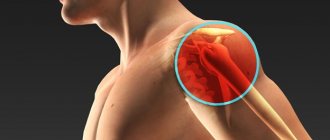
Joint diseases—arthritis, arthrosis—cause a lot of suffering for patients. Medicine relieves pain and swelling with various drugs and physiotherapeutic agents. To speed up the healing process as much as possible and relieve severe pain when moving, hyaluronic acid injections are used, when the drug is injected directly into the joint. Such injections are recognized as one of the most advanced and effective methods that can significantly improve the patient’s condition.
Hyaluronic acid is a drug that is widely used as a universal remedy for osteoarthritis, accompanied by severe pain in the knee and hip joints. With arthritis, the protective tissue of the joints wears out, and swelling and pain of varying intensity often occur. It is rational to use hyaluronic acid as injections when other methods of treating osteoarthritis do not provide complete relief from pain.
What is a joint injection?
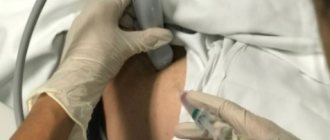
In the absence of a significant effect from drug treatment, many turn their attention to intra-articular injections. This method allows you to quickly achieve improvement, and the effect lasts for a long time.
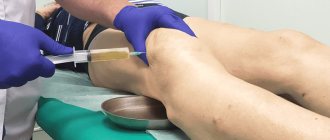
The definition is already included in the name - this is an injection that the doctor makes into the cavity of the affected joint. With the help of a blockade, medicinal substances penetrate into the joint, which relieve pain and inflammation and rehabilitate cartilage tissue.
Intra-articular injections are indicated for joint damage, hemorrhage and carpal tunnel syndrome. Using an injection, steroid hormones, B vitamins, hyaluronic acid and painkillers are injected into the joint cavity or periarticular tissue. Using this manipulation, you can also remove accumulated pathological fluid.
In orthopedics, such injections are performed on a regular basis and are part of clinical recommendations for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee and hip joints. When contacting a medical institution, you should find out in advance whether the necessary drug is available or should be ordered in advance, and whether treatment is free if you have a compulsory medical insurance policy if you go to a public clinic.
Features of therapy with hyaluronic acid preparations in our center
- Intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate are performed by highly qualified orthopedic traumatologists with extensive experience, under sterile conditions in compliance with all safety rules for the patient.
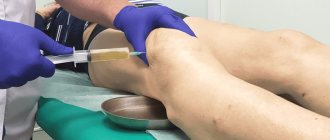
- The procedure is carried out under ultrasound control, which ensures 100% accurate delivery of the optimal dose of the drug into the joint cavity.
- The recommended course of treatment is 3-5 injections into each affected joint with an interval of 1 week. You can inject the drug simultaneously into several joints at the same time. If necessary, the course of treatment should be repeated after 9-12 months.
Conditions for intra-articular injections
- Availability of radiographs of the affected joints (can be performed in our Center).
- Absence of local inflammatory reactions from the joint (redness, local and general increase in temperature, pustular skin rashes, effusion in the joint) and the body as a whole (colds and other diseases accompanied by inflammation, increased body temperature).
Patient Information
Hyaluronic acid is not an analgesic or anti-inflammatory agent, nor is it a fast-acting drug.
Indications for intra-articular administration of hyaluronic acid preparations
- Osteoarthritis of large joints stages 1-2, 2, 2-3.
- Prevention of complications and joint pain in patients after arthroscopy
The determination of indications and contraindications for intra-articular injection, as well as the selection of the optimal drug, is made by a doctor based on an examination of the patient with an assessment of the condition of the joint using radiographs.
Contraindications for intra-articular administration of hyaluronic acid preparations
- the patient has an allergic reaction to hyaluronic acid, poultry (chicken) protein, as well as intolerance to the auxiliary components of the drug
- the patient has liver disease (cirrhosis, hepatitis, liver failure)
- pregnancy and breastfeeding
- pronounced inflammatory process inside or near the joint (increase in the joint in volume due to the accumulation of fluid in it, increased body temperature, pustular lesions of the skin around the joint)
- severe stage of joint damage (osteoarthritis grade 3-4).
Possible side effects
Hyaluronic acid preparations are usually well tolerated. Rarely, unwanted effects may occur:
- swelling, inflammatory, pain reaction from the joint for several days after administration;
- burning, soreness at the injection site, redness of the affected area.
To relieve unwanted reactions, it is necessary to take antiallergic, anti-inflammatory and painkillers.
Hypothermia and overheating of the joint are not recommended for 2-3 days after administration of the drug, as well as excessive stress on the joint during the entire course of administration (5-7 days after each injection).
Types of joint injections
Three types are used:
- paraarticular;
- periarticular;
- intra-articular.
Paraarticular
The method involves injecting medication into the tissue of the damaged joint. At the moment, this is one of the most effective ways to help the patient relieve pain and relieve inflammation. In this case, intradermal and subcutaneous administration is performed using thin and short needles. The injections are practically painless, and the procedure itself is completed quickly.
Periarticular
blockades are indispensable for osteoarthritis affecting a large area, arthritis and periarthrosis. The drug is injected into the tendon and muscle tissue.
Intra-articular
The method involves introducing a substance into the joint tissue.
Who is indicated for intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid?
This manipulation is recommended for patients with the following diseases:
- arthritis, including complications of gout, osteoarthritis, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis;
- synovitis and injuries that provoke it;
- severe pain;
- damage to periarticular tissues;
- adhesive capsulitis;
- carpal tunnel syndrome.
In addition, this method is ideal for those people who experience gastrointestinal dysfunction, since as part of complex therapy for the underlying disease it will help reduce the amount of medications taken orally.
Preparations for intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid are very diverse. In each specific case, the specialist selects the appropriate concentration of the substance depending on the condition of the patient’s tissues.
The principle of action of an injection with hyaluronic acid
Preparations for intra-articular injections with hyaluronic acid, which have been produced in Russia for several years using Swiss technology, are Ripart and Ripart Long. They are produced by fermentation, which allows for optimal action on affected cartilage tissues.
Medicines injected into the joint create favorable conditions for the restoration of cartilage tissue, providing better shock absorption and mobility. Since drugs containing hyaluronate can remain in the joint for a long time, from six months to 12 months, the recovery process occurs gradually, and its effect lasts for a long time.
In this way, the manifestations of arthrosis in the future can be reduced to a minimum. So-called “liquid prostheses” are indispensable for elderly patients who want to avoid surgery.
Efficiency of the procedure
Sodium hyaluronate is used, as a rule, in cases where corticosteroid drugs do not bring a visible effect and do not relieve the patient of pain. This procedure cannot be avoided when treating elderly people due to changes in the composition of the intra-articular fluid, which over time loses its nourishing and shock-absorbing functions. The cartilage becomes thinner and dries out, causing bone deformation.
In cases where the patient wants to do without surgery, and it is necessary to reduce pain as quickly as possible and at the same time avoid the use of anti-inflammatory drugs, hyaluronic acid is the only way out.
Possible side effects
With strict adherence to the rules of manipulation, side effects can be completely avoided. Specialists at the Yuzhny clinic recommend carefully ensuring that the doctor thoroughly cleans his hands before the injection, puts on gloves and disinfects the injection site. The syringe must also be in individual sterile packaging, and the ampoule with the drug must be hermetically sealed. After the injection, the doctor places a sterile napkin on the joint; in this case, unwanted infectious complications can be avoided.
One of the common mistakes is an incorrectly selected needle, which, when inserted, can damage the periosteum or enter a nerve or vessel. With careful adherence to technique and good knowledge of anatomy, such errors should not occur.
Common adverse reactions to injections of drugs containing hyaluronan are slight swelling at the injection site and slight pain. The patient’s condition can be adequately assessed within two days, when the primary symptom disappears.
Some forms of injection can cause significant swelling, inflammation and increased pain - the so-called pseudoseptic reaction.
Recommendations for the recovery period
A successful procedure requires the patient to comply with some important rules.
- It is necessary to keep the injection site dry under a sterile bandage for 24 hours. Do not apply warming compresses to the joint. If pain bothers you on the first day, you can apply a cold compress several times a day for no more than 15 minutes. The injection site should also not be exposed to local agents (ointments, gels, creams) for the first 24 hours.
- Water activities and the use of baths and saunas are strictly contraindicated. Any contact of the affected limb with water should be avoided.
- Stiffness and unusual sensations when walking will disappear after a few days. In some cases, tolerable pain remains until the completion of the treatment course.
- After the procedure, you can take a painkiller that the patient usually uses to reduce pain. Or choose gentle over-the-counter medications (Tylenol®, Aleve or Advil) after consultation with your doctor.
- Patients are often concerned about prolonged pain at the injection site: if discomfort persists for several days after the injection, you can ask your doctor to prescribe a suitable pain reliever.
- During the rehabilitation period, it is worth checking with your doctor when you can start morning exercises, playing sports, standing for long periods of time, or lifting weights.
- Also, during the treatment process and after a course of injections, you should refrain from stress and physical exertion, and it is absolutely necessary to refrain from drinking alcoholic beverages.
Drugs used
Substances that are used to treat arthritis and osteoarthritis are divided into several types:
- local anesthetics;
- chondroitin and glucosamine;
- steroid drugs;
- preparations containing sodium hyaloranate;
- specific medicinal substances, for example, platelet-rich plasma or ozonated solutions.
With the help of local anesthetics or painkillers, you can quickly achieve the effect of reducing pain and reducing sensitivity in the affected area, but it is worth keeping in mind that this will not be enough to treat joints.
To reduce swelling, glucocorticoids are used, the effect of their use lasts up to one month. These are the same corticosteroids that come in tablet form. When injected directly into the joint cavity, they are much more effective; in addition, this method avoids side effects such as dizziness and gastrointestinal problems.
Since these drugs are hormonal, it is recommended to use them no more than 3-5 times a year. For a disease such as infectious arthritis, the use of corticosteroid drugs is strictly prohibited. Instead, specialists use rinsing of the joint capsule and administer antibacterial drugs.
Drugs from the group of chondroprotectors help improve metabolic processes due to the human body producing its own collagen. This is a fibrillar protein that lies in the connective tissue of the body, the main building material for cartilage tissue and joints. A sufficient amount of it in the human body helps to cope with minor injuries on your own, without visiting a doctor.
The optimal solution for joint damage is the use of a so-called synovial prosthesis. A healthy human joint contains viscous and elastic synovial fluid; it protects the surface of the joints from chafing and protects against injury. Using intra-articular injections with hyaluronic acid, specialists managed to obtain the required consistency of injections, which will help not only relieve pain, but also restore damaged cartilage tissue.
The so-called PRP method, or injection of the patient’s blood plasma into the joint, is also often used. The plasma is first enriched with platelets. The advantage of this manipulation is that the patient cannot have allergic reactions to his own plasma, side effects are excluded.
Carboxytherapy is one of the new methods based on carbon dioxide injections. Its introduction into the joint accelerates blood circulation and metabolic processes. Its administration requires the use of special equipment, so this procedure is not so popular.
PRP therapy
Scientists are getting closer to unraveling the self-healing of worn-out tissues and entire organs. A revolution in the understanding of the body's ability to renew itself was brought about by the discovery of autoplasmolifting technology. PRP therapy is a new, even more powerful and advanced step in the development of regenerative medicine. And it is available to everyone at the Doctor Ost Spine and Joint Treatment Center.
In essence, the principle of action is the same - blood plasma enriched with platelets is injected into the affected area. The expected effect of treatment is active tissue regeneration, relief of inflammation and pain.
However, there are still differences. Externally: a different hourglass-shaped test tube is used. But in essence: PRP therapy is an improved technology that allows you to achieve much more pronounced dynamics in the treatment of various pathologies in fewer procedures.
Let's look at it in more detail:
| № | Comparison criterion | Plasma injections | PRP therapy |
| 1 | Volume of blood taken and plasma obtained | less | more |
| 2 | Platelet concentration in vitro | About 350 thousand | About a million |
| 3 | Additional plasma enrichment | Not provided | Combines with hyaluronic acid |
| 4 | Number of appointments during a course of treatment | 10 procedures | 3 procedures |
| 5 | Duration of the break between procedures | 7-10 days | 7 days |
What are the benefits of hyaluronic acid?
An important component of PRP therapy for joints, as well as PRP therapy for the spine, is hyaluronic acid, which greatly enhances the effectiveness of the technique.
Hyaluronic acid is a natural component of the synovial fluid of the joint. Depletion of this “lubricant” leads to stiffness.
Hyaluronic acid increases the activity time of platelets and the amount of growth factors they release into the joint.
The simultaneous introduction of platelets and hyaluronic acid during PRP joint therapy creates a “friendly environment” for cells and favorable conditions for rapid tissue restoration, greatly accelerating the healing process.
Indications for PRP therapy are diseases of the joints and bones, pain in the spine, injuries associated with damage to ligamentous tissues, muscle strains, tendons, damage to nerves, blood vessels, etc. The main diagnoses for which it is possible to obtain a good result thanks to the use of prp therapy:
- Arthrosis, coxarthrosis, gonarthrosis - prp therapy of joints for these diseases allows you to quickly stop degenerative processes and - more importantly! - restore worn cartilage, make it smoother and more elastic.
- Arthritis and chronic inflammation in the joints - prp therapy for joints allows you to stop the development of inflammation and calm the tissues.
- Rehabilitation treatment after injuries of varying severity: spinal injuries, severe sprains or ruptures of tendons and ligaments - plasma with a large number of platelets accelerates the regeneration process many times over.
- Prevention and treatment of spinal diseases - prp therapy of the spine is often a real salvation from back pain. As part of complex treatment, it helps to avoid surgery.
- Chronic and recurrent pain syndromes in the neck, head, and lower back. The introduction of plasma with platelets effectively relieves pain by affecting the cause of these ailments: eliminates muscle tension, frees blood flow, lymph flow, restores healthy tissue trophism and innervation.
- Neuralgia of various etiologies, vascular diseases and consequences of strokes.
How does PRP therapy work in a medical setting?
A PRP therapy session begins with venous blood sampling. The hourglass-shaped tube of blood is then placed in a centrifuge to separate the plasma and enrich the platelets. And the last stage is the introduction of healing components from plasma and hyaluronic acid into the problem area.
Patients who undergo PRP therapy sessions at Doctor Ost Medical Center note that the procedure is painless. The anesthetic makes it easy to endure the injection when collecting venous blood, and then injecting it into the diseased area. But these unpleasant sensations are insignificant in comparison with the debilitating pain that you have to endure before treatment.
Another plus is the short duration of the PRP joint therapy session – from 5 to 10 minutes. Immediately after, you can return to your daily routine. The course consists of only three procedures, which are done once a week. This is very convenient, especially with the busy schedule of modern people.
When going for a session of PRP joint therapy, take care of your diet and drinking regime. It is better that the blood is as free of toxins as possible and sufficiently fluid. Therefore, it is worth giving up a heavy dinner the night before, and eliminating smoking and alcohol.
Before prescribing PRP therapy for joints, you will need to check yourself for infections, viruses, and acute diseases. Tests can be taken right there, at the Doctor Ost MC.
Benefits of PRP Therapy
- Safety.
The patient's own blood is used. This means there is no risk of allergies or addiction. The preparation of biomaterial is carried out in a closed cycle, in one stage, in the presence of the patient: the risk of infection is also eliminated. - No age restrictions.
PRP therapy is suitable for people of any age. - Stable healing result.
Allows you to forget about pain in the joints, back, and lower back for a long time. - Ideal compatibility with other medical procedures.
Which together gives an even greater effect. - Reducing medication load.
During the healing process, there is no need for painkillers. Self-healing of damaged tissues after a course of treatment, as a rule, allows you to completely stop taking medications. - It does not require special preparation and rehabilitation of the patient,
which cannot be said about endoprosthetics surgery.
High efficiency of PRP therapy
The Russian Ministry of Health has approved and registered the PRP therapy method. The technique with Russian roots is recognized throughout the world. Today, PRP therapy is actively used in rehabilitation and sports medicine, orthopedics, traumatology, and neurology. This is a godsend for cosmetologists and serves as a highly effective anti-aging procedure. The technology also gives excellent results in the treatment of alopecia (baldness). The method has been widely researched and its effectiveness has a growing evidence base.
Prp therapy helps solve many serious problems with the health of the musculoskeletal system, as it not only alleviates the course of the disease, but reconstructs damaged tissue, restoring lost motor functions.
From 2021 Thousands of patients of various ages with pathologies of varying severity received PRP therapy for the spine and PRP therapy for joints at the Doctor Ost Medical Center in 10 cities. Positive changes are noted after the first sessions.
After the course of treatment, patients at Doctor Ost MC unanimously note that the pain has decreased and it has become easier to move. As a result of the course of procedures, the following results can be achieved:
- Eliminate the inflammatory process, remove tissue swelling
- Reduce muscle spasm
- Eliminate acute pain
- Restore blood circulation
- Replenish range of motion
- Reduce the recovery period after surgery and injuries.
Using PRP therapy for the knee joint at stages 1-2 of arthrosis as an example, you can see the following brilliant results:
- pain reduction in 1 injection
- replenishment of joint fluid in 1-3 injections
- improvement in joint function by 84%, on average cessation of exacerbations for a period of 6-12 months
Thus, PRP therapy for the knee joint effectively relieves most symptoms of arthrosis and helps to delay or completely avoid the need for knee replacement.
Contraindications to PRP therapy
- Infections;
- Oncological disease (relative contraindication);
- Diabetes mellitus (relative contraindication);
- Sepsis;
- Epilepsy;
- Anemia, if it is diagnosed in grade 3;
- Thrombocytopenia and thrombocytopathy.
GOOD TO KNOW
- Patients with chronic joint pain should know about another technology of modern regenerative medicine. This is an injection of stem (stromal) cells isolated from the patient's adipose tissue. Just one such injection can stop arthrosis at a late stage and even at the stage of necrosis. Read here.
Intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid for osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis occupies a leading place in prevalence; the number of people suffering from this disease in Russia is more than 15 million people.
Nowadays, there are many drugs based on hyaluronic acid, which vary depending on the production method, molecular weight and concentration of hyaluronates.
In the knee joint
Intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid into the knee joint will help compensate for the deficiency of intrinsic fluid in the joint. They are indicated for diseases such as synovitis, bursitis and tendinitis.
The use of injection techniques as part of an integrated approach to eliminate degenerative-dystrophic pathology has shown good results in almost all patients, especially in the early stages of pathology development.
Contraindications to an injection into the knee joint are allergic and autoimmune reactions that increase inflammation in this area, and the complete destruction of articular cartilage.
Oral medications and ointments or creams for external use are prescribed as accompanying medications. After the injection, the patient is advised to avoid excessive exercise.
In the hip joint
This movable joint of the bones of the human skeleton is one of the most complex components of the musculoskeletal system. Pain in the hip joint, unlike the knee, can occur even at rest, especially at night, which causes a lot of inconvenience and leads to a sharp deterioration in the quality of life.
Injections are usually used in cases where an effective method of treating elderly people diagnosed with coxarthrosis is needed.
Intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid into the hip joint allow you to quickly deliver the drug to damaged tissues. Sodium hyaluronate in the injection will help improve the sliding of the surface of the contacting cartilages and restore their elasticity.
As a rule, in cases with the hip joint, it is necessary to first take an x-ray. Often there is a need to remove accumulated fluid from the joint capsule.
The essence of the method
The non-surgical treatment method will significantly reduce the patient’s dependence on analgesics, eliminating the purchase and long-term use of anti-inflammatory drugs that have a negative effect on the gastrointestinal tract. Injections with hyaluronic acid have a pronounced long-lasting effect and slow down the rate of progression of osteoarthritis.
Intra-articular administration of the drug prevents the development of degenerative changes in tissues and cartilage and has a positive effect on metabolic processes. The injection, which is given inside the joint, will deliver sodium hyaluronate to the damaged cartilage. Next, the process of restoring the tissue that protects the joint from destruction will begin. The medicine will improve the sliding of the surface of the contacting cartilages, restore their elasticity and firmness.
Even if severe degenerative processes in the joints are diagnosed, cartilage thinned by arthrosis can restore its functions and provide the required shock-absorbing properties. Also, sodium hyaluronate will reduce pain, stiffness will go away, and the limb will regain the ability to have a wide range of motion.
An intra-articular injection is prescribed to the patient after undergoing diagnostics and additional examinations - x-rays of the affected joint and a detailed consultation with an orthopedic doctor. When treating with this method, the doctor takes into account all the diseases associated with osteoarthritis.
Injections are usually prescribed as a course, but injections are given no more than once every three months. If the effect is weak and there is short-term relief from pain, therapy is abandoned, and the attending physician turns to another option for therapy suitable for the patient.
Price of intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid at the Yuzhny clinic
The cost of the service depends on the pricing policy of the institution and the degree of damage to the joint. The cost of the administered drug plays a big role. Corticosteroid drugs are the most inexpensive, their cost ranges from 300 to 600 rubles per ampoule. Preparations containing hyaluronic acid are much more expensive, their cost ranges from 13 thousand rubles and more.
The cost of the injection itself, as a rule, does not exceed two thousand rubles. If necessary, the doctor can use additional tests, for example, ultrasound diagnostics or fluoroscopy, which is paid separately.
The price of intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid at the Yuzhny clinic varies depending on the number of procedures required, the stage of the disease and the concentration of the drug, which is selected by a specialist individually in each case.
Intra-articular ozone therapy in the complex treatment of coxarthrosis
Authors: G.M. BURMAKOVA
, MD, senior researcher,
A.M.
, Federal State Institution “Central Research Institute of Traumatology and Orthopedics named after. N.N.Priorova", Moscow
The experience of conservative treatment of 108 patients with osteoarthritis of the hip joint is presented. The patients were divided into two groups identical in gender, age, and severity of changes in the hip joint. In the control group, patients received traditional conservative treatment of coxarthrosis, and in the main group, intra-articular injections of an ozone-oxygen mixture and Zeel T were added to the treatment. Analysis of the results indicates the high effectiveness and safety of intra-articular ozone therapy for coxarthrosis of varying degrees. Degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the hip joint occur in 37–49% of all cases of osteoarthritis. Coxarthrosis usually affects people aged 40–60 years and in most cases progresses steadily. Severe pain syndrome forces the patient to lead a sedentary lifestyle, reduces his functionality and leads to social isolation. About a third of patients with coxarthrosis have some degree of disability. With a rapidly progressing variant of the disease, especially with bilateral lesions, complete disability of the patient occurs within several years. After 10 years of illness, 30 to 50% of patients require total arthroplasty surgery [6, 14]. Replacing a hip joint with an artificial one is a difficult surgical procedure and has a number of medical and social contraindications. According to the literature, 4–30% of patients after surgery experience severe pain, sometimes of a different quality than before surgery [3].
The effectiveness of osteoarthritis treatment increases significantly when standard conservative treatment is supplemented with intra-articular injections.
Thus, the problem of conservative treatment of coxarthrosis is still relevant. In the initial stages of coxarthrosis, timely and effective treatment is of great social and economic importance, because allows you to stop the development of degenerative-dystrophic changes in joint tissues. In case of severe coxarthrosis (if there are contraindications to endoprosthetics, the patient refuses surgery, etc.), conservative treatment can achieve remission of the pain syndrome. Doctors have a large number of different medications, physiotherapeutic, manual and other non-surgical methods for treating coxarthrosis in their arsenal. However, even with their combined use, it is possible to achieve remission lasting on average no more than 4 months [9].
The effectiveness of osteoarthritis treatment increases significantly when standard conservative treatment is supplemented with intra-articular injections. Unfortunately, the use of such injections is limited. This is due to the complex anatomy of the hip joint, the depth of its location, as well as the technical difficulties of performing injections. In some studies, drug injections into the hip joint were performed using X-ray or ultrasound navigation [15, 21]. It should be noted that the use of echography significantly complicates the puncture of the hip joint, and excessive radiation during X-ray control is undesirable.
We have developed an anterior approach to the hip joint, which is a modification of the anterior arthroscopic approach. The puncture is performed with the patient lying on his back. The needle insertion point is located 1–1.5 cm below the Pupart ligament on a line drawn from the tip of the anterior superior iliac spine distally to the thigh. The advantage of this approach over others (lateral, standard anterior, perineal) is that it is carried out at a distance of 3–4 cm outward from the femoral neurovascular bundle, which eliminates the need to necessarily identify it and use it as a guide [2]. In addition, this approach does not require X-ray or ultrasound guidance. The needle reaches the anterior part of the hip joint, adjacent to the neck of the femur. Even in the presence of adhesions in the joint with severe arthrosis, this part of the joint is the most accommodating, which allows the administration of drugs.
Corticosteroids are most often used for intra-articular injections. They reduce swelling of joint tissues and pain, which, however, often recurs. Many studies have proven the negative effect of steroids on articular cartilage and underlying bone, leading to the progression of degenerative changes in the cartilage, the emergence of subchondral cysts and foci of avascular necrosis [10]. V.A. Nasonova, L.I. Alekseeva, E.L. Nasonov [13] believe that such injections are contraindicated for administration into the hip joint.
Hyaluronic acid preparations (Ostenil, Fermatron, etc.) are very popular for intra-articular administration. They also help relieve pain and improve joint function, which occurs later than with hormonal injections (on average after 13 weeks). According to studies conducted by CTWang et al. [23], improvement is less likely with significant narrowing of the joint space and age over 65 years. In addition, no significant evidence has been found for the structure-modifying properties of hyaluronic acid. In the Clinic of Sports and Ballet Trauma of the Federal State Institution CITO, a method of intra-articular ozone therapy was developed [12]. The rationale for this was studies proving that hypoxia of joint tissue develops in osteoarthritis [19]. Active oxygen improves the metabolism of joint tissue and integumentary cartilage, preventing its further destruction, restores microcirculation in the affected tissues and has a regenerative effect [1, 16]. Recently, more and more evidence has emerged that inflammation plays a significant role in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis, which is why in foreign literature osteoarthritis is called “osteoarthritis” [4, 20]. As a result of modulation of the prostaglandin system, which forms the intracellular antioxidant defense of the body, the anti-inflammatory effect of ozone is realized during ozone therapy [8, 11, 22]. The analgesic effect of ozone therapy is due to the oxidation of pain-inducing mediators, as well as inhibition of catabolic cartilage enzymes. As a result of the increased release of oxygen in the tissues, the cation-anion ratio in the altered cell membrane is restored, i.e. ozone is a pain antagonist [17].
Takeaway 2. In the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis, inflammation plays a significant role, therefore, with the use of intra-articular ozone therapy, both anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects are achieved.
From 2005 to 2011, 108 patients with coxarthrosis were treated as outpatients in the research and outpatient department of the Federal State Institution CITO, of which 45 were men and 63 women aged from 25 to 75 years. According to the degree of clinical and radiological changes, they were distributed as follows: degree I was detected in 19 patients, II – in 54, III – in 23, IV – in 12 patients.
The patients were divided into two groups identical in gender, age, and severity of changes in the hip joint. In the first (control) group, patients received traditional conservative treatment of coxarthrosis; in the second group, intra-articular injections of an ozone-oxygen mixture and the drug Zeel T were added to the treatment. The complex of conservative measures includes physical therapy aimed at strengthening the periarticular muscles, massage of these muscles, and physiotherapy , in severe cases - walking on crutches to unload the sore joint. An important place in the complex treatment of coxarthrosis is occupied by the use of various medications. The leading role is played by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), the pharmacological action of which is due to the suppression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), which is responsible for the synthesis of the most important mediators of pain and inflammation - prostaglandins, in areas of damage or inflammation. We give preference to drugs belonging to a number of selective COX-2 inhibitors (meloxicam, nimesulide, Nise), the main advantage of which is good tolerability and a relatively low risk of serious complications from the gastrointestinal tract. Nise (nimesulide) also exhibits a number of pharmacological effects independent of the class-specific effect on COX-2. Thus, this drug suppresses the synthesis of the main pro-inflammatory cytokines (interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor-?), reduces the activity of metalloproteinases (responsible, in particular, for the destruction of the glycoprotein complex of cartilage tissue in osteoarthritis), and has an antihistamine effect. One of the most interesting “non-COX-2-associated effects” of Nise is its ability to suppress the activity of the enzyme phosphodiesterase IV, which stimulates macrophages and neutrophils - cells that are of fundamental importance for the development of acute inflammation [5]. Nise has high bioavailability - within 30 minutes after oral administration, a significant concentration of the drug in the blood is reached, at least 25% of the maximum. The maximum therapeutic effect appears after 1–3 hours.
In order to normalize metabolic processes in cartilage and stimulate its regeneration, the drugs Rumalon, Chondrolon or Mucosat are prescribed, and to improve microcirculation - Trental or Detralex.
In the second group of patients, intra-articular injections of an ozone-oxygen mixture and the drug Zeel T were added to conservative treatment. Ozone therapy is contraindicated in hyperthyroidism, thrombocytopenia, a history of convulsive syndrome, bleeding from any organ, ozone intolerance, and pregnancy. It should also be used with caution in case of decompensated conditions: heart failure, severe acute poisoning, incl. and alcohol, hypoglycemic conditions, as well as in cases of simultaneous use of anticoagulants.
To obtain the ozone-oxygen mixture, the Medozon generator (Arzamas) was used. With the patient lying on his back, the joint is punctured through our modified anterior approach. After local anesthesia, a 15 cm long needle is used to reach the femoral neck and intra-articular injection is carried out: first, an ozone-oxygen mixture (with an ozone concentration of 20 mg/l), then 2.0 Zeel T. During the first injection, 5.0–7.0 is administered ml of gas mixture. With good tolerance, the volume of the ozone-oxygen mixture increases with each injection (maximum volume - 20.0 ml). Five injections are performed in a similar manner at intervals of 2–3 days. Bed rest is indicated for 2–4 hours after intra-articular injection. We did not observe any complications during or after intra-articular ozone therapy in our patients.
Ozone therapy is characterized by an “aftereffect”, i.e. patients note continued improvement in their condition even after treatment ends. This is explained by an increase in the content of oxyhemoglobin in the blood, which is reduced with the release of active O2 very slowly, over several weeks. Thus, high oxygen content in the blood has a therapeutic effect even after the end of treatment [7].
Takeaway 3. Numerous clinical studies confirm that ozone therapy, when used correctly, is well tolerated and is extremely rarely accompanied by side effects, without causing any negative reactions in the human body. Numerous clinical studies confirm that ozone therapy, when used correctly, is well tolerated and is extremely rarely accompanied by side effects, without causing any negative reactions in the human body. During procedures, patients may occasionally complain of weakness, slight dizziness, and drowsiness, which are short-lived. Allergic skin manifestations to the local use of ozone in the form of urticaria are possible (very rare). When conducting ozone therapy in patients after the first procedures, it is possible to increase the number of leukocytes in the peripheral blood and a simultaneous decrease in the number of platelets. These changes are transient in nature and do not require additional correction. The reason for the occurrence of extraordinary reactions during ozone therapy is considered to be an imbalance between the intensity of the formation of reactive oxygen species and the state of the body's antioxidant defense system. Therapeutic doses of medical ozone are a stress stimulator for the enzymes of the defense system, therefore, in order to prevent the depletion of endogenous antioxidants, treatment begins with small doses of ozone, gradually increasing them to the required values [1].
More serious side effects are mydriasis, intense sweating, transient decrease in blood pressure, bradycardia, pressing pain in the chest, dyspnea, allergic reactions, cardiac arrest (vasovagal reaction). According to Jacobs M.-Th. [18], the rate of complications in relation to the total number of procedures is 0.006%. Compared to other types of treatment, this is an insignificant amount. Most often, side effects of ozone therapy occur during intravenous procedures, especially with intravenous administration of an ozone-oxygen mixture, which has now been practically abandoned. The most dangerous in terms of toxic effects on the vagus nerve and the occurrence of a “vasovagal reaction” with a drop in blood pressure and depression of the respiratory center are peroxide radicals. Despite the low incidence of complications, a doctor involved in ozone therapy must be prepared for such emergency situations.
When carrying out ozone therapy, an exacerbation of chronic infections may occur, but this is not a reason to interrupt the treatment course. Ozone therapy must be continued, which helps relieve inflammation [1]. Ozone therapy is combined with the use of any medications, except anticoagulants, and most physiotherapeutic procedures (except ultrasound therapy - until the gas mixture, which is a poor conductor of ultrasound, is absorbed). In most cases, you can reduce the dosage of painkillers, sedatives, antibacterial, antihypertensive drugs, because ozone enhances their effect. The effect of complex use of ozone therapy with other types of treatment is greater than the arithmetic sum of the effects of each of these types, and the presence of side effects is minimized.
Results. The effectiveness of treatment was assessed using Lequesne's total algofunctional index with an assessment of pain using a 10-point VAS, the WOMAC index, and biomechanical examination data (determining the degree of support, podography, stabilography). In patients of the main group, faster and more significant relief of pain was noted, regardless of the severity of radiological changes in the hip joint, and a longer remission was achieved. In most cases, with grade 1–2 coxarthrosis, limb function, according to biomechanical studies, was completely restored. With grade 3, improvement was noted in 15 people (among them 11 were patients of the main group), with grade 4 and severe flexion-adduction contracture, a slight improvement in limb function was observed in only 2 patients of the main group.
Intra-articular ozone therapy significantly increases the effectiveness of conservative treatment of coxarthrosis (pain syndrome is reduced or completely relieved, limb function is improved) and promotes long-term remission.
Literature
1. Alyokhina S.P., Shcherbatyuk T.G. Ozone therapy: clinical and experimental aspects. – N. Novgorod, 2003. 2. Arthroscopic surgery of the hip joint. – M., 2004. 3. Akhtyamov I.F., Kuzmin I.I. Errors and complications of hip replacement: A guide for doctors. - Kazan, 2006. 4. Badokin V.V. The importance of inflammation in the development and course of osteoarthritis // Consilium medicum. - 2009. - T. 11, No. 9. – pp. 91–95. 5. Barskova V.G. Significance for clinical practice of the properties of nimesulide not related to the suppression of cyclooxygenase-2 // Consilium medicum. - 2009. - T. 11, No. 9. – P. 96–100. 6. Buachidze O.Sh. Endoprosthetics of the hip joint // Vestn. traumatol. and orthop. - 1994. - No. 4. - pp. 14–17. 7. Zmyzgova A.V., Maksimov V.A. Clinical aspects of ozone therapy. – M., 2003. 8. Idov I.E. Aspects of the use of ozone in medicine // Anest. and resuscitator. - 1997. - No. 1. — pp. 90–94. 9. Landa V.A., Meshcheryakova T.I. Relief of pain in certain diseases and consequences of damage to the hip joint // Travmatol. and orthopedist. Russia. - 1995. - No. 2. – pp. 21–23. 10. Lesnyak O.M., Maksimov D.M., Popov A.A., Solodovnikov A.G. Osteoarthrosis: drug treatment of osteoarthritis (osteoarthritis) of the knee and hip joints // Rheumatology. – 2005. – T. 7, No. 8. 11. Maknassi S.T. Ozone therapy in the complex treatment of patients with osteoarthritis of the knee joints: Abstract of thesis. dis. ...cand. med. Sci. - M., 2006. 12. Mironova Z.S., Mironov S.P., Sibeldina L.A., Natsvlishvili Z.G., Zuev V.V. Application of ozone therapy for degenerative-dystrophic joint lesions // Vestn. traumatol. and orthop. – 1997. – No. 4. — pp. 24–27. 13. Nasonova V.A., Alekseeva L.I., Nasonov E.L. Osteoarthrosis of the hip joint: course, treatment and prevention // Consilium medicum. - 2003. - T. 5, No. 8. 14. Nuzhdin V.I., Popova T.P., Kudinov O.A. Total hip replacement // Vestn. traumatol. and orthop. – 1999. – No. 1. – P. 4–7. 15. Cherkes-Zade D.D., Miti A. Treatment of the initial stages of coxarthrosis by intra-articular injections of chondroprotectors under x-ray control // Vestn. traumatol. and orthop. – 2010. – No. 1. — pp. 88–89. 16. Bocci V. Ozone: A new medical drug. Springer 2005. 17. Fahmy Z. Immunological effect of ozone (O3/O2) in rheumatic diseases // Proc. Ozone Application in Medicine. – Zurich, 1994. – P.62. 18. Jacobs M.-Th. Untersuchung ?ber Zwischen f?lle und typische Komplikation in der Ozon-Sauerstoff Therapie //Ozonachrichten. - 1986. - N 5. - S. 1–5. 19. Lohmander LS Markers of cartilage metabolism in arthrosis // Acta Orthop. Scand. – 1991. – N 62. – P. 623–632. 20. Pinkus T. Clinical evidence for osteoarthritis as an inflammatory disease // Curr. Rheum. Rep. – 2001. – N 3. – P. 524–534. 21. Qvistgaard T., Kristofferssen H. Guidance by ultrasound of intraarticular injections in the knee and hip joints // Osteoarthritis cartilage. – 2001. –Vol. 9, N 6. - P. 509–511. 22. Sies H. Oxidative stress: from basic research to clinical application // Am. J. Med. – 1991. – Vol. 91(3C). – P. 31–38. 23. Wang CT, Lin J., Chang CJ, Lin YT, Hou SM Therapeutic effects of hyaluronic acid on osteoarthritis of the knee. A metaanalysis of randomized controlled trials // J. Bone Jt Surg. - 2004. - Vol. 86A, N 3. - P. 538–545.