Piriformis syndrome is a uncomfortable condition that affects the gluteal region. It may affect the upper thigh, groin or lower leg.
There are many reasons for the development of this disorder. To make an accurate diagnosis, it is worth analyzing the symptoms.
What is the essence of piriformis syndrome?
This term refers to a set of pains that appear in the buttock area. Piriformis syndrome ICD-10 belongs to group G57.0 Damage to the sciatic nerve.
The appearance of the disease is caused by a variety of factors - pathologies of the pelvic organs or unsuccessful injections. Regardless of the cause of the disorder, a person experiences severe pain in the buttocks, which also affects the legs.
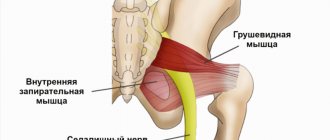
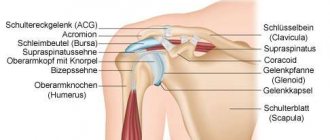
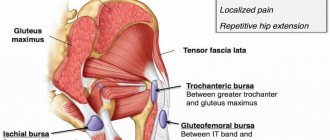
The piriformis muscle according to ICD-10 helps to abduct the hip and restore it to its original position. At the beginning of the movement, it protects the hip from rotation and is responsible for its swing.
In 90% of situations, the sciatic nerve leaves the pelvic cavity under the piriformis muscle in the direction of the buttocks, and in 10% it goes through it.
If the piriformis muscle becomes tight, there is a risk of compression of the sciatic nerve. This provokes the occurrence of intense pain syndrome.
Traditional methods of therapy
Traditional therapies include the use of decoctions, tinctures and homemade ointments that have anti-inflammatory properties, eliminating piriformis syndrome. It is recommended to use the following recipes for home remedies, the effectiveness of which has been proven over time.
Compress made of honey, bran and vegetable
To prepare this folk remedy you will need to take 0.5 kg of wheat bran, 2 tbsp. l. honey collected from herbs, as well as 1 tsp. unrefined sunflower oil.
All components are thoroughly mixed, and then an oval-shaped cake is formed on their basis, which is placed on the back of the thigh, covering the maximum area of the buttock. A plastic film or bag is placed on top of the cake. The procedure is performed once a day for 2 hours. The duration of the therapeutic course is 10 days.
Larkspur tincture
You need to collect it yourself or purchase larkspur root at the pharmacy. This is a medicinal plant that relieves inflammation in joints, bone and connective tissue, and muscle fibers. Indicated for use in cases of pinched nerve endings. You should take 50 g of larkspur root, chop it, pour it into a glass jar, and then pour in 0.5 liters of ethyl alcohol or vodka.
After 5 days, this product is used to rub the lumbar spine, buttocks on the side where the pain is located, and the inner part of the thigh. Therapeutic manipulations are performed 2-3 times a day for 12 days. If a local allergic reaction to larkspur occurs, use of the product should be discontinued.
Chamomile decoction
This is a general-spectrum homemade anti-inflammatory remedy. Used in combination with other medications or traditional medicine methods.
In order to reduce the degree of inflammation in the tissues of the piriformis muscle, you need to take 2 tbsp. l. dried chamomile, pour them into a metal container, pour 0.5 liters of running water and boil over low heat for 15 minutes. The resulting decoction is taken in the morning and evening, 200 ml per 20 minutes. before the meal. The course of treatment is 15 days.
Piriformis syndrome, complicated by sciatic nerve entrapment, is a serious and dangerous disease that can impair the mobility of the lower limb. The use of folk remedies is possible only with the permission of a doctor. If the doctor insists exclusively on drug treatment, then you need to listen to the opinion of a specialist.
Etiology
Pathology provokes abnormal changes in the piriformis muscle. Provoking factors include:
- injury;
- spasm;
- fibrosis;
- inflammatory process;
- increase in size.
The human piriformis muscle can be damaged due to intramuscular injections, which can provoke the occurrence of an intramuscular abscess and the formation of an infiltrate. The main etiological factors of pathology include the following:
- Injuries. The cause of problems is excessive stretching of muscle tissue, tearing of fibers, and the development of fibrosis. With fibrotic processes, shortening and thickening of the muscle is observed.
- Post-traumatic hematoma.
- Vertebrogenic pathologies. This category includes spondyloarthrosis and osteochondrosis. These also include intervertebral hernias in the lower back. In addition, spinal and vertebral tumors are provoking factors. Damage to the fibers of the sacrum and spinal nerves causes a reflex spasm.
- Inflammation. These include inflammation and prostate adenoma, damage to the bladder. Spasm of the piriformis muscle is associated with endometriosis, sacroiliitis, and myositis.
- Muscle overload. Their cause is the prolonged stay of the pelvic-iliac segment in a forced position. With radicular syndrome, a person tries to take an antalgic position. Some sports can cause the disease - in particular, running and weightlifting.
- Malignant tumors in the sacrum and proximal femur. They provoke anatomical processes in structures. Neoplasia can provoke spasm and inflammation of the piriformis muscle.
- Pelvic asymmetry. It is observed with shortened legs or scoliosis.
- Removal of the thigh. In this case, the muscle is in a state of constant spasm, which leads to the appearance of phantom pain.
Pathogenesis
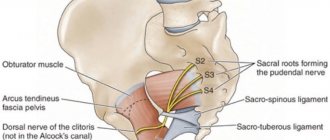
The narrow part of the piriformis muscle is fixed on the greater trochanter of the femur, and the wide part is attached to the sacrum. It is responsible for external rotation and helps to abduct the hip inward. This part of the muscle tissue passes through the sciatic foramen. Nerves and blood vessels are located in this area.
Due to the constant contraction of muscle tissue, the size of the infrapiriform opening decreases. As a result, blood vessels and nerves are compressed. First of all, the sciatic nerve is affected, which leads to severe pain.
In addition, compression of blood vessels disrupts blood circulation in the nerve trunk. This is considered an additional factor in the development of sciatica.
Technique for performing therapeutic blockade
To avoid the development of side effects or complications of the procedure, surgeons or traumatologists who perform it adhere to the following algorithm of actions:
1. The patient is on the couch in a lying position on his stomach or healthy side with the lower limbs slightly bent at the knee joints.
2. The doctor treats the skin of the buttock with an antiseptic solution and marks the point at which the skin will be punctured. It is located in the middle of the triangle, its vertices are the ischial tuberosity, the posterosuperior iliac spine and the apex of the greater trochanter of the femur.
3. The doctor inserts a long thin needle into a given point to a depth of 6-8 cm, and as it moves, gradually saturates the skin, subcutaneous fatty tissue and muscles with an anesthetic solution. When the needle rests on the sacrospinous ligament, located under the piriformis muscle, the specialist feels tissue resistance. He partially, by 1-2-3 cm, removes the needle and, slightly changing its angle, slowly injects a solution of an anesthetic, glucocorticoid or a cocktail of these drugs.
4. When the entire dose of the drug has been administered, the needle is removed, the puncture site is re-treated with an antiseptic and sealed with a band-aid.
There is no need to carry out injections in a course, and there are no official recommendations on how many times to carry them out. The procedure is done once, then the effect is assessed, which persists after the administration of the hormone for up to 4-6 weeks. Due to the long list of side effects and complications of glucocorticoid therapy, it is not recommended to use them too often. A weak effect from the injection or the need to use this type of treatment many times in a row are signs that the pathology is of a secondary nature, and that the underlying disease should be treated first.
Clinical picture
Manifestations of the syndrome include a whole range of disorders:
- local symptoms;
- signs of sciatic nerve compression;
- clinical picture of vascular compression.
Local manifestations include the following:
- Drawing and aching pain. It is located in the buttock, sacrum, and hip joint. The pain increases in a vertical position, with movement, with adduction of the hip. It progresses when a person squats.
- Vilenkin sign. In this case, discomfort appears during percussion. It is localized in the area of the piriformis muscle.
- Reducing pain in a horizontal position. It also decreases if a person sits with his legs apart.
- Bonnet-Bobrovnikova sign. When the large gluteal muscle is completely relaxed, a compacted piriformis muscle is felt underneath it. When pulled, it causes pain.
- Discomfort in the ischial spine. It is this area that the finger feels when quickly moving from the ischial tuberosity straight up.
Quite often, tonic tension of the piriformis muscle is complemented by the same condition of other muscle tissues of the pelvic floor. Almost always the deviation is accompanied by unexpressed sphincter deviations. In this case, there is a delay in the onset of urination.
When the sciatic nerve and vessels of the infrapiriform region are compressed, the following symptoms occur:
- Dull pain. In this case, a vegetative coloration is observed, which manifests itself in the form of chilliness, decreased sensitivity or burning in the affected area.
- Distribution of pain throughout the lower extremities. It mainly passes through the area of innervation of the peroneal and tibial nerves.
- Weakening of the Achilles reflex. A person experiences a deterioration in surface sensitivity.
- Symptoms worsen when exposed to stressors or heat. Also, the clinical picture may intensify when the weather changes.
If the abnormal process predominantly involves the fibers that form the tibial nerve, discomfort affects the posterior group of muscle tissues of the lower leg. It occurs when walking.
When the blood vessels are compressed, a sudden spasm of the lower limb occurs, which provokes lameness. In such a situation, a person is forced to stop while moving. Dermanogi acquires a pale tint. After resting, the person can continue to move, but soon the attack recurs.
Symptoms
In approximately 70%, the gluteal-sacral area is affected first. The pain is constant, often nagging and aching. They intensify during walking, squats, and hip adduction. To reduce discomfort, the patient has to spread his legs to the sides. Over time, pain along the sciatic nerve - sciatica - is added to the symptoms. Shooting marks appear running from the foot to the buttocks. In the area where the SGM is located, pain sensitivity decreases and a burning sensation occurs.
Hypotonia of the muscles of the foot and lower leg gradually develops. With total compression of nerve fibers, “dangling foot” may develop. The main manifestations include intermittent claudication, which is a consequence of vascular compression. The same disorder leads to a decrease in leg temperature, pale skin and numbness of the fingers.
The main reasons for the development of SGM
The main factor in the occurrence of pain in the buttock area is considered to be compression of the sciatic nerve. The disruption of its normal functioning is due to high tension of the piriformis muscle. This is due to various factors.
These include hypothermia, incorrect injections, pathologies of the hip joints, diseases of the spine, damage to the connective tissues of the pelvic area, and increased physical activity.
Weakness of the gluteal muscle associated with injury or compression of the nerve root also leads to problems. In such a situation, the piriformis muscle will take on part of the load of the gluteus maximus, which will cause its overstrain.
How can exercise help?
- First, gently stretching the tight muscle will help it relax.
- Secondly, improve blood circulation in the area where the sciatic nerve is pinched.
- Thirdly, help achieve general relaxation, which will lead to partial muscle relaxation.
- Fourth, improve the functioning of the sacroiliac joint and hip joints.
It should be noted that these exercises are of an auxiliary nature. It is necessary to receive comprehensive treatment from a neurologist and use exercises only as an important addition.
Manual therapy, particularly PIR (Post Isometric Relaxation), can help relax a spasmed muscle.
Surely massage of the affected buttock, or self-massage using rolls on a tennis ball, is positive.
Secondary pathology
Secondary syndrome is associated with the influence of external factors. These include the following:
- Traumatic injury to the buttocks. It can cause inflammatory damage to soft tissues, muscle spasms, and a combination of both. As a result, compression of the nerve occurs.
- Direct damage to the piriformis muscle, postoperative injuries, increased stress on the lower back. Under the influence of these factors, muscle spasms appear.
- Shortening of muscles. The syndrome is caused by changes in the biomechanics of the leg and lumbosacral region. This often causes compression and irritation of the sciatic nerve.
Secondary pathology is associated with microtraumas. They appear due to overuse of the piriformis muscle. These include long distance movement or direct impact.
Osteopathic treatment
Osteopathic treatment does not just act on the sore spot, but treats the entire body as a whole; the doctor “listens to the body with his hands.” All organs and systems constantly pulsate, and spasms and tensions distort the picture characteristic of the body of a healthy person. The magnitude of these pulsations is insignificant, but is accessible to the sensitive hands of an osteopath.
Having examined these micropulsations, the doctor determines the cause of the syndrome and eliminates muscle tension. Muscle tissues and ligaments are stretched and relaxed, and the doctor uses gentle movements to move organs and tissues to return them to their normal anatomical position.
Osteopathic correction of the bones, muscles and ligaments of the pelvis, as well as the lumbosacral spine, plays a special role in osteopathic treatment. Soft muscular-fascial relaxation of the Musculus piriformis quickly restores the normal state and eliminates the cause of the syndrome - compression of the sciatic nerve and blood vessels. In especially severe cases, the treatment program is supplemented with drug blockade of the brain.
Preventing piriformis muscle spasm
There are no specific methods for preventing pathology. It is recommended to avoid excessive stress on the muscles and injuries.
It is important to contact a specialist in a timely manner. This will help in the initial stages to diagnose and treat pathologies that can provoke piriformis syndrome.
In addition, following these rules will help prevent the development of the disease:
- avoid hypothermia;
- do not engage in heavy physical labor;
- Do not stay in a position for a long time that reduces pain.
Piriformis syndrome is a fairly serious pathology that causes severe pain. It is caused by a whole complex of factors - increased physical activity, injuries, hypothermia.
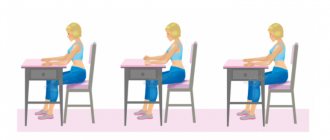
Exercise therapy in the treatment program
After the acute pain syndrome is relieved, the results of osteopathic treatment are consolidated with the help of physical therapy. This allows you to avoid re-exacerbation of the syndrome. Exercises are performed under the guidance of an instructor. The program includes the implementation of special complexes aimed at strengthening: • the muscular corset of the lower back; • buttocks; • lower extremities. Work is also carried out with other parts of the musculoskeletal system.
Treatment of BMS is not aimed at relieving symptoms, but at eliminating the root cause of the syndrome. Therefore, any pain relief without treating the provoking factor is pointless. The exercises that are prescribed to patients are aimed at fully relaxing the muscular-ligamentous system, as well as activating antagonists in the movement of the lumbosacral region