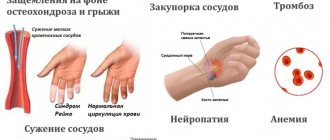
Today, more and more often, people are faced with a very unpleasant problem - numbness of the knee joint. In medicine, the term “numbness” means loss of sensation in a certain area of the human body. Today there are two large groups of this disease, these are:
- partial numbness of the limb in the knee area;
- complete loss of sensitivity.
This disease requires urgent treatment immediately after its occurrence. It is known that numbness does not go away on its own, and untimely treatment can lead to various complications. There are a huge number of methods that will help you recover in the shortest possible time and forget about the disease forever. In order to correctly determine which method should be used, it is necessary to know the reasons that contribute to the appearance of numbness.
Causes of knee numbness
During the examination, the specialist checks for the presence of pathologies:
Central nervous system disorders
- dysfunction of the central nervous system;
- problems in the functioning of the musculoskeletal system (most often the spine);
- diseases of the cardiovascular system.
The knees become numb with heavy physical labor and constant standing. Numbness of the lower extremities is common among cashiers, workers, salespeople, postmen, and postmen.
Numbness in the knee of the right leg may indicate neuropathy of the sciatic nerve on the right side (intervertebral hernia, foraminal and sequestered). Numbness in the left knee is caused by protrusion of the intervertebral disc to the left side. There is a loss of sensitivity, tingling and numbness in one lower limb, right or left, then the second limb goes numb.
Main reasons: why knees go numb
The reasons why knees go numb are very diverse and include not only pathologies of the musculoskeletal system. The main reasons, of course, lie in the structural changes in the tissues surrounded by the entire innervation channel. It can be:
- destruction of the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral discs in the lumbosacral spine, causing compression of the radicular nerve by pressure on it from the vertebral body;
- instability of the position of the vertebrae due to stretching of the ligamentous and tendon apparatus;
- syndrome of the piriformis muscle, when overstrained, the path of the sciatic nerve is blocked;
- violation of the position of the fascia of the muscles of the femoral group;
- disruption of the outflow of lymphatic fluid in the thigh area, which leads to swelling of the soft tissue and pinched nerve;
- tunnel syndrome at the site where the sciatic nerve splits into the lesser and greater tibial nerves in the area of the popliteal fossa.
In addition to these reasons why the knee goes numb, there may be others. These are diseases of soft tissues and endocrine disorders, vascular pathologies and consequences of injuries. So, very often numbness in the knees is a sign of impaired blood supply to the soft tissues in the lower legs and feet. A similar symptom occurs with obliterating endarteritis and varicose veins of the lower extremities.
Diabetic angiopathy, gout, deforming osteoarthritis of the knee joint, tunnel syndrome, muscle fiber dystrophy, bursitis - this is not a complete list of diseases that may be accompanied by a feeling of numbness in the knees and the parts of the leg located below them.
If bending the leg is accompanied by severe pain and the knee goes numb
Numbness does not go away on its own; it is a symptom of more serious health problems.
A disease accompanied by numbness of the knee is primary osteochondropathy, or Osgood-Schlatter disease. This is a pathological lesion of the knee joint. Characterized by intolerable, sharp and severe pain. This lesion is a consequence of trauma to the lower extremities. Patients find it difficult to climb stairs and stand for long periods of time. With timely treatment with anti-inflammatory and painkillers, knee numbness and discomfort disappear within a month,
Knee numbness due to bursitis
Partial loss of sensation in the knee area is a symptom of progressive inflammation - bursitis. This is an inflammation of the joint capsule located in the knee. Bursitis can:
- Why does my leg go numb from the knee to the foot? How to treat numbness?
- provoke a feeling of heat;
- limit movements of the lower limb;
- bring pain and discomfort.
Knee pain
Why does the knee of my left leg go numb after a dislocation?
Very often the left knee goes numb after various injuries. This could be a sprained ligament. This is a common problem for people who are fond of outdoor and team sports. Sprains and tears of the greater cruciate knee ligament always result in the appearance of rough scar tissue. It disrupts the normal path of innervation fiber. As a result, normal sensitivity may be disrupted. The patient experiences a feeling of numbness, coldness in the knee area or behind it. All this can be accompanied by quite intense pain.
Many patients are interested in why their left knee goes numb after an injury, the treatment of which was carried out in a timely manner and was quite successful. There are several aspects to this. It is important to understand the following principles:
- with any injury in the area of the ligamentous, tendon or muscular system, hematomas occur in the thickness of the tissue;
- accumulated blood causes a process of aseptic (non-infectious) inflammation;
- inflammatory reaction factors (special cells of the immune system) are drawn into the area of injury;
- they cause increased blood flow in small capillaries, release of fluid and swelling;
- when fibrin falls out, strong scar compounds are formed, which are designed to restore the integrity of the damaged tissue.
Features of treatment of numbness of the knee and lower extremities
In order to restore sensation in the knee or lower extremities, the following recommendations should be followed:
- engage in sports exercises (without heavy loads on the legs, for example, swimming);
- eat cottage cheese, fish, chicken, cereals, which are rich in vitamins, microelements and nutrients (special attention to iron);
- take contrast baths, which have an effective effect on the degree of sensitivity of the knee, reducing the degree of discomfort below and inside the knee;
- avoid hypothermia;
- avoid injuries and strong, intense physical stress on the knees and feet.
When playing sports, the knee joint strengthens, blood circulation increases, reducing discomfort and pain. Stop drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking. Do not drink tea or caffeinated drinks.
Lotions and compresses are useful - tinctures based on walnuts, lilacs, and alcohol. Treatment is not recommended without prior consultation and diagnosis by a specialist.
In order to prevent numbness of the lower extremities, people who spend most of their time on their feet should control the degree of physical activity and pay attention to their diet.
- What to do if your elbow hurts and your hand goes numb
According to the anatomical interpretation, the knee is a joint connecting the thigh and lower leg. It is entrusted with a large functional load to ensure mobility in the leg and a person’s ability to walk.
If the knee goes numb, it becomes uncomfortable to move, the gait looks uncertain, and performing some movements becomes completely impossible.
Features of treatment
Self-medication is unacceptable. If a certain disease is detected, it will be necessary to prescribe adequate therapy, and it will be individual in each individual case. Only after an examination will it be possible to identify the cause of the numbness, after which the doctor most often prescribes:
- A certain diet. Be sure to include poultry, fish, porridge, and cottage cheese in your diet. Pay special attention to foods rich in iron.
- Medicines. Their composition, dosage and method of administration are determined by the doctor in each individual case.
- Physiotherapy.
- Therapeutic exercise. Swimming is recommended for such patients, which ensures the proper level of exercise and eliminates overexertion. Other types of physical activity may be prescribed.
Sometimes surgery may also be required.
Operations are prescribed when the patient cannot be helped by other means. However, the speed of recovery and quality of life depend not only on medications and other manipulations. Much will determine the patient's behavior. With active movement, proper nutrition, acceptable exercise, and a good mood, the chances of a speedy recovery increase significantly.
How the process develops
Signs of knee numbness can appear in a person of any age, regardless of his occupation. They are determined by:
- Uncomfortable posture.
- Staying in one position for a long time.
- Intense physical work or sports activity.
- Wearing tight clothes.
- Trauma.
- Anatomical features.
Such factors cause temporary loss of sensitivity in the kneecap area. It goes away as a result of independent actions: rubbing, light injections, changing body position, and implementing gradual flexion and extension movements.
Such disorders are caused by mechanical compression of nerve fibers and endings or insufficient blood supply to the tissues of the knee joint.
If a person notices regular loss of sensitivity in the knee area, it begins to hurt, be hot to the touch, “goosebumps” run through it, or the tingling sensation worsens, it is possible that this is a serious illness.
What diseases can cause
First of all, when the knees go numb, problems with the spine are suspected. Due to osteochondrosis changes (flattening of the intervertebral discs), pinching of nerve fibers and poor sensitivity of the innervated areas becomes possible. For the knee area, the symptom may be caused by pinching of the sciatic nerve and its branches.
- Pain in the back of the knee, numbness in the lower leg and foot
In addition, risk factors are:
- bursitis (inflammation of the periarticular bursa);
- arthrosis and arthritis of the knee joint;
- atherosclerosis of blood vessels or a decrease in their lumen for other reasons;
- tendinitis and tendinosis (inflammation of tendon tissue).
Osgood-Schlatter disease occupies a special place. The injured knee hurts, goes numb, and limits physical activity. The skin over the provoked area may turn white and be colder or hotter than the adjacent skin. The causes of the pathology sometimes do not “lie on the surface”, but affect deeper knee tissues.
Numbness of the knee due to bursitis is caused, for example, by a decrease in the amount of shock-absorbing fluid or hyaluronic acid in the joint capsule.
As a result of this, friction of bones and cartilage occurs against each other with possible pinching of the nerve processes. Bursitis develops not only due to a knee injury, but is also a consequence of heavy physical activity, and can also occur as a result of a number of infectious diseases (joint tuberculosis, syphilis, gonorrhea and others).
When a patient is diagnosed with arthrosis of the knee joint , numbness of the knee is not a necessary but possible symptom. It is easy to differentiate this condition if the following are noted in parallel:
- burning sensation, especially when climbing stairs;
- pain in the knee if you walk or stand for a long time (possibly even after lying in one position for a long time);
- weakness in the legs, even to the point of giving way.
Symptoms of arthrosis tend to progress. In the absence of adequate treatment, within a few months, “moving” pains can turn into “resting pains”.
If the knees become numb, defects in the blood supply, which in this area is carried out through the popliteal vessels, cannot be excluded. The location of the corresponding veins and arteries is characterized by similarity with the directions of the nerve branches, so their combined lesions can be observed.
Vascular disorders that begin with numbness of the knees can lead to oxygen starvation of the knee tissues, turning into hypoxia and even atrophy. As anaerobic processes develop, gangrene develops and the subsequent need for amputation of the leg.
How to make a diagnosis
The uniformity of the clinical picture of diseases with complaints that the knees are numb determines the possibility of incorrect diagnosis and inadequate treatment. This often happens during self-diagnosis and self-prescribed treatment. To prevent this from happening, you need to contact a traumatologist, orthopedist, surgeon, or neurologist.
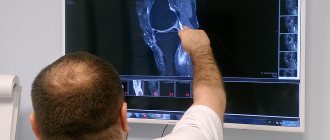
To get an idea of the changes in the knee joint that have resulted in numbness of one or both knees, the following types of examinations are prescribed:
- X-ray (allows you to identify or exclude bone tissue defects, pathophysiological problems of the knee joint).
- CT or MRI (for diagnosing tumor processes, assessing the condition of soft tissues, blood vessels and nerve branches).
- Ultrasound (Doppler studies will allow you to diagnose atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels and make a diagnosis of ischemic tissue damage).
- Electroneuromyography (allows you to assess the usefulness of peripheral nerves and muscles, analyze the speed of passage of a neuroimpulse from the central part to the innervated area).
- Clinical and biochemical tests of blood and urine.
- Bacteriological tests (to identify the infectious nature of the disease).
It should be remembered that neurological symptoms can have a mental origin, i.e. manifest itself in patients with “psychogenic” diseases. In this case, consultation with a psychiatrist is necessary.
In some cases, patients report complaints that their knees are going numb, among other problems: blurred vision, dizziness, general weakness, involuntary urination, numbness of muscles, including the face on the right or left side, difficulty coordinating movements, slurred speech, and others . In this case, this is part of the clinical picture of serious neurological diseases, the treatment of which is a matter of professional medicine.
Diagnostics
To determine the “provocateur” of the pathology, it is necessary to undergo a full examination. You can request laboratory tests from a traumatologist and neurologist, therapist and orthopedist, rheumatologist and therapist. They provide referrals for diagnostics and laboratory tests:
- Blood test - studies may concern the study of the composition, as well as the number of leukocytes, erythrocytes, which will help detect the infectious process. General biological indicators are determined by a complete blood count. In some cases, studies of the patient's hormonal status may also be required.
- Urinalysis is a test that will detect or exclude nephrological diseases.
- Ultrasound - a thorough assessment of the patency of all blood vessels in the legs is carried out.
- X-ray – a picture of the knee joint will be required. This is especially true if the knee is numb and painful due to the presence of an intervertebral hernia. A relevant diagnostic procedure for any other organ pathologies.
- CT and MRI - computer technologies allow you to obtain multiple images of the leg from different angles and angles.
What are the treatment approaches?
The order of therapeutic prescriptions depends on the cause of the disease, the presence of concomitant pathologies, characteristics of the development process and the patient’s life history.
If the symptom of knee numbness is functional in nature, it may be worth changing your working conditions, rest habits, hobbies, and lifestyle. It is necessary to exclude factors that contribute to delayed blood supply and uneven innervation.
A symptom that is a sign of a disease will not go away on its own. Its manifestation is the result of the physiological inability of the knee joint to perform its functions. Therefore, the main focus is on treating the primary disease.
Along with targeted medications (anti-inflammatory, muscle relaxants, neuroprotectors, atherosclerotic, anticoagulants, statins and others), doctors recommend taking physiotherapeutic procedures, as well as:
- follow a diet rich in vitamins and microelements;
- develop a scheme of physical activity on the legs and practice according to it with a gradual increase in strength;
- avoid hypothermia;
- take contrast baths and shower procedures;
- do not drink alcohol and stop smoking;
- Limit your consumption of coffee, carbonated drinks and foods prepared with artificial flavor enhancers.
About traditional methods of treatment
Many people prefer to treat knee numbness on their own. They have a large arsenal of natural medicines at their disposal to help cope with the symptom. However, you should be sure that due to the individual characteristics of each person, the use of such drugs may have negative effects. So:
- Pumpkin compress. Place the peeled and coarsely grated pumpkin in gauze and apply it to your knees. You can dilute the paste a little with warm milk. A similar method for preparing an onion compress. Fresh scratches and abrasions on the skin are not allowed.
- Honey applications. Apply warm honey to your knees, cover with plastic wrap and wrap. Keep this application for half an hour, then rinse with warm water. It is recommended to add rye flour, chicken egg yolk, and a few drops of olive oil to honey.
- Rubbing from bogulnik. Pour the crushed plant with alcohol (1:3) and let it brew in a dark place for a week. Rub into numb knees three times a day.
- Oil rubbing. Mix 100 g of ground black pepper with a liter of any vegetable oil. Boil the product over low heat for half an hour and cool. The irritating baking effect is alleviated by oil components, but at the same time, it activates blood supply processes.
- Compress based on lilac. Place the flowers in a glass, pour half a liter of alcohol (or vodka) and place in a dark place for two weeks. The course of using this compress is 10 days. A tincture for compresses from Kalanchoe leaves is prepared in the same way.
- Black radish tincture. Pour one and a half glasses of juice into 0.5 glasses of vodka. Add a tablespoon of salt and half a glass of honey. Rub on sore knees at night. Sometimes it is recommended to take this composition internally. Then its dosage is 30 ml per dose three times a day.
Most popular recipes
- Burdock and elecampane root baths. Pour boiling water (1 liter) over the crushed mixture of herbs. Leave for a couple of hours and use for baths daily.
- Ointment based on bay leaf. Mix 6 parts of chopped bay leaves with 1 part of juniper needles. Add 12 parts of any fat to the mixture. Grind and leave for a couple of hours. After preparation, rub into the mixture with circular massaging movements.
- Camphor ointment. You can buy it at the pharmacy or prepare it yourself. Mix 100 g of alcohol with 50 g of camphor. Add the same amount of dry mustard and two egg whites. Mix everything thoroughly and start rubbing. Condition: no allergy to any of the components used.
- Blueberry applications. Crush ripe blueberries, collect the pulp in gauze and apply to your knees at the end of the working day. The product has a good anti-inflammatory, soothing, vitaminizing effect on the skin and subcutaneous layers.
You can prepare the medicine for oral administration:
Garlic drink. Squeeze the juice from three large heads. Pour it into a half-liter jar and top up with water. Leave in a dark place for a week, shaking occasionally. Take a tablespoon, you can wash it down or first dilute it in a third of a glass of water.
For the treatment of numbness of the knees of vascular etiology, it is recommended:
- Drops based on beets, cranberries, black radish. Mix the components in equal quantities and add alcohol. Leave for two weeks in a dark, ventilated place, then strain and take 30 ml half an hour before your morning meal.
- Lemon tincture with added garlic. Squeeze the juice from 4 lemons and 4 heads of young garlic. Pour two liters of water and close the lid. It must stand for at least three days. Take half a glass daily, preferably in the middle of the day. The product is good at cleaning blood vessels from cholesterol plaques and preventing atherosclerosis.
What is prevention?
Knee numbness is a condition that, in the absence of a serious illness, can be corrected. To eliminate the symptom of tingling, goosebumps, and hypoesthesia, it is necessary to ensure unlimited functioning of the knee joint, as well as adequate blood supply and innervation. To do this you need:
- organize uniform physical activity of feasible intensity;
- Avoid smoking and drinking high doses of alcoholic beverages;
- enrich the diet with vitamins and microelements;
- breathe more fresh air;
- do not take medications without medical supervision;
- promptly treat emerging diseases;
- undergo periodic medical examinations for early detection of emerging pathologies.
If you have numbness in your arms, neck or legs, do not self-medicate; consult a doctor.
Knee numbness is an unpleasant but treatable symptom. The problem can be solved by timely seeking medical advice and following medical recommendations.
Adjustment of diet and lifestyle for numbness and pain in the legs Diseases that cause numbness in the knee Causes of numbness in the knees Numbness and pain in the knee
Almost everyone experiences numbness in the lower extremities. The feeling of “running goosebumps”, tingling, loss of sensitivity and pain when trying to move the knee are the main symptoms of numbness. The knee becomes numb due to numbness in the leg due to being in one position for a long time. But it may be a sign of the development of a dangerous pathology.
Doctors classify knee numbness into:
- Complete loss of sensitivity;
- Partial decrease in nerve impulses.
Expert opinion!
Knee numbness should not be ignored. It is necessary to contact a neurologist. The specialist will prescribe clinical and instrumental studies, based on the results of which a diagnosis will be made and treatment will be prescribed. The numbness of the knee joint does not disappear on its own.
Why does the skin on my knee go numb and tingle at night?
The fact that the knee goes numb at night may indicate both improper organization of a place for night rest, and pathologies associated with the patency of the nerve fiber. If your knee hurts and goes numb, then you need to try to change the position of your legs. If this does not help, then you need to undergo an examination and detect a pathology that disrupts the conductivity of the nerve fiber.
It must be remembered that sometimes the skin on the knee becomes numb with complicated lumbosacral osteochondrosis. Therefore, if there is pain in the lower back, then you must first establish its cause, carry out appropriate treatment and then (if the symptom persists), look for the factors causing numbness.
Symptoms of numbness
When your knee goes numb and hurts, it is impossible not to notice it. Initially, tingling and goosebumps appear around the joint, then the unpleasant sensation spreads throughout the leg. The following are signs of knee numbness:
- The appearance of heaviness in the legs;
- Burning and tingling in the knee joint;
- Decreased sensitivity to external stimuli (temperature changes, sharp objects);
- Feeling of cold appears.
Numbness and pain in the knee
Symptoms
The first and main signs of the onset of the disease are:
- tingling in the joint, as well as in the entire limb;
- pain;
- discomfort when moving;
- increased body temperature;
- burning;
- crunch.
If any sign occurs, you should immediately contact a medical facility to determine the cause of the numbness accompanying the development. To do this, they examine the numb joint using the following types of diagnostics:
- ultrasound examination;
- magnetic resonance therapy;
- X-ray;
- blood analysis,
- ultrasound examination of blood vessels.
Remember, quickly identifying the cause of numbness is the key to quickly getting rid of the disease.
Share:
Why does my knee go numb?
The causes of knee numbness are divided into physiological and pathological. Typically, loss of sensation is caused by nerve compression and impaired blood flow. Staying in one position for a long time or being outside at low temperatures can cause discomfort. In this case, numbness is a normal reaction of the body, which disappears on its own within 15-20 minutes and does not require treatment.
Physical inactivity, lack or excess of sports activity, overwork, stress and lack of sleep can also cause numbness.
On a note!
Typically, patients complaining of numbness in the knees are diagnosed with a deficiency of B vitamins (especially B12). These vitamins participate in metabolic processes and regulate the functioning of the CNS (Central Nervous System).
Another physiological reason why knees go numb is wearing narrow or small shoes. Feet in such shoes swell and go numb.
The cause of numbness may be work. People whose professional duties require heavy physical labor or long periods of standing (unskilled workers, builders, loaders, salesmen, hairdressers) are more likely than others to experience numbness in their knees.
However, the cause of numbness can also be diseases:
- Pathologies of the central nervous system;
- Dysfunction of the musculoskeletal system;
- Diseases or injuries of the spine;
- Diseases of the heart and blood vessels.
On a note!
If the knee on the left leg is numb, this may be a sign of an intervertebral hernia with a displacement of the disc to the left side. This condition is accompanied by decreased sensitivity and tingling, first in the left and then in the right leg.
Causes of numbness in the knees
Osteochondropathy as a cause of knee numbness
Numbness of the knee may indicate the development of a disease such as osteochondropathy (Osgood-Schlatter disease), characterized by degenerative changes in the knee, accompanied by severe pain. Usually occurs after a leg injury. The patient cannot climb stairs or stand for long periods of time. It is possible to eliminate unpleasant symptoms with the help of painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Numbness due to bursitis
Bursitis is a disease caused by inflammation of the joint capsule of the knee. The following symptoms are typical for knee bursitis:
- Pain in the knee joint;
- Local increase in temperature;
- Limited mobility;
- Knee numbness.
Arthrosis and numbness
Osteoarthritis of the knees is accompanied by severe pain, swelling and loss of sensation in the joint. During movement, a characteristic crunching sound is heard and the patient experiences pain. As the disease progresses, a sharp deterioration in the patient's well-being is observed. Gradually, numbness spreads to the entire limb and leads to its immobilization.
Numbness of the knee due to inflammation of the sciatic nerve
Inflammation of the sciatic nerve leads to pinching. The knee becomes numb and swollen. The limb loses mobility.
Only a doctor - a surgeon, orthopedist, traumatologist or rheumatologist can diagnose inflammation of the sciatic nerve.
Tendinitis - the cause of numbness
Tendinitis is an inflammatory process in the tendons surrounding the knee joint. Pathology occurs after an injury or strain of the tendon. It is not always possible to diagnose the disease at the first stage, due to mild symptoms and absence of pain. As tendonitis progresses, the knee becomes swollen and numb, and pain occurs when walking.
Atherosclerosis of blood vessels and numbness of the knee
Atherosclerosis is a common vascular pathology that leads to narrowing of the lumen. Cholesterol plaques accumulate on the walls of veins and arteries. Blood flow slows down, oxygen and nutrients do not reach tissues and muscles in sufficient quantities, metabolic products (carbon dioxide, toxins and waste) accumulate in them.
The progression of atherosclerosis leads to changes in skin color, pain, swelling and numbness of the knee, and lameness. The lack of adequate therapy can provoke the development of a dangerous complication - gangrene, the treatment of which involves amputation of the leg.
Diseases that cause numbness in the knee
Why does my leg behind the knee go numb?
Why does the knee go numb without visible pathological tissue changes? This may be a consequence of incorrect leg positioning during night sleep or prolonged sitting. Try to choose a chair or armchair in such a way that the bottom pillow does not rest against the popliteal area. Large nerve plexuses of axons pass there. And they are located quite close to the surface of the skin. Therefore, the habit of sitting with legs crossed can lead to the development of carpal tunnel syndrome and the feeling that the leg under the knee is numb.
This condition can be classified as physiological and transient only if the symptom completely disappears without a trace 2-3 minutes after changing the position of the legs. If the leg behind the knee goes numb for 30 minutes or more, this already indicates the presence of a serious pathology and you need to see a doctor to clarify the diagnosis.
Here are just a few reasons why the leg behind the knee goes numb:
- cicatricial changes in the ligamentous apparatus;
- bursitis and tendovaginitis;
- pinching of the sciatic nerve;
- cracks in the heads of the bones entering the cavity of the knee joint;
- diabetic angiopathy;
- swelling of the lower leg.
You can find out exactly why the back of the knee goes numb only during an in-person manual examination. If it is difficult to make a diagnosis, the doctor may recommend an x-ray or CT scan. In surgical and traumatology practice, arthroscopy is used for examination. It also allows endoscopic restoration of the integrity of the ligamentous, tendon and muscular apparatus.
Diagnostic measures
When visiting a doctor, a visual examination of the knee is performed and the patient is interviewed. However, these measures are most often not enough to determine the cause of numbness. To make a final diagnosis, the doctor issues a referral to:
- Ultrasound;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- X-ray examination.
Additionally, a general blood test, vascular ultrasound, electrocardiogram and consultation with a cardiologist are prescribed.
The exact list of instrumental and clinical studies depends on the symptoms of the pathology characteristic of individual diseases.
Therapy
The treatment regimen depends on the diagnosis of a systemic disease. Since the therapy will be aimed at eliminating the disease that caused numbness in the legs.
If the decrease in sensitivity is not associated with illness, simple recommendations will help:
- When your knees go numb in the cold, you should warm them up in a warm (not hot) shower or bath. And then gently rub;
- If the cause of discomfort is staying in one position for a long time, you should carefully change your position and massage the stiff joint;
- Morning exercises will help to cope with the loss of sensitivity caused by physical inactivity. It prevents the development of vascular pathologies. If your job is sedentary, it is recommended to do simple exercises throughout the day. Better yet, join the gym.
On a note!
Strength exercises, swimming, and water aerobics will help strengthen the knee joint, normalize blood flow, and relieve tension and pain.
Adjusting diet and lifestyle for numbness and pain in the legs
It is important to change your diet:
- Avoid any alcohol;
- Replace drinks with high caffeine content (black tea, coffee, cola, energy drinks) with juices, still water and herbal teas;
- Include fermented milk products (cottage cheese, yogurt, kefir), low-fat fish and poultry, as well as porridge in the menu.
A contrast shower or foot bath will help restore knee sensitivity. If possible, you should avoid traumatic sports, high physical activity, prolonged stay in one position, and hypothermia of the joints.
The use of lotions or compresses with alcohol (tinctures of walnut, lilac, cinquefoil) can relieve unpleasant symptoms. But their use must be agreed with the attending physician.
Proper nutrition, a healthy lifestyle, giving up bad habits, and moderate exercise are excellent prevention of decreased sensitivity. A responsible attitude towards your health, timely diagnosis and treatment of pathologies will help to avoid the development of severe complications and disability.
Numbness, or paresthesia, of the lower leg, from the ankle to the kneecap, is common. The pathology can affect the left leg, the right leg, as well as both limbs - each type of phenomenon has its own causes and treatment features.
Why do my legs start to go numb?
The main cause of leg numbness ( 85% of cases
) – problems with the spine. The rest of the pathologies are caused by diseases of the central nervous system or cardiovascular system. Most often, numbness is a sign of osteochondrosis. Pathology occurs due to a sedentary lifestyle or genetic predisposition.
The second most common disease that causes numbness is intervertebral disc disease
. This symptom does not always appear; it is characteristic only of progressive forms of the disease.
Among the causes of numbness that are not related to the functioning of the musculoskeletal system are the following:
- lack of important microelements and vitamins in the body;
- poor blood circulation in the lower body;
- excessive blood sugar;
- multiple sclerosis;
- joint deformation and diseases associated with this process.
Numbness in the legs occurs in women during pregnancy. Most often, the sensitivity of the upper leg decreases, and the area below the knee only swells. But sometimes the numbness can spread to the entire leg.
Diseases that cause numbness in the legs
It is important to understand that leg numbness is a consequence of a previously formed disease, therefore it is important to correctly establish the root cause and direct treatment specifically to it.
| Cause of numbness | Features of the course |
| Osteochondrosis | Develops due to structural changes in the spinal column. Nerve fibers in the spinal cord are pinched, which provokes a decrease in sensitivity of the lower extremities. The main reason for the development of osteochondrosis is the sedentary nature of life. |
| Intervertebral hernia | Numbness of the leg from the knee to the foot also occurs due to pinched nerve roots. Changes occur in the interdisc space after disruption of the integrity of the fibrous ring and displacement of the disc nucleus. |
| DVT (deep vein thrombosis) | Significant blood clots form in the veins, which leads to stagnation. The legs feel heavy, swell, and the skin becomes dry. In advanced cases, skin color may change. |
| Atherosclerosis | A disease of the blood vessels, most often seen in people over 50 years of age. Due to cholesterol deposits, the walls lose their elasticity, subsequently painful sensations arise in the legs, periodic attacks of numbness occur, and constant fatigue persists. |
| Raynaud's disease | Damage to the arterial endings in the extremities occurs. In the initial stages, only the arms are affected, but over time, painful spasms, swelling and numbness can also occur in the legs - in the area below the knees. Symptoms usually appear symmetrically. |
| Neuropathy | Characterized by damage to the nerve endings in the legs. Often the disease occurs as a consequence of multiple sclerosis or diabetes. |
| Gout | It develops due to a large accumulation of uric acid salts in the joints. First of all, numbness occurs in the big toes, later the affected area may expand. Numbness is accompanied by constant pain. |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | An infectious disease. During development, the nerve endings that are responsible for the mobility of the lower extremities are pinched, which leads to numbness. The patient also experiences severe pain in the knees, and severe swelling is possible. |
Main symptoms
Numbness in the leg from the knee cannot be confused with anything else. The following symptoms are typical for this condition:
- An unpleasant burning sensation that can only increase over time;
- Tingling in the lower extremities;
- There is a feeling of coldness in the lower extremities;
- There is no pronounced reaction to temperature changes, and sometimes to pain;
- Pain and itching appears in the extremities.
One or more symptoms may appear at once. A serious problem needs to be addressed quickly, but a full diagnostic workup will need to be done before a diagnosis can be made.
It will allow you not only to find out why the knee of your left leg or other limb is numb, but also to quickly prescribe adequate treatment and prevent complications.
How does numbness in the leg manifest?
Most often, patients experience numbness on the inside or side of the leg, in the calf muscle. Along with this, the following symptoms may appear:
- the lower part of the leg itches, pricks, aches;
- the skin becomes dry and its color may change;
- “goosebumps” periodically tingle in the lower legs;
- pain appears in the lumbar region, in the buttocks area;
- the affected leg freezes more often, the skin on the lower leg becomes a little colder;
- Stiffness in the ankle joint becomes more frequent, discomfort increases when bending over.
Numbness in the right and left leg
It matters which limb the numbness is felt in:
- If the right leg is numb, most likely there is neuropathy of the right sciatic nerve, caused by osteochondrosis or a hernia. With timely treatment, it is not difficult to get rid of the disease;
- You should be wary of situations where a decrease in sensitivity is observed in the left leg, but there are no other painful sensations. This condition may be a prerequisite for a stroke, mini-stroke or transit ischemic attack. Ignoring numbness in this case will only make the situation worse;
- In rare cases, the patient experiences numbness in both legs at the same time - this is a sign of a serious spinal disease. In the initial stages, sensitivity decreases only periodically, but as the disease progresses, the phenomenon can become permanent.
In order to correctly diagnose the disease that caused the numbness, the patient needs to undergo a full examination, in particular, an ultrasound and MRI of the spinal column and lumbar region.
Treatment of numbness in the legs
After the patient has undergone a comprehensive diagnosis and the doctor has established an accurate diagnosis, a treatment program is formed on an individual basis. Therapy directly depends on the background of the disease causing the numbness.
The main reason for reduced sensitivity of the lower extremities is pinching of the nerve roots caused by lumbar osteochondrosis and its complications. Therefore, the main goal of treatment is to ensure the normal functioning of pinched ends and develop mobility of the lower body.
The therapy program may include the following methods:
- Drug treatment
. Basically, the doctor prescribes painkillers and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. It is also possible to take steroid medications (in particular, with severe symptoms of intervertebral hernia). The treatment complex may include vitamins and minerals the body lacks, muscle relaxants (to relieve tension in muscle tissue), as well as medications to stimulate microcirculation; - Manual therapy methods, the main goal of which
is to remove muscle blocks, release pinched nerve endings and blood vessels and restore the natural mobility of the affected joints; - Exercise therapy
. Therapeutic gymnastics exercises help ensure normal blood supply to the affected area and strengthen muscles, which prevents recurrent numbness; - Physiotherapy
. In order to stimulate regenerative processes in destroyed tissues, the doctor may prescribe ultrasound, electrophoresis, laser radiation (low intensity), magnetic therapy;
Alternative oriental medicine. Acupuncture, hirudotherapy (treatment with leeches), and stone therapy (using heated stones) will help speed up the recovery process.
Simultaneously with the main therapy, the patient can undergo additional procedures aimed at relieving tension and fatigue from the spinal column. By regularly performing exercises and adhering to the recommendations listed below, it is quite possible to remove discomfort and restore sensitivity to numb limbs.
What to do if your knee goes numb: treatment with manual therapy methods
If your knee goes numb, the first thing to do is contact an experienced doctor who can conduct an examination and make an accurate diagnosis. Very often in practice there are cases when feelings of numbness arose against the background of ongoing deforming osteoarthritis. Patients actively use ointments based on non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They relieve pain well, but increase the process of destruction of cartilage and bone tissue. As a result, numbness remains almost the only symptom of gonarthrosis. Such patients come to us for treatment with already advanced cases, in which help can only be provided through surgery.
Therefore, we strongly recommend that if you feel numbness, you promptly seek medical help. At the first and second stages, almost any disease of the knee joints is highly treatable using manual therapy methods. If your knee is numb, treatment can be carried out as quickly as possible. We are waiting for you at your initial free consultation. Call and make an appointment at any time convenient for you.