Since the inflammatory process does not spread to the tissues of the joint, the range of motion in it is maintained. The main signs that indicate periarthritis are aching knee pain and muscle tension. Symptoms of knee periarthritis usually occur when walking, running, or carrying heavy objects. This disease can easily be confused with arthritis, and only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis. If left untreated, the inflammatory process progresses, swelling, swelling, redness and increased temperature in the knee joint, and rapid fatigue of the knee.
Like glenohumeral periarthritis, this disease usually occurs with regular overload of periarticular tissues (muscles, tendons) and multiple microtraumas. However, other reasons are also possible - hypothermia, metabolic disorders in the body, endocrine diseases. Periarthritis can also occur as a result of the spread of the inflammatory process during arthrosis, arthritis of the knee joint. In each case, the disease requires individual complex treatment. The methods of oriental medicine used in the ITVM clinic can effectively eliminate the inflammatory process and cure periarthritis of the knee joint at the cause level.
Causes of periarthritis:
- hypothermia of the body;
- age (over 60 years);
- prolonged exposure to dampness;
- complications after infections;
- concomitant chronic diseases (arthrosis, spondylosis);
- congenital pathologies of the musculoskeletal system.
Endocrine disorders and vascular diseases also lead to the development of periarthritis.
In turn, the cause of post-traumatic periarthritis, which leads to inflammation, is microscopic injuries to tendons and muscles (professional sports, heavy physical labor).
Diagnostic measures
The first step in diagnosing the disease is inspection and palpation of the lesion. Patients experience pain when pressing on the inflamed joint. To confirm the diagnosis of hip periarthrosis, a number of additional measures are taken:
To confirm the diagnosis, the patient undergoes an ultrasound of the joint.
- X-ray examination - gives a visual picture of the disease;
- ultrasound diagnostics shows the exact condition of the joint and bursa;
- magnetic resonance and computed tomography - double-check the correctness of the anamnesis;
- laboratory and biochemical studies - reveal the process of inflammation and the presence of inflammatory markers in the blood.
The main symptoms of periarthritis are:
- aching pain (usually increases with movement);
- muscle tension;
- swelling in the area of the affected joint;
- limitation of mobility.
Upon palpation, the specialist identifies lumps and nodules, pressing on which causes very painful sensations.
Types of periarthritis
Periarthritis can be primary or secondary (develop against the background of another pathology), and also occur in acute or chronic form. Absolutely all joints are susceptible to this disease. Depending on the affected joint, there are:
- humeroscapular periartitis;
- scapular periarthritis;
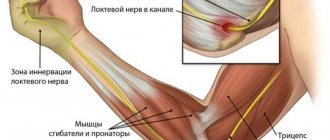
- periarthritis of the elbow joint and fingers;
- periarthritis of the knee joint;
- periarthritis of the foot;
- periarthritis of the crow's foot bursa;
- periarthritis of the ankle joint;
- periarthritis of the hip joint.
An important goal of the upcoming therapy is to limit the motor functions of the affected joint. Moreover, if the doctor diagnosed “periarthritis of the knee” or “periarthritis of the hip joint”. The same applies to damage to the upper extremities, for example, the elbow joint. In this case, periarthritis leads to degenerative damage to the extensor tendons of the hand and fingers.
People whose work involves heavy load on the joint, which leads to repeated microscopic injuries, are susceptible to pathology.
Periarthritis of the fingers, which leads to inflammation of the interphalangeal joints, in turn, makes itself felt:
- swelling in the area of the fingers;
- redness of the periarticular tissues;
- painful sensations;
- limitation of mobility.
And glenohumeral periarthritis, which is caused by cervical osteochondrosis and injuries to the shoulder joint, is manifested not only by aching pain, but also by impaired coordination of movements.
How to treat hip periarthrosis?
Before treating hip periarthrosis, it is necessary to carefully conduct a differential diagnosis and identify the potential cause of damage to the ligaments and tendons of the joint. After this, procedures are prescribed that will enhance blood flow and tissue regeneration naturally. In our manual therapy clinic, therapeutic massage, acupuncture, and special gymnastics are most often used. In some cases, osteopathy is indicated to restore the normal position of the bones that make up the hip joint.
In traditional medicine, mainly symptomatic means of influence are used. These are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, biological reparants (Actovegin, Solcoseryl), drugs that promote the resorption of scar tissue. By reducing the physiological blood supply to damaged tissues, all these drugs have little effectiveness. When using them, manual intervention is desirable in order to improve the trophism of tendons and ligaments.
Treatment methods for periarthritis
Regardless of the type of periarthritis, treatment should be comprehensive. And the most effective treatment for this pathology is physiotherapeutic procedures, including laser and shock wave therapy, as well as therapeutic exercises and massage.
For periarthritis of the fingers, treatment may also include paraffin or ozokerite applications, as well as warm compresses.
When diagnosed with periarthritis of the knee, it is important not only to immobilize the limb, but also to properly select drug therapy, which includes taking non-steroidal drugs to prevent the development of the inflammatory process and eliminate pain.
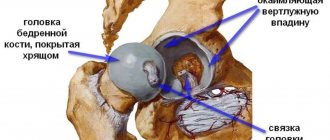
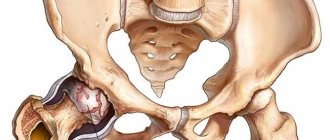
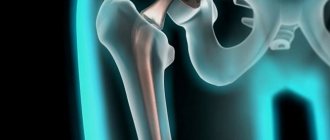
Joint structure and periarticular tissues
To better understand the nature of periarthritis, let us remember the structure of the joint. The rounded, thickened ends of the tubular bones are articulated using articular surfaces - convex and concave (articular head and fossa). On these surfaces there is articular cartilage, which is necessary for their shock absorption. Periarthritis does not affect them; its “specialization” is periarticular tissues:
- The joint capsule is a shell of connective tissue that is a sealed cavity in which the joint is located. It is attached to the surface of the joint and adjacent bones. The inner membrane of the capsule produces synovial fluid - a lubricant that prevents friction and wear of bone joints. Inflammation of this part of the joint is called capsulitis;
- ligaments are short and elastic connective tissue parts of the joint, attached to the bones, fixing the joint capsule. They stretch when flexed and then help the joints return to their physiological position; prevent excessive joint mobility and dislocation. The inflammatory process in ligaments is ligamentitis;
- tendons are structural units of muscles necessary for attaching them to bones. Like ligaments, they fix the joint, but most importantly, they are responsible for its movement: during muscle contractions, they tense, stretch, and bend towards the working muscle. Low elasticity and stretchability make tendons easily damaged by sudden muscle jerks or overloads. Inflammation of the tendons is referred to as tendinitis.
- bursae, or synovial bursae, are small cavities formed by synovial tissue and filled with gel-like synovial fluid, located near the joints, but not connected to the joint capsule; serve to protect the joint and cushion it when it bends. There are about 160 of them in the human body. Bursitis is inflammation of the bursae;
- periarticular muscles. Their inflammation is called fasciitis. Inflammatory, destructive, degenerative processes and pathological changes in the listed structures are called periarthritis.
Why does the disease occur?
When it comes to periarthritis, the disease does not relate to pathological processes of an infectious nature and is not transmitted from person to person. The hip joint is constantly exposed to a number of unfavorable factors: microscopic injuries to soft tissues and joint capsules.
Often the hip joint is subjected to significant physical stress. Exposure leads to the development of degenerative and inflammatory processes in the tissues of the joint and adjacent tissues. The main pathogenetic mechanism is joined by aseptic inflammation of surrounding tissues, which is reactive in nature. Taking into account the peculiarities of the pathogenetic mechanisms, the disease was named periarthrosis.
The human body has colossal recovery reserves and is able to withstand intense stress. Since the joints of the lower extremities, including the hip, are subjected to significant daily physical stress, the regenerative potential of the articular tissues is gradually depleted, and degenerative processes develop.
Characteristics
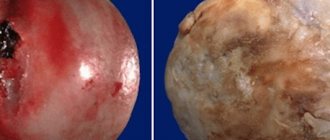
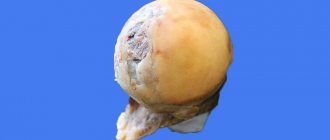
Periarthritis is characterized by the formation of an inflammatory and dystrophic process in the periarticular bursa and soft tissues. The frequency of diagnosis of “periarthritis” is about 30% of all cases of patients visiting traumatologists and orthopedists.
This type of pathological changes can be divided into 2 types:
- inflammatory type of periarthritis, which is characterized by the formation of a local reaction in the hip joint;
- dystrophic type of periarthritis (characterized by the predominance of processes of destruction of the hip joint).
Read also
Joint pain
The joint may simply be painful (arthralgia) or may also be inflamed (arthritis).
Arthritis usually causes warmth, swelling and rarely redness of the overlying skin. Pain may occur during movement and... Read more
Arm and neck pain
A man's neck hurt. He walks, periodically independently twists it from side to side, kneads it with one hand, then with the other... Brings his neck to the extreme degree of tilt to the left... then to the right... slowly... and...
More details
Chest pain
The first thing a patient thinks about when he feels chest pain is a heart attack. Of course, chest pain is not something that can be ignored. But you need to understand that chest pain is not...
More details
Shoulder pain
There are two main causes of shoulder problems. One is associated with overexertion as a result of prolonged repetition of the same type of movements, and the other is associated with aging. However, having identified segmental changes...
More details
Pain on the inside of the knee and sphenoid neuralgia
Clinical manifestation of pain on the inside of the knee and sphenoid neuralgia Sphenoid neuralgia is usually observed when the nerve passes through Gunter's canal, or what...
More details
Diagnostics
Before making a diagnosis, the doctor must conduct the necessary research. Often the disease is discovered by chance during a medical examination or during a medical examination, since the pathological process does not cause severe pain.
Before prescribing examinations, the doctor examines the patient, collects anamnesis and complaints.
When palpating the soft tissues in the area of the hip joint, nodules (foci of calcification) are identified that hurt when pressed.
Laboratory diagnostics
Includes:
- blood for biochemistry, CBC (in pathology, pronounced leukocytosis and an increase in ESR are observed);
- Analysis of urine;
- if necessary, joint puncture and examination of the obtained material in the laboratory.
Instrumental diagnostics
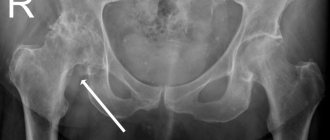
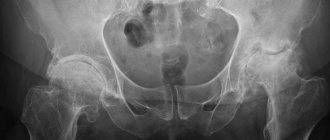
One of the reliable examination methods is radiography. The image shows salt deposition and the growth of osteophytes.
Additionally, the doctor may prescribe an ultrasound and MRI to determine the cause of the disease and treatment tactics.
If concomitant ailments are detected, consultation with specialists is necessary.
Therapy for periarthritis of the joint is long-term and includes several techniques.
- A gentle regime for a diseased joint. You cannot give the joint a full load during the treatment process and for some time after it, as this can lead to a relapse of the disease. In advanced situations, the doctor may prescribe wearing an orthosis or plaster cast.
- Symptomatic therapy:
- Taking anti-inflammatory drugs for a long time. The course and dosage are selected individually and taking into account concomitant chronic diseases. The drugs are available in several forms; the patient can determine the most convenient method of treatment for himself.
- In case of severe pain, lidocaine blockades with hormones are applied to the joint or periarticular tissue. The procedure is performed in a small operating room once every two weeks.
- Physiotherapy. It includes: hydrogen sulfide baths (balneotherapy), UVT, laser, magnet, paraffin baths, mud therapy.
- Massage sessions.
- Exercise therapy. Classes are conducted after inflammation and acute pain have subsided. All movements must be smooth. If you experience discomfort, you should stop training until the pain is eliminated. Therapeutic exercise is performed daily, if possible twice a day, gradually increasing the number of approaches and repetitions. Classes for older people should be conducted in the presence of an instructor or relative.
Read also: Deformity of the knee joint treatment
Approximate course of exercises:
- in a supine position, lifting the lower limbs up and bending them at the knees;
- roll over onto your right side. The lower leg is straightened, the upper leg rises and falls. Repeat for the other side;
- lying on your back, imitate riding a bicycle;
- in the same position, alternately pull the legs bent at the knee joints to the stomach;
- standing at a support, do shallow squats;
- bending back and forth, circular movements of the body;
- swing the lower limbs to the sides;
- sit on a high chair and bend and straighten your knees.
In cases where periarthritis occurs against the background of rheumatic diseases, cytostatics (methotrexate, etc.) can be prescribed.
If periarthritis is accompanied by an infectious process, it should be treated with antibiotics.
Indications for surgical intervention are the absence of positive dynamics from conservative therapy and persistence of pain.
ethnoscience
Methods of non-traditional exposure are suitable for persons with hypersensitivity to pharmaceutical drugs.
It is impossible to completely cure periarthritis of the joint with the exclusive use of traditional medicine methods. They are of an auxiliary nature, helping to alleviate the patient’s condition and cope with unpleasant sensations before going to the doctor.
- Drink tinctures of yarrow, rose hips and lingonberries throughout the day instead of tea.
- Mix chamomile flowers, mint and burdock root, chop and add hot water. Leave for 1 hour and rub the product on the affected joint.
- Mash fresh burdock leaves and heat. Apply to the hip joint at night, change the bandage every two days.
- Pour calendula flowers with alcohol or vodka and keep in a dark place for at least 14 days, shaking occasionally. Use the mixture to rub the affected area.
- Finely chop the horseradish root and place it on a bandage. Apply to the sore joint at night as a compress.
- St. John's wort in the amount of 1 tbsp. pour boiling water, leave for 30 minutes and take a teaspoon 4 times a day.
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, conservative methods give positive dynamics after 14 days of therapy. During this time, the pain goes away, and the joint affected by periarthritis returns to its usual range of motion.
In advanced cases, the patient is offered to regularly engage in exercise therapy and undergo a course of treatment in sanatoriums or health centers.