Shortening of the thumbs is the result of a genetic disease, namely brachydactyly. The length of the hand or foot becomes shorter, as abnormal processes lead to shortening of certain phalanges on the fingers of the upper and lower extremities.
The disease occurs equally in boys and girls. The first signs can already be detected by ultrasound examination during pregnancy. In most cases, the pathology is not life-threatening. People with this disease feel external discomfort, so they turn to a surgeon for surgery to eliminate the problems.
What is brachydactyly
Brachydactyly is an inherited disorder. Congenital anatomical changes are passed on to children from parents with a mutation gene. The pathology is characterized by external changes in the development of the fingers of the upper and lower extremities.
The big toes and fingers become shortened or do not fully develop. Congenital anomalies occur equally on all limbs, regardless of gender.
Brachydactyly is a common pathology that does not require serious therapy. But most patients feel discomfort and become the subject of ridicule from others. Therefore, they go to the hospital to see a surgeon to eliminate the defect. It is surgical intervention that allows you to restore the size of your fingers.
Parents whose family has already had similar congenital pathologies are advised to carefully plan their pregnancy and undergo a full medical examination before conception.
In some cases, brachydactyly occurs with other genetic abnormalities. Then the decision to terminate the pregnancy is made by the parents, taking into account the seriousness of the situation.
Physiological nature of the disease
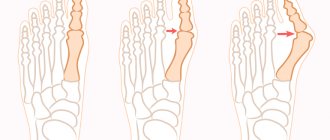
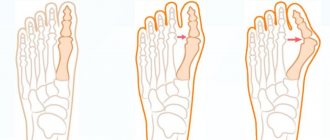
Clinodactyly affects the little fingers, but in medical practice there are known cases of changes in other fingers. The upper limbs are more susceptible to modification than the toes.
The disease affects both hands symmetrically. With clinodactyly of the fifth finger, the axis of the little finger is shifted laterally at the level of the middle phalanx relative to the hands.
The photo confirms the fact that the disease is difficult to identify in the children's age category, because the process of curvature of the fingers is quite long in time, so it is difficult to examine an already existing deformity. Only at the age of 18–20 years does the disease stop progressing.
It is possible to diagnose the presence of deviations in the development of the osteoarticular apparatus only through x-ray examination
It is important to differentiate this disease from a disease caused by another pathology
Clinodactyly does not cause pain. Treatment is carried out only in case of obvious discomfort and daily difficulties encountered by the patient. A person, for example, cannot write or hold certain objects firmly enough in his hands.
It is necessary to consider what stages of development of the disease there are:
- The angle of lateral deflection of the finger is no more than 10 degrees.
- There is a slight shortening of the little finger.
- The finger is severely deformed. The tilt angle is 20 degrees.
Causes
Brachydactyly of the thumb belongs to the category of hereditary pathologies. Medical research can help identify genetic changes. In making an accurate diagnosis, a special gene that children receive from their mother or father is important. This is the main reason for the appearance of pathology in a child. A mutational gene controls the development of arms and legs.
The following are the main reasons that provoke the development of a genetic disease:
| Name | Description |
| Hereditary factor | A person inherits certain genes that can cause serious congenital anomalies. They are passed on from their parents and are called dominant. It is not always possible to detect the disease at an early stage of development. The risk of short-fingered children increases if the mutation gene is passed on from two parents at once. Therefore, experts recommend undergoing preventive tests and seeing a doctor before conceiving a baby. This applies not only to those who are carriers, but also to people whose family had patients diagnosed with thumb brachydactyly. |
| Wrong life of a mother while carrying a baby. | We are talking about the abuse of alcohol, cigarettes and narcotic substances. A healthy lifestyle reduces the likelihood of developing defects. It is important to be constantly monitored by an obstetrician-gynecologist in order to promptly identify pathological changes. Correctly selected medical care will help mitigate the progression of genetic abnormalities. |
A self-developing form of the disease is rare. More often, patients are diagnosed with brachydactyly along with concomitant severe genetic abnormalities (Down syndrome, Baymond syndrome).
Prevention
In most cases, pathology does not require careful diagnosis. The anomaly is visible immediately after birth and is determined by a pediatrician. Because the condition can cause significant limitations and discomfort in a person's daily life, a doctor should always be consulted if a child develops a serious disability. This way you can avoid additional complications and difficulties in adult life.
If serious mental dysfunction or inferiority complex occurs, you should consult a doctor to avoid depression.
There is one way to prevent this deformity in a medical sense. Poor nutrition, nicotine and alcohol during pregnancy and an overall unhealthy lifestyle can contribute to the development of defects in the child. Drugs and prescription medications make the situation worse.
There are no direct methods to prevent the disease
If a child develops additional symptoms or concomitant pathologies, it is important to contact a doctor. Timely treatment of developmental abnormalities can mitigate the course of the disease in adulthood
Advice! It is not recommended to treat the disease at home. Correction of defects and doing exercises must be done under the strict supervision of a doctor.
Incorrect therapy at an early age can worsen the course of the disease. Any symptoms or abnormalities that occur in a child should consult a doctor. Timely treatment helps reduce symptoms and prepare the child's joints.
Classification: types and types
Brachydactyly is a hereditary disease in which the fingers are shortened due to incomplete development of the phalanges. The pathology is transmitted at the genetic level, it is difficult to prevent it, but you can reduce the likelihood of occurrence or soften the course in a child after he is born.
In medicine, the following types of thumb brachydactyly are distinguished:
| Name | Description |
| Type A | The disease affects the development of the middle phalanges, disrupts the formation of the nail, and leads to curvature of the fingers. |
| Type B | The phalanges on the fingers and toes are underdeveloped, the 2nd and 3rd fingers are fused. Pathological changes also affected the teeth, skull and vertebral bones. |
| Type C | There is inadequate development of the metacarpal bones and middle phalanges on the fingers. In children, brachydactyly type C slows mental development and growth. |
| Type D | An underdeveloped distal phalanx leads to shortening of the big fingers and toes. In medical language, this phenomenon is called brachymegalodactyly. |
| Type E | The pathology is characterized by incomplete development of the metatarsal and metacarpal bones. |
Doctors more often diagnose thumb brachydactyly types A and D in patients. The most severe form of the pathology is type B, and E is rare.
Taking into account also the localization of pathological processes in type A disease, the following subtypes are distinguished:
| Name | Description |
| A1 | The middle phalanges of the fingers are shortened, and sometimes they merge with the terminal areas. This type of disease is characterized by short and wide hands. Growth also slows down. |
| A2 | The 2 fingers and toes become shortened, deformed, acquire a triangular shape and deviate from their axis. |
| A3 | Dramatic changes affect the little finger and its middle phalanx. The finger becomes shortened and curved. |
| A4 | Congenital changes affect the 2nd and 5th fingers. They may be absent on the legs, which causes a person to have club feet. There are also situations when the nail plate is not developed or is completely absent. |
| A5 | A rare type of disease in which all fingers lack the middle phalanx except the thumb. Nail dysplasia is present. |
| A6 | The hands and feet are short because the middle phalanges are completely absent. |
The disease can be diagnosed during pregnancy, using the first screening (11-12 weeks). On the second ultrasound examination, you can also notice genetic changes in the baby (20-22 weeks). Diagnostics and treatment are carried out by a pediatric orthopedist and geneticist.
Postoperative period
The recovery period after surgery can last from 2 to 6 months. A set of rehabilitation measures, individually designed for each patient, can significantly reduce this period and completely restore the function of the limb.
After the sutures are removed, rehabilitation measures begin, the goal of which is to restore full finger movements.
Physiotherapeutic treatment includes:
- massage of the operated limb;
- electrophoresis;
- ultraphonophoresis;
- thermal applications with ozokerite, paraffin;
- acupuncture;
- mud applications.
Patients are recommended to attend physical therapy classes. Following the recommendations of specialists, it is advisable to continue to perform exercises and develop the limb at home.
Types of hand exercises that can be performed after eliminating syndactyly:
careful flexion and extension of each phalanx; rotation of the operated fingers; grip training (sequential connection of the thumb with other fingers); folding small objects (puzzles, beads, coins, buttons); rolling a rolling pin on the table; modeling from plasticine, salt dough; rolling the ball in the palms.
How long does it take for a toe to grow together? The wound healing process lasts up to 3-4 months. The postoperative stage of treatment for complete restoration of function is no less important than the operation itself. In the postoperative period, the limb is fixed and its movement is limited. A plaster cast (splint) is used to fix and restrict movement. During this period, in order to avoid a possible relapse and to speed up the healing of the sutures, it is necessary to wear special spacers for 4-6 weeks to prevent the fingers from touching.
To speed up wound healing, various antibacterial drugs are used - Dermazin, Contractubex. In adults and children, the sutures will heal within five to seven weeks, which will allow the start of physiotherapeutic procedures aimed at developing the fingers - massage, ultraphonophoresis, the use of paraffin, therapeutic mud. These procedures can be combined
After the operation, the child will require special care and attention from the parents: with good care, the baby’s condition will quickly improve, the likelihood of an unfavorable outcome in this case is low
Symptoms
Brachydactyly of the thumb often appears and develops independently.
But sometimes it occurs together with other genetic syndromes and anatomical changes in the human body:
Thumb brachydactyly
deforms the ribs, skull and chest;- the neck shortens;
- frontal sinuses are underdeveloped;
- growth slows down;
- disturbances in support function and movements are observed;
- the patient quickly gets tired mentally;
- some patients have no phalanges or fingers at all (adactyly);
- nails are deformed;
- recurrent hypothyroidism develops.
The nail phalanges are underdeveloped or completely absent.
Brachydactyly occurs in isolation, but as already mentioned, other genetic anomalies develop along with it:
| Name | Description |
| Down syndrome | The disease is characterized by a short neck, symptoms of cataracts, and strabismus. Dental problems and congenital changes in the functioning of the cardiovascular system appear. The chest is also deformed. |
| Baymond syndrome | Vision problems and cerebellar ataxia appear. |
| Frontonasal dysplasia | A serious disease in which problems arise not only in the functioning of the thyroid gland. The patient has a severe deformation of the skull, and there are also signs of mental retardation. |
| Aarsky-Scott syndrome | The pathology provokes problems with joints and mental abilities, and human growth slows down. |
| Poland syndrome | Associated genetic disorders are deformation of the ribs, lack of muscle tissue in the chest area, and the development of syndactyly. |
There are also certain clinical signs that occur with any type of thumb brachydactyly:
- fingers split or flatten;
- joint mobility is impaired;
- some fingers grow together (syndactyly);
- muscle weakness;
- more fingers and toes grow (polydactyly);
- The extreme phalanges and the nail plate do not fully develop.
The absence of phalanges is called adactyly in medicine. Their incomplete development is ectrodactyly. An orthopedist will help establish an accurate diagnosis by prescribing special examinations for the patient. Muscle weakness and joint stiffness impair the functioning of the feet and hands.
Complications and consequences
Thumb brachydactyly does not cause dangerous health problems, but it can disturb a person, disturbing his psychological balance. Frequent depression appears, against the background of which an inferiority complex is developed.
Serious lesions and concomitant genetic diseases provoke more severe complications in the form of growth retardation. Some fingers also fuse together, causing a decrease in functional ability. The patient has difficulty moving or picking up objects. The same thing happens when the bones in the foot and hand are bent or deviated. Muscles weaken and joint mobility deteriorates.
The genetic disease is accompanied by abnormal changes, against the background of which the activity of many internal organs is disrupted, defects or defects occur (fingers are missing). In boys, this is a problem with the development of the penis, which leads to a decrease in male self-esteem.
Disorders and psychological trauma cannot be hidden from others in everyday life. A man’s sex life is limited, which provokes serious mental problems.
Character of a person based on the ring finger
The ring finger is the finger of Apollo (and in astrology is associated with the Sun), which reveals our inner interests.
Strong and even: Emotionally balanced. Smooth, with straight joints: Creativity. Long: Self-confident, hungry for fame, wanting to be the center of attention - a good sign for those pursuing a career in show business or advertising. Very long: Introvert. Short (E): Shy, poor control of emotions. The third phalanx is the longest: Speaks of the desire for money and luxury. Inclined towards the second finger: Worry-ridden, always on the defensive. Second and third fingers lean towards each other (F): Secretive.
The phalanx of the nail bends towards the second finger. Heart problems - emotional or physical. Leans towards the palm when the hand is relaxed: Difficulty with intuitive aspects. Twisted or crooked, or out of proportion to the overall arm: Emotional difficulties.
This finger is often called the art finger. The Finger of the Sun provides invaluable information if you are looking for a person who is able to enjoy beauty. The long finger of the Sun reveals a character with artistic and creative inclinations; but if the finger is too long, the person's enthusiasm may spread to gambling. This is a businessman - both in business and in love. When this finger is too short, a person may lack artistic sense.
Diagnostics
Laboratory tests, which are carried out while the baby is still in the womb, help the doctor establish an accurate diagnosis. Additional tests are prescribed by an obstetrician-gynecologist. When the baby is born, an orthopedist is involved in diagnosis and treatment.
| Name | Description |
| Initial examination |
|
| Instrumental diagnostic methods |
|
| Genetic tests |
|
The most informative and definitive analysis that helps establish a correct and accurate diagnosis is a DNA test. The expectant mother should know that brachydactyly is not a reason to terminate the pregnancy. The situation is aggravated if concomitant genetic diseases are discovered along with short-fingeredness.
Diagnostic methods
The disease can be detected even in
intrauterine period using ultrasound, which is performed in the sixth month of pregnancy of a woman. During the procedure, the doctor may notice a developmental deviation, this is especially true when using a 3D volumetric study. No special preparation is required for the procedure at this stage of pregnancy. When brachydactyly is detected in an isolated form, the woman decides whether to have an induced abortion or not.
When the disease is accompanied by the development of chromosomal syndromes, the doctor often prescribes termination of pregnancy. In some cases, genetic counseling may be required.
After the birth of a child, a diagnosis is made after examining him and carrying out certain diagnostic measures:
- Radiography and rheovasography;
- MRI;
- Electromyography and stabilography;
- Podographies;
- Genealogical analysis and DNA diagnostics.
Which doctor should I contact?
An orthopedist or surgeon can help diagnose hereditary pathology. In 90% of cases, specialists prescribe surgical treatment to patients to correct external defects.
Before the operation, a complete diagnosis is carried out; the doctor needs to know the severity of the disease. Successful surgery will completely restore impaired finger function.
Genetic consultation is recommended for women in the following situations:
- The father or mother of the unborn baby was previously diagnosed with thumb brachydactyly.
- The expectant mother and father already have a child with a similar genetic disease.
- There are close or distant relatives in the family who have been diagnosed with thumb brachydactyly.
The same applies to women or men who decide to marry a person whose relatives have such a disease. Married couples in such a situation are advised to adopt children to completely avoid thumb brachydactyly.
Consanguineous marriages increase the likelihood of genetic inheritance of the disease, the probability approaches 100%.
Finger plastic surgery in Israel: how an accurate diagnosis is carried out in 3 days
Day one – consultation with a doctor
On the first day, the doctor examines the patient’s hands, collects anamnesis, and refers him for diagnostic procedures.
Day two – examination
- X-ray in several projections.
- CT and MRI.
- Ultrasonography of the hand.
- Dopplerography of hand vessels.
- Arthroscopy.
- Electromyography.
Day three – diagnosis
Having received the examination results, doctors make an accurate diagnosis and develop a plan for surgical intervention and subsequent rehabilitation.
Treatment
Various methods and means are used to combat brachydactyly. Medicines improve the functioning of the musculo-ligamentous system. Physiotherapeutic procedures help restore the mobile functions of the legs and arms. The same goes for massage and therapeutic exercises.
Brachydactyly is not treated with the help of traditional recipes from healers and healers; changes in the thumb are not observed. All patients are prescribed surgical intervention, especially if functional impairment is present.
Some patients experience psychological disorders due to genetic pathology. It is difficult for a person to perceive his external changes. He develops an inferiority complex, as a result of which it is more difficult for him to communicate with people around him.
Brachydactyly surgery
Modern medicine offers patients with genetic abnormalities exclusively surgical treatment. The doctor can completely replace or lengthen underdeveloped phalanges on the fingers. After surgery, patients are advised to engage in physical therapy. Gymnastics and exercises will help the patient relearn how to control his arms and legs.
Surgical treatment is indicated for patients under the following circumstances:
- serious external discomfort;
- impaired functioning of arms and legs;
- finger fusion;
- the hands and feet are short.
To eliminate defects and restore functions, the following types of surgical intervention are performed:
| Name | Description |
| Pollization | The surgeon moves 1 of the fingers to the place of the thumb. |
| Distraction | During medical procedures, the doctor stretches bone tissue that has not fully developed. |
| Autotransplantation | Fingers are being transplanted. |
| Plastic surgery (syndactyly) | The operation allows you to separate adjacent elements of bones, skin, tendons or muscles. |
Surgery is performed if the child is 3 years old. The method of surgical treatment is selected by an orthopedist. The specialist takes into account the degree of development of pathological processes and the state of the skeletal system of the child’s body.
The main purpose of the operation is the correction of the fingers and toes (lengthening the shortened parts, restoring functions, as well as correcting external defects on the hands and feet).
Microsurgical operations are most often used. In some situations, a special Ilizarov apparatus is used. It helps to lengthen deformed phalanges and also restore the normal length of the lower and upper limbs.
Frequency of occurrence
Brachydactyly accounts for almost a quarter of the total among all hereditary diseases of the hands and feet. Its occurrence in the population is approximately one and a half cases per 100 thousand population. This anomaly occurs with equal frequency in both boys and girls.
According to statistics, approximately fifteen out of one million people suffer from brachydactyly.
Forecast
Brachydactyly of the thumb disrupts a person’s life, limiting his numerous opportunities and abilities. But the situation can be corrected if there are no associated genetic abnormalities. Surgical intervention gives a person a favorable prognosis for the future. Surgical treatment will help get rid of external defects and restore the functions of the legs and arms.
It is important to remember about disease prevention, especially for women who are planning a pregnancy. It is necessary to undergo a full examination before conceiving a child, since brachydactyly is transmitted with parental genes.
It is impossible to prevent the development of thumb brachydactyly, but it is possible to influence the clinical processes of congenital pathology. During pregnancy planning, it is important for parents to know all the consequences and possible problems, especially if the family has relatives with this disease. Together with a geneticist, you can determine the likelihood of congenital abnormalities in your baby.
Article design: Vladimir the Great