Structure FunctionsCausesSymptomsTreatmentDrugs
Cartilage tissue is present in many organs, but it is subjected to the greatest stress in the joints. Cartilage covers the vulnerable areas of the bones in the joints and provides shock absorption, as well as resistance to stress, thanks to which we do not even think about what tests the joints face in the life of an ordinary person, not to mention the categories of people who subject their bodies to excessive stress. Unfortunately, cartilage can deteriorate over time for various reasons, leading to limited joint movement, pain and discomfort. Therefore, it is so important to take the necessary measures in time to restore the cartilage tissue of the joints.
Structure of cartilage tissue
Cartilage is a type of connective tissue, and there are three types of it in the body:
- Hyaline (vitreous) - has a bluish color, with a high content of fine collagen fibers, covers the articular surfaces of bones;
- Elastic (mesh) - characterized by increased elasticity and flexibility, it is dominated by elastin fibers, it forms small bronchi and auricles;
- Fibrous - connects tendons and ligaments to the hyaline cartilage of the articular surface.
Like any tissue, cartilage consists of cells and intercellular substance (matrix), the proportion of the latter significantly predominates in it. The matrix contains a lot of water, which does not compress or stretch, but circulates freely in the intercellular space. It is water that provides high elasticity to cartilage tissue, distributing loads and cushioning. Another important component of the matrix is protein fibers: collagen and elastic. The hyaline cartilage of articular surfaces is dominated by collagen, which provides high strength. Its large molecules, twisted into a triple helix, are resistant to any deformation and quickly return to their original state. The matrix also contains glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans, and hyaluronic acid, which retain water and participate in metabolic processes.
Cartilage cells - chondrocytes and their young forms, chondroblasts - play an equally important role: they synthesize all the components of the matrix and joint fluid. There are very few chondrocytes, only 1-5%, but they are responsible for the renewal and restoration of cartilage.
One of the main differences between cartilage tissue is the absence of blood vessels. As a consequence, cartilage must receive nutrition in an alternative way. Synovial, or joint, fluid reduces friction between articular surfaces and provides nutrition to cartilage tissue. Therefore, the delivery of nutrients and the removal of breakdown products is ensured by synovial fluid.
Why does the cartilage in the knee deteriorate?
Throughout life, a person bends and straightens the knee many times. If there is enough synovial fluid in the joint, this process is painless, since the lubricant softens friction. As soon as there is not enough lubricant, the joints begin to rub against each other. This leads to rapid wear and destruction of cartilage.
Cartilage cells (chondrocytes) feed through the synovial fluid, since there are no vessels directly in the joint that transport nutrients. That is why, to restore normal function of the knee, it is important to replenish the lack of lubrication, as well as perform a number of other procedures.
Without replenishing the deficiency of synovial fluid, any other manipulations become meaningless
Causes of destruction of cartilage tissue
The cartilage in the joints is subjected to significant stress, and in certain circumstances it cannot withstand it: it begins to collapse. Especially if changes occur in the body that reduce its regenerative abilities. In this case, osteoarthritis develops - a disease caused by degenerative changes or destruction of the cartilage and bone tissue of the joints. Previously, another name for this condition was used - osteoarthritis, emphasizing the age-related nature of the changes. But, since inflammatory processes inevitably develop against the background of destruction of osteochondral structures, and it is they that cause characteristic symptoms, the term “osteoarthritis” is now predominantly used, and according to the international classification of diseases (ICD-10), both of these diagnoses are considered synonymous. In relation to dystrophic changes associated with the destruction of cartilage and bone tissue of the spine, it is customary to use the term “osteochondrosis”.
The causes of destruction of cartilage tissue are varied:
Proper nutrition for joint cartilage
There is a lot of information about mucopolysaccharides - substances that are part of various types of connective tissue and some biological fluids. Due to their ability to retain and bind water, they serve as a natural lubricant for joints and determine the elasticity of connective tissue. Such substances in the joint cavity participate in the formation of synovial fluid, which is an intra-articular lubricant. The main representatives of mucopolysaccharides are hyaluronic acid, heparin and chondroitinsulfuric acids.
Many modern dietary supplements and medications that are used for the treatment and prevention of diseases of the human musculoskeletal system contain hyaluronic acid, glucosamine and chondroitis sulfate.
Mucopolysaccharides can be easily introduced into your diet through food products, for example, jellied fish, jellied meat. Even in ancient times, people knew about the healing properties of jellied meat and strong broths, since in addition to mucapolysaccharides, they contain collagen, which plays a significant role in the treatment of the musculoskeletal system.
It is also good to use seafood, animal or poultry by-products for the treatment and prevention of joint diseases and to strengthen the immune system. It should be remembered that during the cooking process there is no need to remove ligaments, cartilage, tendons, bones - these are the main parts rich in mucopolysaccharides. Various jelly and fruit jellies are perfect as a dessert (gelatin also contains mucopolysaccharide).
Calcium and phosphorus are also needed to strengthen bones. These elements are found in the right quantities in sea fish and seafood, for example, shrimp, sardines, mussels, herring, mackerel. Quite a lot of calcium is found in dairy products such as cheese and cottage cheese.
Raw vegetables contain a large amount of vitamins that are necessary for the synthesis of cartilage tissue. It is better to use vegetable oils as a dressing, which have an anti-inflammatory effect.
To prevent excess salts from accumulating in the joints, it is necessary to drink only purified or still mineral water and eat soy products. It is contraindicated to eat smoked meats, fatty meats, beans, dried fish and marinades. It is beneficial to drink a glass of grapefruit juice daily. It is imperative to replace smoked dishes with baked ones in foil, fried ones with stewed ones, and high-calorie carbohydrate sweets with fruit jellies, fruit drinks or jelly.
By adhering to the principles of proper nutrition, you can saturate your body with healthy vitamins and minerals and thereby avoid weight gain, and the mucopolysaccharides obtained from foods will become an excellent nutritional cocktail for cartilage and joints.
Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Restoration of cartilage tissue
Why does cartilage tissue break down?
Cartilage tissue ensures the musculoskeletal function of the body.
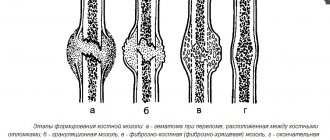
The structure of cartilage allows it to be reversibly deformed. The difference between cartilage and other tissues: a small number of cells that are surrounded by an elastic intercellular space with structural supporting elements (matrix). Cartilage takes a long time and is difficult to recover from injuries due to the small number of cells capable of regeneration. They contain a large amount of water, collagen and elastin. In hyaline cartilage on the intraarticular surface, 50% of the matrix is collagen. The largest percentage of collagen is found on the surface of articular cartilage. Collagen has a special structure that makes the fibers strong and resistant to tearing and stretching.
The main disease caused by cartilage damage is osteoarthritis. It reduces the elasticity of cartilage and the ability of joints to actively move. Joint problems negatively impact your quality of life by limiting activity and preventing you from performing daily tasks.
Diagnostic methods
To determine the degree of destruction of cartilage and surrounding tissues, informative diagnostic methods are needed. These include radiography and MRI, which are indispensable for the early diagnosis of joint damage, as well as for determining degenerative changes.
These types of diagnostics do not provide complete information about the structure and morphological quality of cartilage.
Ultrasound of joints with elastographic analysis of cartilage tissue is the most promising method for diagnosing joint diseases. It allows you to determine degenerative pathological changes in joint tissue, monitor the effectiveness of treatment, reparative processes in articular cartilage and other intra-articular structures, and identify changes in the synovial membrane, as well as in chondral tissue.
Ultrasound of joints with elastography allows you to obtain quantitative and qualitative indicators:
- condition of the synovial membrane (thickness, inflammatory changes);
- the amount of intra-articular fluid and its distribution;
- cartilage thickness, degenerative changes, ability to regenerate;
- the condition of the subchondral structures that provide blood supply and nutrition to the cartilage;
- elasticity;
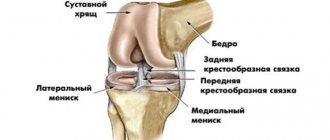
- condition of the menisci (their traumatic or degenerative changes, transposition and functional stability);
- traumatic or degenerative damage to the stabilizing apparatus of the knee joint.
The necessary measures to restore cartilage tissue make it possible to stop degenerative processes caused by age-related changes and excessive physical activity.
In modern medicine, there are effective methods and techniques for restoring cartilage tissue.
The choice of technique, as well as the appropriateness of a particular drug for treatment, is determined by the doctor after consultation and diagnostics. The doctor selects a treatment and recovery regimen based on the patient’s age characteristics and concomitant pathologies.
Treatment methods
Specialists at the Scandinavian Health Center use progressive methods for increasing cartilage tissue: “Orthokine Therapy®”, PRP (platelet rich mass), SVF (stromal vascular fraction), as well as shock wave therapy, administration of reparative drugs for cartilage tissue, taking chondroprotectors .
A set of therapeutic measures aimed at restoring the structure of the joint has a high level of effectiveness and helps prevent the progression of pathological changes, favors the restoration and growth of cartilage tissue.
In cases where the disease progresses, doctors may prescribe surgical treatment - arthroscopy and joint replacement.
Conservative therapy
As a conservative therapy, moderate physical activity is used: gymnastics, swimming, Nordic walking, etc. As well as physiotherapeutic procedures: shockwave therapy, acupuncture, magnetic therapy, etc.
The Scandinavian Health Center has created all the necessary conditions for diagnosis, high-quality treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system and rehabilitation after injuries and operations. Doctors at the Scandinavian Health Center will conduct all the necessary examinations and select the necessary course of treatment to restore motor activity.
An integrated approach to treatment allows the patient to return to active activities and sports.