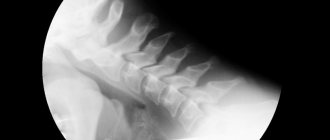
Osteoarthritis of the joints is a group of diseases of a degenerative-dystrophic nature, the unifying feature of which is damage to articular tissues (bone, muscle, etc.).
The disease is classified as chronic and occurs as a result of tissue wear and tear. The development of secondary pathologies is often observed, including arthritis and arthrosis.
There are two types of osteoarthritis:
- primary is a frequently diagnosed type that affects joints of various sizes and locations. They manifest themselves predominantly as pain and stiffness, but may have various features;
- secondary – quite rare. This type of pathology is often caused by various types of injuries and pathologies.
Most often, osteoarthritis occurs as a result of inflammation or tissue damage and can be localized in various parts of the musculoskeletal system. The rate of development of the pathological condition is quite slow, which significantly complicates the diagnostic process.
In order to identify the first signs of the disease in time and be aware of the general clinical picture, it is important to know the answers to a number of important questions that are covered in this article.
How does osteoarthritis develop?
The health of the joint directly depends on the synovial fluid, which acts as an important lubricant and eliminates the possibility of friction on the surfaces of the articulation elements. In this regard, metabolic disorders play a key role in the development of joint osteoarthritis.
Biochemical disorders lead to a deterioration in the quality of synovial fluid, which significantly reduces its properties and is the starting point of destructive processes. When the lubricant deteriorates, the first thing that is negatively affected is the shell responsible for filtering the most important nutrient for connective tissue (cartilage) - hyaluronic acid, which is not only synthesized, but is also retained in the tissues with its help.
Consistently correct circulation of synovial fluid in the joint cavity ensures a full volume of substances. If this process is disrupted, there is a lack of nutrition of the cartilage, due to which its surface is deformed, which inevitably leads to the appearance of various types of defects.
Degrees of osteoarthritis
Today, it is customary to distinguish three key degrees of osteoarthritis, each of which is characterized by a specific clinical picture.
1st degree of osteoarthritis – initial
There is a certain soreness that occurs mainly with excessive stress on the affected joint.
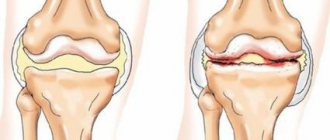
As a result of the instrumental diagnostic method (radiography), a slight reduction in the joint space can be determined.
2nd degree of osteoarthritis – formation of osteophytes
At this stage, pain may appear with normal levels of physical activity, however, it can only be eliminated with the help of medications.
A characteristic feature of this stage of pathology development is a visually noticeable deformation.
Based on the results of the X-ray examination, you can notice not only a narrowing of the joint space, but also obvious bone growths.
Grade 3 osteoarthritis – severe arthrosis
The patient complains of constant pain. There is a visually noticeable, persistent deformity that leads to a noticeable violation of the axis of the limb.
Limitation of mobility leads to atrophy of the muscle frame, which can lead to a change in limb length.
Based on the results of an X-ray examination, it is impossible to determine the joint space. The surface of the articulation elements is greatly changed, and numerous bone growths are observed.
Symptoms and diagnostic methods
Symptoms are usually similar regardless of the location of the lesion.
It manifests itself as follows:
- Severe pain in the affected area. Manifests itself in the form of attacks after being in stationary positions and physical activity. If a person gets up and stretches, the pain may go away, but as the disease progresses, it may become permanent.
- Joint deformation occurs.
- During an exacerbation, the affected area swells.
- Due to deformation of the vertebrae, the vessels are pinched and blood circulation worsens. This can provoke migraines and toothache.
- The patient feels constantly unwell.
- Movement is limited due to pain.
- With sudden movements, a crunching sound in the affected vertebrae is possible.
In order to diagnose a disease, the doctor needs to study the history of its development, interview the patient and, through palpation, determine the location and intensity of pain.
However, this is rarely enough, so an x-ray, blood sampling (to rule out rheumatism), or an MRI (to identify disc lesions) may be indicated .
Video: “What is osteoarthritis of the spine?”
More about degenerative processes in the spine in the following articles:
- The clinical picture of spinal arthrosis is described on the page
- Why do degenerative changes in the lumbar spine occur?
- You can learn about the symptoms and diagnosis of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the neck here
What are the causes of osteoarthritis?
The disease in question has a fairly variable clinical picture, which depends on a large number of factors. However, despite this, a large number of diagnosed cases made it possible to identify a list of the most likely causes of osteoarthritis, which include:
- systematic loads caused by the characteristics of work or hobbies (sports, etc.);
- systematic stress, depressive states and other neurological disorders;
- genetic predisposition;
- previously suffered arthritis and arthrosis of the inflammatory type;
- the presence of infectious diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- complications after surgery or serious injury;
- lack of muscle tone;
- excess body weight;
- natural age-related changes;
- abuse of bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol, overeating).
Who is at risk for joint osteoarthritis?
As with any other disease of the degenerative-dystrophic type, taking into account certain characteristics and causes of osteoarthritis, a risk group can be identified, which includes:
- people over 45 years of age, overweight and leading a sedentary lifestyle;
- women during periods of serious hormonal changes (during natural or surgically induced menopause);
- men and women of different ages who have suffered musculoskeletal injuries;
- specialists practicing heavy professional work (mainly physical), for example, loaders, drivers, sellers, etc.
What are the key symptoms of joint osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis is one of the special pathological conditions that have a fairly low rate of development, which indicates difficulties in diagnosis at the initial stages. For this reason, it can be seen that the symptomatic picture becomes more pronounced over time, but at the same time carries serious consequences.
Among the main symptoms of the pathological condition are:
- the appearance of painful discomfort/severe dull aching pain in the upper/lower extremities or lumbar/sacral spine;
- accompaniment of movements with a characteristic crunch;
- limitation of mobility of varying degrees, reduction in the amplitude of available movements;
- stiffness in the morning after waking up;
- barely noticeable visually, but quite noticeable inflammatory processes localized in the upper/lower extremities or various parts of the spinal column;
- aching pain that occurs mainly at night or at rest;
- inability to perform basic physical exercises;
- local swelling, swelling of tissues at the location of the disease;
- formation of osteophytes (bone growths).
It is important to note that the earlier symptoms are identified, the greater the chances of successful completion of complex and relatively quick treatment.
Causes of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
The causes of pain syndromes in osteochondrosis of the thoracic region, as well as in other types of osteochondrosis, are pathological changes in the intervertebral discs (thinning of the disc due to dystrophy of the nucleus pulposus, protrusion; intervertebral hernia) and spinal joints (destruction of cartilaginous surfaces, formation of osteophytes).
As a result of these changes, compression of the radicular structures of the spinal nerves (radiculopathy), compression of the spinal cord (thoracic compression myelopathy), damage to the spinal cord due to impaired blood supply due to constriction, narrowing of the supply arteries and veins (compression-vascular myelischemia) may occur.
What is the diagnosis of joint osteoarthritis and which doctor is best to consult?
A rheumatologist diagnoses and treats diseases of the musculoskeletal system. To seek advice and receive a referral for treatment, you must first of all see a therapist who will conduct an examination, collect anamnesis and make the best decision on further actions.
Before starting treatment, each patient who seeks professional medical help with characteristic symptoms is sent for a comprehensive diagnostic examination, which involves the following stages:
- passing laboratory tests - conducting a general biochemical analysis allows you to get a fairly detailed picture of the existing disease and makes it possible to assess the level of substances contained, as well as the beginning of the development of pathological processes;
- X-ray examination - X-ray examination allows you to obtain images that clearly display the structure of the tissues and clearly visible damage to the bone or other elements of the joint, and bone formations (if any) are easily determined;
- arthroscopy is a minimally invasive diagnostic operation involving endoscopic examination of synovial fluid, the results of which provide the specialist with the opportunity to accurately assess the presence of any pathology, infection or inflammatory process.
Regardless of how intense the manifestation of the symptoms of a degenerative-dystrophic disease, in order to eliminate the possibility of making a false diagnosis, as well as to clarify the existing stage of development of pathological processes, each patient is required to undergo laboratory and x-ray examination.
What is an orthopedic regimen for neck arthrosis?
Patients with arthrosis of any joint, including those using synovial fluid prosthetic preparations or other medications, are shown a special orthopedic regimen that will help avoid complications:
- It is necessary to carefully control your posture, avoiding curvature.
- During sedentary work, short breaks for physical activity are required.
- Orthopedic collars from Shants help relieve stress from the cervical region - according to the doctor’s indications.
- An orthopedic mattress and pillow will not be superfluous.
How to choose and wear a Shants collar?
Complex treatment of arthrosis of the cervical vertebrae also includes special gymnastics and professional massage. With the help of turns and rotations, bending and throwing back the head under the supervision of an instructor, it is possible to develop the motor capabilities of this part of the spine.
Intra-articular injections of the synovial fluid substitute “Noltrex” are not practiced for this type of arthrosis due to the specific localization. Instead, the patient may be offered professional massage or hardware methods for local and safe development of the deep and superficial back muscles. The main thing is to find a good specialist, trust him and not let the course of the disease run its course.
How is osteoarthritis of the joints treated?
The treatment plan is determined individually, taking into account factors such as:
- collected anamnesis;
- existing complaints;
- results of diagnostic examination;
- individual characteristics of the patient.
In order to achieve the most effective result, complex treatment is used, involving procedures such as:
- drug therapy (taking drugs from groups: analgesics, glucocorticosteroids, muscle relaxants, chondroprotectors) – aimed at preventing the development of pathological and activating regenerative processes;
- physiotherapeutic methods (massage, physical therapy, exposure to electric current/magnetic field, etc.) - play the role of supportive therapy, providing the opportunity to accelerate conservative treatment and activate regenerative processes;
- surgical intervention (endoprosthetics, etc.) is important when diagnosing advanced cases. Such a radical method involves removing the source of pathological processes followed by plastic surgery of the affected fragment of the joint.
It is worth noting that drug therapy plays a vital role in the treatment of osteoarthritis, because by taking drugs it is possible not only to get rid of symptoms, but to literally eradicate the problem/its consequences.
One of the most significant groups of drugs is considered to be chondroprotectors, which help joint tissues regenerate. The most commonly prescribed drug is considered to be Artracam.
Treatment
Without proper treatment, osteoarthritis of the spine will progress, which will subsequently lead to constant severe pain.
The treatment program depends on the severity of the disease. In some cases, especially in the early stages, wearing special support bandages is indicated.
Physiotherapeutic procedures are effective: massage, acupuncture, electrical nerve stimulation, therapeutic baths, electrophoresis, therapeutic exercises.
Nutritional supplements and vitamin complexes are prescribed as supportive medications. To reduce pain, analgesics, anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs, ointments and topical creams are indicated.
In case of serious damage to tissues and bones, surgery is indicated for the patient.
What is the prognosis for osteoarthritis of the joints?
It is literally impossible to make unambiguous predictions in the situation under consideration.
The chances of recovery and the success of the upcoming treatment are largely determined by the timeliness of seeking professional help.
It can be noted that, considering the issue of predicting the situation from the point of eliminating morphological changes, the conclusions are not comforting, which is due to the impossibility of complete restoration of the affected tissues.
The presence of pathology in old age indicates the complexity of the course of the disease, relative to the clinical picture of younger patients.
To summarize, we can come to the conclusion that, regardless of the situation, the most positive prognosis (elimination of complaints and full/partial restoration of motor function) is possible only if you contact your doctor in a timely manner, as well as if all recommendations and prescriptions are followed.
What complications can occur in advanced cases or untreated osteoarthritis of the joints?
If the disease develops uncontrolled and there is no treatment, a person will most likely have difficulty moving independently, which significantly increases the risk of injury due to numerous bruises and falls.
Damage to the foot can lead to pain during walking and inflammation of the big toe of the lower extremity.
In the vast majority of cases, the severe form, when refusing to seek medical help, negatively affects the patient’s performance. In some cases, this can be avoided by making some changes.
Other complications include:
- loss of motor ability;
- the occurrence of chronic arthritis and arthrosis;
- loss of spinal column stability;
- complete immobilization of the limb and disability.
It is worth noting that, among other things, there are also risks of postoperative complications, for example, after arthroplasty - inflammation caused by various factors.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
The main symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine are as follows:
- pain in the chest, increasing with prolonged stay in one position and with physical activity;
- dull pain in the interscapular space;
- pain when lifting your right or left arm;
- pain with inclined movements of the body, with rotational movements of the upper part of the body;
- increased pain with deep inhalation and exhalation;
- pain in the intercostal spaces that appears while walking;
- a feeling of squeezing of the chest or back (as if by a hoop);
Signs of thoracic osteochondrosis can also be:
- a feeling of goosebumps crawling across the body, numbness in certain areas of the skin;
- itching, burning and coldness of the lower extremities;
- increased brittleness of nails and peeling of the skin (a sign of vascular disorders);
- causeless disorders of the gastrointestinal tract: constipation, diarrhea, flatulence, nausea.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine are often very similar to the symptoms of other diseases - in particular, angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, gastrological diseases, pneumonia. Therefore, it is very important to carry out differential diagnosis using additional instrumental and laboratory examination methods.
What is the prevention of osteoarthritis of the joints?
The best way to treat pathologies of any type is, of course, their prevention. We share recommendations that will reduce the risk of developing such an unpleasant and difficult to treat disease.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and maintaining a level of regular physical activity
There is an opinion that physical activity contributes to the wear and tear of tissues, however, in practice, things are somewhat different. Indeed, excessive loads can have a detrimental effect on the condition of the joints, but measured ones will only be beneficial.
According to studies, activity of any type, aimed primarily at strengthening the muscular frame or improving coordination, primarily supports the motor function of the joints, enriching them with useful substances due to the activation of blood circulation.
It is known that people who prefer walking are less susceptible to the risk of developing osteoarthritis.
Monitoring optimal body weight and using adequate measures to reduce it (if necessary)
Excess body weight significantly increases the load on the body, which negatively affects the functionality of the joints. Over time, due to increased load, the lower limbs and spine of an obese person may be subject to degenerative-dystrophic pathologies. For this reason, regardless of the collected anamnesis, the severity of symptoms, and other factors, physical activity (visiting exercise therapy) is necessarily included in the treatment and rehabilitation protocol.
Work on the correction and elimination of congenital deforming conditions
By deforming conditions of the congenital type, it is customary to understand a large number of diseases, among which is flat feet.
The absence of proper measures to eradicate deformities of this type can lead to a confusion of the axis of the lower extremities, as well as improper distribution of the load on individual fragments of the joints.
Compliance with the principles of balanced nutrition
“You are what you eat” is a great saying that accurately conveys the importance and significance of a nutritious, balanced diet.
Refusal of a large number of useful microelements, diet, irregular nutrition, and other factors can become a point of development of pathological processes of the degenerative-dystrophic type.
Timely seeking qualified medical care
Since the times of the USSR, it was instituted to undergo medical examination, which made it possible to timely identify pathological conditions and begin their treatment. Today, this practice is more of a advisory nature, which inevitably leads to a deterioration in the health of patients.
Refusal to consult a doctor when the first signs of illness appear sometimes leads to irreversible consequences.
Preventive use of drugs from the chondroprotector group
Proper nutrition and an active lifestyle are certainly good. However, in a situation where the body is under increased stress or for some reason cannot absorb absorbed microelements, their preventive intake comes to the rescue.
An excellently proven drug is Artracam, which belongs to the category of chondroprotectors and is one of the most effective in its segment.
There are plenty of obstacles to a full, rich life. Only the person himself can ensure the desired level of quality of life, adhering to recommendations for the prevention of various types of diseases, as well as finding positive aspects in everything and enjoying every minute he lives.
Take care of your health from a young age!