Growths on the spine cause a lot of inconvenience and cause severe pain. They can contribute to poor circulation in the soft tissues surrounding the spinal column. This negatively affects the condition of cartilage discs.
Why bone growths form on the spine and how they can be detected is described in the material provided. It also provides information about modern effective treatment methods. How to remove a growth on the back in the spinal area without surgery and without causing harm to your health? You can read about this too.
It’s worth starting with the fact that any growth on the spine has a certain structure. Depending on the part in which it is formed, it may be the deposition of calcium salts, the growth of cartilage or fibrous tissue, excess fat deposits, atheroma, etc. it is necessary to correctly carry out the initial diagnosis, since therapy, for example, of spinal hemangiomas differs in a cardiac manner from the effective treatment of osteophytes.
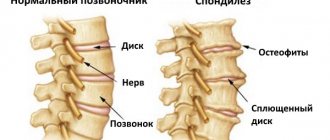
To understand the etiology of the development of various types of growths, you need to familiarize yourself with the structure of the spinal column. In each person, it consists of individual vertebral bodies separated from each other by intervertebral cartilaginous discs. The connection of the vertebrae occurs due to the joints. These are facet and facet joints of bones, which under normal conditions always ensure the physiological position of the vertebral bodies. The stability of the spinal column is achieved through the work of the ligamentous apparatus. It includes two long longitudinal ligaments that begin in the coccyx area and reach the back of the head. There are also short yellow transverse ligaments present here. They record the stability of two adjacent vertebrae relative to each other.
The paravertebral muscles surrounding the spinal column provide mobility of the body and are responsible for a very important function. This is diffuse nutrition of the cartilaginous intervertebral discs and ligamentous apparatus. These structures do not have their own circulatory network and can receive fluid and all the necessary nutrients only when the muscular frame of the back is actively working.
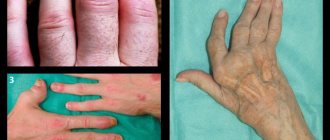
A growth on a person's spine is initially detected as something protruding above other tissues. This protrusion may feel soft, doughy, squishy, dense, etc. Depending on the texture it could be:
- neuroma is a tumor of the nerve fiber, dense, soft, but causes burning pain when touched;
- lipoma - soft, round, not fused with surrounding tissues and moves freely upon palpation, usually painless;
- atheroma - dense, but fused with the surrounding tissues, when trying to move it provokes a dull pain;
- the sequestered part of the nucleus pulposus is palpated as a dense, painful ball, moves from its place, but returns back;
- osteophyte - bone growth - does not move, pain on palpation, very hard, like bone.
This is not a complete list of those growths on the spine that can be felt by a person independently through the skin. If malignant neoplasms. They usually have an uneven, rough surface, are painless, quickly increase in size, compress surrounding tissues and grow through them.
You will not be able to make an accurate diagnosis on your own. Therefore, if you find any growth on the spine, immediately run to the doctor. A vertebrologist, neurologist or chiropractor will help you. These doctors have extensive practical experience and will be able to make a preliminary diagnosis during the initial examination. The patient will then be advised to undergo further laboratory tests if necessary.
In Moscow, you can have a free appointment with a vertebrologist, neurologist, orthopedist or chiropractor at our clinic. Call the number indicated on the page and agree on a time convenient for your visit.
Surgical treatment
If growths on the spine are detected in an advanced form, surgical intervention becomes the solution, since in the severe stage dangerous ring-shaped and posterior osteophytes of adjacent vertebrae appear.
The purpose of the operation is to release the nervous structures (decompression) of the spine from the pressure of osteophytes by removing growths. If the blocking of the nerve endings did not last long, the result of the intervention will be positive for the patient. Excessive and prolonged presence of this pathology on the vertebrae can lead to irreversible changes in the nerve fibers and neurological symptoms may remain after the operation. The decision about surgery is made individually for each patient and depends on his general condition, the presence of certain diseases (diabetes, heart, hypertension), making its risky. You need to understand that osteophytes are not an independent disease, but the result of destruction of bone tissue, and their treatment must be comprehensive.
Advantages of treatment at Top Ikhilov
- Qualified doctors with extensive experience.
- Advanced medical equipment for the diagnosis and surgical treatment of spinal diseases.
- Minimally invasive and robotic spine surgeries, after which patients recover in a matter of days.
- Loyal pricing policy, the possibility of stage-by-stage payment for each service performed.
- Extensive experience working with foreign patients. Availability of an international department and a staff of professional translators (if necessary).
- Accompanying a foreign patient at all stages of diagnosis and treatment of the disease.
- The opportunity to combine treatment with a holiday in Israel.
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(8 votes, average: 4 out of 5)
Treatment of spinal spondylosis
Every person should know that bone growths do not resolve on their own. Complex treatment of osteophytes can be carried out using the following treatment methods:
- Drug therapy - taking anti-inflammatory and painkillers (Ibuprofen, Voltaren, Butadione, Diclofenac, Analgin), muscle relaxants (drugs that contain phosphorus, niacin, calcium, magnesium and B vitamins). Ointments that have a distracting and warming effect: Viprosal, Finalgon, Capsicum, etc.
- Manual therapy. Good results can be achieved with physical therapy. It promotes better blood supply to the entire spine and has a positive effect on its flexibility and condition.
- Physiotherapy. According to indications, acoustic laser, electrophoresis procedures, etc. are recommended.
Symptoms of cervical vertebrae enlargement
Proliferation of the cervical vertebrae can begin at a young age. The risk group includes people engaged in sedentary work. These are mainly office employees who, when working at a computer or with documentation, are forced to hold the muscles of the neck and collar area in static tension for a long time.
In this case, microcirculation of blood and lymphatic fluid is disrupted, degeneration and transformation of intervertebral discs occurs. As a compensatory reaction, beak-like growth of the vertebrae develops and gives specific clinical signs.
If the beak-like growths of the vertebral bodies are not treated, the process of absorption of the vertebral bodies and their fusion with each other may begin. This will lead to loss of mobility of the cervical spine and disruption of the patency of the posterior vertebral arteries.
Clinical symptoms of damage to this part of the spine are as follows:
- periodically occurring sharp, cutting, tearing, stabbing pains, which intensify with any movements;
- crunching, clicking and other extraneous sounds when tilting and turning the head;
- limited mobility and feeling of stiffness in the morning;
- muscle tension in the area of bone growths;
- pain on palpation.
The x-ray image shows bone growths.
Symptom complex
Symptoms of the disease depend on the stage and location of osteophytes. There are general and local symptoms, so first you need to consider the general ones, and then, taking into account the location of the growths, the local ones.
The general symptoms of the disease are:
- pain in the affected area of varying intensity;
- impaired mobility;
- crunching and creaking in the affected joint;
- damage to surrounding tissues with the development of inflammation in them;
- local swelling, swelling.
If the disease is not treated, the symptoms gradually increase, until the patient becomes immobilized in one area or another. In addition, as the disease progresses, there is a risk of developing severe complications leading to disability.
If we talk about local symptoms in a pathology such as spinal osteophytes, then they complement the above-described clinical picture and the location of the growths affects certain additional manifestations of the disease. So, if a person has osteophytes of the cervical spine, in addition to those described above, the following symptoms are observed:
- difficulty turning and tilting the head;
- irradiation of pain to the shoulders, arms and even legs;
- headache;
- tinnitus;
- the appearance of a kind of limiter, due to which it is impossible to turn the head.
Signs that a person has developed bone growths in the thoracic region may include the following:
- a specific localization of pain (in the shoulder blade, shoulder, arm or even fingers);
- increased pain when sneezing or coughing.
Symptoms that damage to the lumbar vertebral bodies have occurred will be as follows:
- localization of pain in the lumbar region;
- irradiation to the feet, buttocks;
- changes in sensitivity in the lower extremities, up to the appearance of numbness;
- twisting of the foot while walking;
- urination disorder.
Marginal osteophytes of the vertebral bodies are manifested by symptoms such as:
- rapid increase in pain;
- pronounced intensity of pain.
Depending on where exactly the marginal osteophytes of the vertebral bodies are formed, visual disturbances, ringing in the ears, weakness of the limbs and disruption of the intestines and bladder may occur. If the growths strongly compress the bone marrow, numbness in the extremities, loss of motor sensitivity and vascular disorders, including dizziness, surges in blood pressure, tinnitus, and visual disturbances, may occur.
With such a form of pathological condition as osteophytes of the hip joint, the patient may complain of:
- pain while sitting and standing;
- impaired mobility and joint deformation;
- gait disturbance.
Osteophytes of the hip joint
The symptoms that occur when the knee and elbow joints are affected are similar to those described above - the same pain, impaired mobility and deformity. Deformation develops if the disease is not eliminated in a timely manner, so it should be treated in the early stages, when the destruction process can be stopped, and not when irreversible changes have occurred.
Bone growths on the heel bone are popularly called “spurs” and many people over the age of 40 face this scourge. Heel bone growths develop with regular increased load on this area, or due to injury.
Growths on the heel bone (called heel spurs or Haglund's disease) always cause severe pain and impaired mobility of the foot.
In the early stages, pain occurs only with prolonged standing, walking or physical activity, but as it progresses it becomes constant, and the mobility of the foot is limited, up to complete immobilization. In order for a person to get out of bed in the morning, it takes some time to develop the joint, since the hallmark symptom of calcaneal bone osteophytes is severe morning pain.
Further progress of the disease leads to the impossibility of correctly positioning the foot when walking, which is why the person’s gait changes - he tries not to stand on his heel, which leads to lameness.
OSTEOCHONDROSIS
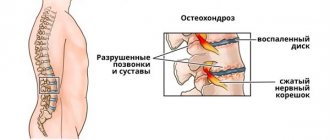
Osteochondrosis is a degenerative-dystrophic process that develops in the cartilage and bone tissue of the spine. This is the most common spinal disease, affecting more than 70% of the population. The resulting pain syndrome is explained by the fact that the intervertebral disc cannot withstand the load and its protrusion forms.
Nerve processes, blood vessels and the spinal cord are located around the intervertebral disc. A disc herniation, affecting any of the nerve processes, causes its inflammation, which leads to pain. The second cause of the pain symptom may be pinching of the spinal nerve at the site where its root exits the lumbar spine, and compression of the root can be caused by bone growths (reactive growth of marginal osteophytes).
Osteochondrosis most often affects older people, as well as overweight people. The disease is a serious medical and social problem, because has a chronic course and often leads to temporary or permanent disability.
Clinical trials conducted in a number of clinics in Russia and the CIS countries have proven the high effectiveness of laser therapy for osteochondrosis.
Considering the fact that with this therapy, the paravertebral vessels running along the sides of the spine enter the treatment zone, i.e. Simultaneously with the local effect, the effect on the blood is also carried out; laser hemotherapy (LHT) is not carried out separately.
Drevmass simulator
The main causes of problems with the spine are described in the article https://drevmass-spina.ru/printsipy-zdorovogo-pozvonochnika/. Unfortunately, we often start taking care of our health when irreversible processes have already started and time is hopelessly lost. But in order to remain physically active and athletic, just 10-15 minutes a day and a Drevmass exercise machine are enough.
People with spinal problems are wary of various massagers. Not surprising, since many of them do not provide even a fraction of the effect promised by the manufacturer and are tiredly gathering dust on distant shelves. We assure you that this will not happen with Drevmass. This exercise machine with a carefully thought-out design will become a true friend for your entire family.
Drevmass is not just another advertised exercise machine, but a certified device, approved by medical professionals and successfully used in medical institutions. The massager is made of safe, impact-resistant material that is resistant to any load. The main part of the design is replaceable rollers, thanks to which you can effectively work all parts of the back. In combination with sports and physiotherapy, you will get truly amazing results!
We advise you to study - How to correct scoliotic posture
Symptoms of spinal osteophytes
Osteophytes of the spine give characteristic clinical symptoms, which in many ways resemble an exacerbation of osteochondrosis, but also have a number of differences. Typical signs of salt deposition are accompanied by the appearance of extraneous sounds when making movements. This may include clicking, crunching, grinding, and even squeaking. Attempts to bend over and turn with twisting of the spine cause not only the appearance of extraneous sounds, but also pain.
Typical clinical symptoms of spinal osteophytes are as follows:
- constant pain of a cutting or stabbing nature, which intensifies when performing very specific movements (for example, when turning in one direction there is pain, but when turning in the other direction there is no pain);
- crunching, clicking, creaking in the spine;
- rapid fatigue of the muscular frame of the back, even when simply standing for a long time;
- a feeling of numbness in some parts of the body, for the innervation of which the radicular nerve, located at the location of the osteophyte, is responsible;
- stiffness of movement, especially in the morning;
- limitation of the amplitude of habitual movements in the spinal column.
If you have similar symptoms of spinal osteophytes, we recommend that you see a vertebrologist as soon as possible. You can schedule a free consultation with this doctor right now. In our manual therapy clinic, each patient is offered a 30-minute consultation, during which the doctor conducts an examination, makes an accurate diagnosis and talks about how to carry out treatment.
Edge growths
Marginal bone osteophytes are most often detected in patients. Spinal pathology is accompanied by the growth of bone tissue on the vertebral body. Externally, they look like thorns or bumps, are characterized by large sizes and rapid growth, and can be rear, anterior or lateral (based on the specific location).
Even “advanced” joint problems can be cured at home! Just remember to apply this once a day.
In addition to spondylosis, they can be caused by subchondral sclerosis, oncological pathologies of the bones or breast. Sometimes they develop against the background of benign tumors.
Frequent signs of marginal osteophytes of the spine and other articular surfaces:
- headache;
- attention disorder;
- decreased vision;
- tinnitus;
- pain when walking (if growths are localized in the knee joint or on the child’s heel);
- sleep disturbance;
- radiating pain;
- heart pain (with small growths in the cervical or thoracic region).
Treatment depends on the location and severity of the disease. Doctors even take into account the size of the growth (more than 06 mm or not).
Classification
In medicine, bone growths are divided into the following types:
- Post-traumatic - appear in the area of fractures and severe bone damage. In addition, they are formed in the part of the tear in the periosteal tissue, which ossifies and turns into an osteophyte.
- Degenerative-dystrophic - created as a result of strong loads on the joint, which can immobilize part of the joint. With deforming spondylosis and arthrosis, the articular surfaces grow together and, as a result, the joint immobilizes.
- Periosteal - a consequence of the inflammatory process of the periosteum, which undergoes partial ossification.
- Massive - the consequences of the formation of malignant bone tumors and metastases of cancer. Takes the form of a spur or visor.
Osteophytes have different cellular structures:
In medical practice, it is customary to distinguish several types of osteophytes:
Conservative treatment of cervical osteophytes
Both local and general effects are used to treat spondylosis.
Anti-inflammatory ointments are indicated - Nice, Voltaren, Diclofenac, as well as painkillers and warming ointments - capsicam, finaogon, viprosal. Medicines of magnesium, calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin complexes with a high content of vitamin B combat muscle spasms and ossification of the cervical vertebrae.
Analgesics in the form of tablets are used only for severe pain, and their long-term use is undesirable, since most of these drugs negatively affect the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Physical therapy is an important part of the conservative treatment of osteophytes. The procedures usually prescribed are:
- therapeutic exercises - for general strengthening of the back muscles, including the shoulder girdle, and the formation of a strong muscle corset;
- massage - to eliminate spasms that cause pain;
- reflexology - eliminates increased muscle tone and tension;
- hirudotherapy (treatment with leeches) - relieves swelling of nearby tissues;
- wearing an orthopedic collar - to bring the position of the vertebrae to normal.
Usually, not all procedures from this list are prescribed, but only the most necessary ones. Treatment of osteophytes is always purely individual and depends on the degree of the disease, the severity of bone growths and their characteristics.
During treatment for spondylosis, intense physical activity and lifting heavy objects are prohibited. It is not recommended to sit for a long time without support on your back (sitting on a stool, for example).
Calm walks and baths with soothing herbs or sea salt are helpful. The diet should be enriched with foods high in calcium (natural cottage cheese, milk, cheese), magnesium (nuts, persimmons) and vitamins.
SCHLATTER'S DISEASE
This disease refers to necrosis of the epiphysis of the head of the tibia in combination with destruction of the bone core, which is caused by local overloads, chronic injuries and local circulation disorders. Boys aged 10 to 15-18 years are most often affected. Schlatter's disease develops for no apparent reason, more often on one side, less often on both.
Sometimes a link can be made to re-injury or increased quadriceps function (eg, sports). Clinic. There is swelling and local pain in the lower part of the knee, which increases with pressure. Movements in the knee joint are painful, especially after physical activity. An extreme degree of flexion of the limb at the knee joint is possible, but sharply painful. The pain does not go away even at rest. The course of Schlatter's disease is long. The chances of recovery are quite high, since this disease is cured after the period of growth of the body is completed. But until complete recovery, it is necessary to avoid overloading the limbs.
Laser therapy. The impact of laser radiation on the pathological focus is carried out in the same way as with other pathologies of the knee joint.
Additional Methods
Traditional methods of treatment do not have a direct effect on osteophytes, but can significantly relieve pain and discomfort, and in addition, their use usually does not cause side effects.
So, for such an ailment, it is useful to use a decoction of hawthorn flowers. Fresh flowers in the amount of 3 tbsp. pour 0.5 liters of boiling water. The decoction is infused for 30-40 minutes, after which it should be taken 50 g 15-20 minutes before meals.
Elderberry also has a good therapeutic effect. 1 tbsp. dry leaves, pour 200 g of boiling water, and after that the broth is heated for 10 minutes in a water bath. You need to take it 50 g 3-4 times a day.
help yourself
The patient must not only strictly follow all instructions, but also independently monitor his health. Any strong physical activity is contraindicated; you need to sit only with emphasis on your back, for example, you cannot sit on stools for a long time.
Moderate walking is very good, as well as taking baths with herbal solutions or sea salt. You should forget about smoking and alcohol. The diet should be supplemented with foods rich in calcium, such as cottage cheese, milk, and cheeses. It is healthy to eat nuts, persimmons, fresh vegetables and herbs.
For preventive purposes, a person needs to constantly monitor his posture and not allow his neck to protrude sharply forward. People with sedentary work should regularly do a little warm-up of the neck and back muscles; this should become a habit.
People who have problems with excess weight need to take all measures to eliminate this problem, since it is this that creates additional stress on the muscles and vertebrae of the neck. Shoes should also be comfortable. Sleeping on very soft surfaces should be avoided. It is best to use an orthopedic mattress and special pillows. Nutrition should be strictly balanced and rich in vitamins and minerals.
It is important to lead an active lifestyle, not allowing the years to get the better of a person.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=wtD-bWtvSf4
Prevention
To prevent violations, you should follow the rules:
You cannot self-medicate, which mainly leads to the operating table.
To study Perineural cyst at the level of S2 vertebra
It is easier to avoid a disease than to treat it; for this you need to move actively, carefully plan your diet, the menu should contain as many products as possible, which contain calcium, magnesium, potassium, and other vitamins.
It is important to constantly monitor how you hold your back, it should be straight, your neck should not stick forward, do not sleep on a soft one, it is best to prefer an orthopedic mattress and a hard surface. If you have a sedentary job, you need to warm up once every 2 hours, do exercises for your neck and back
If you have a sedentary job, you need to warm up once every 2 hours and do exercises for your neck and back.
It is worth abandoning self-medication, most often it becomes the cause of surgery, after which it is difficult to recover. It is better to undergo a course of conservative treatment in time. You should not endure the pain; you must immediately be examined and undergo the necessary course of treatment.
Thus, osteophytes are a serious problem that must be addressed in a timely manner.
Treatment of any disease, especially advanced ones, is always a long process. In this regard, prophylactic agents play an important role, capable of preventing both the disease itself and reducing the damage it causes to health.
source
Treatment for osteophytes of the cervical spine
To get rid of osteophytes, you need to seek qualified help. In the early stages of development of the pathological condition, complex therapy is used, which includes drug treatment, means of physical rehabilitation and correction of the patient’s lifestyle. In severe cases, when conservative methods do not bring results, osteophytes are removed surgically.
Drugs
To relieve pain, a person can take Ibuprofen.
First of all, the severity of negative symptoms decreases. To relieve pain, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as Ibuprofen, Nurofen and Diklak are used. To reduce pathological muscle tone, muscle relaxants are used, which include Tolperil and Structum. Chondroprotectors (“Chondroxide”) can improve the regeneration of cartilage tissue. To reduce inflammation in soft tissues, injections of B vitamins are used.
Traditional methods
Alternative medicine acts as an auxiliary means of treatment and helps reduce the severity of pain in the neck. For this purpose, decoctions of medicinal plants are used. For example, hawthorn has a good pain-relieving effect. To do this, pour boiled water over the dried flowers of the plant and leave for 30 minutes. You need to take the decoction orally, in small portions before meals. Compresses based on animal fats with the addition of bee products have a beneficial effect on local blood circulation.
Physiotherapy
The well-being of patients noticeably improves with hirudotherapy.
We advise you to study - Which doctor treats osteochondrosis
Physiotherapeutic procedures have an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect. To reduce the negative manifestations of osteophytes in the cervical region, procedures such as:
- drug electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- hirudotherapy;
- acupuncture;
- phonophoresis;
- manual therapy;
- balneological procedures;
- mud applications.
Exercise therapy is mandatory. Physical exercise helps improve blood circulation, reduce pathological muscle tone, restore mobility of the affected area and normalize cell nutrition. The exercise therapy complex is selected according to the physiological characteristics of the patient’s body and the degree of spread of osteophytes. Exercises are performed at a slow pace to prevent secondary damage to the arteries and nerves.
Surgery
Laminectomy helps get rid of the troubling problem.
It is impossible to cure osteophytes conservatively. You can stop their growth and spread, and reduce the severity of symptoms. Large formations that put strong pressure on the nerves need to be treated surgically. To remove the growth, an operation such as laminectomy is performed. To increase the intervertebral space, in order to reduce pressure on the nerve fibers, foraminotomy is used. The most radical operation is considered to be a facectomy, which consists of complete removal of the affected joint of the spinal column.
Treatment
Conservative course
A conservative course is prescribed in the early and middle stages of the disease, when the osteophyte can still be cured without surgery. During such treatment, the patient uses either medications, or alternative methods of treatment, or a combination of medications and physiotherapeutic procedures and special gymnastics.
A patient with early stage spondylosis will be prescribed non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs aimed at relieving inflammation and swelling, as well as improving the patient’s general condition. This type of medicine includes Voltaren, Butadione, Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Naproxen, Aspirin, Nise.
If the muscles are very tense, then the following remedies are taken: nicotinic acid, medications containing vitamin B, magnesium, phosphorus and calcium.
To get rid of pain and suppress inflammation, the doctor prescribes solutions, ointments and gels that are applied to the sore spot. If it is necessary to “warm up” the inflamed area, then “Viprosal”, “Finalgon” and “Capsicam” will help.
Physiotherapy
In the treatment of osteophyte, physical therapy, as well as drug treatment, shows good results. However, it is worth mentioning some nuances:
- During the period of an acute form of the disease or acute inflammation, you should never engage in physical therapy.
- At the beginning of the physical therapy course, light exercises are performed. The load is increased gradually.
- The exercises are performed slowly. With sudden movements you risk harming the body.
Manual therapy
Manual therapy is an unconventional means of combating osteophytes. It will help improve blood circulation, relieve pain in damaged joints or vertebrae, relieve muscle tension, and restore normal functioning of the musculoskeletal system. If a specialist uses a “soft” technique during the massage, he will speed up the regenerative processes of cartilage.
Physiotherapy
This group of osteophyte treatment methods includes HILT therapy and UVT therapy.
High-intensity laser therapy, or HILT therapy, is a treatment technique that is based on the use of a pulsating impulse that can block pain and reach deep tissues and bone formations. This therapy relieves swelling and inflammation, heals tissue, and reduces pain syndromes.
Despite its advantages, HILT therapy has contraindications. This procedure is contraindicated if:
- chills and epilepsy;
- problems with tactile perception;
- taking medications, the side effect of which is increased sensitivity to light;
- detection of high levels of cortisone in the patient’s blood.
This procedure is contraindicated for pregnant women.
Shock wave therapy, or SWT therapy, is a treatment technique based on the use of low-frequency acoustic or shock waves. This method is effective, and this has been proven in practice: ninety percent of people reported an improvement in their well-being after UVT therapy. The therapy itself is aimed at reducing inflammation and pain, strengthening tendons and ligaments, healing tissue, improving blood flow and, most importantly, destroying calcium salts that accumulate in the patient.
There are the following contraindications to this therapy:
- patient’s age (does not apply until twenty-three years of age);
- pregnancy;
- blood diseases;
- presence of a pacemaker.
Causes
All cervical vertebrae are unique in their structure. The neck experiences more static and dynamic load, which provokes the formation of microtraumas and the development of degenerative processes. More often, osteophytes of the cervical spine grow in the area of the C5-C6 vertebrae. Bone growths significantly worsen a person’s quality of life, as they put pressure on nerves and large vessels, which leads to brain hypoxia and disruption of innervation in many parts of the body.
The formation of growths is not considered an independent phenomenon, but develops with concomitant pathologies. Most often, osteophytes in the cervical spine occur as a complication of degenerative processes against the background of osteochondrosis or osteoarthrosis. With dystrophy of the intervertebral cartilage, there is a spread of connective tissue with further fusion of the vertebrae, which leads to spondylosis.
There are a number of negative factors that can provoke the development of osteophytes in the cervical spine, these include:
Kyphosis can cause this pathology.
- physical inactivity;
- spinal injuries;
- heavy loads on the neck;
- obesity;
- inflammatory processes in bone tissue;
- disruption of hormonal levels and metabolic processes;
- heredity;
- kyphosis and scoliosis;
- concomitant pathologies of a degenerative nature;
- psycho-emotional stress;
- neoplasms.
Features of formations in the cervical spine and their types
The shape of marginal osteophytes of the cervical spine may resemble:
- thorns;
- tubercles with blurred edges;
- teeth.
There are bone growths of different sizes, single and multiple origins. Both cases require treatment.
Types of formations in cervical cartilage:
- front;
- rear;
- anterolateral;
- posterolateral.
Osteophytes in the cervical spine come in different types and appear for several reasons:
- Osteochondrosis is characterized by thinning, compression, pinching of the intervertebral cartilage layers - discs. The progression of the disease leads to friction between the vertebrae of the department. The body builds up tissue to protect the discs, and the intervertebral space decreases. Formations that arise due to this factor are called degenerative-dystrophic.
- With a compression fracture of the spine, strong compression occurs in the cervical region, which is a consequence of changes in the vertebral body. New bone tissue grows at the site of damage. Without treatment, its excess forms a tubercle, which turns into an osteophyte. Large growths can be felt by palpation and are defined as traumatic.
- Degenerative changes in bones after the age of 40–50 lead to deformation of the spinal column. Due to the complex wear and tear of bones, the compensatory functions of the body are activated, which actively builds up bone tissue.
- Spondylosis is the fusion of vertebrae. A chronic disease that develops due to gradual deformation of the spine, leading to the appearance of bone bridges and osteophytes. The progression of the disease leads to partial or complete immobilization of the cervical region.
- Neoplasms of a malignant or benign nature that affect the bone can cause massive growths.
To study Spinal cord puncture
Conservative therapy
At the initial stages, conservative therapy involves the use of drugs that relieve pain, stop negative processes and help restore the mobility of the vertebral discs.
If a person consults a doctor in time, at the initial stage of the disease, local medications, primarily ointments and gels, are prescribed. Among them are the drugs Ibuprofen, Voltaren, Capsicum, Naproxen. They have anti-inflammatory and warming properties. To relieve muscle tension, taking B vitamins, as well as preparations of phosphorus, calcium, magnesium, and nicotinic acid are recommended.
Tablet analgesics can only be used for very severe pain and for a short time, since they negatively affect the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
In parallel with drug treatment, treatment with other methods is also indicated.
Among them, an important place is occupied by special therapeutic gymnastics exercises, which should be carried out only under the supervision of a specialist. These exercises are designed to strengthen muscles and form a strong muscle corset.
Therapeutic massage eliminates spasms, which cause unpleasant and painful sensations. Reflexology is also actively used, the purpose of which is to get rid of increased muscle tone and excessive tension.
The attending physician may also recommend hirudotherapy, that is, treatment with leeches. In this way, it is possible to relieve swelling of nearby tissues.
During treatment, the patient must wear a special orthopedic collar, which helps bring the position of the vertebrae to a normal anatomical state.
It is not at all necessary that a person will be prescribed all types of treatment from the above list. The strategy is selected strictly individually, based on the patient’s age, gender, general health, and degree of disease. During the treatment process, certain methods may be replaced by others.
Reasons for education
With a high axial load, the cartilage disc can be damaged, resulting in the formation of osteophytes.
The formation of pathology is provoked by several factors:
- Heavy loads on the back, which cause damage to cartilage tissue.
- Excess weight.
- Arthrosis, which provokes pathological changes that destroy cartilage tissue.
- Hormonal disorders affecting intervertebral discs.
- Mechanical injury to the neck.
Most often, osteophytes are formed due to pinching of nerve tissue and disturbances in metabolic processes.
Reasons for appearance
Bone growths in the cervical region appear as a result of wear of the vertebrae and abrasion of intervertebral cartilaginous tissue. And the cervical vertebrae are the thinnest and most mobile, so they are subject to wear more often than others. The following reasons may contribute to this:
- Hereditary predisposition. But in parents, the disease could be localized in another part of the back, and in a child it could appear in the neck area.
- Poor posture. It leads to increased load on this part of the spine, leading to deformation of the intervertebral discs.
- Neck injuries from a fall or blow. During mechanical stress, microcracks appear on the vertebrae, so they become vulnerable to inflammatory processes. Due to inflammation, the condition of the bone tissue deteriorates, and the cartilage is gradually worn away.
Sometimes the cause of cervical osteophytes can be metabolic disorders in the body. Due to poor metabolism, salt accumulation is observed. They are usually deposited in the area of joints and vertebrae.
Types of osteophytes ↑
There are several types of osteophytes:
- post-traumatic;
- degenerative-dystrophic;
- massive;
- periosteal;
- osteophytes resulting from systemic changes in the skeleton;
- neurogenic origin.
Post-traumatic osteophytes are a consequence of various damage to bone structures.
Most often, this type of growth appears with dislocations of the elbow and knee joints, accompanied by separation of the ligaments and rupture of the bursa. Post-traumatic osteophytes are rare in the spine.
Degenerative-dystrophic bone growth manifests itself in a disease such as arthrosis deformans.
The exception is cases of spondylosis deformans, as a result of which the surfaces of the joint become fused and its mobility is completely lost.
Such growths are divided into:
- osteophytes of a general nature - occur with senile arthrosis;
- of a local nature - are the result of overload of a local joint. In this case, the elasticity of the cartilage is lost and beak-shaped growths form on the bone, which cover the joint, limiting its movement. In rare cases, the mobility of individual parts of the vertebra is lost.
Massive, or so-called marginal, osteophytes develop when:
- malignant bone tumors;
- metastases of breast or prostate cancer.
On an x-ray, they are visible in the form of a spur or visor, which is one of the important signs during the diagnosis of the disease.
After inflammatory processes, growth of periosteal osteophytes, which are formed from useful components of the periosteum, can be observed.
As a result of endocrine disorders and due to systemic changes that occur for this reason in the skeleton, osteophytes can also appear.
Hypertrophy of the bone relief leads to the formation of growths on:
- ischial tuberosity;
- nail phalanges;
- trochanters of the femur, etc.
The appearance of osteophytes can also be provoked by psychological disorders - for example, the formation of growths due to disordered bone formation can be observed during a nervous breakdown.
Osteophytes are also classified according to their location:
- anterior - appear on the anterior sections of the vertebral bodies. They form mainly in the thoracic region and rarely cause pain;
- posterior - “grow” on the posterior surfaces of the spine. Unlike the anterior ones, their formation is accompanied by severe pain, as mechanical pressure occurs on the nerve trunks of the intervertebral foramina;
- anterolateral bone growths have a horizontal direction and an unusual shape in the form of a bird’s beak. Sometimes there are so-called kissing osteophorites, in which the ends are pointed and approach each other. Formed in areas with the highest pressure, where changes in the intervertebral discs are observed;
- posterolateral occur mainly in the cervical vertebra and cause compression of the spinal cord.
Do you feel pain in the lumbar region? Find out the possible causes of lower back pain from our article.
How to treat lumbosacral radiculitis? The answer is here.
Treatment structure
Osteophytes of the cervical spine are treated with the following methods:
- Taking specialized medications, depending on the severity of the disease.
- Undergoing physiotherapeutic procedures, taking into account the effects of medications.
- Correct mode.
- Surgical type intervention.
In case of acute pain, as well as exacerbations, there is a need to treat the disease exclusively with medication; physiotherapy is used after the general condition of the patient has improved. In severe cases, medications are unlikely to give the desired result, so surgical intervention is used.
Drug therapy:
- Means for relieving inflammatory processes - Diclofenac, Ibucrofen.
- For severe pain, Ketorol and Ketanov are prescribed.
- To relax muscle tissue and eliminate discomfort, muscle relaxants are used (selected individually, taking into account all the patient’s characteristics), as well as nicotinic acid.
- To actively combat inflammation processes, ointments are used - Diclofenac, Voltaren, Nice, and warming-type options are also used - Viprosal, Finalgon.
- In certain cases, a specialized orthopedic collar, the Shants device, is used to reduce friction of the vertebrae.
Physiotherapeutic procedures that are indicated for this disease:
- Hirudotherapy.
- Specialized massage.
- Gymnastics of a therapeutic format.
- Reflexology.
Surgical intervention is used if other methods have not produced the necessary results. The following methods are used:
- Facetomy is the removal of cartilage tissue on which growths form.
- Foraminotomy - the formation of gaps (between the vertebrae). In this way, the release of nerves from clamps is formed.
- Laminectomy is the complete removal of a bone type plate.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the cervical spine in Israel takes 3 days. During this time, doctors manage to establish a diagnosis and prescribe a set of treatment measures.
First day – consultation with a doctor
Diagnosis of any disease in Top Ikhilov begins with a consultation with the attending physician. It is noteworthy that you can get a second opinion from an Israeli specialist without visiting Israel. To do this, you will need to send diagnostic data to our clinic, after which you will be scheduled for a video consultation with our doctor. If after the video consultation you decide to be treated in our clinic, then the initial in-person consultation will be free for you.
During the initial examination, the doctor examines medical documents in detail, asks the patient about the symptoms of the disease and examines the patient. Then the doctor refers the patient to undergo instrumental examinations of the cervical spine.
Second day – instrumental diagnostics
- X-ray studies of the cervical spine.
- CT and MRI.
- Myelography.
- Electromyography.
- Electroneurography.
- Other research methods.
Third day – doctors’ conclusions
On the third day of diagnostic activities, an expert group of doctors Top Ichilov studies the diagnostic data in detail, establishes an accurate diagnosis and determines the treatment tactics for cervical osteophytes.
Osteophytes of the vertebral bodies: what is it?
Anterior or posterior osteophytes of the spine are formations that arise when bone tissue grows directly along the vertebrae themselves; can have different shapes and sizes and look like spikes, humps, etc.
We advise you to study - Which doctor treats osteochondrosisThe main causes of bone growths on the vertebrae:
Inflammatory processes that led to osteomyelitis. This disease gradually provokes severe damage to all bone structures.
- Osteomyelitis can occur due to damage by tuberculosis or dangerous staphylococcal bacteria. The mechanism of its development is simple: in adult patients it usually occurs against the background of an open bone fracture. Bacteria enter the wound, which contribute to the onset of a long-term inflammatory (often purulent) process.
- If the fracture is linear, inflammation will be limited only to the affected area of the bone. If the damage is splintered, the infection will spread to the entire bone area - this creates all the conditions for the eventual formation of bone growths.
Degenerative bone diseases. They develop due to excessive physical exertion and are often detected in older people (due to physiological disorders).
- The most common causes are spondylosis and osteoarthritis. During deforming spondylosis, the patient's intervertebral discs are affected, and over time, osteophytes of the lumbar, thoracic or cervical regions are formed.
- Development mechanism: during damage to the intervertebral discs, they become deformed. Tissue degeneration and the appearance of pathological growths occur.
- The second common degenerative bone disease is osteoarthritis. Pathology leads to extensive damage to the cartilage tissue of the joints. This disease can be caused by trauma, congenital defects in the joint structure, or a history of inflammation.
- At the very beginning of its development, osteoarthritis affects only the fluid that nourishes the cartilage. As the pathology progresses, degenerative changes are observed in the joint itself, due to which it can no longer withstand strong physical stress.
- The formation of growths in osteoarthritis is observed in the second stage of the disease, when complete destruction of cartilage occurs.
Staying in one position for a long time (standing or sitting), when the joints are subjected to heavy stress. This increases pressure on the cartilage and causes deformation.
Destruction processes exceed tissue regeneration. The entire load is placed on the bone, which gives impetus to the development of osteophytes.
- Oncological pathologies. Pathological growths occur in benign and malignant cancers.
- Endocrine disruptions. Acromegaly most often contributes to the development of osteophytes. The disease occurs due to increased production of growth hormone. The root cause is the development of a benign tumor in the anterior region of the pituitary gland.
- A person with multiple small or large marginal osteophytes of the vertebrae has a pronounced curvature of the spine and an increase in body weight. Due to the impact of stress, cartilage does not cope with its tasks and is destroyed. If left untreated, the patient develops osteoarthritis, which leads to pathological growths.
Why do osteophytes appear?
Intervertebral discs are a thin layer of cartilage between the vertebrae. If, for some reason, the discs become thinner, the vertebrae are left unprotected and rub against each other. Osteophytes appear to protect the joint from damage.
To study myositis of the neck
Due to their appearance, the intervertebral space becomes smaller, nerve fibers are compressed and the person experiences pain.
Sometimes bridges of bone tissue appear and the vertebrae fuse together, causing a disease called spondylosis. As a result, partial or complete immobilization of the cervical spine may occur.
Bone spurs occur in people over 40 years of age. The cause is degenerative changes in bones that begin in youth and manifest themselves with age.
The main reasons for the formation of osteophytes:
- flat feet;
- improper metabolism;
- heredity;
- osteochondrosis.
Causes may also include injuries, incorrect posture, standing or sitting for a long time, excessive physical activity, and for women, walking in stiletto heels.
Types of osteophytes:
- Post-traumatic. When a bone is fractured, a bone callus grows around the fragments. Sometimes the bone is not damaged, but a tear of the periosteum occurs. Then it ossifies and transforms into an osteophyte. They usually form in the elbow or knee.
- Degenerative-dystrophic. Formed during severe physical stress on the joint or as a result of senile arthrosis. With spondylosis and deforming arthrosis, the surfaces of the joint grow together and the joint loses mobility. This can also happen in the spine.
- Osteophytes that arise as a result of inflammation of the periosteum. Then ossification of its individual sections occurs.
- If there is a malignant tumor, large osteophytes may form, shaped like a visor. They sometimes occur with benign tumors, when changes in cartilage tissue occur.
- Osteophytes occur as a result of endocrine diseases in degenerative pathologies of the musculoskeletal system.
- Less commonly, osteophytes are formed as a result of neurogenic diseases.
Diagnosis and treatment
Undoubtedly, if you discover some signs or even suspect their presence, you need to visit a doctor for advice and appropriate diagnostics.
First of all, the doctor must conduct a neurological examination to adequately assess the condition of the nerve roots and spinal cord. But this is only the first stage, which allows us to identify only large-sized osteophytes.
The information obtained at the initial stage of diagnosis will serve as the basis for subsequent research, which may include electroneurography, radiography, computer and magnetic resonance therapy.
The first of the presented diagnostic methods determines the degree of conduction or damage to nerve fibers. X-rays reveal osteophytes in the spine. Computer and magnetic resonance therapy evaluates the condition of the spinal tissues and identifies possible compression of the roots and spinal cord. The data obtained as a result of the examination, as a rule, forms the basis for treatment.
Treatment for osteophytes of the thoracic spine involves an integrated approach:
- drug therapy;
- manual therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- administration of epidural steroid injections;
- physiotherapy.
With a moderate course of the disease, treatment with anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs is possible. The group of such drugs includes Diclofenac, Analgin, Ortofen, Baralgin, Voltaren, etc. Warming ointments like Viprosal can help relieve pain a little, but not get rid of it completely.
Along with drug treatment, physical therapy and manual therapy are widely used.
In addition, epidural injections and physical therapy are often prescribed.
If the conservative treatment methods described above do not result in positive effects, doctors have to resort to surgery: only a surgeon can decompress the nerve roots. The decision on the need for surgery is made on an individual basis.
To relieve pain and alleviate the condition, you can use folk remedies.
Consequences and prevention of spondylosis
Spondylosis that is not detected in a timely manner or left without the necessary treatment can cause partial or complete paralysis of the body . This can occur when osteophytes actively grow and injure the spinal cord.
One of the consequences of osteophytes in the spine is pinching of the nerve roots.
Compression of blood vessels by bone growths can cause circulatory problems in the brain and make a person disabled for the rest of his life. In the future, osteophytes can grow throughout all elements of the spine.
At best, the disease can lead to complete immobility of any part of the spinal column and cause loss of ability to work.
Treatment of spondylosis is not an easy process and can take several months. Therefore, it is easier to apply preventive measures that will help maintain the health of the spine.
For the prevention of spondylosis it is recommended:
- pay attention to at least minimal sports every day, which will help strengthen the muscle corset, which plays an important role in the health of the spine itself;
- control periods of sedentary work and rest, during which it would not be superfluous to warm up a little by doing 2-3 exercises;
- monitor the amount of healthy food consumed, enriched with all necessary microelements and vitamins;
- for sleeping, prefer an orthopedic pillow and mattress;
- control your weight and prevent it from going overboard.
How to treat marginal osteophytes
Bone formations can only be removed surgically, but this cannot always be used. Such an operation has many contraindications, especially if the patient is elderly. Conservative methods give effect only in the early stages of the disease. The more advanced the condition, the less likely it is to restore motor activity.
Conservative therapy
Conservative treatment methods can stop the growth of formations, relieve pain and increase the mobility of the vertebrae. Start with taking medications:
- analgesics - eliminate muscle spasms and pain, normalize the general condition of the patient;
After relieving pain and relieving inflammation, other methods are used:
- therapeutic massage - competent impact on the spine helps reduce muscle tension and improve blood supply to the affected areas;
You cannot choose the treatment method and medications on your own, so as not to harm yourself even more. Therapy is prescribed only by a specialist after appropriate examination.
Treatment usually takes a long time, so it is very important to adhere to medical recommendations throughout this period in order to avoid complications or relapse of the disease.
Surgery
If conservative methods are unsuccessful, surgery may be prescribed to remove the growths. It must be done before irreversible changes occur in the spinal cord and nervous tissue. If time is lost, even the most skilled surgeon will not be able to help. Surgery has contraindications:
- severe disorders of the cardiovascular system;
- hypertension 3 degrees;
- diabetes.
It should be noted that surgery also does not guarantee a complete cure, and in most cases it can only alleviate the patient’s condition. When the growths are removed, the compressed nerve roots are released, which helps to get rid of pain and restore (fully or partially) the mobility of the spinal column. In this case, individual osteophytes may remain inaccessible and begin to grow again over time.
That is why it is necessary to pay special attention to the prevention of the disease: eat right, lead an active lifestyle, maintain posture, and regularly undergo examinations by a vertebrologist.
SPINAL HERNIA
Intervertebral hernia is one of the most complex diseases of the musculoskeletal system. The cause of the disease can be excessive stress on the spinal column, injuries, incorrect posture, and age-related changes. Under the influence of these factors, the membrane of the spinal disc is destroyed and its contents enter the spinal canal, compressing the spinal roots or the spinal cord itself. At an early stage of changes in the lumbosacral spine, they make themselves felt by aching pain in the lower back. If the disease is advanced, then the pain caused by the hernia depends on which roots it compresses, and clinically it can manifest itself as impaired movement in the legs, impaired urination and potency.
Treatment. Surgical intervention for this pathology gives quick results, but is fraught with postoperative complications and the development of diseases in other parts of the spine. It is indicated for only 10-12% of patients. The most effective method is a combination of laser and manual therapy. Laser therapy allows you to relieve swelling and inflammation in the hernia area, and manual therapy, which is carried out after a course of laser therapy, allows you to achieve stable and long-term remission, and live your life without surgery at all.
The disc is a completely avascular region, however, in its immediate vicinity the vascular network is quite wide. For example, many vessels are located in the vertebral body itself and along the periphery of the fibrous ring, which carry out exchange and nutrition of the disc. Actually, by improving this metabolism and tissue nutrition, the declared effectiveness of laser therapy is achieved. Blood circulation in the problem area improves, pain goes away, swelling and inflammation are relieved.
Before using laser therapy to treat joints and spine, consult our specialists.