1.What is bunion and what types of surgeries are there?
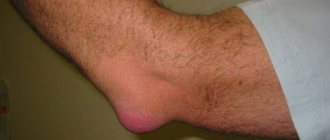
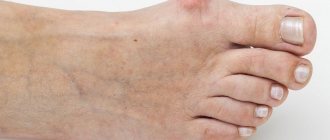
A bunion is a painful bump on the first joint of the big toe. Surgical treatment of bunion involves the removal or reconstruction of soft tissue and bone. The operation is done to relieve pain and restore alignment to the joint. Unfortunately, surgical treatment of bursitis does not always relieve all pain.
During the operation, a local anesthetic is used, which affects only the foot. I can also give you a sedative. The operation lasts about an hour.
Types of operation
There are many different surgical treatments for bunions. Here are some of them:
- Removal of the metatarsal head. This operation is called bursectomy or exostosis removal;
- Restructuring of soft tissues around the joint;
- Osteotomy (cutting the bone) followed by moving it to a more comfortable position;
- Arthrodesis (fusion) of the thumb joint;
- Implantation of a joint or several joints.
The doctor will select the operation specifically for you.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Bursitis of the feet
Inflammation of the joints most often occurs in places that are subject to heavy load:
- At the base of the toes there is a metatarsal bursa.
- Near the big toe is the metatarsophalangeal capsule.
- On the back of the heel. There are 2 capsules here - retrocalcaneal and subcutaneous calcaneal.
Metatarsal bursitis
The metatarsus is the middle part of the foot, consisting of five tubular bones to which the toes are adjacent. Bursitis is caused by increased stress on one of the bones. The soft tissues between it and the skin are compressed, first mechanical deformations begin in the bursa, and then inflammatory processes. Symptoms are worsened if a person walks barefoot on wood or tile floors due to direct pressure on the bag.
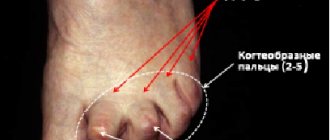
Inflammation may affect the top of the fingers. The main reason is bad shoes, which put a lot of pressure on the joint. Constant friction causes pain, swelling, and redness. Wearing shoes turns into torture; even socks can cause discomfort.
Another variety is the intermetatarsal form. Pathology develops when the capsule between the fingers is compressed. The main causes of bursitis of the arch of the foot:
- narrow boots;
- old age.
As we age, the arch of the foot lowers and the metatarsal bones begin to put pressure on the bursae adjacent to the toes. There is no swelling, the pain spreads along the entire length of the fingers. Comfortable, wide shoes will help reduce discomfort.
Inflammation of the first metatarsophalangeal joint
One of the most common types is inflammation of the metatarsophalangeal capsule at the base of the big toe. There is a large bump on the bone that is subject to increased friction.
The joint becomes deformed, curved, and the big toe may overlap the second toe. The skin thickens, turns red, calluses and corns form, and pain appears. It is difficult for patients to find comfortable shoes; in the summer, sandals that do not put pressure on the affected joint capsule help out.
Heel bursitis
The Achilles tendon is protected by 2 capsules:
- Retrocalcaneal - located between it and the heel bone, protects the tendon from friction. The bag becomes inflamed due to the thinning of the fat pad.
- Subcutaneous heel (Achilles bursa) - located in the area where the tendon connects to the heel bone, below the ankle. The bursa protects the tendon from friction, but it develops with age, so it doesn’t happen to everyone. The cause of subcutaneous calcaneal bursitis is trauma. The pathology is often found in athletes (runners, figure skaters).
- The pathology is difficult to treat due to constant pressure on the heel. Orthopedic insoles help relieve pain, but for complete healing you need to undergo therapy.
2.Recovery after surgery
The recovery period after surgical treatment of bunion takes from 6 weeks to 6 months, depending on the type of operation and the amount of tissue removed. Complete healing can take up to a year.
Remember a few rules to follow after surgery:
- Keep the stitches on your leg dry while washing;
- Do not lift heavy objects and protect your leg from their impact. Do not drop objects on your foot;
- In some cases, special shoes may be required.
Sutures are removed one to three weeks after surgery. Special pins are removed after 3-6 weeks.
Visit our Rheumatology page
Pathogenesis
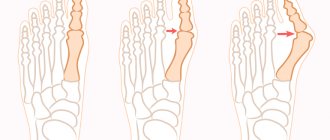
With hallux valgus, patients experience an increase in the angle between the 1st and 2nd metatarsal bones. As a result, the first toe shifts outward, and the head of the bone begins to form a tubercle on the side of it (in simple words, a “bone”). In this case, continuous pressure on the tubercle and friction when wearing shoes cause inflammation of the mucous bursa of the first metatarsophalangeal joint (bursitis), and also provokes changes in the bone structure, swelling and pain of the “bone” and the tissues located around it. The deformation leads to premature wear of the main joint, damage to the cartilage, as well as significant growth of the bone growth, and this, in turn, leads to its traumatization and further development of the pathological process.
3.How it works and possible risks
How it works
In general, after surgical treatment of bunion, there is a noticeable improvement in appearance and a decrease in pain. There are currently no statistics on which type of surgery is most successful. About 30% of patients who have undergone this operation are dissatisfied, despite the reduction in pain and improvement in appearance, because After surgery, you cannot wear certain types of shoes.
Risks of surgery
Surgical treatment of bunion has the following risks:
- soft tissue or bone infection;
- Recurrence of bursitis;
- Curvature, decrease in length, or swelling of the finger;
- Pain;
- Decreased sensitivity;
- Loss of motor functions of the joint;
- Development of callus;
- Degenerative joint diseases (arthritis) or avascular necrosis.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Risk group
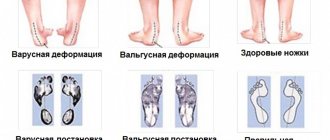
The disease is often observed in women who have reached the age limit of 30 years and above, and in European and American women it occurs more often than in Asian or African women, which is directly related to the traditions of shoe design in these regions. Due to wearing predominantly dress shoes (usually narrow, tight, high and unstable heels), the front parts of the lower extremities are exposed to excessive overloads, an imbalance in the distribution of which over time can cause valgus deformity of the big toe (curvature as a result of instability of the metatarsophalangeal joint and unfolding of the metatarsal joint). bones).
The disease often develops in overweight people and with certain foot pathologies. The risk group also includes those citizens whose professional activities are accompanied by prolonged, monotonous physical activity on the foot area. Also, the disease sometimes occurs due to mechanical injuries.
Therapeutic principles of our clinic
More than 85% of women and men suffer from foot deformities, in particular, transverse flat feet, the manifestation of which is the “flatness” of the forelimb, curvature of the fingers, the appearance and growth of “bones,” as well as rapid fatigue of the legs when walking. The development of hallux valgus is negatively affected by chronic inflammation, leading to the destruction of tendons and weakening of the capsular apparatus, as well as destruction of the articulating surfaces of the joint, especially the head of the 1st metatarsal bone. As a result of the combined action of these factors, different degrees of valgus deviation of 1 finger may occur.
Treatment for this pathology can be:
- conservative (using corrective orthopedic, as well as medications, physiotherapy, kinesiotaping, manual therapy, etc.);
- surgical.
Conservative method
The conservative technique is primarily aimed at fixing the correct position of the foot, uniform distribution of the load, normalization of blood circulation, and stabilization of muscle-ligamentous tone.
Regular wearing of individual orthopedic shoes, insoles and correctors allows you to stop the progression of the disease in the early stages, or slow it down, since the main purpose of these products is to prevent transverse flat feet, “spreading out”, widening of the foot, preventing the appearance and growth of “bones” of the big toe and hook-shaped deformities, as well as eliminating increased fatigue. The therapeutic effect is achieved in this case by neutralizing pathological misalignments of the segments of the lower extremities and improving their spring capacity, unloading the articular structures and supporting the arches of the foot - this is the main principle of basic therapeutic methods and preventing “overload pain,” early wear of the joints and their displacement.
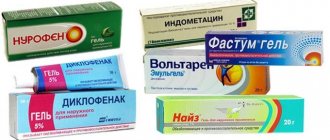
Drug treatment involves the introduction of hormonal agents into the joint cavity in order to slow down the inflammatory process and relieve pain.
Physiotherapy – ultrasound with medications, laser therapy and shockwave therapy. All these methods are aimed at reducing inflammation, swelling, pain, and improving blood circulation.
Kinesio taping – for unloading the feet, legs, thighs and to normalize venous outflow.
Manual therapy - eliminates muscle blocks, tension, spasms, pinching, relieves joints and returns the correct anatomical position of all parts of the limb, improves lymph and blood circulation. It also restores muscle imbalance, however, it is necessary to take into account the phase of the disease because the therapeutic effect is most pronounced in the initial stage.
Surgical intervention
If the deformity progresses, the following factors must be taken into account:
- concomitant pathologies that may complicate the operation (varicose veins with damage to the venous system of the legs, especially with signs of thrombophlebitis), steroid vasculitis in the area of the feet and legs;
- the presence of obvious and hidden foci of infection in the limb area;
- pain in the affected parts of the foot that occurs during exercise, as well as difficulties in selecting and wearing shoes;
- allergic history.
Surgical treatment restores the normal configuration of the limb, relieves discomfort, and improves the quality of life.
Diagnosis and treatment of bursitis
If symptoms of bursitis appear, specialist help is recommended. The doctor makes the diagnosis based on the clinical manifestations of the disease and examination results. A differential diagnosis of arthritis is carried out, which occurs with severe motor limitations. With bursitis, the range of motion is only slightly reduced, and sometimes completely preserved.
Experts prescribe the following types of diagnostics:
- determination of sensitivity to antibiotics (if bursitis is infectious);
- serological and bacteriological studies (used to identify specific infections, in particular syphilis and gonorrhea);
- magnetic resonance imaging of the affected joint;
- radiography.
In the acute form of bursitis, treatment consists of resting the affected joint and carrying out symptomatic therapy. Antibacterial agents are used for purulent complications. Antibiotics are selected taking into account sensitivity, which allows you to quickly suppress the infectious process and avoid serious complications. Sometimes specialists resort to joint puncture to administer corticosteroids and remove accumulated fluid, and perform drainage with rinsing with antiseptics and antibacterial drugs, which requires longer recovery and pain relief over several weeks.
Chronic bursitis is treated with anti-inflammatory and painkillers. But more often surgical excision of the synovial bursa is indicated. The operation is performed for advanced bursitis or when puncture of the synovial bursa does not give the expected effect.
Up to contents