Author
: Grachev Ilya Illarionovich
Editor
: Efremov Mikhail Mikhailovich
Date of publication: 11/14/2018 Date of update: 02/13/2020
Athletes and representatives of some professions are well aware of what acute bursitis is. The disease is associated with constant stress on certain joints, their injury and mechanical irritation. The big problem is that not all patients immediately see a doctor, and the disease becomes more complicated.
Why and how acute bursitis develops
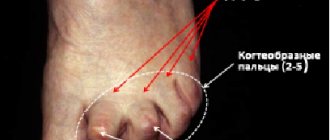
To understand how bursitis differs from arthritis, you need to know the anatomy and physiology of the osteoarticular system. Each joint is surrounded by a joint capsule. Its inflammation is called arthritis. But besides this bag, there are others located next to the bone of the joint, surrounded by a synovial membrane and capsule, which help the tissues slide relative to each other. These synovial bursae (bursae) are closed in nature and act as shock absorbers. If an inflammatory process develops in the bursa, it is called bursitis. When the inner lining of the bursa, which secretes fluid, becomes inflamed, the permeability of the walls of its vessels increases, the fluid collects in the bursa, causing characteristic swelling and increase in volume (protrusion).
The cause of inflammation is open and closed injuries. The inflammation is sterile or infectious in nature. Very often, sterile (without infection) becomes infectious when infection penetrates into the site of inflammation through the skin or with blood from other organs and tissues.
Sometimes bursitis is secondary, developing against the background of an existing infection (tuberculosis, brucellosis, etc.)
Diagnosis of bursitis
Accurate diagnostic methods will help confirm the diagnosis of bursitis:
- X-ray to identify pathologies in the joint - osteophyte deposits or others.
- MRI.
- Puncture and analysis of synovial fluid to look for a possible infectious cause of inflammation.
- A blood test for antibodies to look for possible causes of bursitis such as rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes and others.
The doctor will need to not only conduct a careful examination of the affected joint and find out all the complaints in detail, but also ask many questions. How long ago and when did the symptoms appear? What other diseases are there? Is the patient taking any medications for a long time? All this is needed to understand the causes of bursitis and distinguish it from other diseases with similar symptoms.
When is it definitely time to go to the doctor?
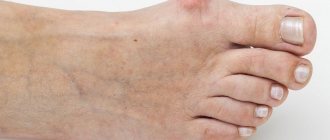
The onset of the disease is acute. A soft, elastic swelling up to several centimeters in diameter appears above the affected joint. Education has clear boundaries. When palpated, a clear point of greatest pain is determined, around which redness can be seen. The pain intensifies at night and with movement.
Any form of bursitis has serious complications, so you should not delay treatment.
See how easily the disease can be cured in 10-12 sessions.
If the inflammation is non-purulent, the patient’s general condition may not suffer. Such patients often trigger the disease, trying to cope with it on their own, which leads to the transition of the acute process to subacute. A sign of chronicity is a decrease in pain intensity.
With purulent bursitis, malaise and high fever appear. The pain intensifies and becomes unbearable. The danger of this condition is the progression of purulent inflammation with the formation of ulcers and fistulas (channels for the release of pus through the skin).
Acute joint injury may be accompanied by hemorrhage, against which acute hemorrhagic bursitis develops. The function of the affected joint is preserved, but movement is limited due to pain.
To avoid complications, it is best to immediately contact a specialist if you suspect inflammation of the bursa and start treatment in a timely manner.
Acute bursitis of the elbow joint
The disease in the area of the elbow joint begins against the background of constant injury to the elbow bags in workers who constantly sit at a computer, watchmakers, etc. Symptoms of this process are: a sharp protrusion of the bursa, pain in the elbow area. Infection of the inflammatory process is accompanied by a rise in temperature, swelling and redness in the elbow joint. Purulent processes are easier to treat if you seek medical help early.
Sometimes the brachioradial bursa is affected, resulting in an inflammatory process called “tennis players’ bursitis.” This disease is often initially mild, which quickly leads to the transition of the acute form of elbow bursitis to subacute.
Acute bursitis of the knee joint
In the knee area, the disease develops in the subcutaneous, subfascial and subtendinous prepatellar bursae. These bursae do not communicate with the joint cavity, so the process is rarely complicated by arthritis.
The onset of acute knee bursitis is usually associated with injury to the joint. A painful lump appears in the knee area. When an infection occurs, fever, hyperemia and swelling appear in the knee area, pain intensifies, and nearby lymph nodes become inflamed.
When the popliteal bursa, located deep in the tissues, is inflamed, the disease is difficult to detect, since it is erased. Due to late detection and treatment, knee bursitis can become more complicated.
Intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid
Chondroprotectors: what are they, how to choose, how effective are they?
Physiotherapy
The basis of treatment for any orthopedic diseases is physiotherapy. To get rid of bursitis, the following physiotherapeutic procedures are recommended:
- Phonophoresis is the effect of low-intensity ultrasonic waves. Ultrasound energy is partially absorbed, turning into heat, producing a relaxing effect on the muscles and tissues of the joint;
- UHF therapy interacts with the body through a high-frequency electromagnetic field, which improves blood circulation and also promotes the restoration of connective tissues of the joint;
- Ultraviolet irradiation is used to produce special pigments in the patient, which help eliminate inflammatory processes and also enhance the body's immune system.
- Ultrasound therapy is used to stimulate: blood and lymph circulation, regenerative processes, in addition, ultrasound has a pronounced analgesic, anti-inflammatory and tonic effect on the human body.
- Acupuncture is designed to influence reflex reactions that lead to changes in the functional state of all parts of the nervous system and preservation of tissue structure.
- Therapeutic exercise is used to develop affected joints and reduce the inflammatory process.
How to hold out until you see the doctor
With acute bursitis, patients may experience severe pain. To alleviate the condition, you can do the following yourself:
- apply a pressure bandage, being careful not to squeeze the tissue too much;
- fix the site of the lesion so that the limb is constantly at rest;
- if there is no purulent inflammation, the patient’s general condition does not suffer, then apply a warm compress; with elevated body temperature, swelling and hyperemia of the skin over the joints, it is better to apply cold
- give the limb an elevated position.
All this will only reduce the pain and allow you to wait for qualified assistance. Therefore, you should not postpone your visit to the doctor.
Folk remedies
To treat bursitis of the foot with folk remedies, the following methods are used:
- Warming up;
- Compresses;
- Coniferous baths;
- Propolis lotions;
- Infusions.
Warming up
Warming is used to reduce pain, as well as to improve blood circulation in the joint. To use this procedure, you will need salt and a piece of dense material. Pre-heat the salt in a frying pan for 8-10 ten minutes. After which the heated salt must be wrapped in a clean cloth. Apply to the affected area and hold for fifteen to twenty minutes. This procedure must be carried out twice a day for two weeks.
Compresses
Compresses are used to relieve joint inflammation. Compresses differ in the main ingredient and the method of their preparation, here are some types of compresses:
White cabbage compress
A compress of white cabbage leaves is made as follows: take a leaf of a suitable size and cut off the hard vein, after which the leaf is tapped with the handle of a knife (to release the juice). Prepared sheets are applied to the affected area and wrapped with a bandage or gauze, then put on a warm sock. The compress must be changed every four hours for seven days.
Beetroot and potato compress
To use a compress of beets and potatoes, you need to take one potato and grate it. Apply the resulting substance to the joint, wrap it in polyethylene, and put a sock on top. This procedure should be repeated for seven days, holding the compress for exactly two hours; for the next week, use beets instead of potatoes. The general course of treatment is fourteen days.
Burdock root compress
To prevent bursitis from becoming chronic, use a compress made from a decoction of burdock roots. For production you will need one tbsp. a spoonful of crushed burdock roots, filled with 0.5 liters of water. Bring the resulting mixture to a boil, and then keep it on low heat for five minutes. After cooling, the decoction is ready for use. Soak gauze in it and apply to the affected area for two hours. The total duration of the course is three weeks.
Kalanchoe compress
Also, to combat the disease, a compress of Kalanchoe leaves is often used. To make a compress, take a large number of large plant leaves and place them in the refrigerator overnight. In the morning, pour boiling water over the leaves and tap (to release the juice), after which the leaves are applied to the joint. After the sheet dries, it is replaced. The general course of therapy is two weeks.
Coniferous baths
Pine baths are used to relieve inflammation and joint tension. To make a bath you will need: branches, green cones and spruce or pine needles. The ingredients are placed in a saucepan and poured with cold water (at the rate of 300 grams of raw materials per 5 liters of water), then bring to a boil and hold for an additional thirty minutes. Upon completion of preparation, the broth must be left for a day. To use, pour 100 grams of the decoction into a bowl of warm water, lower your feet there and hold them for twenty minutes.
To make a lotion from propolis, you need to add twenty grams of finely chopped propolis to a glass of vodka, close the lid, and then put it in a dark place for one week. Soak gauze or bandage in the resulting liquid and apply to the sore spot for forty minutes. The procedure should be repeated twice a day for two weeks.
Infusions
One of the most effective methods of treatment is taking an infusion of celery seeds. To make it, pour two tablespoons of seeds with two glasses of boiling water, cover with a lid and leave for one and a half to two hours. This infusion should be taken twice a day, one glass. The general course takes two weeks.
What happens if acute bursitis is not treated?
The appearance of protrusion and pain should be a reason to consult a doctor. If treatment is not started in time, bursitis can become more complicated:
- development of an acute purulent process, infection of surrounding tissues, phlegmon;
- development of arthritis with subsequent decrease in limb function;
- the acute course will turn into chronic with constant pain that forces you to leave your profession or sports.
We combine proven techniques of the East and innovative methods of Western medicine
Read more about our unique method of treating bursitis
Operations
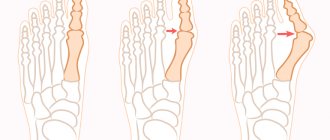
Surgical treatment for foot bursitis is used in severe forms of the disease. Excessive or purulent-containing fluid is removed from the bursa through surgery. This treatment method is also used to straighten the bones of the joint. There are two main techniques: distal (far) and proximal (near) osteotomy. With a distal osteotomy, an incision is made at the far end and the bone is subsequently displaced, thereby reducing the angle of deformation of the big toe. Using a proximal osteotomy, the distal portion is incised to adjust the tendons and reconstruct the bone. Fixation of the changed position of the bones is carried out with special pins.
Recently, laser treatment has been practiced. The peculiarity of this type of surgical intervention is the evaporation of excess tissue under the influence of directed light rays. Surgeries to remove affected tissue are faster and have virtually no side effects.
Why self-medication is dangerous
Self-medication is no less dangerous. A doctor at an appointment can recognize bursitis even by minimal signs. To confirm the diagnosis, he will prescribe an ultrasound, x-ray, MRI and will know exactly where the inflammatory process is located. After this, the doctor prescribes treatment for acute bursitis, which may include:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) – Ibuprofen, Dexalgin, etc.; these drugs also have an analgesic effect;
- in case of a purulent process, the doctor pierces the bursa, removes the pus and rinses the cavity with antiseptics and administers antibiotics;
- in case of severe inflammation, hormonal drugs are injected into the bag;
- prescribes physiotherapeutic procedures.
If all this is not done and treatment is carried out at home with folk remedies, then the risk of developing complications increases sharply, the treatment of which is problematic even for a specialist.
Acute bursitis rarely develops without chronic joint injury. Joint pain requires immediate medical attention. If this is not done, the consequences may last a lifetime.
Sign up for a free initial appointment
Drug treatment
Drug treatment involves the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as: indomethacin, clofezone, ibuprofen, ketoprofen, naproxen, diclofenac, flubiprofen, peroxicam, celocoxib.
These drugs help to: stop the inflammatory process, relieve swelling, relieve pain, prevent spread to neighboring tissues and prevent relapses. When complications occur, hormonal corticosteroids, painkillers and antibiotics (ciprofloxacin, erythromycin, tetracycline, etc.) are used for treatment.
Also, to relieve swelling, it is recommended to use warming ointments, such as diclofenac, diclakgel, dimexide, deep-relief. Drug treatment is always prescribed as an element of complex therapy, which also includes physiotherapy and corrective massage.