In what cases is ultrasound of the hip joints prescribed?
Diagnostics can be prescribed by a traumatologist, surgeon or orthopedist. Typically, ultrasound examination of the hip joints is indicated in the following cases:
- Limited mobility, difficulty getting out of bed after sleep;
- The appearance of stiffness when moving;
- Painful sensations;
- Suspicion of a dislocation or dislocations in the past;
- Change in skin color in the hip joint area;
- The appearance of a distinct crunch in the joint during physical activity;
- Frequent muscle spasms in the buttocks and thighs;
- Different lengths of the lower limbs.
Who is indicated for ultrasound of the shoulder joint?
In most cases, the following factors are direct indications for diagnosis:
- Injury to the shoulder area;
- History of musculoskeletal diseases;
- Pain in the shoulder area;
- Restricted mobility of the shoulder joint;
- Swelling of the area;
- Upcoming joint surgery.
In addition, diagnostics is used to assess the dynamics of treatment.
The shoulder joint has a complex anatomical structure, so its diagnosis must be carried out by competent specialists using high-quality equipment. Contact only trusted medical centers to get the most reliable information.
Advantages and disadvantages of ultrasound of the hip joints
Today, there are many different diagnostic procedures, such as x-rays, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging. Of course, these studies provide more detailed information, but such methods have a higher cost. Ultrasound examination, in turn, is cheaper, completely safe and allows you to identify pathological processes even in the early stages. In addition, the diagnostic result can be obtained within 10 minutes after the end of the examination.
Let's look at a few more benefits:
- The procedure is non-invasive;
- It is painless;
- It is also possible to study the condition of the blood vessels in the area under study.
Who should not have an ultrasound?
Anyone can take the study, regardless of age and other characteristics. This procedure is completely painless, does not cause discomfort and has no negative effect on the body. However, if the patient experiences limited joint motion, this can complicate the diagnosis. Before manipulation, make sure that there is no allergic reaction to the silicone that is included in the gel for ultrasound examination.
If there are fresh burns or severe injuries in the shoulder area, then it is worth postponing the examination until the wounds have healed.
How is the procedure carried out?
The patient removes clothing below the waist (except underwear) and lies down on the couch. Diagnosis is made using a sensor, with which the doctor reads information about the condition and density of bone, cartilage and soft structures. To obtain a complete clinical picture, the doctor uses several access options.
Anterior approach
The ultrasound doctor asks the person to lie on his back, and a small cushion is placed under the femoral surface. This position helps to better examine the structural elements of the hip joint. By observing the image on the screen, the specialist receives information about the condition of the ilium, femoral head, ligaments, muscles and lymph nodes of the groin.
Rear access
For such an examination, the specialist asks the patient to lie on his side and bend his knees slightly closer to his chest. During the study, it is possible to identify the functioning and characteristics of the sciatic nerve, obtain information about the surface of hyaline cartilage, and examine the superficial and internal structure of muscle fibers in the gluteal region.
Medial access
The person lies on his back, bends the lower limb and moves it to the side. This position allows for a detailed examination of the pelvic flexor muscles and articular ligaments if a pathological process is suspected.
Lateral access
The person lies on his side, and the specialist asks him to rotate his hip inward. In this position, the protruding elements of the tibia and the trochanteric bursa are clearly visualized.
On average, this manipulation lasts no more than 30-40 minutes. The patient is given the results of the examination; in some cases, additional images are attached so that the doctor can independently assess the clinical picture.
Ultrasound of the knee joint
Ultrasound of the knee joint is an informative method for studying the musculoskeletal system. It is completely safe for the patient, does not cause pain or discomfort, and at the same time reflects in detail the condition of the different structures of the knee.
Description of the knee joint
Ultrasound of the knee joint
The body pays close attention to the health of the knee joint. The knee is a joint with a complex structure that combines the patella, femur, and tibia. It is quite large and often suffers from injuries, inflammatory and degenerative diseases.
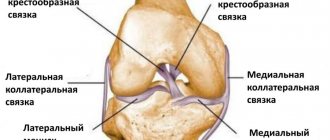
The ligaments responsible for the integrity and stability of the joint are the anterior and posterior cruciate, medial and lateral, patellar and transverse ligaments. They are located in the knee cavity and prevent the leg from moving excessively forward or backward. The kneecap, or patella, is connected to the thigh muscles by tendons.
The articular surfaces of the bones are covered with hyaline cartilage; the menisci, crescent-shaped cartilages located between the tibia and femur, are also built from similar tissue. The knee joint has several synovial bursae (bursae) filled with fluid.
Why is ultrasound prescribed to examine knees?
An ultrasound diagnostic method, or ultrasound of the knee joint, is a popular type of examination that involves the use of a special ultrasound machine.
Ultrasound becomes the first method of examining a patient with complaints of pain and other unpleasant symptoms in the knee joint. It is considered more popular than CT, MRI, and radiography.
The reason for the demand for knee ultrasound is its high efficiency and ease of implementation. Ultrasound has no obvious contraindications and meets the requirements for diagnosing diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
A person receives results almost immediately after execution; their decoding is minimal in time.
Ultrasound can be performed even on pregnant or breastfeeding women - the procedure will not harm the baby. Even children with an injury or other problem can be examined without consequences or crying, because it is carried out quickly and easily. Considering the low price compared to MRI and CT, ultrasound is used everywhere, helping to examine soft tissues, cartilage in detail and identify pathologies at any stage of their development.
What knee diseases can be detected using knee ultrasound?
Who should do this research and why?
The knee joint undergoes serious loads every day when walking and other movements, while it has to constantly withstand body weight, which can be significant.
This area of the musculoskeletal system is subject to severe wear and tear. Pathological changes in some patients begin in young and middle age.
Early detection of problems is possible using ultrasound, although this type of examination also reflects advanced stages of degenerative processes.
They carry out examinations both routinely and for any indication. Routine (preventive) examinations are needed for athletes and people who experience heavy loads on their knees.
Diagnostic sessions for athletes help prevent joint pathologies in the future. The examination is also carried out before competitions, after heavy loads, or if an injury is suspected. It is shown even in childhood when playing professional sports.
The main purposes of knee ultrasound are:
- diagnostic measures;
- determination of professional suitability;
- preoperative preparation;
- identifying the consequences of injuries;
- assessment of ongoing therapy;
- postoperative control.
Most often, an ultrasound scan is prescribed to patients who have suffered domestic or sports injuries to the lower extremity, therefore this technique is widely used in emergency rooms and during the initial appointment in traumatology departments.
The study will reveal:
- bruise - damage to soft tissue;
- hemarthrosis – bleeding into the joint;
- complete or partial damage to ligaments;
- tear, rupture of tendons;
- meniscus injuries;
- fracture of the patella, tibia condyles;
- displaced fractures;
- combined injuries;
- foreign body in the joint.
Ultrasound of the knee joint is recommended if symptoms regularly appear:
- palpable lumps and tumors;
- swelling in the morning or evening;
- stiffness and decreased mobility of the knee;
- local redness;
- hyperemia and hyperthermia.
When interpreting an ultrasound of the knee joint, you can find the cause of pain, deformation of bones and articular surfaces. Most often, such signs become part of the symptom complex of bursitis, synovitis, arthritis, arthrosis, and tendonitis.
The technique is indicated during operations, punctures, and arthroscopy. If Doppler ultrasound is additionally used, it is possible to simultaneously study the function of blood vessels, identify problems with blood flow, defects in the walls of veins and arteries, and a tendency to develop blood clots in the knee area.
If a patient develops joint pathology, the following data are revealed:
- the presence of free fluid in the intra-articular cavity, an increased volume of fluid in the bags (bursae), including those mixed with blood and pus;
- the presence of a foreign body (usually due to trauma), bone fragments;
- changes in the length, width, thickness, volume of various structures - joint space, cartilage, fat accumulations, folds, connective tissue elements;
- violation of the integrity of the ligaments - partial rupture of individual fibers or even complete rupture of the ligament;
- the presence of neoplasms - cysts, bone growths, tumors.
As a rule, all pathologies can be combined into the following groups:
- Injuries of the tendon-ligamentous apparatus (this is a rupture of the patellar ligament, and an injury to the tendon of the quadriceps femoris muscle or the lateral collateral ligament, etc.). Injuries of this kind occur if the joint was suddenly loaded due to improper sudden movement. There may even be a complete rupture with the formation of hematomas. As a rule, this is clearly manifested on an ultrasound of the knee in the form of a violation of tissue integrity, the formation of hypoechoic zones and other signs of serious injury. If the tendon ruptures only partially, its contours are clearly visible on ultrasound, then the site of damage will be designated as a hypoechoic area. So, if, for example, the patella is broken, then hypoechoic areas are clearly visible inside the bone fragments.
- Damage to the meniscus, as well as postoperative condition. A meniscal injury may not always be detected. As a rule, to understand whether it is damaged or not, they look at its outline. When its lines are distorted, hypogenic stripes form in parts of the organ, the leg itself swells, displacing the ligaments to the side, and the articular cavity accumulates fluid, it’s time to change the meniscus.
- Degenerative tissue change. Knee joints, like other groups of cells, can be subject to deformation. This can be easily determined. So, if a patient has arthrosis deformans, in the ultrasound image of the knee joint the hyaline cartilage looks very damaged, and the width of the joint space itself decreases.
- Visualization of cysts in the form of cavities with a certain fluid.
- Dysplastic process.
- Tendinitis, the peculiarity of which is a decrease in the echo density of the tendons to the maximum.
- Inflammation of the synovial membrane and increase in its size.
Ultrasound of the knee joint is indicated for suspected other joint problems:
- various injuries;
- meniscopathies;
- hemorrhages;
- inflammatory pathologies;
- dysplasia;
- neoplasms.
Using ultrasound, specialists can make a prognostic calculation: for example, based on the height of cartilage and the volume of intra-articular fluid, it is possible to determine the presence of initial signs of degeneration and recommend preventive measures. The procedure is indispensable for damage to the knee area; it will help differentiate sprained ligaments from their rupture, bone fractures from injuries to the menisci and kneecaps.
The study will allow us to draw a conclusion about the benignity or malignancy of the tumor process and identify a Baker's cyst, which is characteristic of sports injuries. It can be done as often as required. Repeat sessions are usually needed to evaluate the results of the treatment.
Ultrasound of the knee joint is also prescribed for:
- frequent fractures, dislocations in this area;
- in children with congenital dysplasia, structural anomalies;
- increased body weight, severe obesity;
- rupture of Baker's cyst.
Direct indications for ultrasound of the knee joint:
- Suspicion of defects or structural anomalies in adults or children, suspicion of birth injury.
- Chronic or acute pain (including if the knee hurts only on palpation, but in a calm state does not bother the patient).
- Unsteadiness of gait, development of flat feet for no apparent reason, feeling of instability in the joint.
- Shortening or lengthening of one limb (in this case, it is recommended to simultaneously do an MRI of the pelvic area).
- Destabilization of the knee joint (its movement out of the groove, visible to the naked eye) during physical activity.
- The patient’s ability to independently move (displace) the joint (this is abnormal).
- Development of tumor neoplasms in the joint area of any consistency (hard, soft, containing liquid).
- The feeling of heat in the knee is both subjective (felt only by the patient) and objective (felt by the doctor during palpation).
Diagnosis of the knee joint using ultrasound is indicated for different groups of patients of all ages and genders. Most often, the technique is prescribed to people in the older age group and athletes.
Preparation and technique for ultrasound examination of the knee joint
No preparation is required from patients, with the exception of those receiving intra-articular injections. The last injection should be given no later than 5 days before the examination of the knee joint. Otherwise, visualization may deteriorate. You should definitely take with you the results of previous procedures and a doctor’s prescription (referral).
Ultrasound is most often performed in the supine position. The person is asked to lie down on a couch, and the doctor applies a special conductive gel to the skin, after which he moves the sensor over the desired anatomical area. To study the condition of the knee in more detail, the patient is asked to change the position of the body and legs several times during one study.
Four approaches are usually practiced, which help to study the structure of the knee joint in different ways:
- Anterior access. Provides information about the thigh muscles, patella with ligaments, patellar bursae, and fatty tissue. At this time, the patient lies on his back with his leg straightened.
- Rear access. Allows you to visualize the menisci, nerves and vessels of the popliteal zone, tendons, calf and calf muscles, and the cruciate ligament. For the examination you need to lie on your stomach.
- Medial access. Helps identify all problems of the joint capsule, collateral ligaments, inner part of the meniscus, articular surfaces of bones, cartilage and synovial fluid. From a lying position on your back, you need to extend your leg straight.
- Lateral access. Detects pathologies of the fascia lata, large tendons, external meniscus, external collateral ligament, and joint capsule. For the procedure, the leg should be bent at the knee 30-40 degrees.
If there are unpleasant symptoms in one limb, the doctor in any case examines the condition of both knee joints. The information is displayed on the screen, after which the data is entered into a protocol, printed and handed to the subject. The duration of an ultrasound of the knee joint in a medical setting usually does not exceed 15-20 minutes.
How is an ultrasound of the knee joint performed?
As already mentioned, there is no need to prepare for the procedure. It is carried out quickly, the doctor records the results along the way and reports them to the patient. Then the doctor fills out a protocol (conclusion) of the ultrasound of the knee joint, with a detailed description of what he saw. And then the radiologist determines further treatment. But that's it in a nutshell. Let's consider the procedure itself in more detail.
- First, the patient is placed on his back and his limbs are straightened. This is necessary to take a picture of the anterior and lateral parts of the joint. If you need to examine the meniscus, the legs are bent. Then they move on to the back of the knee - for this the patient is asked to lie on his stomach. To assess what the degenerative changes are and how they compare with the norm, pictures of the healthy leg are taken at the same time.
- To obtain complete information from an ultrasound examination of the knee joint, filming is done in many projections (described in more detail below). Thus, the patella, its bursa and the presence of effusion in it are examined in the anterior projection. And just below are the contours of the tibia. If you rotate the transducer to a transverse view, you can examine the contours of the femur, suprapatellar bursa, hyaline cartilage, etc.
- If the joint cavity is examined, there should be no effusion inside it, and the capsules themselves should not be changed. Hyaline cartilage should be echo-homogeneous, with clear and even contours. In this case, the synovial membranes are not visible, the patellas are located strictly in the center, without displacement, and the menisci remain intact, with the correct structure.
Advantages and disadvantages of knee ultrasound
In addition to ultrasound, there are other ways to examine joints. Ultrasound is leading in popularity due to a number of advantages. The strengths of this study are:
- no need for preparation;
- complete absence of pain, discomfort, skin irritation during the procedure;
- hypoallergenicity of the gel used;
- safety of the method for children, pregnant and lactating women, as well as people with severe chronic diseases;
- absence of invasive manipulations, radiation exposure, speed and ease;
- no contraindications for implementation;
- high speed of obtaining results;
- sufficient information content for most joint diseases;
- the ability to detect pathologies at the earliest stages;
- low cost;
- availability of the service in most clinics, hospitals, private clinics;
- detection of problems in all joint structures, nerves and blood vessels.
The disadvantage of the ultrasound method is that it does not reflect the condition of the bones in too much detail, so in some cases it is necessary to carry out further examination in the form of radiography or CT.
You can always make an ultrasound appointment with an ultrasound doctor in Sochi at the medical ]VegaMed[/anchor], ultrasound prices start from 400 rubles, you can visit an ultrasound doctor on the same day as the clinic has free rooms for receiving patients.
You can make an appointment by calling +7 (862) 295-00-95 We also invite you to follow us on Instagram You can use WhatsAPP Make an appointment without a phone call to the medical center “Click here to sign up”
Decoding the results
An orthopedist, surgeon, or orthopedic surgeon can interpret the results. The research protocol usually contains the following information:
- the presence of pathological processes, a detailed description of the deviation.
- congenital or acquired changes inside the joint;
- condition of ligaments and nerve bundles;
- increase in the thickness of the joint capsule;
- functioning of adjacent muscles;
- features of cartilaginous structures;
- the amount of synovial fluid inside the joint.
- the presence of neoplasms, if any, their shape, structure, size and individual characteristics;
- information about the ilium, labrum and femoral head;
- metastasis of nearby tissues;
- presence of hematomas.
Please note that the result of an ultrasound examination is not a basis for making a diagnosis. If any inconsistencies or pronounced pathological processes are detected, it is additionally necessary to perform a computed tomography scan and pass various tests for laboratory research. In some cases, a biopsy may be necessary (for example, if the doctor suspects a malignancy). The final diagnosis and necessary treatment are prescribed only after additional studies.
Normal hip joints according to ultrasound
If the patient does not have various pathological processes, the protocol indicates that the hip joints have a clear and smooth surface, without deformations and bone growths. The joint capsules should have folds and branches; their structure is normally hypoechoic.
The following information is also usually indicated:
Right joint:
The bony part of the acetabulum is normal. No major changes. Rectangular bony protrusion. The overlap of the cartilaginous part of the roof of the femoral head is sufficient. The limbus is projected laterally from the femoral head, is presented, and has a normal angle of inclination. The head of the femur in the acetabulum is located correctly. The ossification nucleus is located. Angle a is less than 60 degrees. Angle b is greater than 55 degrees.
Left joint:
the roof of the acetabulum is moderately flattened, without structural changes. The femoral head is centered correctly. The ossification nucleus is located. Angle a is more than 60 degrees. Angle b is more than 55 degrees. The angular parameters of the joint are not changed. When performing functional tests, the joint is stable.
Please note that these indicators may vary depending on age - deviations from them do not always indicate the presence of diseases or some problems.
What pathologies can be identified
Most often, during an ultrasound examination of the hip joints, the following diseases are detected:
- Arthrosis (it develops as a result of congenital dislocation of the hip, a disturbance in the circulatory system, or as a result of a fracture of the femoral neck);
- Arthritis (may occur due to infection of joint joints by pathogens);
- Synovitis, which is characterized by inflammation and fluid accumulation inside the joint;
- Necrosis of bone tissue (can occur due to frequent fractures, dislocations, bruises);
- Tears and spasms of muscle fibers;
- Swelling of the joint.
The hip joints are most susceptible to various pathological processes. Diseases can be either congenital or acquired. If you visit a medical facility as soon as the first symptoms appear, you can hope for a favorable outcome and complete recovery. Otherwise, your doctor may recommend surgery.