Posture and its violations[edit | edit code]
Posture should be understood as the habitual pose of a casually standing person, which he takes without excessive muscle tension. In a broader sense, posture is the position of the body in various static positions, and the characteristics of muscle function when walking and when performing various movements. But it is too difficult to determine what kind of posture a person has while dancing, working, or just walking, so when assessing posture and diagnosing its disorders, the characteristics of a standing posture are used. Read more:
Posture and its complications
Posture correction in rehabilitation
One of the leading areas of work of the rehabilitation center, based on the Center for Medical Radiology in St. Petersburg, is the correction of postural disorders in adults and children. Rehabilitation measures aimed at eliminating provoking factors, unloading the spine, stopping the progression and reversibility of the deformity take place in comfortable conditions, under the supervision of experienced professionals. The individual treatment and rehabilitation program includes:
- differentiated, acupressure, vacuum massage
- Exercise therapy (symmetrical and asymmetrical exercises to develop the femoral, tibial, gluteal, lumbar-iliac muscles, stretching and strengthening of the back, corrective gymnastics)
- physiotherapeutic procedures (electromyostimulation, ozokerite, ultrasound, magnetic therapy, SMT therapy, fluctuarization, electrophoresis, etc.)
- acupuncture
- kinesiotherapeutic techniques
- exercises on therapeutic simulators
- correction with orthopedic corsets
- mechanotherapy
- health systems of yoga therapy, Pilates
- psychotherapeutic correction
The integrated use of non-drug treatment methods allows, without pharmacological load, to form and consolidate the skill of correct posture, stabilize the functioning of internal organs, and achieve the possible complete correction within the existing defect.
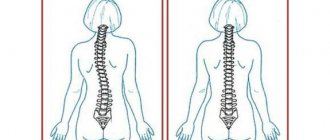
Scoliotic posture[edit | edit code]
Scoliotic posture
is a functional curvature of the spine, which cannot be considered as an independent disease. Poor posture can be caused by many factors.
The most common causes of scoliotic posture are:
- True shortening of one of the lower extremities as a result of traumatic injury, massive infection of joints and bones - arthritis, osteomyelitis;
- Consequences of birth trauma - for example, torticollis, hypotension or muscle hypertonicity on one side;
- Severe general diseases, pathologies of internal organs;
- Consequences of extensive burns with the formation of scars on the back, sides of the body, lower extremities;
- Similar consequences of surgical interventions;
- Weakness of the muscular framework around the spine - the condition can be congenital or develop as a result of low physical activity of the child, as well as as a consequence of an inflammatory process or an autoimmune lesion.
The difference between scoliotic posture and scoliosis[edit | edit code]
It is important to distinguish between these two completely different pathologies, although scoliotic posture may well lead to the development of true scoliosis. It is very important to prevent such a complication, since the treatment of scoliosis is much more complex, lengthy and is not always accompanied by successful completion.
Scoliotic posture is characterized by the occurrence of a single curvature in the frontal plane of the spine. It is usually localized in the lower thoracic area or even in the lumbar region. In this case, an asymmetrical position of the shoulders is noted - one shoulder moves down, which coincides with the concave side of the impaired posture, the second shoulder, accordingly, is in an elevated state. Changes of the same type are observed in the location of the shoulder blades.
An important feature of scoliotic posture is the absence of changes in the pelvis - the bones are in the correct position. In addition, all these disturbances disappear if you ask the patient to straighten up or place him on a flat, hard surface. At the same time, it is clearly visible that the curvature is purely functional in nature, and there are no morphological changes in the spine.
With scoliotic posture, the disappearance of curvature is also observed when the patient hangs, while holding himself with his hands, on the trapezium and when bending, during any movement when the muscles are tense, when standing on one leg, etc.
All these manifestations are confirmed, first of all, by X-ray examination. Magnetic resonance and computed tomography also provide comprehensive information.
When scoliotic posture is diagnosed, treatment is prescribed by a doctor and may include the following methods: swimming, massage, physical therapy, the use of manual therapy techniques, physical therapy to normalize the position of the body and form a strong muscular frame around the spine.
Diagnostics
Poor posture is detected during a medical examination by determining the coordinates of anatomical landmarks. If it is necessary to differentiate compensatory postural deformities from persistent deforming diseases of various parts of the spine, instrumental diagnostic methods are prescribed:
CT
(additional information about the condition of the curvature area)
Radiography
(functional spondylography in direct and lateral projections, to determine the degree of displacement in relation to the vertical line)
MRI
(clarification of the diagnosis in the presence of neurological symptoms).
Magnetic resonance imaging is recognized as the safest and most informative method. Advanced imaging technology, without radiation exposure, creates a three-dimensional reconstruction of the spine, assesses the condition of the spinal structures and their true relationship with the vertebrae.
Causes of poor posture in children
As we have already mentioned, deformities can be congenital or acquired. Moreover, 90-95% of cases belong specifically to the second group. The prerequisites for the disorder influence the symptoms and characteristics of the course of the pathology.
Congenital causes include the following factors:
- incorrect position of the fetus in the womb;
- intrauterine pathologies of the formation of the spine (for example, the formation of additional vertebrae, their wedge-shaped deformation, etc.);
- connective tissue dysplasia;
- myotonic syndrome;
- injuries during childbirth (torticollis, subluxation of the first cervical vertebra, dislocation of the hip joint, etc.).
Some congenital abnormalities can correct themselves as the body grows. But only on condition that the child is absolutely healthy. Otherwise, pathologies progress, causing curvature of posture and severe forms of deformation.
The causes of acquired curvature include:
- Insufficient physical activity. If parents focus only on the child’s intellectual abilities, he spends a lot of time sitting and moves little. Accordingly, the muscular framework that holds the spine in the correct position does not develop.
- Unphysiological pose. If a child slouches, always carries a backpack in one hand, or sits at an inappropriate desk height, asymmetry of the musculoskeletal system will develop over time. This same group of prerequisites also includes planting the baby too early or putting him on his feet, or placing the baby on one arm.
- Injuries, illnesses. Past illnesses can cause complications that affect the joints and cause curvature of the spine. At risk are children who have had polio, tuberculosis, osteomyelitis, children with diagnosed myopia, strabismus, astigmatism, and fractures. Obesity and a deficiency of nutrients in the body can also be a prerequisite.
Stages of development of incorrect posture
Violation of correct posture occurs gradually, in several stages:
- unfavorable background - this stage is characterized by the presence of biological defects or unfavorable conditions that contribute to poor posture (provided there are no static and dynamic pathologies);
- pre-disease - a period of unfixed deformities. There are initial signs of functional insufficiency of the mechanisms for ensuring correct posture, symptoms of its violation arise, and a deterioration in general development indicators is noted. With targeted therapeutic intervention or normalization of physical education, such changes are completely reversible;
- disease is a stage of static changes in the spine, which is characterized by the presence of difficult-to-reversible or irreversible disorders.
There are fixed and functional disorders of posture. With functional changes, a person can accept the correct position of the spinal axis, but with a fixed one, he cannot. Most often, functional disorders arise as a result of a weak muscular corset of the trunk. Deformation of posture at school and preschool age causes deterioration in the functioning of systems and organs of a growing organism.
Symptoms of scoliotic type of posture
In most cases, the scoliotic type of posture in children develops in the very first days of life. Already when lying in a crib, the baby can deviate the upper part of the body. In the future, the scoliotic condition only gets worse. The first clinical signs can be noticed already at the age of 5 years. But not many parents at this period of the baby’s life show him to a specialist vertebrologist or orthopedist. For the first time, clinical symptoms of scoliotic curvature of the spine are detected during a medical examination before the first class. Then, during annual follow-up, progression or stagnation of the disease can be seen.
Please pay attention to the following characteristic signs of the development of scoliosis in a child or adult:
- uneven location of the lower angles of the scapula;
- bringing one corner of the scapula closer to the spinous processes of the spinal column and abducting the opposite corner;
- when standing with arms hanging freely along the body, a significant difference in the width of the spaces between the body and limbs is visible;
- difference in the height of the shoulder line on the left and right sides;
- When the body is tilted forward from the back, a deviation from the normal vertical axis is clearly visible.
If you notice such signs, immediately make an appointment with a vertebrologist. An experienced doctor can make the correct diagnosis at an early stage of the disease. This will allow for comprehensive, comprehensive treatment and return to normal posture.
Treatment of scoliosis
Treatment methods for scoliosis in children depend on how far the disease has progressed. In case of pathology of the 1st-2nd degree, it is enough to eliminate the causes of the curvature. Correction of the position of the spinal column is carried out using massages and therapeutic exercises. Children are recommended to practice swimming, horse riding, sleep on a hard surface, and control their posture. To treat grade 2-3 scoliosis, additional methods are used:
- physiotherapy;
- manual therapy;
- corseting.
Surgical correction of the vertebrae is carried out at the 3rd-4th stage of the disease, if scoliosis leads to compression of internal organs.
The best period for surgery is between 10 and 14 years of age. The essence of the surgical intervention is to install anchors or implants that support the spinal column. The operations are traumatic and have a long rehabilitation period. The prognosis for treatment of scoliosis in childhood is favorable. As long as the spine remains flexible, its position can be adjusted.
General information
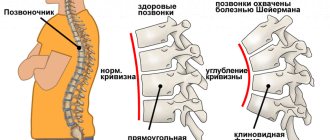
Scoliosis is a pathological curvature of the spine in which rotation occurs around the longitudinal axis.
Changes also affect internal organs. They are compressed and change their position, which subsequently leads to disruption of their functionality. Scoliosis is diagnosed in 5-10% of children. Girls get sick 9 times more often than boys. The risk category includes children aged 5 to 12 years. During this period, the spine grows rapidly. If a child sits incorrectly at a desk or does not play sports, scoliosis develops especially quickly. Depending on the age of the baby, there are 3 types of scoliotic deformity:
- infantile, or infantile - occurs up to 3 years;
- children's or juvenile - from 3 to 10 years;
- youth - from 10 to 18 years.
Parents usually bring children with scoliosis to the doctor at the age of 8-14 years. During this period, the symptoms of the disease become especially noticeable. Sometimes pathology is diagnosed only during a routine medical examination.
Kinds
Scoliosis of the spine in adolescents can take different forms, which have letter designations:
- C – with one scoliotic arch;
- S – 2 arcs;
- Z – 3 arcs.
Spinal curvature has several degrees, which determine the severity of symptoms and methods of orthopedic correction. The degrees are determined by the magnitude of the deviation angle using radiography:
- 1st degree. The spine deviates no more than 10°, the rotation of the vertebrae is small;
- 2nd degree. The arc angle is 10–25°, the vertebrae at the maximum point of curvature are rotated relative to the axis and are moderately deformed;
- 3rd degree. Deviation of 25–50°, pronounced rotation of the vertebrae, the presence of a costal hump, persistent deformity of the spinal column;
- 4th degree. The angle is greater than 50°, severe curvature causes significant distortion of the entire body and displacement of internal organs with disruption of their functioning.