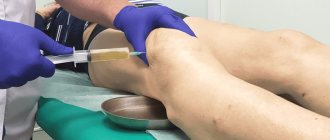
What drugs are injected into the joint?
Depending on the desired effect, on the stage of gonarthrosis or coxarthrosis, on the diagnosis, drugs with the following effect are prescribed:
- local anesthetics – pain relief for a short time (combined with other drugs);
- glucocorticoids – anti-inflammatory effect lasts from a week to a month;
- chondroprotectors – stimulation of cartilage tissue restoration;
- synovial fluid prostheses – restoration of joint fluid and joint functions;
- platelet-rich plasma – stimulation of joint self-healing.
The injection drug is selected by the doctor depending on the goals and clinical picture.
In what cases are hormones prescribed?
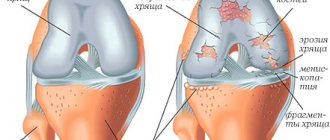
In the later stages of arthrosis of the hip joint or any other, when pain almost always bothers the patient and painkillers do not help, a stronger remedy may be prescribed. This is an emergency treatment measure that can quickly relieve pain and improve well-being. Unfortunately, this coin also has a downside, especially if you resort to this method more often than necessary.
Kenalog, diprospan and other corticosteroid drugs quickly stop inflammation, eliminate edema and swelling. However, they do not cure arthrosis at all, do not restore nutrition to the cartilage and do not improve the condition of the joint. This is only an ambulance - a powerful blow to the body, especially if you resort to such treatment for osteoarthritis too often.
No organism can withstand frequent injections of hormonal drugs.
What rules should you follow if you have been prescribed hormone injections into a joint?
If you cannot do without hormone injections, remember this:
- Keep a break of at least 2 weeks between injections. The drug does not start working instantly, so you need to wait a while for the doctor to evaluate its effectiveness.
- Remember that the first injection is the most effective. If there is no relief after the first injection, avoid repeated injections in the same place. It would be more correct to change the injection site or choose a different drug.
- You should not give hormone injections to one knee more than 4-5 times, as the risk of complications increases. Each time, the likelihood of needle injury, infection, or ligament damage increases.
Hormone injections are a last resort for arthrosis
In the video you will see how a synovial fluid prosthesis is injected into the knee joint in a medical office:
Hydrocortisone ointment for external use approx 1% 10 g x1
Trade name: Hydrocortisone International name: Hydrocortisone Pharmacological group: glucocorticosteroid, glucocorticosteroid for local use Pharmacological group according to ATC: D07AA02. Hydrocortisone, H02AB09. Hydrocortisone, S01BA02. Hydrocortisone Pharmacological action: glucocorticosteroid, local glucocorticosteroid, immunosuppressive, mineralocorticoid, antiallergic, anti-inflammatory, local anti-inflammatory Pharmacodynamics: GCS has anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic effects. Inhibits the release of cytokines (interleukins and interferon) from lymphocytes and macrophages, inhibits the release of inflammatory mediators by eosinophils, reduces the metabolism of arachidonic acid and the synthesis of Pg. By stimulating steroid receptors, it induces the formation of lipocortin. Reduces inflammatory cell infiltrates, reduces the migration of leukocytes and lymphocytes to the area of inflammation. When prescribed in recommended doses, it does not cause suppression of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system.
Pharmacokinetics: After application, it accumulates in the epidermis (mainly in the granular layer). Metabolized directly in the epidermis, and subsequently in the liver. Excreted by the kidneys and bile.
Indications for use: Eczema, dermatitis (allergic and simple), atopic dermatitis, diffuse neurodermatitis, erythroderma, psoriasis, prurigo, lichen planus, anogenital itching, insect bites, photodermatoses.
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity, post-vaccination period, bacterial, viral and fungal skin diseases (pyoderma, mycosis), skin tuberculosis, violation of the integrity of the skin (ulcers, wounds), syphilitic skin lesions, skin tumors, rosacea, acne vulgaris, perioral dermatitis, childhood (up to 2 years, with itching in the anus - up to 12 years).
With caution: diabetes mellitus, tuberculosis (systemic damage) Pregnancy (1st trimester), lactation period.
Dosage regimen: Locally. Apply a thin layer of ointment to the affected skin surface no more than 3-4 times a day. The course of treatment is 1-3 weeks. The dose of the drug used for 1 week should not exceed 30-60 g. If itching in the anus, before applying the drug, wash the affected area with warm water and soap, then with water and dry the skin surface with a towel or napkin. For weeping skin diseases and lesions of the scalp, lotion and emulsion are used for external use.
Side effects: Skin irritation, with prolonged use (especially with occlusive dressings and/or application to large surfaces) - systemic side effects.
Special instructions: Avoid contact of the ointment with the eyes. For children under 12 years of age, the drug is prescribed only under strict medical supervision. If after 7 days of use there is no improvement or worsening of the condition, as well as if symptoms recur a few days after discontinuation, use of the drug should be discontinued and consult a doctor. The drug should not be used without consulting a doctor in cases where itching in the genital area in women is accompanied by vaginal discharge. For long-term treatment and/or application to large surfaces, it is recommended to prescribe a diet with limited Na+ and a high K+ content, and introduce a sufficient amount of protein into the body. It is necessary to monitor blood pressure, the concentration of glucose and cortisol in the blood, blood clotting, diuresis, and the patient’s body weight.
Update date 10/22/2010
Manufacturer: Nizhpharm OJSC, Russia Registration certificate holder: Nizhpharm OJSC, Russia Forms of release: ointment for external use 1% (aluminum tubes) 10 g, ointment for external use 1% (two-layer plastic bags, three-layer plastic bags) 150 kg Ingredients: hydrocortisone acetate 1 g - 100 g Dispensed without a doctor's prescription Minimum pharmacy range Preferential dispensing DLO Expiration date: 3 years Registration data: R No. 001130/01 dated 05/10/2007, 05/26/2006 Status of the registration certificate: valid HS codes: 3004 32 100 9
Is there an alternative?
Hormone injections reduce pain due to arthrosis of the ankle, knee, and hip, but also have a negative effect on the body. They are especially dangerous in case of diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension, stomach ulcers, and also if the patient’s kidney function is impaired. In addition, corticosteroids only temporarily relieve pain, which means that a person will need a larger dose each time.
Instead of harmful corticosteroids, which also do not cure, you can choose other therapeutic methods:
- injections of chondroprotectors, which are aimed at restoring damaged cartilage tissue and normalizing metabolism in the joint (the course ranges from 3 to 15 injections);
- injection of a synovial fluid prosthesis, such as Noltrex, which expands the damaged cartilage surfaces, mixes with the joint fluid and returns the joint to normal functioning.
The course of injections of synovial fluid prosthesis is 2-5 procedures. After this, you can forget about arthrosis for 1-1.5 years. The drug based on hyaluronic acid or synthetic Noltrex is safe for the gastrointestinal tract and other body systems and will not harm diabetics or people with high blood pressure.
If you are experiencing severe joint pain, do not rush to relieve it with hormones. Consider a future-proof treatment option instead of drugging your body with corticosteroids for a long time.
Hydrocortisone, 1%, ointment, 10 g, 1 pc.
From the endocrine system: decreased glucose tolerance, steroid diabetes mellitus or manifestation of latent diabetes mellitus, suppression of adrenal function, Itsenko-Cushing syndrome (including moon face, pituitary type obesity, hirsutism, increased blood pressure, dysmenorrhea, amenorrhea, myasthenia gravis , striae), delayed sexual development in children.
Metabolism: increased excretion of calcium ions, hypocalcemia, increased body weight, negative nitrogen balance (increased protein breakdown), increased sweating, fluid and sodium ion retention (peripheral edema), hypernatremia, hypokalemic syndrome (including hypokalemia, arrhythmia, myalgia or muscle spasm, unusual weakness and fatigue).
From the central nervous system: delirium, disorientation, euphoria, hallucinations, manic-depressive psychosis, depression, paranoia, increased intracranial pressure, nervousness or anxiety, insomnia, dizziness, vertigo, pseudotumor of the cerebellum, headache, convulsions.
From the cardiovascular system: arrhythmias, bradycardia (up to cardiac arrest); development (in predisposed patients) or increased severity of chronic heart failure, ECG changes characteristic of hypokalemia, increased blood pressure, hypercoagulation, thrombosis. In patients with acute and subacute myocardial infarction - the spread of necrosis, slowing down the formation of scar tissue, which can lead to rupture of the heart muscle; with intracranial administration - nosebleeds.
From the digestive system: nausea, vomiting, pancreatitis, steroid ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, erosive esophagitis, bleeding and perforation of the gastrointestinal tract, increased or decreased appetite, flatulence, hiccups; rarely - increased activity of liver transaminases and alkaline phosphatase.
From the senses: sudden loss of vision (with parenteral administration in the head, neck, nasal turbinates, scalp, deposition of drug crystals in the vessels of the eye is possible), posterior subcapsular cataract, increased intraocular pressure with possible damage to the optic nerve, tendency to develop secondary bacterial , fungal or viral eye infections, trophic changes in the cornea, exophthalmos.
From the musculoskeletal system: slower growth and ossification processes in children (premature closure of the epiphyseal growth plates), osteoporosis (very rarely - pathological bone fractures, aseptic necrosis of the head of the humerus and femur), rupture of muscle tendons, steroid myopathy, decreased muscle mass (atrophy); with intra-articular administration - increased pain in the joint.
Dermatological reactions: delayed wound healing, petechiae, ecchymosis, skin thinning, hyper- or hypopigmentation, steroid acne, stretch marks, tendency to develop pyoderma and candidiasis.
Allergic reactions: generalized (including skin rash, skin itching, anaphylactic shock), local allergic reactions.
Effects due to immunosuppressive effects: development or exacerbation of infections (the appearance of this side effect is facilitated by jointly used immunosuppressants and vaccination).
Local reactions: with parenteral administration - burning, numbness, pain, paresthesia and infection at the injection site; rarely - necrosis of surrounding tissues, scar formation at the injection site; with intramuscular injection (especially into the deltoid muscle) - atrophy of the skin and subcutaneous tissue.
Other: leukocyturia, withdrawal syndrome.
With intravenous administration - blood flow to the face, convulsions.
For external use: rarely - itching, hyperemia, burning, dryness, folliculitis, acne, hypopigmentation, perioral dermatitis, allergic dermatitis, skin maceration, secondary infection, skin atrophy, stretch marks, prickly heat. With prolonged use or application to large areas of skin, systemic side effects characteristic of GCS may develop.