been determined, but doctors have identified some factors that can trigger the development of arthritis. Let's look at them:
- infections caused by bacteria, fungi, viruses;
- allergies;
- metabolic disease;
- injury;
- lack of vitamins (vitaminosis);
- insufficient intake of nutrients into the body
- diseases of the nervous system;
- disturbances in the functioning of the immune system;
- excessive stress on joints;
- poor nutrition, incl. consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- overweight;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine gland;
- genetic predisposition;
- insect bites, such as wasps, bees, etc.;
- hypothermia (hypothermia);
- some diseases: tuberculosis, brucellosis, gout, dysentery, gonorrhea.
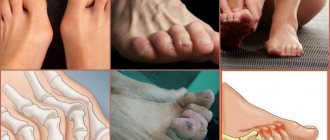
Arthritis symptoms
The leading symptom of arthritis is pain in one or more joints. At first they are weak and have practically no effect on a person’s ordinary life. Over time, the pain syndrome increases: the pain becomes wave-like, intensifying with movement, at night and closer to the morning. The intensity of pain varies from mild to very strong, severely complicating any movement.
Secondary symptoms:
- morning stiffness,
- swelling,
- skin redness,
- increase in local temperature in the area of inflammation,
- deterioration of the patient's motor activity,
- restriction of his mobility,
- formation of persistent joint deformities.
It is important to remember that the first signs of arthritis are pain. At the initial stages they are weakly expressed, in the acute period they are especially pronounced, and in chronic arthritis they can change (weakly expressed to strongly expressed and vice versa). As mentioned above, signs may vary for different types of disease.
| Types of Arthritis | Symptoms |
| Reactive |
|
| Rheumatoid |
|
| Infectious | Characterized by:
The type of infection can be determined using tests. |
| Gout attack |
|
| Psoriatic | Distinctive features of psoriatic arthritis are the following:
|
| Osteoarthritis |
|
| Traumatic arthritis |
|
Risk factors
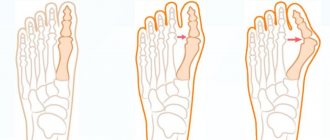
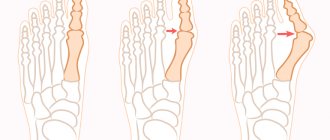
Despite its clear localization (joints only), arthrosis of the big toe is a multi-cause disease. The manifestation of its symptoms is preceded by a number of reasons. Among them:
- hereditary predisposition;
- domestic and professional injuries (arthrosis of the thumb is a characteristic disease of football players and ballet dancers);
- narrow and uncomfortable shoes;
- excess weight with regular loads on the legs;
- severe hypothermia;
- congenital and acquired leg deformities (flat feet, developmental pathologies);
- problems with the endocrine system, hormonal imbalances and changes (thyroid disease, diabetes, menopause, steroid use, etc.);
- long-term loads on the foot area (with low physical activity);
- age-related changes.
If you notice that you have two or more risk factors for the development of arthrosis of the big toe, you should think about undergoing preventive examinations. We have extensive experience in identifying arthrosis at the earliest stages and treating all stages.
Degrees of the disease
The symptoms of arthritis differ in stages by the manifestations of pain and the aggravation of pathological processes. So, if the disease develops into a complicated form, then the symptoms will be more noticeable. Let's look at all four stages of arthritis:
1st degree
The disease does not manifest itself clinically, but X-rays of the joints show the first signs of inflammation. Sometimes there is a slight stiffness of movement and periodic pain during physical activity.
2nd degree arthritis
The progressive inflammatory process leads to thinning of the tissues of the articular structures and erosion of the heads of the bones. Swelling appears in the area of the affected joints; A local increase in temperature and redness of the skin are often observed, movements are accompanied by crunching.
3rd degree
The third degree of the disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- X-ray examination shows severe deformity;
- Often a person at this stage is assigned a disability;
- Mobility is limited, it is difficult for the patient to move if the lower part of the body is damaged;
- Hand movements are performed with great difficulty. It becomes difficult for the patient to perform even basic self-care actions. The hands are affected symmetrically;
- Pain haunts a person even when he is at rest;
- Due to muscle spasm caused by pain, the limbs are fixed in the wrong position. This ultimately leads to even greater deformation of the joints.
Arthritis 4 degrees
Leads to almost complete immobility of damaged joints, with severe round-the-clock pain. It is impossible to move independently. Negative changes in the bones are already becoming irreversible. When the knees are affected, muscle contractures form.
When are antibiotics needed?
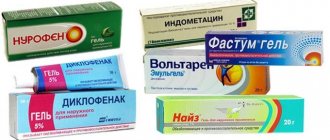
It is worth remembering that only a doctor can prescribe the correct treatment for your arthritis. Antibiotics are indicated in the presence of extensive inflammatory processes, purulent arthritis, and also if the pathology was provoked by infectious diseases.
Antibacterial drugs of many groups are used:
- macrolides;
- penicillins;
- 2nd and 3rd generation cephalosporins.
The course of treatment ranges from 7 to 14 days. Antibiotics can be administered intramuscularly and orally.
Complications
Ignoring the symptoms of arthritis can lead to serious complications that provoke other diseases:
- Diseases of internal organs.
- Heart failure.
- Damage to soft tissues.
- Tendon ruptures.
- Dislocation of the spine.
- Numbness of arms and legs.
Although arthritis is a common condition that most people experience, its treatment should be taken seriously. Timely diagnosis and treatment will help maintain flexibility and mobility of the joints, which will make it possible to lead an active lifestyle even in old age.
Diagnosis of arthritis includes:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- Analysis of urine;
- X-rays can determine the condition of the bones and identify changes caused by arthritis;
- computed tomography to assess the condition of soft tissues;
- magnetic resonance imaging helps to more clearly examine the condition of bone structures, as well as soft tissues;
- isotope scanning of the skeleton;
- Ultrasound helps determine the extent of damage to large joints;
- analysis of synovial fluid helps to identify features of infectious arthritis of inflammatory agents and choose an adequate method of treatment;
- arthroscopy is an endoscopic method that involves inserting a special sensor into the joint cavity to study their condition;
- arthrography determines the condition of the cartilage and soft tissues that surround the joint;
- myelography evaluates the condition of the spinal cord, spine and its roots, and is used in conjunction with a computed tomograph.
Arthritis treatment
The sooner you worry about treatment, the greater the benefit will be. The first stages of arthritis already affect the joints, and with proper treatment it is quite possible to slow down the process. Special exercise therapy exercises have been developed and are prescribed during the period of improvement so that the muscles develop flexibility. Effective medications are also prescribed.
Treatment for arthritis depends on the stage and form of the disease. Therefore, at the first signs, be sure to contact a specialist and do not self-medicate.
How to treat arthritis without drugs?
Reducing stress on diseased joints:
- selection of orthopedic shoes with comfortable soles;
- weight loss;
- use of knee pads, instep supports, canes when walking;
- a complex of therapeutic and health-improving physical education, which can be performed in different starting positions and in water.
Gymnastics should not cause discomfort or pain. Squats and exercises with bent knees should be avoided. A visit to the pool is recommended.
Physiotherapeutic procedures:
- heat treatment;
- magnetic therapy for joints;
- ultrasound;
- massage;
- hydrotherapy;
- acupuncture;
- laser therapy;
- electrical pulse stimulation of muscles.
To prescribe any physiotherapeutic procedures, the patient must have no contraindications. The patient must forever get rid of bad habits and drinking coffee in large quantities.
Diet
The goal of therapeutic nutrition for arthritis is to normalize the immune response, reduce inflammatory reactions and restore full range of motion of the affected joint.
Nutrition for arthritis is selected by your doctor and depends on:
- forms of the disease;
- degree of joint damage;
- concomitant diseases;
- severity of clinical manifestations.
Regardless of the type of arthritis, general nutritional rules for recovery have been developed:
- food should be low-calorie, the diet is aimed at not gaining excess weight, which puts stress on the joints - it is necessary to remove extra pounds;
- it is necessary to balance the supply of all necessary components;
- Food should be steamed; it can be boiled or stewed, but not fried;
- to restore the damaged structure of the joint, it is recommended to eat food from boiled bones (jellied meat), which you can eat as much as you like, they contain natural chondroprotectors that restore cartilage tissue, but such dishes cannot be consumed if you have gout;
- You can’t eat fatty meat – fats can only be of plant origin;
- freshly squeezed juices from fruits, beets and carrots help enrich the body with vitamins, remove toxins and waste from it;
- You should give up alcohol, strong coffee and tea, limit the use of pickles, seasonings and hot spices, except ginger and turmeric.
In general, nutrition for arthritis corresponds to the standard diet (general version) or treatment tables according to Pevzner No. 15, 10, 6, which are prescribed for different types of arthritis. The energy value of the diet is 2170-2400 kilocalories per day, and the nutrient content corresponds to the following scheme:
- proteins - 85-90g, of which 45-50g are animal proteins;
- fats – 70-80g, of which 25-30g are vegetable fats;
- carbohydrates - 300-330g, of which no more than 30-40g complex sugars.
If you are overweight, a hypocaloric diet is indicated, the energy value of which is 1340-1550 kilocalories per day.
Diet
The patient should adhere to the correct principles of nutrition. The diet should contain:
- eggs (no more than 1 per day);
- lean meats – 250-300 g per day;
- fish of fatty and lean varieties - herring, mackerel, hake, salmon, crucian carp, notothenia;
- cereals;
- potato;
- jelly, jellied fish;
- pasta from durum wheat;
- vegetables;
- fruits.
It is worth excluding fatty, smoked and fried foods from your diet as much as possible. It is preferable to steam, boil and stew food.
All foods rich in chemicals and preservatives should be avoided. The list of prohibitions includes alcohol, canned food, chocolate, high-fat dairy products, flour and bakery products.
Folk remedies
Before using traditional methods for arthritis, be sure to consult with your doctor.
- Birch leaves (2.5 teaspoons), stinging nettle leaves (2.5 teaspoons), tricolor violet grass (2.5 teaspoons). Take the infusion 1/2 cup 4 times a day before meals.
- Lubricate the knee with honey, apply mustard plaster and tie it. Hold until a burning sensation appears, then remove the mustard plaster, and wrap the knee with honey, as with a compress, and keep it overnight.
- Mash the ranunculus flowers and apply to the knee for 2 hours, then remove and wrap the sore spot overnight.
- Grate the radish or horseradish on a fine grater. Apply the paste or the juice itself to the painful area. Leave for 40 minutes. The course for arthritis is 10 procedures every other day.
- If salts are deposited in the joint, cut the onion head in half. Pour one drop of tar into the middle of each half and apply to the sore spot.
- Beat the yolk with apple cider vinegar. Apply the application until dry. Use several times a week for a month.
- Garden purslane for arthritis. Grind the grass. Mix with cold water, in a ratio of one spoon per glass of liquid. Place on the fire and boil for ten minutes. Cover the container with a towel and place in a warm place for two hours. Then strain. Take the finished infusion three times a day, one tablespoon.
Prevention
People who are at risk due to their professional activities should take care of the prevention of joints. And also for patients:
- with heredity to arthritis;
- those who have had viral diseases;
You can reduce the risk of developing pathology if you adhere to several rules. The attending physician is obliged to talk about preventive measures, especially for elderly people. Prevention of joint arthritis includes:
- weight control;
- avoiding injuries while walking and playing sports;
- protecting joints from excessive stress.
If you feel pain returning or notice redness or swelling, consult your doctor. Timely seeking medical help will prevent severe joint destruction.
Diagnosis and treatment of toe diseases at the MART clinic
If you suspect that your finger joints have undergone deformation changes due to illness or injury, you should contact an orthopedic traumatologist. For purulent infections, ingrown toenails, cuts and burns, you must make an appointment with a surgeon.
Depending on the nature of the damage, pain in the toes may require joint diagnostics (X-ray, MRI, CT), general blood test, urine test, and skin scraping.
Based on the results of the study, the doctor will prescribe a course of treatment for you, based on the characteristics of your body, its sensitivity to a particular method, as well as your wishes.
At the MART medical center, physiotherapeutic procedures, prescription of medications, and, if necessary, surgical intervention are used to treat diseases of the toes.
If you have any questions, ask our specialist! Ask a Question