Starting from the second and throughout the third trimester of pregnancy, many women are often bothered by discomfort in the back and lower back. The pain is initially aching in nature and becomes more intense and more frequent closer to childbirth. Back discomfort can occur even in women who did not have any problems before pregnancy.
The appearance of painful sensations in different women appears at different points in pregnancy. But, as a rule, the back hurts from 20-21 weeks of pregnancy. However, pain can appear much earlier, in this case it all depends on the woman’s lifestyle.
Back pain is worse during the end of pregnancy, this is approximately 34, 35, 36 and 37 weeks of pregnancy. The reason in this case lies not only in excess weight, but also in the fact that the child begins to put pressure on the lower back. Around this time, the body begins a kind of “preparation”, as a result of which some women feel quite intense and severe pain, although others may not feel it at all. In this case, you can notice that the abdominal wall itself sometimes tenses, becoming noticeably hard. This is clearly noticeable when a woman has to exert herself physically, or when she is angry, but this happens without any reason.
To understand why your back hurts during pregnancy, you need to understand the causes of pain.
- Shifting center of gravity due to increased weight.
- Problems with the spine before pregnancy.
- Wearing high heels during pregnancy.
- Weakening of the ligamentous apparatus during pregnancy.
- Hormonal changes in the body of a pregnant woman.
- Infectious and colds.
- Increased uterine tone and threat of miscarriage.
- False Braxton-Hicks contractions in late pregnancy.
- Stress.
- Poor physical fitness, weak back muscles.
- Lack of calcium in the body.
Shifting the center of gravity in a pregnant woman is the main cause of back pain
All women experience weight gain during pregnancy. Throughout pregnancy, a woman gains up to 16-20 kg. Accordingly, the load on the legs and spine increases, and back pain appears during pregnancy.
The fetus grows and gains weight every week, and the uterus also begins to enlarge. At the same time, the abdominal muscles stretch and weaken, the load on the back muscles begins to increase and the center of gravity shifts. To maintain balance, a woman has to strain her back muscles. A pregnant woman's posture changes. The woman involuntarily tilts her shoulders back, bends her neck and sticks her stomach forward in order to maintain balance and not fall.
Throughout pregnancy, the uterus continues to increase in size and becomes a cause of discomfort for the pregnant woman. An enlarged uterus can put pressure on the diaphragm, blood vessels and nerve endings, causing back pain. This can especially manifest itself in the later stages and often in a lying position.
Treating pain with your hands
Almost all painkillers are contraindicated for pregnant women. However, in the treatment of the back and spine, pharmacological drugs are in any case not the basis, but an auxiliary agent that can temporarily relieve symptoms. What’s more difficult is that physiotherapy is prohibited. Many physiotherapeutic methods are excellent for relieving spasms and restoring blood flow.
In fact, three methods remain in the arsenal of neurologists and vertebrologists. These include osteopathy, exercise therapy (including neuromuscular rehabilitation) and gentle manual therapy methods. The opinion that this method of treatment is inadmissible during pregnancy was justified until recently, but with the development of medicine, techniques have appeared that can and should be used.
Hormonal changes in the body that cause back pain
Hormonal changes can contribute to pain. The body and all its systems are intensively preparing for the pregnancy and birth of a baby. A woman’s hormonal system plays one of the main roles in rebuilding the body of the expectant mother. Under the influence of the hormone relaxin, which is secreted by the placenta, the pelvic joints and intervertebral ligaments expand and become elastic. Mobility of the pelvic joints is necessary for the passage of the baby through the birth canal during childbirth. But at the same time, relaxed ligaments and joints cause pain in the lower back and back.
Closer to childbirth, the production of estrogen in a woman’s body increases, and the level of progesterone decreases. An increase in estrogen stimulates the production of hormones that will be responsible for contractions of the uterus during childbirth.
The uterus will “train” intensively before giving birth. Women will increasingly experience false contractions, which will not only cause pain in the abdominal area. Tone muscles can provoke attacks of back pain. Sometimes a woman’s hormonal system cannot cope with its functions. The result is an imbalance in hormone production. The tone of the uterus may increase, which leads to sharp pain in the lower abdomen and back. Along with bloody vaginal discharge, these symptoms may indicate a threat of miscarriage. In such cases, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance, do not endure and do not self-medicate.
Find the cause of pain without X-rays and MRI
As you know, during pregnancy, radiation diagnostic methods are undesirable. You can almost always do without pictures if the doctor knows how to compare the existing symptoms and has time for this. We study the tone of certain muscles, reflexes and sensitivity in the various peripheral nerve systems and this gives us enough information. Such an examination may take 30-40 minutes, but it is informative and 100% safe.
As a last resort, you can resort to examining peripheral nerves and the spinal cord using electromyography (during pregnancy, some electromyography methods are allowed).
Pain in late pregnancy (38,39 and 40 weeks)
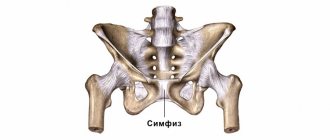
In principle, many women experience lower back pain during such periods. Most often, the appearance of pain is due to the high load on the spine and the fact that due to overstretching, the abdominal muscles weaken. In other words, in this case, the back hurts from the 27th week of pregnancy until childbirth. At the same time, it can radiate to the leg, intensify after prolonged walking, physical activity, or simply standing for a long time. Also, pain may appear in the pubic area and sacroiliac joint, which is due to the natural softening of the ligaments.
It is quite possible to cope with such pain if you follow some simple rules. First of all, foods rich in calcium (dairy products, fish, nuts, herbs, meat) will help with this. If pain bothers you regularly, then it makes sense to start taking calcium supplements. You should also limit movements that may increase stress on your back. For example, to pick something up from the floor, you do not need to bend down, but squat down. In this case, the muscles of the legs and shoulders will become tense, not the back.
It is much worse when the cause of pain is a variety of neurological diseases, such as radiculitis, intervertebral disc herniation, etc. In this case, problems can begin as early as 14-15 weeks of pregnancy, and the back hurts quite severely. However, such diseases can also affect the later stages of pregnancy. In this case, it is assumed that bed rest is established, the use of a soft corset or bandage is used, and sometimes painkillers are used, but this is rather an exception.
How to deal with lower back pain
If pain in the lumbar region is associated with an infectious disease, it is first necessary to eliminate the causes of its occurrence. When the cause of pain is osteochondrosis, flat feet or intervertebral hernia, a sharp increase in load can provoke a worsening of the condition and difficulty in straightening the spine.
Staphylococcus, enterococcus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli can lead to inflammation and pain in the back. They are accompanied by an increase in body temperature and a change in the characteristics of urine, which becomes cloudy and different in composition from normal.
Experts recommend that pregnant women get up from the couch as smoothly and carefully as possible, and also avoid lifting even minor weights.
Most often, lower back pain occurs in late pregnancy, and the discomfort completely disappears only after childbirth. If severe pain is associated with pathologies of the musculoskeletal system, the doctor may prescribe wearing a special prenatal bandage, which helps cope with high loads and overcome most of the negative effects of prolonged walking.
If your back hurts or your bones are aching, you should reduce the load on the spinal column by adopting the following recommendations:
- use an orthopedic mattress for sleeping;
- wear shoes with low heels and good foot support;
- when sitting on an armchair or chair, you need to use the back as a support;
- it is important to avoid high physical activity;
- You should keep your own weight within normal limits.
No ads 3
Swimming is considered one of the most effective means to overcome pain in the back. Water aerobics can also be an excellent effective method to strengthen the lumbar region, however, before exercising, you should consult with your doctor to determine whether there are any contraindications. Hydromassage and exercises using a fitball have a good effect.
Thanks to manual therapy, it is possible to correct vertebral displacements and other disorders with virtually no medication. If you have pain in the lower back during pregnancy, you should limit yourself to magnetic resonance imaging, since X-ray examination is contraindicated in all trimesters. In order to relieve pain, medications with anti-inflammatory effects, special ointments, tablets and vitamins of groups B, C, D and A are often required.
Women who are forced to engage in sedentary work are recommended to use breaks to perform simple sets of physical therapy exercises. Instead of bending your torso, for example, to pick up a fallen object from the floor, it is recommended to leave your back in a flat position by changing the bend of your legs. The maximum load should fall on the lower limbs.
What to do if your lower back hurts during pregnancy? In order to overcome pain, analgesics with minimal side effects and other auxiliary agents are usually prescribed. Among the non-traditional methods of treatment, the most common are: aromatherapy, homeopathy, reflexology, acupuncture, reflexology and herbal medicine.
Other causes of pain
The reasons given above are the most common, so when it is said that the back hurts a lot during pregnancy, then they are almost always talking about them. But there are a number of other problems that can lead to such pain.
Pancreatitis
This disease is an inflammation in the pancreas. Fortunately, this disease is quite rare, but it is precisely when the back hurts at the beginning of pregnancy. The development of this disease is facilitated by disturbances in the outflow of bile, alcohol consumption, poor diet (rich fatty and meat foods), stress and hereditary predisposition. Pancreatitis in the acute phase makes itself felt by acute pain in the lower back and abdomen (upper part), while the pain is girdling in nature. Abnormal bowel movements, vomiting, and low blood pressure are common. In such a situation, you need to urgently go to the hospital.
Diagnosis of this disease requires a number of laboratory tests of urine and blood, it is necessary to undergo ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging, etc. Most often, treatment has to be done in a hospital. In this case, a strict diet is prescribed, a number of drugs that should normalize the functioning of the pancreas, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. If the situation does not improve, then sometimes it is necessary to resort to surgery.
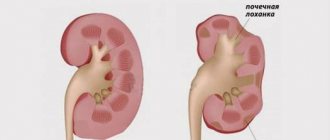
Pyelonephritis
This is a kidney disease that causes nagging and aching pain. In this case, during pregnancy, your back hurts in the lumbar region on the left or right. It’s even worse when you have to deal with renal colic, which is associated with the movement of a stone into the ureter from the renal pelvis. With colic during pregnancy, the lower back hurts very much, and it is not possible to find a position in which the pain will ease. The pain may also spread towards the urethra or groin. Another noticeable symptom is that the urine becomes quite cloudy, and sometimes blood can be seen. An increase in temperature may also occur.
To determine the diagnosis, the doctor sends the patient for an ultrasound; it is also necessary to conduct laboratory tests of urine and blood tests. When treating pyelonephritis, antibacterial drugs are first prescribed, which are selected individually, taking into account the sensitivity of microorganisms that caused the inflammatory process. Treatment in some cases is carried out on an outpatient basis, but it is preferable to be treated in a hospital. In case of renal colic, antispasmodics and painkillers are used to reduce pain, and certain inflammation prevention is also carried out.
Exercises for back pain during pregnancy
The second trimester is the best time to work on the muscles of the pelvic girdle.
Training the pelvic floor muscles allows the sacral bone to take the correct position, stretches the muscles of the groin area and gives a slight turn of the legs outward, which makes the legs straight and also improves the situation with flat feet.
Weak pelvic floor muscles cannot hold the pelvis in an upright position. Over time, the pelvic floor descends, along with it the pelvic organs descend and their blood circulation is disrupted.
Here are some example exercises:
1) Lie on your back, tense your pelvic floor muscles as you exhale, and relax as you inhale. Feel how the perineum retracts and returns.
2) Lying on your back, bend your knees, do not press your lower back to the floor, let it lie naturally. Tighten your pelvic floor muscles as you exhale, feel your lower back lower towards the floor.
In the last months of pregnancy, you need to be especially careful when performing exercises. During this period, the baby takes the correct position for childbirth; the “cat” exercise will help him in this.
Cat Pose:
While kneeling, lean on your forearms and sway smoothly from one side to the other. It is also good, when portraying a cat, in the same position, turn your head first to the left and look over your shoulder at the buttocks, then to the right, as if you were looking for a tail.
You can arch your back like a cat, while tensing the muscles of your abdomen and buttocks, and then relax, returning to the starting position. This exercise helps train the oblique abdominal muscles and relaxes the lower back.
Lateral Pulls:
We lie down on our right side. We rest our left foot on the right ankle. For convenience, surround yourself with pillows or a blanket and make yourself more comfortable. And stretch slightly, clinging to the floor with your right hand as far away from you as possible. Feel the right side of your body stretch and lengthen. If you feel so comfortable, then try to stretch your arm so that your elbow does not touch the floor and raise your legs above the floor. Then repeat on the other side.
Paschimottanasana.
During pregnancy, you should not bend forward deeply or lie on your stomach. Therefore, expectant mothers should perform a variation of Paschimottanasana. We sit in dandasana, exhale and clasp our big toes (if possible). We place our feet hip-width apart. We lower our shoulders down, try to connect our shoulder blades behind our backs, and keep our spine straight. This asana stretches the spine well and relieves back pain, which often occurs during pregnancy.
Urdhva paschimottanasana.
This pose perfectly stretches the spine, eliminates back pain and strengthens muscles. Lying on your back, bend your knees, place your palms on your feet and pull your straightened or semi-straightened legs behind your head. Do not try to place your feet on the floor behind your head; your pelvis should only slightly lift off the floor. Feel how your spine stretches. Hold for 15-30 seconds and slowly lower down.
Stretching:
It is important to remember about stretching during exercise. Stretching during pregnancy is needed, surprisingly, for relaxation. A muscle has two states: tense and relaxed. In an untrained person in a calm state, some muscles seem to tense by themselves. We don’t feel it, but in the evening there comes an inexplicable fatigue, heaviness throughout the body. A stretched muscle cannot be tense - therefore, by doing stretching exercises, we help the body “remember” how to relax.
Spinal reaction to pregnancy
Most women experience discomfort in the lumbar and back areas during pregnancy. Some expectant mothers experience varying degrees of pain, while others experience only mild discomfort. This is due to the increasing load on the lumbar and thoracic spine.
The localization and intensity of pain depend on many factors: individual characteristics, the presence of chronic diseases, lifestyle, nutrition, and physical activity. In general, the female spine is able to withstand heavy loads without damage. This is provided by nature so that the expectant mother can safely bear and give birth to a child.
What to do to avoid spinal pain
Almost every pregnant woman experiences discomfort in the thoracic or lumbar spine. Unpleasant sensations reduce the quality of life and limit physical activity. To prevent or reduce pain, you need to follow simple recommendations:
- from the first weeks of pregnancy, monitor your weight (body weight is considered normal if your BMI is below 30 units);
- eat a nutritious and varied diet, include calcium-rich foods in your daily diet (cottage cheese, cheese, milk, yogurt, herbs, vegetables, fruits, fish);
- after 20–22 weeks of pregnancy, wear a special bandage to support the lumbar spine (the type is selected by the doctor).
It is also useful to lead an active and healthy lifestyle, move more, and engage in gentle sports.
What not to do during pregnancy to prevent back pain:
- lift and carry heavy objects;
- jump;
- pump up the press;
- do exercises with a barbell (you need to cancel intense workouts).
If a woman’s work involves heavy physical activity, then it is recommended to switch to light work (this is a right enshrined in the Russian Labor Code). It is better to choose a computer chair with a comfortable, possibly orthopedic backrest.