Back pain in children is rare, most often during periods of intensive growth and is not that much of a concern. Therefore, when a child complains of more severe back pain that does not go away within a few days, the problem should not be taken lightly.
Back pain is a common symptom in sedentary adults. It occurs rarely in children, most often during periods of intensive growth and is not so worrisome. Therefore, when a child complains of more severe back pain that does not go away within a few days, the problem should not be taken lightly.
What can cause back pain in a child?
Back pain in children can have the same causes as in adults: minor or more serious injuries, overloading the back with a heavy backpack or bag, incorrect posture while sitting and slouching. In these cases, tension in the back muscles and intervertebral joints causes unpleasant pain.
Pain can be caused by congenital or acquired defects in posture and structure of the back, when curved vertebrae irritate neighboring nerves.
But the cause of the illness can be much more serious. Back pain in children can be a nonspecific symptom of developing infections, kidney disease, and even cancer.
Do not delay visiting your doctor if, in addition to back pain, you experience fever, digestive tract upset, wet sweat, or cramps.
An X-ray, magnetic resonance imaging, or CT scan can help diagnose the cause of the pain.
Causes of pain
During growth peaks, body proportions may change unevenly. The bone grows faster than the muscles that support it develop; the tendons do not have time to “get used” to the new sizes. In addition, the development of tissues occurs faster than the development of the network of vessels that nourish them. The vessels become thinner, bone and muscle tissues receive less oxygen. All this is the result of hormonal surges. Such phenomena lead to painful sensations, especially at night.
This is not a pathology, but in order not to lose sight of the real disease, pay attention to the teenager’s condition: observe how often pain appears and whether there are other symptoms.
What are the most common back problems in children?
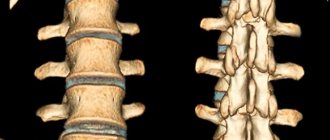
The three most common back defects in children and adolescents are called scoliosis, kyphosis, and lordosis.
Scoliosis is a lateral curvature of the spine. Kyphosis looks like a hump or round back because the spine is too far back in the thoracic region. Lordosis, in turn, is associated with a forward curve of the spine in the lumbar region.
The causes of the disorders often lie in persistent poor posture while sitting, excessive back strain due to lifting heavy objects or carrying bags on one shoulder. Defects can also be congenital or result from disease or a diet low in calcium and vitamin D3. Most often they appear during a period of intensive growth.
What are the consequences of back deformation?
Back deformation is not only an aesthetic problem.
The spine is the support of the whole body, it is the support of the chest, so it affects the functioning of most organs. A curved spine is not only a source of pain. This limits the child's physical capabilities and can cause nervous system disorders. Back weakness causes problems with breathing, heart function and can lead to permanent disability.
For mild postural problems, corrective exercises or rehabilitation are sufficient. More severe cases may require an orthopedic brace and even surgery to correct the curvature of the spine.
What to do if your child has back pain
The first thing to do if a child has back pain is to conduct a full diagnosis. You cannot self-medicate. Many dangerous diseases, including cancer, manifest themselves in the early stages as pain in the muscular frame of the back. If you see a doctor when such a symptom appears and do a simple clinical blood test, it will show the development of inflammation and intoxication. Based on the data obtained, the doctor will be able to recognize leukemia, sarcoma and many other types of oncology.
You should not try to use compresses, lotions, or rubbing with folk remedies. In this way, it is possible to suppress the symptoms and transfer the disease state from the acute phase to the chronic course. Treating such pathologies will be much longer and more difficult.
Remember that almost all types of diseases of the musculoskeletal system in childhood are perfectly treatable using manual therapy methods. An experienced osteopath and massage therapist will restore the structures of damaged tissues and increase blood flow. Therapeutic gymnastics and kinesiotherapy will contribute to the formation of a strong muscular frame of the body. Reflexology speeds up the process of restoring the health of the child’s musculoskeletal system.
How to prevent back pain in a child
- Monitor the correct posture of the child in the first months of his life. Place your baby on his tummy as lifting his head exercises and strengthens his back muscles.
- Avoid too soft a mattress and high pillows for your baby.
- Take care of proper nutrition. During the growth and development of the skeletal system, calcium and vitamin D should not be missed, so the daily menu should be rich in dairy products (milk, cheese, yogurt), lean meat, vegetables and fruits. Flavored calcium syrups can be used to replenish lime deficiency, and tablets in soluble form can be offered to older children. It is recommended that breastfed infants receive 10 mcg of vitamin D. This amount corresponds to one vitamin D3 oil capsule, which can be squeezed directly into the baby's mouth or added to food.
- A proper diet will ensure proper mineralization of bones and development of teeth, and will also prevent the development of rickets.
- Encourage your child to be physically active. The best workout for your back is swimming. In water, the body is less vulnerable to injury and all parts of the muscles are used.
- Try exercising your child's back muscles several times a week. Carrying a book on your head or pressing your torso against your cat's back can be fun.
- School period is a big challenge for the back. Choose a suitable backpack that hugs your child's entire back rather than hanging on his shoulders or butt. The backpack should have a rigid back and wide adjustable straps. Make sure your child wears the backpack on both shoulders.
- Make your child sit at the table in a comfortable position. Provide him with a height-adjustable chair with a concave backrest at the level of the lumbar spine. In order to develop an upright body in a child, you can use the so-called spider. This simple harness attaches to your child's back. The spider forces the shoulder blades back and the chest to push forward. When a child slouches, the hearing aid suggests straightening the back.
Low back pain in a teenager
A teenager has periodic pain in the lower back. Most parents think that the child pulled a muscle or was tired. First of all, these are problems with the spine. Lumbar juvenile osteochondrosis has a similar clinical picture to the disease in adults.
Low back pain in a teenager: causes of pain, treatment, prevention
Every year, the number of teenagers seeking medical help with back pain is increasing. Many parents do not pay due attention to this, believing that the child is exaggerating symptoms, is capricious, or thinking that lower back discomfort will go away as they grow older. This approach to the problem can result in a progressive illness and difficulties in everyday life for your child.
On average, lower back pain syndrome in adolescents manifests itself between the ages of ten and sixteen to eighteen years. This is largely due to the fact that the child is actively growing, spends a lot of time sitting at school and at home doing lessons or on the computer, or, on the contrary, often exposes himself to active physical activity.
The development of all structures of the spine ends only by the age of 22, until it is completely strengthened. Therefore, it is very important to immediately diagnose problems associated with back pain and correct them before the spine is completely formed.
What can cause lower back pain in a teenager?
Parents should remember that if your child has had a lot of activities throughout the day, and at the end of the day he complains of slight back pain, this is not a reason to sound the alarm. Pain may indicate mild fatigue, which goes away after good rest and exercise. But if the pain appears periodically or accompanies the child constantly, you need to consult a specialist.
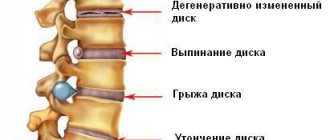
Pain and discomfort in the lower back in a teenager can be caused by various factors. First of all, these are problems with the spine. Incorrect posture, a child staying in one position for a long time with a hunched back, long-standing injuries - all this, if it does not manifest itself as pain immediately, then makes itself felt after a while. Juvenile osteochondrosis has become quite common in recent decades. This is a disease based on degenerative-dystrophic changes in the intervertebral discs during adolescence. They are caused by the rapid growth of adolescents, disturbances in the processes of skeletal formation, as well as inadequate physical stress on the growing spine. Also, the development of osteochondrosis in children can be influenced by the habit of often carrying a heavy bag on one shoulder and sitting in an unnatural position for a long time.
Aching, mild pain in the lower back is the main symptom of juvenile osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine. In addition, with such osteochondrosis, the child experiences limited mobility in the lumbar region, a decrease in range of motion, and a local imbalance of muscle tone.
Lumbar juvenile osteochondrosis has a similar clinical picture to the disease in adults. But there are still some features that make diagnosis difficult. Pain syndromes that occur against the background of lumbar osteochondrosis are characterized by a blurred clinical picture and unclear symptoms, which leads to difficulties in diagnosis and diagnosis.
In addition, the causes of lower back pain in adolescents may include:
- infections, diseases of internal organs (gastrointestinal tract, kidneys);
- incorrectly selected furniture, mattress and pillow;
- muscle strain after exercise;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- menstrual pain in girls;
- obesity (excess weight puts additional stress on the spine).
Prevention of low back pain in adolescents
From early childhood, your child needs the prevention of spinal diseases. Children themselves do not monitor their posture, the position of their back in a sitting position, the timeliness of doing exercises, and so on. Usually, this matter falls on the shoulders of the parents.
One of the main guarantees of a healthy back for your child is proper physical activity. Correct does not mean excessive or too intense; systematic exercise is enough to keep the spine in good shape. It’s not for nothing that we were told all the time at school: “Your health is fine—thanks to exercise!”
The first thing you need to know is that exercises need to be mastered gradually, methodically increasing the load, especially if the child is not used to regular physical activity. You need to exercise for 10-15 minutes, no more, but preferably 2 times a day (morning and evening).
Pay due attention to the selection of furniture. It is optimal if the seat of the chair is 42-53 cm behind the floor, and the surface of the seat itself is proportionate to your sensitive area. The backrest should correspond to the physiological curves of the back. The height of the table should correspond to the anthropological characteristics of the body, usually a distance of 75 cm.
The mattress should be of medium hardness and be able to easily adapt to the shape of the body without sagging. The pillow should be such that the head does not lift up to the ceiling and does not fall back in the opposite direction.
It is necessary to ensure that the child does not carry a heavy backpack on one shoulder. It is better if the load is distributed on both sides, and even better not to overload the child until the spine is fully formed, that is, until about 22 years of age. This does not mean that the spine does not need to be trained, just give the child adequate loads relative to his age and build.
It is also important to teach your child how to lift weights correctly, avoid hypothermia, often change body position while studying, and not sit in one position for a long time. Pay attention to the child's nutrition - it should be balanced, varied, rich in proteins, calcium, vitamins and microelements necessary for proper skeletal growth.
How to treat lower back pain?
If your child complains of lower back pain, do not delay consulting a doctor. Statistics show that the earlier a back disease is diagnosed and the earlier treatment is started, the more effective and faster the recovery.
Often, parents mistakenly attribute back pain to diseases of the internal organs, therefore, in order not to start treating something that does not need treatment, you should first consult a neurologist.
Treatment of juvenile osteochondrosis, incorrect posture or the consequences of injury must necessarily be complex and long-term. This is a labor-intensive and important process, because the further harmonious development of the entire child’s body and its health directly depend on it. Treatment should first begin with correcting the child’s lifestyle and body weight.
At the Bersenev Medical Center, unique metameric technologies are used to treat juvenile osteochondrosis. Clinic specialists develop an individual treatment program for each child. All procedures are carried out in a certain sequence and only as prescribed by the attending physician.
The clinic conducts sessions of metameric injections, which involve repeated injection of certain areas with drugs with neurotrophic properties. As a result of such therapeutic effects, sensory, reflex and trophic disorders in this metamere are normalized. Thus, osteochondrosis is treated and damaged intervertebral discs are restored.
The comprehensive treatment program also includes metameric acupressure, which has a direct effect on the damaged area.
If we talk about the treatment of postural disorders, it is also performed using metameric technologies. For each child, the clinic’s specialists develop an individual comprehensive program for posture correction and prevention, which includes non-drug and medicinal methods of influence.
Many years of experience of specialists at the Bersenev Medical Center shows that paravertebral metameric acupressure, which is performed in the clinic by specialists (with further training of parents in this technique), is highly effective.
The doctor provides recommendations on organizing the child’s therapeutic and motor regimen, providing adequate nutrition and accurate selection of shoes. By fulfilling all the specialist’s instructions, parents and the child will do everything possible to form the correct motor stereotype and develop a full-fledged muscle corset.
Since the speed of restoration of vertebral structures depends on the speed of biological and physiological processes in the body, we strongly recommend that you consult a doctor as soon as the first symptoms appear. You can make an appointment with a pediatric neurologist by calling the children's department or calling the contact center.
What medicines to use when it hurts
The only safe painkillers for children are paracetamol and ibuprofen. Depending on the age and weight of the child, you can choose syrup, suppositories or tablets.
If these medications don't help your pain, only your doctor can decide what to do next.
Warming patches and ointments with anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties are intended for adults and older adolescents.
A child's thin skin allows medications contained in patches or ointments to be easily absorbed, and is too sensitive to the effects of the substances they contain.
How to help a teenager
There is no specific treatment for such pain - it is a natural process, the symptom goes away on its own within 2-3 years. However, the child’s condition can be alleviated with the help of certain measures.
The most effective way is massage. 10 minutes of gentle rubbing is enough to restore normal blood circulation, relax muscles and relieve pain. Teach your child self-massage: consult a doctor, exercise therapy specialist, or find simple techniques yourself. Stroking, pinching and rubbing are allowed. This must be done in the direction from the hips to the feet.
Dry heat also improves blood flow and relieves muscle spasms: apply a heating pad to the area of concern for 10-12 minutes. For pain in the ankle joints, foot baths will help. Regular cycling exercises will also make the pain less severe.
Physical activity should be somewhat limited if the child plays sports: race walking and swimming are allowed. It is better to avoid long-distance running, team sports, and cycling. After consultation with an orthopedic doctor, you can take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and use warming ointments.