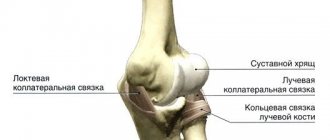
The prevalence of diseases of the musculoskeletal system ranks second in the world after pathologies of the heart and blood vessels. Every third inhabitant of the Earth suffers from diseases of the joints, spine, ligaments, muscles or bones.
However, any illness can be countered if you arm yourself with information against it. The portal osustave.com tells you how to regain the joy of free movement and live a physically active life at any age.
The site materials were prepared for you by practicing doctors. Each author has a wealth of academic knowledge behind him, as well as experience in successful treatment and prevention of diseases of the musculoskeletal system in adults and children. Their recommendations are based on scientific research and proven traditional medicine methods.
The articles are addressed to readers without medical education and are written in easy to understand language. If you have any questions, ask them in the comments.
For convenience, the articles are divided into thematic sections. Each of them contains information about the causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of a group of diseases, as well as the medications that are prescribed for them.
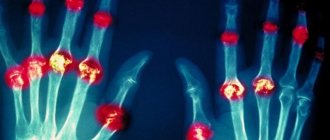
Arthritis
Different types of arthritis: 1 – reactive;
2 – rheumatoid; 3 – psoriatic Inflammation of the joints – arthritis, is considered to be an ailment of the elderly. However, youth is not a guarantee that an insidious disease will not one day burst into your life. According to WHO statistics, every third person suffering from this pathology is under 65 years of age. People of all ages, even infants, are susceptible to arthritis in one form or another. But they occur in different ways, and making an accurate diagnosis is not so easy.
From this section you will learn:
- Which doctor should you contact if you suspect arthritis?
- Why and how joint inflammation affects the heart.
- How to get rid of debilitating pain from chronic arthritis.
- Who is more at risk of loss of joint mobility due to arthritis.
- What consequences can reactive arthritis cause in children?
Incidence (per 100,000 people)
| Men | Women | |||||||||||||
| Age, years | 0-1 | 1-3 | 3-14 | 14-25 | 25-40 | 40-60 | 60 + | 0-1 | 1-3 | 3-14 | 14-25 | 25-40 | 40-60 | 60 + |
| Number of sick people | 0 | 0 | 1.8 | 8.6 | 8.6 | 9.2 | 8.8 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 |
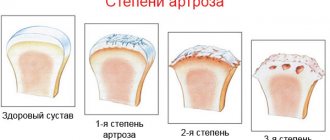
Arthrosis
Arthrosis: 1 – knee joint;
2 – hip joint; 3 – elbow joint “If the doctor diagnosed arthrosis, then all is lost,” - for some reason many who have encountered this disease still think. Although arthrosis - a chronic joint pathology associated with damage to the cartilage lining - is no longer a death sentence. Gymnastics and properly selected medications successfully restore mobility to diseased joints, if the disease has not gone too far.
In this section you will find answers to the questions:
- Why do some people develop arthrosis and others do not?
- Is it possible to cure arthrosis with folk remedies?
- Which diagnostic methods most accurately determine the stage and form of joint damage.
- Who is given a disability group for arthrosis?
- What are the most effective methods of treating arthrosis?
Treatment
Treatment of prepatellar bursitis depends primarily on the cause of the bursitis and secondarily on pathological changes in the bursa. The main goal of treatment is to control inflammation.
Friends, this and other questions will be discussed in detail at the seminar “Diagnostics and treatment of problems in the joints of the lower extremities.” Find out more...
- In the first 72 hours after injury or when the first signs of inflammation appear, adhere to the RICE regimen (rest, ice, compression (pressure bandage), elevated position of the limb).
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may relieve pain. Topical agents may also be a good choice for reducing gastrointestinal side effects. In cases of septic prepatellar bursitis, antibiotics are used to suppress the inflammatory process.
- Corticosteroid injections.
Surgery
If conservative treatment of chronic/post-traumatic prepatellar bursitis is ineffective, outpatient arthroscopic bursectomy under local anesthesia is an effective procedure. Arthroscopic or endoscopic excision of the bursa shows better results than open surgery.
Physical therapy
The RICE method is effective for the initial treatment of prepatellar bursitis (level of evidence: 2a). The “rest phase” implies a short period of immobilization. This period should be limited to the first days after the injury. Rest reduces the metabolic demands of damaged tissues and reduces blood flow. The use of ice leads to a local decrease in temperature, vasoconstriction and reduction of bleeding. Cold also reduces the severity of pain, which is associated with an increase in the threshold of irritation of free nerve endings and synapses. Do not leave the ice in for too long (no more than 20 minutes at a time, 30-60 minutes apart). Compression allows you to reduce intramuscular blood flow in the affected area, as well as reduce swelling. Elevating the limb ensures that the hydrostatic pressure will decrease, resulting in a decrease in the amount of interstitial fluid. It also reduces pressure in local blood vessels and helps limit bleeding. However, the effectiveness of the RICE method has not been proven in any randomized clinical trial.
Once the inflammation has subsided, you can move on to gentle stretches and exercises, which will restore range of motion and strengthen the muscles, as well as reduce stress on the tendons and knee joint. Therapeutic exercises for strengthening and stretching the knee muscles include exercises for static contraction of the quadriceps femoris muscle. These should be exercises that the patient can perform at home 1-3 times a day. The goal of rehabilitation is for the patient to resume his daily activities.
To understand if the exercise is working, you should place your fingers on the inside of the quadriceps muscle - as you perform the exercise, you will feel its contraction. The patient must hold it in this position for 5 seconds. The exercise can be repeated 10 times with maximum strength. It is important to remember that this exercise should be painless.
Stretching the quadriceps muscle is also a good exercise because it reduces friction between the skin and the patellar tendon. When the patellar tendon is more flexible, less friction occurs. A physical therapist can help a patient using electrotherapy techniques. It is of great importance to explain to patients the role of knee pads when performing professional activities.
Bursitis
1 – bursitis of the elbow joint;
2 – ankle bursitis; 3 – bursitis of the knee joint Bursitis is an inflammation of the periarticular bursa, unlike arthrosis and arthritis, it often attacks the young and active. It can be either an independent pathology or a manifestation of systemic diseases that affect organs and tissues of the entire body. Often this disease is disguised as other diseases of the musculoskeletal system - arthritis, myositis, tendonitis. To bring the “cunning” person to light, you need a consultation with an experienced rheumatologist or orthopedist.
The section dedicated to bursitis contains the following information:
- How to effectively relieve pain when the bursa of the elbow, shoulder, knee, and ankle joints is affected.
- What can long-term bursitis lead to if it is not treated?
- What methods of treating bursitis give the fastest results?
- What is more dangerous in terms of consequences – chronic arthritis or bursitis?
- How to avoid developing bursitis when playing sports.
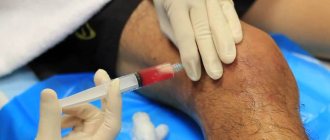
Diagnostics
Puncture of synovial fluid allows you to determine the bacterial nature of inflammation
The affected articulation in the knees and deep infrapatellar bursitis, like other forms of the disease, are helped by diagnosis. Without it, the doctor will not be able to give the patient a correct diagnosis. Initially, the specialist must collect an anamnesis of the patient and his relatives. This information will help him identify a person’s genetic predisposition to certain disorders.
Upon completion of the history taking, the rheumatologist or arthrologist will ask the patient to tell about all the symptoms that bother him
It is very important to indicate the exact time when signs of inflammation appeared
The infrapatellar form of bursitis is easily diagnosed. This is because the area inflamed with this disease is located close to the surface of the skin.
To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor may ask the patient to undergo the following diagnostic measures:
- Taking a puncture to determine the composition of the exudative fluid. Additionally, culture is carried out on special media, which helps determine the bacterium and its sensitivity to specific antibiotics;
- X-ray, CT and MRI. These measures are necessary if the inflamed knee is severely injured. These investigative procedures can identify a crack or fracture.
Only after carrying out all the diagnostic procedures will the doctor be able to understand what exactly is bothering his patient. If necessary, the rheumatologist will refer the patient for consultation to another doctor if he is diagnosed with concomitant diseases that affect the course of bursitis.
Dislocation of joints
Appearance of a dislocated patella
Joint dislocations occur as a result of injuries - perhaps everyone knows about this. However, they are not only acquired, but also congenital. And also chronic, or rather habitual, which occur from careless movements or light impact on the affected joint. Habitual dislocation is the result of weak joint ligaments, which some people inherit.
This section tells:
- About the symptoms of a dislocated joint and the rules of first aid for the victim.
- About the difference between a dislocation and a subluxation.
- How to strengthen joints and ligaments with habitual ankle sprains.
- How to recognize congenital dislocation in a child.
- What are the consequences of untreated congenital dislocation of the hip joints?
Knees
The knees are the largest and most complex joints in the human body. And one of the most susceptible to injuries and pathologies. They bear the load almost all the time a person is awake, even when sitting and standing. Therefore, it is not surprising that with age, diseases of the knee joints make themselves felt among the first. However, if you take care of the health of your knees from a young age, there is a chance you will never know how much they hurt.
The section on knee health will help you find out:
- What diseases are a sign of a crunch when bending the legs?
- How does damage to the meniscus of the knee joint manifest?
- What does pain indicate when bending and straightening the knee?
- How to treat Baker's cyst.
- About the most effective first aid remedies for severe knee pain.
Clinical signs
The symptoms of suprapatellar bursitis directly depend on the course of the inflammatory process, which can be acute or chronic. In the acute period of the disease, the clinical manifestations are quite pronounced and are accompanied by the appearance of a soft elastic tumor above the knee, swelling and redness.
As the disease progresses, the symptoms increase, the patient notices external changes in the knee joint and a deterioration in overall health.
Typical signs of acute suprapatellar bursitis include:
- rounded swelling above the knee, which can be more than 11 cm in diameter;
- sharp and burning pain that intensifies with any movement of the joint;
- stiffness of movements;
- redness and hyperemia;
- increased body temperature;
- general signs of intoxication of the body.
When palpating the knee, the pain increases, and you can feel the fluid moving inside (fluctuation). If the disease manifests itself against the background of an injury, the symptoms may be less pronounced than with the penetration of an infection, the pathogens of which release toxic products of their vital activity, thereby causing severe intoxication of the body.
The clinical manifestations of the chronic course of the disease are not as pronounced as those of the acute form. When palpating the knee, an elastic formation is felt, which causes slight pain when pressed. It can intensify with changes in weather, increased physical activity, hypothermia, or exacerbation of concomitant pathologies. At times, the knee may swell slightly, turn red, and the overall body temperature rises. Despite the absence of pronounced symptoms, the chronic form causes discomfort and therefore requires competent therapy.
In the absence of proper treatment or the presence of an acute infection, purulent inflammation with a pronounced clinical picture can develop in the bursa cavity. The patient experiences elevated body temperature, acute attacks of pain, severe swelling, and redness of the knee.
With such symptoms, it is extremely important to consult a doctor in time in order to exclude serious complications in the form of an abscess or phlegmon, which require surgical treatment
Osteoporosis
The seemingly harmless diagnosis of “osteoporosis” is actually very insidious. In old age, this disease poses a serious threat to life, along with heart attacks and strokes. Osteoporosis is a pathological decrease in bone density that threatens fractures from minor injuries, which leave a person bedridden for months and years, or even for life. Its main cunning is its imperceptible asymptomatic development.
From the section on osteoporosis you will learn:
- Are there effective methods for strengthening damaged bone tissue?
- Why osteoporosis should be treated before it makes itself felt.
- How to avoid fractures if osteoporosis has already developed.
- How to eat properly with this disease.
- What habits increase the risk of osteoporosis complications.
Osteochondrosis
Pathological changes in spinal osteochondrosis.
Spinal osteochondrosis is the scourge of our time. Today, almost everyone who consults a doctor with complaints of back and neck pain receives this diagnosis, if other pathologies cannot be identified. However, a number of experts consider osteochondrosis to be an imaginary disease, under the mask of which a variety of ailments are hidden - from diseases of the digestive system to neuroses. Therefore, approaches to its treatment also vary greatly.
In this section you will find information:
- About an effective set of exercises to relieve pain in the neck and back.
- About the relationship between osteochondrosis and surges in blood pressure.
- On the prevention and approaches to the treatment of osteochondrosis in pregnant women.
- About massage and self-massage techniques to relieve muscle spasms in the spine.
- About medicinal and non-traditional methods of treating osteochondrosis.
Gout
Gouty tophi of various localizations
The “royal” disease of gout is by no means a reason for joy. This disease is associated with the deposition of sharp crystals of uric acid salts in the joints, which cause extremely intense attacks of pain accompanied by symptoms of inflammation. In addition, the affected joints become overgrown with nodules - gouty tophi, which leads to deformation of the affected area of the body. And this area most often turns out to be the feet and hands.
The section on gout says:
- About the differences between gouty arthritis and its other forms.
- About which remedies relieve gout attacks faster.
- About ways to remove uric acid salts from the body.
- About the prevention and treatment of gout with diet.
- About the prospects for complete recovery at different stages of gout.
Drugs
Every patient needs to know medications that are used in the treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system. This section is a reminder that contains information about the types and groups of medications; about dosages, courses and rules of administration; about combinations of drugs with each other; about in what cases this or that drug is prescribed. And remember, this is not a self-medication guide! Everything you take orally must be prescribed by a doctor!
It also says:
- About the latest advances in the field of drug therapy for diseases of the joints, ligaments, muscles and bones.
- About affordable and effective analogues of expensive drugs.
- About what chondroprotectors are and how effective they are.
- About contraindications and side effects when taking medications.
- About means for relieving pain attacks that can be used without prescription.
Drug therapy
The basis of treatment for suprapatellar bursitis is the use of medications that help cope with the symptoms of the disease, its causes, improve the functionality of the knee, and reduce the risk of complications. In practice, doctors often use the following medications:
- NSAIDs - relieve inflammation, reduce pain, have an antipyretic effect: Diclofenac, Movalis, Ortofen, Ketorolac, Nimesulide, Ketorol.
- Steroid hormones - prescribed for severe inflammation in the knee joint: Diprospan, Depo-Medrol. Used for intra-articular administration. Such a procedure can only be performed in a hospital setting by a doctor or medical professional.
- Anesthetic ointments, gels, applications - contain synthetic or natural components, have the ability to relieve inflammation, eliminate pain: Espol, Fastum gel, Espol, Apizartron, Diclofenac.
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed only if there is an infectious focus in the joint cavity. Their intake has a detrimental effect on pathogenic microorganisms, causes their destruction, and stops the spread: Ceftriaxone, Emsef, Amoxiclav, Panclave. The need to take antibiotics also appears after surgery to remove joint fluid. The course of treatment is prescribed individually, but generally does not exceed 5–10 days.
- General strengthening drugs, vitamin-mineral complexes, supplements.
The effect of drug treatment can be noticed already on the second day of treatment. The main thing is to strictly follow the doses and recommendations prescribed by your doctor.
Rest
The “Rest” section contains articles on topics that are not included in other sections of the site. Here you can find information about rare pathologies of the spine, muscles and bones; about unconventional but worthwhile treatment methods; on the diagnosis and complications of diseases of the musculoskeletal system; about the rehabilitation of chronic patients, obtaining a disability group and much more.
You can also read here:
- About emergency conditions for diseases and injuries of the musculoskeletal system, as well as about the rules for providing first aid for them.
- About the influence of bad habits and nutrition on joint health.
- About how the child’s skeleton and muscles are formed and developed.
- About the influence of diseases of other organs and systems on the musculoskeletal system.
- About the principles of a healthy lifestyle and the secrets of maintaining physical activity into old age.
Forget about pain. Breathe deeply. And let your muscles be strong, your bones strong, and your joints young!