In addition to pain, TMJ arthritis can manifest itself:
- swelling and redness of the skin over the joint;
- an increase in the patient's general body temperature;
- restriction of mouth opening and inability to completely close the teeth.
Diagnosis of inflammatory processes affecting the TMJ consists of analyzing the patient’s medical history, palpation examination of the area of the joint, as well as the results of radiography and CT scans of the affected joint. Therapeutic tactics aimed at eliminating this disease involve the use of jaw immobilization, complex antibacterial therapy, chondroprotectors, physiotherapeutic procedures, intra-articular injections of corticosteroids, as well as muscle exercises.
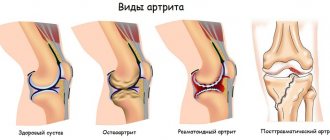
This disease is represented by acute and chronic forms, any of the forms is accompanied by dysfunctional disorders of the TMJ. Among all diseases of the temporomandibular joint, inflammatory lesions occupy about 18%. The category of the population most often suffering from this disease is young and middle-aged people. Based on the etiological factors contributing to the development of this disease, rheumatologists, dentists and traumatologists can treat it.
Anatomically, the TMJ is represented by a paired joint of the mandibular and temporal bones; its main function is to ensure mobility of the lower jaw. The joint itself consists of the head of the joint of the lower jaw, the articular tubercle, the mandibular fossa of the temporal bone, the articular disc, the ligamentous apparatus and the articular capsule. At the onset of the disease, periarticular tissues and the joint capsule are exposed to the pathological process. During the gradation of the disease, inflammation spreads to the surface of the joint, synovial membrane and areas of bone structures, accompanied by deformation of the cartilage and the appearance of connective tissue in the joint cavity. This disease can be complicated by deforming arthrosis, muscle contractures or bone ankylosis of the temporomandibular joint.
Causes of post-traumatic arthritis
In the development of post-traumatic arthritis, injuries play a major role. Acute injuries: bruises, sprains, dislocations, fractures, the victim always notices and associates further inflammation of the joint with them. In most cases, this is a reason to consult a doctor in a timely manner.
The injury can also be chronic. This happens with constant heavy lifting, excess weight combined with a sedentary lifestyle. Sometimes an acute injury seems insignificant to the victim, and he does not associate signs of arthritis with it after some time. These are the most dangerous injuries, since the patient almost never sees a doctor with them on time, misses time and allows the disease to take on a chronic destructive nature.
Athletes, people with heavy physical labor (miners, loaders), people who are obese and lead a sedentary lifestyle are susceptible to the development of traumatic arthritis. The risk group also includes people suffering from chronic inflammatory diseases of the musculoskeletal system: rheumatoid arthritis, gouty arthritis, etc.
Pathogenesis – mechanism of disease development
In recent years, it has been found that even a minor injury triggers the development of the inflammatory process. This happens at the cellular level. Cells of intra-articular tissues produce pro-inflammatory (sustaining inflammation) biologically active substances - prostaglandins, cytokines, etc. The inflammatory process that begins during an acute minor injury (minor bruise) can end with a complete recovery after some time.
But in the presence of risk factors such as reduced immunity, various chronic diseases, obesity, inflammation is maintained for a long time and gradually leads to degenerative-dystrophic changes in the joint and disruption of its function.
In case of severe injuries, in addition to the described mechanism, the process of necrosis (death) of cartilage tissue cells (chondrocytes) directly from mechanical action is activated. In chondrocytes surrounding the necrosis zone, the mechanism of autolysis - self-destruction - is activated. Cartilage tissue is destroyed, the process is supported by long-term inflammation. In place of the destroyed cartilage, connective tissue (pannus) develops, limiting the mobility of the joint. The subchondral bone tissue begins to grow, which leads to joint deformation. Over time, the pannus is replaced by bone tissue and ankylosis is formed - complete immobility of the joint.
Read more about arthritis, its symptoms and treatment in this article.
Forms
According to the nature of the course, post-traumatic arthritis is divided into:
- Acute
- occurs infrequently, occurs with severe symptoms, ends in recovery, sometimes spontaneously, but there is always a risk of the acute course becoming chronic. With open (knife, gunshot) wounds, inflammation can be complicated by purulent infection and then proceeds as acute purulent arthritis. - Chronic
is the most common course. The pathological process begins and proceeds unnoticed with the slow formation of dysfunction of the joint.
Read our article “Chronic Arthritis”.
Prevention and complications
It is always easier to prevent any disease than to subsequently deal with its long-term treatment. To exclude the possibility of developing post-traumatic arthritis, you need to pay special attention to the specialist’s recommendations and follow them exactly in the period after the injury.
How to avoid developing the disease
The most important thing during the recovery period is moderate activity. A sedentary lifestyle can have a bad effect not only on the condition of the joints, but also on the entire body as a whole.
It is useful to do swimming, gymnastics, and cycling. During this period, it is important to reduce the force load on the joint, so it is better to use the elevator than to climb the stairs. Do not lift heavy objects.
For overweight people, you should try to lose weight, this will not only reduce the load on the knee, but will also significantly improve your overall condition. There are a variety of knee pads, canes and splints available for sale. They help restore mobility and reduce pain.
You should also eat rationally, spend more time outdoors, and eliminate bad habits, which will certainly affect the condition of the body as a whole, and the joints in particular.
Possible complications
If there were microdamages and the patient ignored the doctor’s advice, then the problem may worsen significantly over time. Gradually, the joints will lose their functionality, because irreversible processes may begin in their tissues due to inflammation.
At first, the patient experiences minor discomfort, but every day it will become more and more difficult for him to move. This condition can lead to the fact that without outside help, a person will not lose the ability to move and become disabled.
If medical care is not provided in a timely manner after a serious knee injury, the disease can cause immediate complications: tissues may begin to become inflamed and peel off; The possibility of developing a general infection in the body cannot be ruled out either.
Post-traumatic arthritis is not a death sentence. With the right approach, the patient can quickly cope with the disease.
The main rule is to approach solving the problem comprehensively: take medications and vitamins, eat a balanced diet, and lead a healthy and active lifestyle. Listen to your doctor in everything! You can learn more about post-traumatic arthritis of the knee by watching the video in this article.
Symptoms of post-traumatic arthritis
Manifestations of post-traumatic arthritis depend on the characteristics and severity of the injury, the nature of the course and the condition of the patient’s body.
First signs
With severe injury and blood leaking into the joint cavity (hemarthrosis), signs of inflammation in the form of swelling, redness of the skin, and severe pain appear immediately after the injury. With open injuries and the addition of a purulent infection, the body temperature rises sharply, chills, signs of intoxication, severe swelling and redness of the skin over the joint appear. The pain is very severe, the patient cannot move the limb.
But very often the first signs of inflammation are subtle. They appear after a few days or even weeks, increase gradually and are manifested by mild pain during exercise or movement, sometimes by slight swelling of the affected joint.
Immediately after the injury, the first symptoms of post-traumatic arthritis appear
Obvious symptoms
Obvious symptoms of acute post-traumatic arthritis include: redness, swelling of the joint. Characterized by pain that increases with movement. In case of purulent acute arthritis, there is an increase in general intoxication, pain, redness and swelling of the periarticular tissues, and a deterioration in the general condition of the patient.
In a chronic course, obvious signs will be slight but increasing pain in the joint. The movement is accompanied by a crunching sound (this is especially noticeable in the knee and ankle joints). Over time, the pain syndrome becomes constant and limits the movement of the limb. It may take several years for signs of joint deformity to appear. At the same time, first partial and then complete limitation of mobility appears, associated with the proliferation of connective and bone tissue.
Dangerous symptoms
A signal to seek medical help should be any joint disorders that appear, both immediately after the injury and some time (sometimes several months) after it:
- swelling, redness, pain in the joint area that appeared immediately after the injury, increasing signs of intoxication with fever and malaise;
- pain when moving with increasing intensity that occurs several weeks after the injury;
- increased pain after injury in people suffering from chronic arthritis;
- a sudden increase in body temperature combined with redness, swelling and severe pain in the joint after injury in people suffering from chronic arthritis.
If such symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor immediately.
Prevention
To prevent traumatic arthritis from appearing after an injury, you must immediately visit a traumatologist (even if there is no pain in the joint). The inflammatory process is invisible at first, but the doctor will prescribe anti-inflammatory treatment.
The prognosis for recovery is favorable, but you need to be prepared for the fact that the treatment is long. The speed of joint recovery depends on the severity of the damage.
Author: Oksana Belokur, doctor, especially for Ortopediya.pro
Why is post-traumatic arthritis dangerous?
Traumatic arthritis is dangerous because it can occur unnoticed, moving from one stage to another with gradual impairment of joint function and numerous complications.
Stages
The stages of the disease depend on the nature of its course. But most often the pathological process occurs chronically. The following stages of post-traumatic arthritis are distinguished:
- Initial
– inflammation of the synovial membrane – synovitis with effusion in the articular cavity. With severe trauma, the cartilage covering the articular joints is destroyed. The intensity of swelling, redness and pain depends on the severity of the injury. - Expanded
- during an acute process, all symptoms of inflammation intensify. In chronic cases, the inflammatory process proceeds slowly, but gradually progresses. In areas of inflammation and erosion of cartilage, connective tissue grows, covering the surface of the articular joints. All symptoms are smoothed out and go unnoticed. - The final stage in the acute course
is that all symptoms of inflammation gradually disappear and recovery occurs. Or the acute process becomes chronic with gradual progression. - Progressive in a chronic course
- the pathological process progresses during an exacerbation, which is replaced by the proliferation of dense connective tissue (proliferation) during remission. Soft ankylosis develops - partial immobility. The pain in the area of the affected joint increases and worries constantly. Minor swelling and redness appear during exacerbations. The limb bends and unbends with difficulty and to an incomplete extent. - Neglected
is the result of a chronic inflammatory process. Dense connective tissue in the joint cavity is replaced by bone and complete immobility develops - bone ankylosis. Bone tissue grows along the edges of the articular surfaces, deforming the joint. The pain syndrome is constant, the function of the joint is completely lost.
Any form of arthritis has serious complications, so you should not delay treatment.
See how easily the disease can be cured in 10-12 sessions.
Possible complications
It is possible to help a patient with traumatic arthritis at any stage, but the longer the pathology proceeds, the more irreversible changes appear in the joint. All possible complications are divided into early and late. Early:
- the addition of infection and the development of a purulent inflammatory process;
- transition of purulent inflammation to periarticular tissues with the formation of phlegmons and abscesses;
- purulent infection can become generalized, spreading to many organs and systems (sepsis).
Complications of traumatic arthritis - infections, purulent process, abscess
Late complications:
- slow and imperceptible development of the disease with the transition of chronic inflammation to degenerative-dystrophic; constant debilitating pain syndrome with complete loss of joint function.
To avoid complications, you need to seek medical help, preferably from a clinic that has experience in treating such diseases. For example, in medical, Moscow.
What to do if your arthritis gets worse
Algorithm of actions during exacerbation of post-traumatic arthritis:
- call a doctor at home;
- take any painkiller orally: Analgin, Pentalgin, Iburofen, Nise, etc.; Apply ointment or gel with analgesic properties (Volmaren, Fastum-gel, etc.) to the skin in the periarticular area;
- lie down and take a position that ensures the immobility of the joint.
First aid for joint injury:
- call a doctor or ambulance to your home (in case of severe injury);
- take an anesthetic orally; apply heparin ointment externally to the injured area;
- apply cold to the injury site;
- lie down and keep the affected joint immobile.
Chondroprotectors: what are they, how to choose, how effective are they?
Joint pain at rest
Physiotherapy
Phonation
Vibroacoustic therapy involves the transmission of sound microvibration using a special medical device. It creates microvibrations that, with their physical characteristics, are identical to those created by muscle tissue under maximum static physical tension. In short, this therapy is a direct alternative to exercise.
Vitafon.
Phoning Effects:
- Improving lymph flow in the area of influence, which promotes accelerated tissue cleansing, has an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Improves blood flow and, accordingly, nutrition of the treated area.
- Has a beneficial effect on nerve pathways with prolonged exposure.
- Promotes the release of joint lubrication.
Galvanization and electrophoresis
The essence of the procedure is to activate the blood supply to joint tissues in chronic arthritis . Vasodilation occurs in the area of influence, increasing blood supply and improving recovery processes.
Electrophoresis.
UHF therapy
The affected joint is exposed to a continuous or pulsed electric field. For the knees, low-thermal doses are used at a current power of 20-30 W.
The procedure is aimed at reducing swelling, activating regenerative processes in the joint, improving nutrition and blood supply. The method allows you to achieve long-term remission.
Infrared laser therapy
Using a laser applicator, they act on biologically active points located along the lateral surfaces of the joint. The procedure activates blood flow, reduces pain sensitivity, and stimulates healing processes.
Ultrasound therapy
The method optimizes and accelerates the biochemical processes occurring in joint tissues, accelerates healing processes, and reduces swelling.
Hydrogen sulfide and radon baths, peloid therapy, massage, and manual therapy have also proven themselves well.
Localizations
Any joint can be injured. But some of them suffer more often and more significantly than others. These knees, ankles, elbows.
Traumatic arthritis of the legs
The joints of the legs bear the highest load, so they often suffer from obesity, a sedentary lifestyle and constant exposure to minor injuries. These same joints are primarily injured during acute injuries - falls, blows, etc.:
Post-traumatic arthritis of the hip joint
Post-traumatic arthritis is not so common, but is severe, complicated by purulent processes and the formation of immobility. This joint is especially often injured in older people who are overweight and have osteoporosis - brittle bones due to loss of calcium.
Post-traumatic arthritis of the knee joint
It is injured more often than other articular joints. A special feature of the knee is the presence of a flat bone - the patella, which usually takes the blow. Traumatic lesions of the knee joint are varied due to the fact that not only the joint, but also numerous ligaments can be damaged. This will support inflammatory and degenerative processes. Athletes are at risk.
Post-traumatic arthritis of the ankle
The ankle also suffers very often, mainly not from direct blows, but when the foot is twisted and ligaments are torn. At risk are women who wear uncomfortable shoes with high, unstable heels.
Arthritis of the heel - talocaleonavicular joint
Supports the heel bone and transfers shock absorption from the ankle to the foot. Injured in heavyweight athletes, people suffering from obesity and flat feet. Arthritis often occurs chronically with the development of restrictions on joint mobility.
Post-traumatic arthritis of the hands
Post-traumatic arthritis of the shoulder joint
Traumatic lesions of the joints of the arms are less common than those of the legs. Traumatic arthritis usually affects athletes and people who lift heavy objects. Arthritis of individual joints.
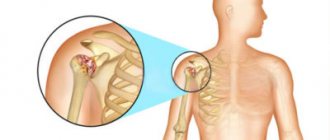
Post-traumatic arthritis of the shoulder joint
Inflammation of the joint most often appears as a result of a fall on the arm, a direct blow to the shoulder, or when the arm is sharply extended at the shoulder. Shoulder-scapular arthritis is dangerous; it tends to have a long course with constant pain and decreased function of the upper limb.
Post-traumatic arthritis of the elbow joint
Frequent minor injuries occur among tennis players. Characteristic is the development of not only arthritis, but also epicondylitis - inflammation of the tendons attached to the outside (tennis elbow). Arthritis lasts for a long time, with increasing pain. If left untreated, it leads to disability.
Post-traumatic arthritis of the wrist and hand joints
Arthritis is not so common, the cause is domestic trauma. Chronic arthritis of the wrist joint occurs in pianists, people who work on a computer for a long time, etc. With severe inflammation, carpal tunnel syndrome is often associated - compression of the median nerve by swollen tissue.
Post-traumatic arthritis of the fingers
Fingers are often injured. These can be acute domestic, sports and professional injuries. Minor injuries cause mild arthritis that ends in recovery. Fractures and bruises of the fingers are dangerous for people with rheumatoid arthritis: the inflammation caused by the injury leads to the development of exacerbation and stimulates the destruction of the joints.
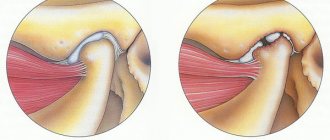
Traumatic arthritis of the temporomandibular joint
Arthritis can be the result of a one-time injury or long-term permanent injury. In the first case, an acute inflammatory process develops; if left untreated, persistent ankylosis may develop with pain and difficulty opening the mouth. Chronic arthritis develops against the background of malocclusion or the absence of certain teeth in the dentition and also, over time, leads to constant pain and impaired joint function.
Post-traumatic cervical arthritis
Traumatic lesions of the cervical spine can lead to the development of arthritis. Acute arthritis begins after a blow or injury to the neck. The course depends on the severity of the injuries: swelling of the periarticular tissues causes compression of the nerve roots and blood vessels supplying the brain. Therefore, this localization requires timely administration of adequate treatment.
Chronic processes can develop from untreated acute ones or be initially invisible. They develop with prolonged incorrect position of the neck (during sleep, while working at the computer), constant minor injuries during sports, etc. It manifests itself in the form of constant pain and limited mobility in the neck, as well as headaches and changes in blood pressure.
Causes
Now that we know that one of the main reasons for the development of arthritis is infectious diseases, let’s talk more specifically about what organisms have a destructive effect:
- fungi;
- viruses;
- gram-negative bacteria;
- streptococci;
- staphylococci;
- gonococci;
- brucellosis;
- Reiter's disease (most often affects the hip joints, but in a proportion of cases the knee joint is also involved in the process);
- helminthic and protozoal infestations;
- chlamydia;
- syphilis;
- hepatitis.
As for non-infectious arthritis, their development is due to many factors:
- DDI of cartilage structures (age factor).
- Injuries of varying severity and their complications.
- Inflammatory processes in tissues close to the joint capsule
- Genetic predisposition
- Disorders of calcium metabolism (for example, rickets).
- Behçet's disease.
- Ankylosing spondylitis.
- Cappilatotoxicosis.
- Osteomyelitis.
Diagnostics
It is impossible to make a correct diagnosis at home, so if you suspect a joint injury, you should consult a doctor. During the examination, the nature of the disease and the degree of damage to the joint are revealed.
Diagnosis begins with an examination by a doctor, then he refers the patient for additional studies:
- Laboratory:
- general clinical examinations of blood and urine
- the presence of an inflammatory process is revealed; - biochemical
– identification of functional disorders in the body as a whole; - immunological
– determine how adequately the immune system responds to inflammation; - PCR and microbiological (seeding joint fluid on nutrient media)
- carried out if an infection is suspected, detects not only the infection, but also its sensitivity to antibiotics. - Instrumental:
- Ultrasound
– volume of joint fluid and degree of soft tissue involvement; - X-ray
– reveals bone abnormalities in the joint; - CT and MRI
– more accurate detection of intra-articular and periarticular disorders; used to clarify details; - diagnostic arthroscopy
– examination of the inner surface of the articular cavity; if necessary, synovial fluid and a piece of tissue are taken for examination.
Crunching in joints - when to worry
Intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid
Cost of arthritis treatment
| Services list | Price, rub |
| Initial consultation with ORTHOPEDIST | 1600 |
| Repeated consultation with ORTHOPEDIST | 1200 |
| Consultation with an ORTHOPEDIST in a cycle | for free |
| Therapeutic puncture of the joint and joint capsule | 5500 |
| Intra-articular administration of drugs, without consumables | 4400 |
| Plasmolifting (Orthoplasma) into the joint | 7000 |
| Intra-articular injection (diprospan) | 5000 |
| Complex taping (joints) 1 zone | 1600 |
| Complex taping (joints) 2 zones | 2200 |
| Intra-articular blockade | 5500 |
| Paravertebral plasma | 7000 |
| Initial consultation with a kinesiotherapist | 1600 |
| Interim consultation with a kinesiotherapist | for free |
| Session with a kinesiotherapist (1 patient) | 3900 |
| Individual lessons with a personal trainer | 2700 |
| Intra-Articular PRP Injection | 6500 |
| Manual therapy 1 department (15 min.) | 2700 |
| Soft manual techniques (45-60 min.) | 7500 |
| Osteopathic techniques (30-75 min.) | 7000 |
| Simple taping 1 zone | 1100 |
| UVT 1 procedure | 2000 |
Contact us
Call now
8 (495) 803-27-45
Make an appointment through our service
Make an appointment
Treatment of post-traumatic arthritis
Acute post-traumatic arthritis is treated by a traumatologist or surgeon, chronic - by a rheumatologist. Based on the results of the examination, treatment for post-traumatic arthritis is prescribed. It should be comprehensive and include: drug therapy, non-drug methods, folk remedies. If necessary, surgical treatment is also prescribed.
Drug therapy
Drugs for the treatment of post-traumatic arthritis
It should be selected individually depending on the nature of the injury, the characteristics of the course of arthritis and the general condition of the patient. The following medications are prescribed:
- Antibiotics
– for open (knife, gunshot) wounds for prophylactic purposes, as well as if infection is suspected. Acute purulent arthritis requires immediate antibacterial therapy, therefore the most suitable group of antibiotics for the treatment of purulent processes is prescribed. They may need to be replaced once test results are received. - Anti-inflammatory drugs from the NSAID group
- suppress inflammation, relieve pain (Nimesulide, Ketorol, Meloxicam, Diclofenac). Depending on the patient’s condition, they are administered intramuscularly or taken orally in the form of tablets. In dosage form for external and local use (ointments, gels), they are applied to the skin in the area of inflammation. - Glucocorticoids (GCS)
are prescribed for severe inflammation, swelling and pain, using drugs from the NSAID group if they do not help. GCS is administered in short courses into the joint cavity intravenously, intramuscularly (Methylprednisolone, Dexamethasone). Swelling and pain are quickly eliminated. - Chondroprotectors
are medications that stimulate the growth of cartilage covering the articular surface (Structum, Chondroxide, Dona). - Basic anti-inflammatory drugs that suppress the increased activity of the immune system
are prescribed for chronic inflammation (Methotrexate, Sulfasalazine, etc.).
Surgery
Sometimes you can't do without surgery. For acute post-traumatic arthritis, the following surgical interventions are performed:
- therapeutic arthroscopy
is a gentle operation that removes blood, purulent exudate, as well as parts of necrotic tissue, small fragments of cartilage and bone; the joint cavity is washed with disinfectant solutions, then antibiotics are administered; - arthrotomy
is an open operation, rarely performed for severe wounds or purulent inflammatory processes; the joint cavity is opened, dead tissue, bone fragments, and sometimes the entire joint are removed; The pus is removed and daily rinsing of the cavity through a drainage tube is prescribed; - osteosynthesis
- in case of intra-articular fractures, bone fragments are connected using various devices; - arthrodesis
is an operation that creates the effect of an immobilized joint; after it the limb can only perform a supporting function; performed when it is impossible to use other treatment methods; - endoprosthetics
– replacement of a completely destroyed joint with an artificial one.
Non-drug methods
These methods are also selected strictly according to indications and may include:
- Immobilization is the main method in the treatment of post-traumatic acute arthritis. For fractures, a plaster cast is applied and removed after the bones have fused. In case of bruises, joint immobility is ensured by special splints and orthoses. They are prescribed in the shortest possible courses so as not to cause muscle atrophy. If the disease is chronic, then immobilization is not required.
- Physiotherapy - various types of procedures are prescribed, both in acute inflammatory processes (electrophoresis with painkillers) and in the recovery process (thermal procedures, magnetic and laser therapy, etc.).
- Courses of massage and physical therapy (physical therapy) - for acute arthritis are prescribed during the recovery period, for chronic arthritis - during remission.
- Good nutrition is of great importance for joint restoration. The diet should contain enough proteins (meat, fish, dairy products - sources of amino acids, from which new tissues are built), fats and carbohydrates (vegetables, grains, fruits - sources of energy), vitamins and minerals - substances necessary for full metabolism. It is worth giving up salty, spicy, smoked foods, and limiting sweets, especially sweet carbonated drinks.
Folk remedies
Methods that have been used in folk medicine for centuries are also sometimes included in the complex treatment of arthritis. But only the attending physician should do this. Here are some effective folk remedies:
- celery juice - prepared immediately before use; chop fresh celery root, strain and drink half a tablespoon 3 times a day 30 minutes before meals for 1 - 1.5 months; relieves pain, inflammation and swelling of joints;
- compresses from large burdock leaves - wash the burdock leaf, mash it slightly, apply to the inflamed area, apply plastic on top, wrap and leave overnight; repeat every day for four weeks; This method relieves inflammation and pain well.
Celery juice and burdock leaf compresses are among the most popular treatments for post-traumatic arthritis.
Read about other methods of treating arthritis in this article.
Is it possible to do without surgery?
Only certain types of gonarthritis are amenable to conservative treatment: acute infectious, reactive and fresh post-traumatic, not accompanied by massive hemorrhage and damage to joint structures. In the presence of hemarthrosis, rupture of menisci and ligaments, patients require surgical intervention. In this case, arthroscopy is most often performed. With purulent arthritis, patients often require puncture of the knee joint. During the procedure, doctors remove accumulated exudate, wash the joint cavity and administer antibiotics. Rheumatoid, psoriatic and other autoimmune arthritis in the initial stages are treated conservatively. However, with late prescription of drug therapy and high disease activity, patients experience impaired knee function and chronic pain. In this case, there may be a need for endoprosthesis replacement, that is, replacing the knee joint with an artificial endoprosthesis.
Approach to treating the disease in our clinic
Treatment of post-traumatic arthritis at Moscow Medical Center has its own characteristics:
- preliminary complete examination of the patient, including using high-tech instrumental techniques such as MRI;
- The complex treatment of traumatic arthritis includes:
- modern medicinal, non-medicinal and surgical methods used in leading clinics in the world;
- traditional oriental methods, which are based on the idea of the unity of all organs and systems; restoring balance in the body leads to recovery and filling the patient with life-giving forces; You can learn more about oriental treatment methods on our website.
The techniques used make it possible to quickly relieve pain and gradually restore joint function completely or partially. Patients trust our specialists!
Treatment
The instructions for medical assistance in case of injury are simple. To begin with, it is necessary to eliminate the pain syndrome, and also prescribe therapy aimed at preventing possible inflammation in the joint.
This will help restore the functioning of the joints and prevent undesirable consequences in the future. It is important to remember that treatment measures must be comprehensive and only a doctor can prescribe them!
Treatment of traumatic arthritis of the knee joint can be carried out according to the following scheme:
| № | A drug | Application |
| 1. | Chondroprotectors | Prescribed for the restoration of cartilage tissue and joints. |
| 2. | Vitamins and antioxidants | Necessary for nourishing joints, stimulating the immune system and strengthening the body. |
| 3. | Analgesics | Used to relieve pain. |
| 4. | Voltaren | Used topically as a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent. |
When there is a wound on a limb, the damage should be treated with antiseptics and a sterile bandage applied. If the knee injury was serious or complications began in the form of elevated temperature, severe tissue swelling, etc., antibiotics, antipyretics, and other medications are added to general drug therapy as indicated.
At the stage of recovery after a limb injury, in addition to medications, the doctor will recommend daily therapeutic exercises to the patient. It is very important to perform gymnastics correctly. Therefore, at first, it is recommended to practice with a specialist who will show you how to perform each exercise correctly. Additionally, the doctor will prescribe physiotherapeutic procedures for the patient.
General clinical recommendations
Those who have had acute or suffer from chronic post-traumatic arthritis should adhere to the following recommendations:
- lead a healthy lifestyle, give up bad habits, alternate between activity and rest, regulate sleep;
- eat well; monitor your weight;
- eliminate heavy physical activity and stress;
- treat all acute and chronic diseases in a timely manner;
- regularly perform therapeutic exercises, go swimming; conduct massage courses several times a year; walk more in the fresh air;
- as prescribed by the attending physician, conduct courses of anti-relapse treatment.
Prevention
To prevent post-traumatic arthritis, you need to improve your health, harden yourself, avoid risky traumatic situations, as well as permanent injury to a joint. It is especially important to comply with all these conditions for people already suffering from chronic arthritis - additional trauma can worsen its course.
We combine proven techniques of the East and innovative methods of Western medicine.
Read more about our unique method of treating arthritis
What happens if arthritis is left untreated?
Most of the population of the CIS countries lives by the principle “if a person doesn’t have any pain, then he is already dead,” thereby continuing to endure pain every day. Some adhere to the views of traditional medicine, but, as practice has shown, such procedures are practically useless in the fight against serious diseases. So what awaits a person who refuses treatment for arthritis?
1. Uncontrolled development of the disease.
Without proper attention, inflammation will grow and develop, which means that arthritis sufferers will experience increased pain and swelling. In addition, the disease will affect new healthy cells, completely affecting the entire body.
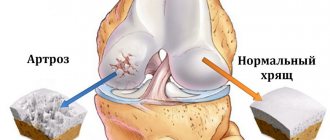
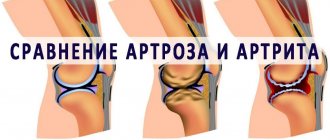
2. Arthrosis of the joints.
Due to the lack of treatment, the disease can develop into the process of destruction of the joint - arthrosis, which can lead to disability.
Therefore, treatment for arthritis must begin as early as possible.
Frequently asked questions about the disease
Is it possible to get disability?
Yes, if there is a persistent limitation of joint function.
Which doctor treats you?
Acute arthritis - a traumatologist or surgeon, chronic - a rheumatologist.
Can children develop post-traumatic arthritis?
Maybe.
What prognosis do doctors usually give?
Depends on the severity of the injury and the timeliness of medical care. In acute arthritis, the prognosis is generally favorable. Chronic progression can also be stopped at any stage.
Post-traumatic arthritis requires careful attention to your health and timely administration of adequate treatment. Our medical center can help you!
Literature:
- Karateev A.E., Barskova V.G. Criteria for choosing a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. Handbook of a practical doctor, 2007.- T. 5.- No. 5.- P. 13-17
- Kramer WC, Hendricks KJ, Wang J. Pathogenetic mechanisms of posttraumatic osteoarthritis: opportunities for early intervention Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2011; 4(4): 285-298.
- Lieberthal J, Sambamurthy N, Scanzello CR. Inflammation in joint injury and post-traumatic osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015; 23: 1825-1834.
Themes
Arthritis, Joints, Pain, Treatment without surgery Date of publication: 03/12/2021 Date of update: 03/15/2021
Reader rating
Rating: 5 / 5 (3)
Joint replacement surgery for knee arthritis
Knee replacement is required in the later stages of arthritis, when degenerative changes in the joints make it difficult to lead a normal lifestyle. In such cases, endoprosthetics is the only effective method of surgical treatment. The operation is performed to get rid of pain and restore normal mobility of the limb.
Indications for total endoprosthetics:
- all types of arthritis accompanied by loss of motor function of the knee;
- Bekhterev's disease with damage to the knee joint;
- severe consequences of injuries (deforming osteoarthritis, intra-articular fractures, improperly healed fractures of the femoral and tibial condyles).
Surgery is necessary if the patient has at least one of these symptoms:
- chronic pain syndrome that cannot be treated;
- hallux valgus deformity of 20 degrees or more;
- varus deformity of 15 degrees or more;
- flexion contracture of 15 degrees or more;
- the presence of complex instability in the affected joint.
Not only people with arthritis and their consequences may need knee replacement. One of the common indications for surgery is deforming osteoarthritis (DOA). The disease develops in old age and is accompanied by degenerative and destructive changes in cartilage and bone tissue. Many patients have concomitant osteoporosis.
Prospects for recovery after surgery
Endoprosthesis replacement is the most effective method of treating pathological changes in the knee joint. It allows you to get rid of chronic pain, completely restore the mobility of the knee and return the person to the ability to move. In the absence of complications and a favorable course of the recovery period, a person can return to a full life within a few months.
However, no prosthesis can completely replace the “native” joint. Therefore, after the operation you will have to take some precautions. You will not be allowed to kneel, engage in certain sports, jump, fall, make sudden movements, etc.
As for patients with rheumatoid arthritis, after surgery they will have to continue to take basic anti-inflammatory and genetically engineered drugs. Drug therapy is necessary to reduce the activity of the disease, avoid further destruction of large joints and another operation.