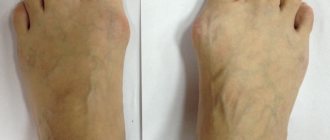
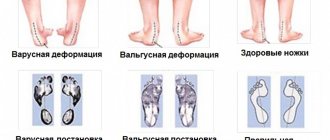
A bowed big toe develops due to deformation or destruction of the joint. Bunion of the big toe, or hallux valgus, is more common in women aged 35 to 40 years. Orthopedic pathology can begin to develop at a fairly young age. It can be caused by incorrect foot placement, injuries, wearing high-heeled shoes, etc.
Deviation in the medial joint between the metatarsal and phalangeal bones of the first toe begins with deformation of the joint capsule. It can become displaced and partially rupture if the base of the foot is disturbed for a long time while wearing high-heeled shoes. In men, such an orthopedic problem is rare and is most often caused by heavy physical labor, injuries to the metatarsophalangeal joints, and the presence of a pronounced degree of flatfoot or clubfoot.
Hallux valgus is characterized by the fact that the head of the metatarsal bone rotates and changes its angle of inclination in the horizontal plane in such a way that it begins to look towards the second metatarsal bone. In this case, the head of the phalangeal bone rushes in the opposite direction. The anastomosis begins to form. As a rule, without timely correction, the process of tissue calcification begins. Osteophytes form between the bones, and gradually they begin to spread around the heads of the bones in the articular cavity. A rather large dense lump is formed, which does not allow for correction of the position of the metatarsal and phalangeal bones.
Hallux valgus can be successfully treated without surgery until a callus forms between the heads of the metatarsal and phalangeal bones. Therefore, if you have any foot deformity, you should immediately seek medical help from an orthopedist. In Moscow, you can sign up for a free initial consultation with this doctor at our manual therapy clinic. The doctor will conduct an examination, review the results of examinations, or prescribe them. Then, after making an accurate diagnosis, he will give all the necessary individual recommendations for correcting the position of the toe.
Causes of curvature of the first phalanx
Curvature of the first phalanx of the big toe can be caused by a variety of reasons. The main factor of negative influence is wearing shoes that are incorrectly selected, too tight or wide, with an uncomfortable last. In women, the pathology may be associated with constant wearing of high-heeled shoes. In this case, such a redistribution of the exerted physical load occurs that it forces the heads of the phalangeal and metatarsal bones to turn out at such an angle as to compensate for the pressure and prevent the destruction of the bones of the big toe.
Curvature and rounding of the big toe may be due to the following risk factors:
- systematic injury to the metatarsophalangeal joint (dislocations, sprains and ruptures of the ligamentous apparatus, bruises, internal hematomas, etc.);
- weakening and degeneration of the muscular and ligamentous apparatus of the foot, often occurs in people with improper foot placement in the form of hyperpronation and hypopronation;
- dysplasia of cartilage and connective tissue in the human body, including those caused by genetic abnormalities and congenital developmental anomalies;
- in children this may be an advanced case of rickets, cerebral palsy or toxicogenic polyneuropathy;
- low arches and weakened muscle tissue;
- neuropathy, including of a discogenic nature (against the background of osteochondrosis, complicated by protrusion, extrusion or herniation of the intervertebral disc);
- arthritis (serous, reactive, rheumatic, gouty, psoriatic, etc.) – inflammation of the cartilage tissue inside the joint capsule, leading to their deformation and destruction;
- endocrine pathologies, including diabetes mellitus, accompanied by diabetic angiopathy and neuropathy, development of diabetic foot;
- excessive joint mobility can be caused by genetic disorders such as Marfan or Down syndrome;
- osteomalacia and osteoporosis (mainly observed in women over 50 years of age);
- hormonal changes in the body (puberty, pregnancy, lactation);
- poor posture and curvature of the spine;
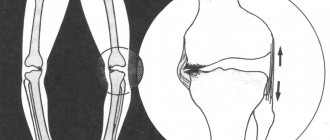
- deforming osteoarthritis of the ankle or knee joint.
Valgus curvature of the big toe can be caused by performing professional duties. Pathology is often observed in waiters, sales consultants, builders, painters, hairdressers, teachers, etc.
With the development of curvature, pathological changes occur in the tissues of the foot. The metatarsal and phalangeal bones are affected. Then the surrounding ligaments, tendons and muscles begin to break down.
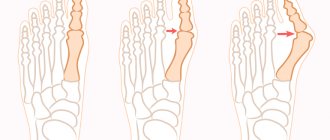
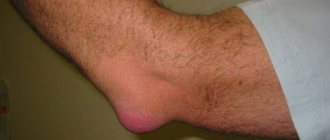
The articulation of the first two metatarsal bones is the first to undergo deformation. The distance between them begins to increase due to divergence. Then, when the displacement of the first metatarsal reaches its maximum, compensatory deformation of the first phalanx of the big toe begins. The adductor muscle weakens and begins to atrophy. The head of the phalangeal bone is displaced and extends slightly beyond the head of the metatarsal bone. A smooth bump appears on the side of the joint. This is the first stage, during which it is possible to restore the normal position of the bones of the toe without surgical intervention.
The second stage of the pathology begins with irritation of the joint capsule and the development of bursitis. Against the background of this disease, the process of destruction of cartilage tissue inside the metatarsophalangeal joint begins. With the complete destruction of the cartilaginous synovial membrane, the process of formation of a massive callus accelerates, which prevents the normal position of the big toe.
Hallux valgus (curvature of the big toe): symptoms, causes, treatment
In this article we will talk about a painful topic in the literal sense - a disease that occurs in every 3 inhabitants of the planet. This disease, like any villain, has several aliases:
- hallux valgus;
- curvature of the thumb;
- growth of a bone on the leg;
- bursitis;
- hallux valgus, etc.
Since this is a foot disease, it brings a lot of discomfort. When a bunion grows, it is difficult to stand on your feet for a long time due to pain, and it is especially difficult to choose shoes that do not squeeze or put pressure on your toes. Almost each of us, if we have not encountered a curvature of the thumb ourselves, have seen it in relatives. This disease does not have a general pattern, is difficult to treat, and sometimes is not treated at all. Symptoms Manifestations of hallux valgus or bursitis are easy to notice. The symptoms are as follows: a small bump appears on the foot near the big toe, which quickly increases in size, turning into a rather voluminous growth. The toes seem to fall to the side, and not only the arch of the foot itself is bent, but the anatomical arches are also disrupted. Self-diagnosis If you find yourself with an actively growing bunion near your big toe, first determine its color - this will help you find out what the problem is. It is better to carry out diagnosis in the morning, as soon as you wake up. If the bone is skin-colored and does not have any specific color or shade, this may indicate that you have one of the types of flat feet. If the bone is red, this indicates inflammatory processes. This reddened bone is called bursitis. Bursitis is an inflammatory disease characterized by the accumulation of fluid. This inflammation is preceded by bruises, abrasions, etc. The injury may even be old, and the inflammation has only just begun. Another cause of bursitis is an infectious disease. If you notice that the bone is red in the morning (that is, this is not a consequence of rubbing the foot with shoes), then you should consult a doctor. Bursitis can only be treated with medication, namely with the help of tablets, anti-inflammatory ointments, etc. Causes of hallux valgus Genetic predisposition. If you have noticed a curvature of the thumb in one of your relatives, then most likely it has been genetically passed on to you. Shoes. One of the main causes of bunion toe is the use of the wrong shoes. This problem is of great concern to girls and women who have to walk a lot in high heels. This worry is justified: orthopedists recommend wearing square heels up to 4 cm - and only those. Anything higher is harmful to the foot, especially stiletto heels, because the entire load while walking falls on the metatarsus of the foot. If you have already succumbed to the influence of the fashion for high heels, there is a way out: you need to use special inserts that will make walking easier, while preventing you from slipping in the last. Flat feet. Not everyone knows that there are two types of flat feet: longitudinal and transverse. Longitudinal is a classic type of flatfoot, known to everyone. It is easily recognized by the lack of bending and the completely flat surface of the foot. It is precisely with this flatfoot that people are not accepted into the army. Transverse is the type of flatfoot that directly relates to the curvature of the foot in the form of valgus deformity. A characteristic feature of this type of flatfoot is the presence of corns and calluses, mainly in the metatarsus area. The ideal foot should have a bend under the big toe; it is this bend that will indicate the presence or absence of transverse flatfoot. Since the arches of the foot do not work with transverse flat feet, accordingly, the toes will shift, collapse, and become deformed. On the right foot the toes will point to the right, and on the left foot to the left. With advanced valgus deformity, the big toe intersects with the middle toe. Treatment Since hallux valgus is mainly a consequence of transverse flatfoot, treatment methods will specifically address this cause. For information: there is no cure for any type of flatfoot. To help those suffering, there are only special orthopedic insoles and inserts that prevent the further development of the disease. Deformation must be dealt with in a comprehensive way. Using only one method will not bring any results, or you will wait a very long time for it. Treatment or correction of a large bone, depending on the stage of neglect, takes from a month to 4 months. What does the complex to combat hallux valgus consist of? Using orthopedic insoles They will help relieve the load, but will also properly align the arches of the foot and give it the correct shape. Orthopedic insoles should have an instep support and a metatarsal cushion (pad under the transverse arch). This is a small insert in the form of an inverted drop, which is placed under the thumb. It is she who raises the transverse arch, while the fingers move apart and take the correct position. There are also many orthopedic devices made from medical grade silicone. For example, interdigital inserts that help adjust and spread your fingers. There are also special bandages designed to straighten the thumb. But they are bulky and cannot be used with most shoes. That's why they are used at night. Proper shoes It is necessary to ensure that the heel height is up to 4 cm. Properly selected shoes will prevent further problems with the foot. Surgical treatment If the process of hallux valgus deformity is severely advanced, that is, the foot is bent, the big toe fits onto the middle toe, and other toes fit on top of each other, bandages or valgus inserts alone will not help the matter. This will require surgery and the work of a surgeon. Hallux valgus is a problem that needs to be noticed in time and treated, then no further problems will arise. With a certain regularity and responsibility, you will definitely overcome this disease.
Curvature of the big toe in a child
Juvenile hallux valgus is a consequence of disproportionate growth of muscle, ligament, tendon and bone tissue. During adolescence, excessive bone growth may occur. At the same time, the development of muscle fiber and ligamentous apparatus lags significantly behind. This creates the preconditions for deformation of the most vulnerable joints. The metatarsophalangeal joint is deformed primarily in those adolescents who lead an active lifestyle and spend a lot of time on their feet. Incorrectly selected shoes for everyday wear and sports, or impaired foot placement in the form of flat feet or club feet can significantly aggravate the course of orthopedic pathology.
Curvature of the big toe in a child at an early age can be caused by congenital genetic abnormalities. Children with cerebral palsy often experience neuropathy and cavus. In this case, the joint between the first phalanx and the metatarsal bone may collapse and deviate. Pathology is often observed in children whose parents chose the wrong shoes for their first steps. Then the habit of placing the foot incorrectly is formed, with an uneven distribution of physical and shock-absorbing load.
Toe deformity
Each of the small toes consists of three phalanges. The proximal phalanx articulates with the metatarsal bone proximally to form the metatarsophalangeal joint (MTP) and the middle phalanx distally to form the proximal interphalangeal joint (IPJ), the middle phalanx articulates with the distal phalanx to form the distal interphalangeal joint (DIJ).
Extensor digitorum longus is an extrinsic muscle of the foot, i.e. a muscle located not on the foot, but on the lower leg, is the primary extensor of the metatarsophalangeal joint (MTP). The extensor digitorum brevis muscle is an intrinsic muscle of the foot that extends the toe at the proximal interphalangeal joint (PIPJ) and distal interphalangeal joint (DIPJ).
The flexor digitorum longus muscle is another extrinsic muscle and flexes all three joints of the finger, but primarily at the distal interphalangeal joint (DIPJ). The flexor digitorum brevis muscle (intrinsic muscle of the foot) primarily flexes the PIPJ. The lumbrical muscles originate from the metatarsal bones and perform flexion of the MCP joint and simultaneous extension of the PIP joint and DMFC.
On the side of the plantar surface in the area of each finger there is a fibrocartilaginous plantar plate, which is a thickening of the capsule that passively resists excessive extension of the finger.
The reasons underlying the development of deformities of the small toes may be:
- Diabetes mellitus with peripheral neuropathy
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Primary neuromuscular disease (poliomyelitis, Friedreich's ataxia, myelopathy, multiple sclerosis, or Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease)
- Other foot deformities, such as hallux valgus, flat feet, or cavus feet
Claw deformity
Claw deformity is a consequence of an imbalance between the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the foot, which leads to flexion at the PIP joint and extension at the MCP joint. The PMJ rises up and begins to constantly come into contact with the shoes, as a result of which a painful callus is formed here (Fig. 1).
Rice. Claw-shaped fingers. Most often, the deformity of the second toe is most pronounced, but in this case there is deformation of all the small toes.
If only one finger is deformed, it is most often caused by injury or an inflammatory disease. More often, all four small toes are deformed, and the reason for this is hereditary muscle imbalance (external muscles > intrinsic muscles) or nerve damage (neuropathy).
Claw-shaped deformity of the fingers can be congenital or acquired; it is observed at any age, but somewhat more often in old age (70-80 years). It occurs 4-5 times more often in women than in men.
Hammertoe and hammertoe deformities
Hammertoes are usually caused by wearing tight shoes that keep the toe in a bent position. Also, this deformity is often found in patients with hallux valgus deformity of the 1st finger.
Hammertoe deformity (i.e., isolated flexion of the DMJ) may result from compression of the toe in the shoe (and gradual thinning of the extensor tendon). Also, the cause of this deformity may be excessive tension of the long flexor of the 1st finger.
How does curvature manifest itself?
Curvature of the big toe manifests itself in the form of clinical symptoms. They may include the following signs of trouble:
- visible violation of the position of the bones with a protruding lump on the side of the joint;
- pain in all toes after even a short walk;
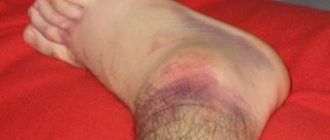
- periodic appearance of signs of inflammation in the area of the affected joint (redness of the skin, swelling, pain on palpation);
- with a long course of the pathology, swelling becomes almost constant and intensifies in the evening hours;
- bone growths form, making it difficult to walk and wear normal shoes;
- a dry callus forms with a core on the plantar part of the foot between the first and second toes.
- Without timely treatment, external curvature of the thumb provokes the development of the following diseases with corresponding clinical manifestations:
- deforming osteoarthritis of all joints between the metatarsal and phalangeal bones of the foot;
- chronic form of bursitis with gradually developing calcification;
- exostosis, osteophytes, contracture;
- transverse, longitudinal or combined flatfoot;
- deformation of the ankle, knee and hip joints.
To carry out diagnostics, the correct choice of specialist is important. Treatment should be carried out by an orthopedist. During the examination, the doctor evaluates the condition of the foot and its joints. Then an x-ray is taken, which shows the position of the heads of the bones in the joint capsule. If necessary, an MRI examination may be prescribed.
How to treat a bowed big toe
Before treating a bowed big toe, the doctor conducts an examination and determines the degree of destruction of the metatarsophalangeal joint. If this is the third degree of development of orthopedic pathology, then correction is best done through surgery. After the early postoperative period has passed, it is important to begin full rehabilitation. A set of procedures will eliminate the cause of the curvature, which will help prevent relapse. Strengthening the muscle, ligament and tendon apparatus will restore the functionality of the foot.
At earlier stages, treatment of a curvature of the big toe is carried out exclusively by conservative methods. The doctor’s efforts should be aimed at restoring the correct position of the bone heads in the articular cavity. Great attention is paid to strengthening the muscular and ligamentous apparatus, since it is this that fixes the metatarsal and phalangeal bones in their normal position.
In our manual therapy clinic, the following types of treatment are used to treat bunion of the big toe without surgery:
- laser therapy – allows you to restore the physiological structure of tissues, eliminate salt deposits and scar deformities;
- therapeutic exercises and kinesiotherapy – strengthen muscles and ligaments, accelerate the correction process, and prevent the development of relapse in the future;
- massage and osteopathy - accelerate microcirculation of blood and lymphatic fluid, enhance nutrition of all damaged tissues, improve their elasticity and permeability;
- physiotherapy can speed up the process of cellular regeneration;
- reflexology has a general strengthening effect, starts the regeneration process by using the hidden reserves of the human body.
If you are looking for effective and safe treatment for your bunion, make a free appointment with a podiatrist at our chiropractic clinic. The doctor will examine you, make a diagnosis and tell you whether you can be helped using manual therapy methods.