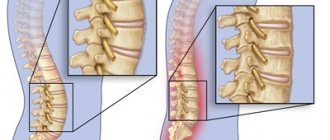
Tendon sheaths are an anatomical formation of connective tissue sheaths surrounding the tendons.
The disease of the tendon sheaths is called tenosynovitis. The most common sites for the development of pathology are the hand, foot, and ankle joint. Tenosynovitis, developing in the forearm, is called radial or ulnar tenobursitis, a disease of the Achilles tendon is called achillobursitis. Typical sites for the development of tenosynovitis are the tendon sheaths of the wrist and ankle joints.
Causes
The disease often occurs in athletes who engage in active sports, such as hockey players, football players, speed skaters or skiers. This is due to unbearable stress on the ankle.
Congenital developmental abnormalities can also be the cause. But the disease may be secondary. In this case, it appears against the background of an infectious process. Tenosynovitis can be caused by tonsillitis, tuberculosis, brucellosis and syphilis. Pathogenic microorganisms can enter tendon sheaths from purulent wounds.
Other inflammatory processes, such as arthritis, bursitis and rheumatism, play an important role in the occurrence of tendon inflammation. Acute tenosynovitis of the ankle joint is most often caused by injury.
Predisposing factors:
- varicose veins of the lower extremities;
- sepsis;
- violation of metabolic processes;
- obesity;
- poor circulation of the joint and periarticular tissues;
- general inflammatory processes in the body;
- frequent and intense loads on the lower limbs.
Causes of tendon tendonitis
Inflammation causes:
— Small, similar actions that are performed for a long time, usually associated with professional activities: typing, playing musical instruments, practicing movements in sports and dancing, etc. It is for this reason that tenosynovitis of the hand often appears, because there are tendons and muscles weaker than in the legs.
- Infections.
- Purulent diseases.
— Traumas and microtraumas.
- Rheumatic diseases.
— Disorders of blood circulation and nutrition of joints and adjacent tissues.
Symptoms
Tenosynovitis is an inflammatory disease, so the symptoms are pronounced, especially in the purulent form.
General symptoms:
- pain during movement;
- accumulation of serous effusion in the tendon sheath, which is manifested by oblong swelling and edema;
- increased local temperature, redness of the skin at the site of injury;
- limitation of joint function due to pain.
Manifestations depend on the form of the disease. Purulent tenosynovitis is accompanied by severe pain, limited joint mobility, increased body temperature and general malaise. Possible enlargement of regional lymph nodes.
In the infectious form, the pain is pronounced and hinders movement. Symptoms of aseptic damage are less noticeable. The disease is characterized by crunching and clicking sounds when moving.
With long hikes and severe ankle strain, a crepitant form of the disease develops. It is characterized by a crackling sound when moving.
In the tuberculous form, tendovaginitis is presented in the form of a hygroma in the lower leg area, which is localized on the outer or anterior surface of the joint.
The symptoms of chronic tendovaginitis are vague. Pain may be felt with intense finger movements or palpation of the affected area. There is no puffiness or swelling.
Symptomatic manifestations
Depends on the type of damage:
- Acute variant of the pathology - occurs under the influence of systematic overloads of a certain area of the lower limb. A slight swelling forms at the site of damage, without changing the color of the skin. Painful sensations occur with active movements of the affected foot.
- Additional symptoms include swollen lymph nodes, decreased appetite and fever. In the absence of therapy, the patient’s condition will begin to deteriorate, and signs of the inflammatory process will begin to cover larger areas. Suppuration can provoke septic lesions and shock of the same name.
- Chronic – progresses with the aseptic form of the disease. Moderate pain is noted at the affected area; upon palpation, cracking and crunching can be heard. The disease is characterized by practically absent symptomatic manifestations. In some cases, the main symptoms correspond to the location of the process and differ in the clinical picture.
Classification
Tenosynovitis of the foot, depending on the nature of the course, can be of several types:
- Spicy. The development of the disease is rapid, the symptoms are pronounced.
- Chronic. Occurs in the absence of treatment of the acute form. Lasts more than 2 months. It is characterized by complications.
By shape
Depending on the origin, tenosynovitis can be:
- Infectious. The disease occurs under the influence of pathogenic microorganisms. More often the cause is pyogenic infections that penetrate the tendon sheaths through wounds and microcracks in the skin. Less commonly, the infectious form becomes a consequence of panaritium.
- Specific. Inflammation is triggered by the influence of specific pathogens, for example, syphilis or tuberculosis bacillus. Very often this type of disease appears against the background of osteomyelitis.
- Non-specific. Caused by pyogenic microorganisms. More often, pathogens enter the tendon sheaths from wounds. A splinter can cause an inflammatory process.
- Aseptic. It occurs against the background of dystrophic changes, as well as monotonous movements, which are an additional load on the foot. The cause may be injury (sprain or bruise of the foot ligaments), as a result of which blood circulation is disrupted and aseptic inflammation develops. The longest and thickest tendons are susceptible to this form of the disease. Aseptic tendovaginitis can be reactive, post-traumatic and occupational.
Non-infectious occupational tenosynovitis is most often diagnosed.
According to the nature of the inflammatory process
Tenosynovitis of the foot can be serous, serous-fibrous and purulent. The first two types are characteristic of the aseptic form, the last - of the infectious form.
Therapy methods
The prescription of medications depends on the subtype of the pathological process.
The infectious form of tenosynovitis requires treatment with antibacterial agents:
- "Ampicillin";
- "Tsiprolet";
- "Ciprofloxacin";
- "Erythromycin."
Experts warn that uncontrolled use of antibiotics can lead to the development of serious abnormalities. The appearance of dysbacteriosis and fungal forms of diseases is provoked by an incorrectly selected drug. During the period of antibiotic therapy, the consumption of alcoholic and low-alcohol drinks is prohibited.
To relieve elevated body temperature, Ibuprofen and Paracetamol are often prescribed.
To stabilize and improve the functionality of the autoimmune system, it is recommended:
- "Complivit";
- "MultiMax";
- "Vitrum";
- «;
- "Duodevit".
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made based on visual examination and palpation. The damaged area is swollen, there is redness of the skin, there is pain when palpated and limited mobility in the joint. All these clinical manifestations indicate an inflammatory process.
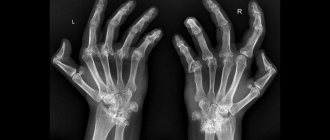
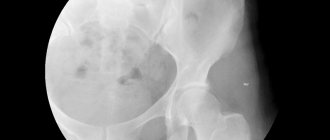
To clarify the diagnosis, additional examination is carried out. In case of tendon inflammation, MRI is informative. X-rays do not show changes in the tendon sheaths, but X-rays can help refute the presence of joint damage.
Against the background of the inflammatory process, changes in the general blood test will be present. The results show an increase in ESR and an increase in the level of leukocytes.
In the case of a purulent form, exudate is collected and subsequently studied by bacterioscopic and bacteriological methods. In case of infectious tendovaginitis, it is important to identify the causative agent, since the effectiveness of treatment will depend on the informativeness of the diagnosis.
Methods for diagnosing the disease
During the examination, the doctor will pay attention to the appearance of the affected area; many signs can indicate tenosynovitis of the joint: rice bodies, compactions, pain, dysfunction. To make an accurate diagnosis, the specialist will prescribe a number of studies:
- a blood test will show the degree of the inflammatory process;
- studies of pus will show what type of bacteria caused the disease and what antibiotics they are sensitive to;
— computed tomography will assess the condition of soft tissues and tendons;
- An x-ray will show whether pathological changes have begun in the bones.
Treatment
Treatment is carried out using local and systemic drugs. The choice of remedies depends on the cause of the disease and its form.
For infectious tendovaginitis, the course of therapy includes antibacterial drugs. If the inflammatory process is caused by tuberculosis, then anti-tuberculosis therapy cannot be avoided.
Treatment of acute tendovaginitis is aimed at relieving pain and inflammation. Local and systemic NSAIDs are used: Indomethacin, Butadiol, Diclofenac, Acetylsalicylic acid are effective. You can also apply warm compresses to the ankle area.
During the treatment period, it is important to provide complete rest to the injured limb. To do this, the ankle is fixed in one position; a plaster splint can be used.
With a large accumulation of purulent exudate, surgical intervention cannot be avoided. The tendon sheath is opened and the cavity is sanitized.
Physiotherapeutic procedures are no less effective in the treatment of tendovaginitis. During an exacerbation, UHF, ultrasound and microwave therapy can be used.
For chronic inflammation it is used:
- electrophoresis with the addition of Novocaine and Hydrocortisone;
- paraffin applications;
- healing mud;
- massage;
- Exercise therapy.
If conservative therapy is not effective, the symptoms increase, then emergency surgery cannot be avoided, which involves excision of the tendon sheath. Recovery lasts 3-4 weeks.
Treatment of tendovaginitis
The course of treatment for infectious tenosynovitis at an early stage includes therapy with antibacterial drugs, limb immobilization and physiotherapeutic procedures. For tenosynovitis, which is accompanied by the accumulation of pus, surgical treatment is recommended. The patient is prescribed rinsing and drainage of the tissues surrounding the tendon. The purpose of surgery is to remove purulent contents, as there is a risk of fistula formation for the release of pus and damage to nearby joints and bones.
Treatment of aseptic (crepitating) tenosynovitis consists of immobilizing the hand, foot or fingers and prescribing physiotherapeutic procedures. The method of UHF therapy, electrophoresis with hydrocortisone, has proven itself well. If the treatment of crepitating tenosynovitis is not carried out in full or with an advanced form of the pathology, relapses of the disease are possible.
For the treatment of post-traumatic tendovaginitis, it is recommended to immobilize the tendon and apply cold on the first day, and then UHF procedures and heat. If, as a result of an injury, there is an accumulation of blood near the tendon, then puncture of the tendon sheath is required.
Forecast
The prognosis is favorable with timely treatment. If you do not pay attention to the symptoms of the disease, then a chronic form develops. It is difficult to treat and there is a high risk of complications.
Inflammation can spread to adjacent joints, bone and cartilage tissue. The most dangerous consequences are observed with purulent tendovaginitis. Pyogenic microorganisms lead to necrotic lesions. They can enter the general bloodstream and cause sepsis. Blood poisoning can cause the patient's death.
Preventive actions
To prevent the secondary occurrence of the inflammatory process, it is necessary to adhere to a number of recommendations:
- Stopping intentional or accidental overstrain of joints - the process leads to a violation of the integrity of the tendons;
- Constantly performing exercise therapy and specialized gymnastics;
- Attending massage sessions - to stabilize the process of blood circulation and lymphatic metabolism;
- Timely treatment of any infectious processes;
- Refusal of uncontrolled use of antibacterial agents;
- Periodic vitamin therapy - in order to increase the functionality of the autoimmune system;
- Wearing specialized orthopedic shoes.
Following simple rules will prevent relapses of the disease and improve the general condition and well-being of the patient.
Prevention
For prevention purposes, do not overload the ankle. During prolonged exercise, you need to take a break.
All wounds and skin damage must be promptly treated with an antiseptic and infectious diseases treated in a timely manner. In case of injury, you should immediately see a traumatologist.
The prognosis and likelihood of complications of tendovaginitis depends on the timeliness of therapy. Without treatment, the infectious and inflammatory process can quickly spread to other tissues.
Author: Oksana Belokur, doctor, especially for Ortopediya.pro
Diagnostic tests
At the first appointment, the specialist enters the patient’s anamnestic data:
- Painful sensations during palpation examination;
- Swelling of local origin;
- Free movement disorders;
- Complaints about the condition and well-being;
- Timing of the occurrence of the anomaly;
- Working conditions.
After making a preliminary diagnosis, the patient is sent for instrumental and laboratory diagnostics:
- X-ray images are necessary to differentiate the desired disease from inflammation of the joints in arthritis (with tendovaginitis, the process does not affect bone tissue);
- Ligamentography - a separate subtype of fluoroscopy, using contrast agents - is recommended to exclude infectious processes;
- Clinical blood test - prescribed to determine inflammatory processes.
X-ray images
Ligamentography
Clinical blood test
In case of problems with an accurate diagnosis, a CT scan is additionally performed.