Is it possible to play sports with this disease? How to choose a section that is suitable for a child in this case and what sports are contraindicated for him? What kind of physical activity should there be? Below we will look at the main issues regarding flat feet and sports.
Flat feet is a deformity of the feet, since the arch of the foot does not acquire an arched shape, remaining flat. If you look at a child’s feet, you can see that from birth the child’s foot is flat, so flat feet can only be diagnosed at the age of three. At this age, the child’s foot takes shape and changes its appearance; according to norms, the arches must rise. Of course, if this does not happen, then we should talk about the presence of this disease.
Flat feet can be cured quite easily, because it is not a very serious disease. And yet, parents often think about whether a child with flat feet should play sports and what contraindications are there for him in physical activity? This is worth looking into in more detail.
Are there any contraindications to sports for this disease?
It is not a true statement that you should not exercise if you have flat feet. Of course, not every sport will be equally useful, but playing sports is not at all contraindicated. It is best to consult with doctors and fully examine your child before sending him to any sports. First of all, restrictions in physical activity may be determined by the severity of the pathology, the type and degree of flat feet, as well as the general condition of the musculoskeletal system.
If your child has flat feet and you really decide to send him to any section, then you need to:
- first of all, consult a doctor;
- take an x-ray of your feet;
- Check if your child has a protrusion that develops with this disease.
After undergoing the examination, you will be able to receive a certificate from the orthopedist with an opinion and recommendations regarding optimal loads, as well as the most suitable sports for you.
Flat feet in a child
Contrary to the good old jokes about evading the army, flat feet are not a trivial ailment at all, but a serious orthopedic problem that can lead to many chronic diseases. Changes in the shape of the foot begin in childhood, so the sooner parents suspect something is wrong and show the child to the doctor, the better. Let's figure out where flat feet in children come from and how to deal with it.
0–3 years
At about a year old, an important event occurs in the baby’s life - the transition to a vertical position: the child takes his first steps, learning about the surrounding space. Up to 3 years of age, children’s feet are surrounded by a developed fat layer and visually have a flat surface, and the musculoskeletal system is not yet sufficiently developed. When a child begins to take his first steps, the fatty “pads” on the soles take on the function of springs. Gradually, the experience of independent active movements in space accumulates, and the foot takes on a normal appearance.
During this period, three pressure points form on the baby's foot, located on the heel, the area near the little toe and in the area under the big toe. These sections are fastened together by ligaments, muscles and tendons, so the entire structure forms three arches - two longitudinal (external and internal) and transverse. When walking, they act as shock absorbers, thanks to them the gait becomes light, and the legs get used to long hours of stress.
Now imagine that the arches of the foot - a kind of arches that pass between every two pressure points - sometimes, due to improper development of the musculoskeletal system (as well as some diseases), turn into straight lines and become flattened. It is no coincidence that when translated from English, flat feet are literally translated as “fallen arch.”
However, young children are not diagnosed with flat feet. However, if the child began to walk very early (before 9 months), suffered from rickets or has a hereditary predisposition to flat feet, the orthopedist can prescribe a prevention program that includes massage of the lower extremities, walking on an orthopedic rug and wearing orthopedic preventive shoes.
The purpose of such shoes is to develop the correct walking skill: the brain “remembers” the sequence of contraction and relaxation of muscles to perform a step, thanks to which the child continues to walk correctly even barefoot.
3–7 years
At this age, children develop the “adult” shape of the arches of the feet, and it is at this time that the orthopedist most often detects signs of pathology. Additional causes of flat feet in children of kindergarten age are excess weight, neurological and endocrine diseases. The disease can be suspected if the child places his legs oddly when walking, and after a long walk begins to limp.
The treatment and preventive program prescribed by the orthopedist involves the child performing special gymnastic exercises every day, swimming with fins, and sometimes physical therapy to improve muscle tone. In recent years, the method of functional taping has become especially popular - gluing special adhesive tapes onto the patient’s body to tighten the skin and ease the load on joints and muscles. The prognosis for treatment among children of this age is favorable.
What sports are not suitable for a child with this disease?
We have already said earlier that without an accurate doctor’s opinion, you will not be able to choose the right sport that will not harm your child and will only be beneficial. So, often, a child with this disease is not recommended for classes:
- figure skating;
- skating;
- hockey;
- ballet;
- classic jumps;
- tennis and badminton.
If you carefully consider the list above, you will notice that those sports that involve skating are most contraindicated for flat feet. This is quite simple to explain, since shoes designed for these sports are specific: when wearing such shoes, the shock absorption of the feet is reduced, which is already a problem for this disease. Those sports in which there is such an element as jumping, as well as ballet and classical running, also put the strongest stress on the feet.
A sport such as football is prohibited for children who have severe foot deformities. However, if you have a mild degree of flat feet, it is possible to engage in this sport, but only with a doctor’s opinion.
Let's discuss what sports you can do if you have flat feet.
Is flat feet a congenital pathology?
Only in 3% of cases is flatfoot of a hereditary nature. In all others, this is the result of improper formation of the foot. Moreover, newborn babies have a flat foot, and before the period of active walking it has a pronounced fat pad. Longitudinal and transverse arches are formed gradually, over several years, and one can even say that in Dosadovo children the flat-valgus position of the foot fits into the normal corridor. That is, if you, say, see the footprints of your baby who has barely learned to run in the sand, and they do not have the usual relief - an “adult” notch - this is absolutely normal. No matter what other mothers or grandmothers say about this.
Choosing shoes for flat feet.
An integral part of playing sports is the selection of the necessary equipment. Let's look at some tips when choosing sports shoes for a child with a disease such as flat feet.
It is necessary that the sole be specially cushioned.
Of course, the shoes must be the right size, secure the foot quite well and not interfere with blood circulation.
It is also recommended to have special therapeutic insoles and instep supports.
How can you tell if you have flat feet?
Why did you even ask these questions? You may have encountered unpleasant symptoms of flat feet. These often include the following:
- pain after a long walk, and sometimes pain can occur at rest;
- difficulties when choosing shoes - most models seem uncomfortable;
Photo: istockphoto.com
- after prolonged wear, the shoes become deformed;
- you don't like the appearance of your feet.
If at least one of these points coincides, you should contact an orthopedist.
In conclusion
To summarize, we can say that a disease such as flat feet is not a death sentence and does not contribute to an absolute refusal of physical activity. It’s just that when choosing a section, you must remember that the exercises should not cause inconvenience or harm to the baby, so this issue needs to be approached as carefully as possible. Consultation with a doctor is an indispensable factor when choosing any sport. After all, it is the doctor who will be able to give the right recommendations and advise which sports are suitable for your child. He will also be able to advise you on the treatment of this disease and the correct distribution of loads.
When deciding that a child should still attend any sports section, the choice of shoes deserves close attention. Since shoes for children with flat feet are specific, differing from ordinary ones with more cushioned soles, their cost will be slightly higher. Such shoes must be comfortable for the child and not contribute to overstraining his muscles.
Scientific and practical article by the speaker of the II International Fitness Convention “T..R.I.U.M.F.” Valeria Baranova
The influence of the foot on the entire body
A healthy foot with its arched structure is a perfect supporting device for human movement. The health of the joints of the legs, the spinal column (and the spinal cord too), and the condition of all internal organs and the brain depend on how the human foot performs its spring (shock-absorbing) function.
Many people are sincerely surprised: their spine and knees hurt. How does this relate to the foot?
Let me give you a few examples.
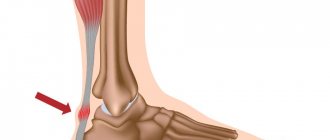
A violation of the ratio of axial load on the knee inevitably occurs when the arches of the foot become flattened. And the flattening of the arches occurs due to weakening of the foot muscles.
When the arches of the foot are deformed, a person steps heavily on all the bones of the foot at once, the foot muscles are switched off from the depreciation process, which causes the knee joints to spring back. This places an unnatural load on the ligaments and muscles of the knee joint.
Another example is the unevenness of the arches of the right and left feet, different lengths of the legs, a misalignment of the pelvis, which should stand symmetrically due to the vertical position of the torso in space, a compensatory curvature to the side is formed in the lumbar spine, i.e., scoliotic disease is gradually formed. This leads to chronic back pain. Intervertebral hernias often form.
The spine is also involved in maintaining balance and ensuring upright walking. Due to a deformed foot, the load on the spine increases. The lumbar region is especially affected. Problems arise due to the need for the spine to constantly maintain shock-absorbing function.
This deformation of the feet also affects the health of the most important organ in the human body - the brain.
Due to impaired shock absorption, shocks from the feet when walking are transmitted along the spine to the brain. As a result, even with short walking, headaches, tinnitus, and blurred vision appear. This foot deformity is called flat feet.
Structure (anatomy) of the foot and its functions
Foot - (pes, PNA, BNA, JNA) the distal section of the lower limb, which is a support organ and performs a spring function when standing, walking, running and jumping (Big Medical Dictionary)
The bones require a more detailed consideration, since they are the main component of the foot. The foot is formed by 26 bones and they are all connected into one mechanism by ligaments and joints.
Let's consider the main ones:
The heel bone is the most powerful. It is located in the back and carries a huge load. Despite the fact that this part has nothing to do with the ankle, it plays a large role in the distribution of pressure. The role of the connector between the calcaneus and the talus is performed by the joints. A strong connection of these two bones is necessary to give the foot a normal shape. The back of the bone holds the Achilles tendon. This place can be found by a small ledge.
The talus is several times smaller than the calcaneus, but massive and forms part of the ankle. In front there are bones: tarsals (talus and calcaneus, scaphoid, cuboid, lateral cuneiform and medial cuneiform bones), metatarsals and phalanges of the fingers. They are involved in the formation of the correct arch of the foot.
What muscles are important for us to know in order to understand how to properly train the foot?
Tibialis posterior muscle. This muscle originates from the fibula and tibia, encircles the lower leg and is attached to the foot on the inside. It participates in the formation of the longitudinal arch of the foot, bends the foot, rotating it outward.
Tibialis anterior muscle. It starts from the tibia, encircles the lower leg in front and is attached to the plantar surface to the medial cuneiform and the base of the first metatarsal bone. She extends the foot and raises its medial edge (supination).
There are also flexors and extensors of the fingers, but we will be most interested in the flexor pollicis longus. The outermost of the deep layer muscles, lies on the posterior surface of the fibula, flexes the foot, supinates it, flexes the big toe and strengthens the arch of the foot.
Extensor pollicis longus. Extends the foot, raises its inner edge (supination), extends the big toe and tilts the shin anteriorly with a fixed foot.
Functions of the foot:
The foot performs the most important functions; it is with its help that a person can walk, run and just stand. She experiences enormous stress, especially if a person is obese or his work involves long periods of standing or walking, or playing sports. Many of the functions of the foot are performed by its arches; thanks to them, shock absorption is provided, protecting other joints and the spine from excessive loads. And it is precisely this shape of the foot that allows it to withstand quite large loads (about 100 tons).
Types of vaults:
A person has two types of arches of the foot - transverse and longitudinal.
The longitudinal arch is located along the inner edge of the foot . It is formed by the calcaneus, cuboid and metatarsal bones, strengthened by the plantar aponeurosis. This structure allows the foot to perform a shock-absorbing function when walking and jumping, and to prevent damage to the anatomical structures of the foot.
The transverse arch crosses the foot, and is supported by longitudinal arches on each side. It is formed by the bases of the metatarsal bones, the cuboid bone and three wedge-shaped bones.
Flat feet and the causes of its occurrence.
Flatfoot is a deformation of the foot with flattening of its arches and loss of shock-absorbing function.
We talked about the types of arches of the feet earlier, now we will look at the types of flat feet and the reasons for their occurrence.
There are three types of flat feet: longitudinal, transverse and combined.
Longitudinal flatfoot is characterized by flattening of the longitudinal arch of the foot. At the same time, its length increases and almost the entire area of the sole comes into contact with the floor. It is noteworthy that longitudinal flat feet are characteristic mainly of women. As a rule, the leg falls inward.
If we are talking about transverse flatfoot , then the five metatarsal bones, on which the entire frontal part of the foot rests, diverge like a fan. The foot becomes wide and flat because the muscles no longer hold the arch. Very often the thumb becomes distorted and the bone begins to grow - a valgus change.
Combined flatfoot is a deformity that combines both transverse and longitudinal flatfoot.
Flat foot test
- You need to take your shoes, which have served for more than one season, and look at the back surface.
If the shoes are worn inward or outward, this means that when walking you do not place your foot straight, but rely on the outer or inner arch of the foot. - The point is to smear your feet with any coloring and easily washed off substance, and stand on any white sheet of paper.
You cannot lean during the procedure. You just need to stand straight. When viewing the resulting picture, draw a conclusion.If the entire area of the foot is painted over, then the disease definitely exists. If there is an indentation on the inside of the foot and space between the forefoot and the heel, then there is no problem with the legs.
If there is no gap between the upper and lower parts of the foot, then one of the varieties of flat feet is observed.
Causes of flat feet.
Flat feet can be congenital (2% of all cases) or acquired.
The acquired goods are in turn divided into:
- Paralytic
(paralysis of the foot muscles, tibial muscles) - Rachitic
(pathologies that cause bone fragility) - Traumatic
(injuries to bones and tendons of the lower extremities)
- Static (most interesting to study):
Wearing tight and uncomfortable shoes with or without high heels.If you wear shoes with high heels, the first thing that will begin to disappear is the transverse arch of the foot (under the toes), as the weight moves from the heel to the forefoot. Excessive load leads to weakening of the ligaments, and a decrease in the area of support and redistribution of weight leads to a flattening of the foot (the bones of the metatarsus move apart).
Shoes without heels are contraindicated; they cannot be worn; you must wear shoes with heels from 2 to 6 cm.
- Hereditary predisposition (if your relatives have flat feet, then there is a high probability of developing flat feet in you).
- Excess weight (including excessive weight gain during pregnancy).
- Muscle weakness of the legs (can be the result of sedentary work, a sedentary lifestyle).
- Great load on the legs.
A set of exercises for the prevention of flat feet
A disorder such as flat feet is quite serious, and in most cases it is easier to prevent than to try to treat it later.
Pay attention to the symptoms of flat feet that you can see on your own:
- shoes are worn down on the inner or upper surface;
- legs get tired quickly when moving and standing for a long time;
- by the end of the day there is fatigue in the legs, cramps, heaviness, swelling in the ankles;
- difficult to walk in heels;
- you have to buy shoes in a larger size because of the width;
- pain in the lower extremities, lumbar region, head.
Exercises are the most effective method of strengthening muscle tone and normalizing blood supply to the foot. It has been proven that with the right choice of exercises and performing them daily for several months, it is possible to stop the progression of foot flattening.
The most effective exercises for flat feet are carried out using complexes to stimulate several muscle systems at the same time. For this, not only exercises are used in standing, sitting or lying positions, but also auxiliary objects are used (gymnastic sticks, inclined planes, geometric cubes).
The first thing we need to know before starting the exercises is that there is a load triangle.
The foot is in contact with the horizontal surface not with its entire area, but only with three points: the calcaneal tubercle, and the heads of the 1st and 5th metatarsal bones. If you connect these points, a triangle is formed, on which the entire body weight is supported.
Exercise No. 1
Distribute your weight evenly across your entire foot, starting to press down on the ball of your big toe, the ball of your little toe, and the middle of your heel. Without stopping the pressure, we raise all five fingers.
This exercise will help to properly distribute the load on the entire foot!
If your foot rolls inward, you need to press harder on the outer edge. Conversely, if the foot falls on the outer edge, then put pressure on the big toe, including it in the work.
Next, we raise our fingers and we need to move them apart (away from the thumb), just as you do on your hands, so that there is a gap between the fingers. After this, we lower all five fingers so that they do not touch each other.
Let's complicate the exercise.
After we have learned to distribute the load over the entire foot, raise the toes and not touch the toes to each other, we lift the big toe and hold it at the top, while pressing four toes into the floor. Lower your thumb and raise four fingers up. At the same time, we distribute the load evenly, without tilting the foot in different directions.
The exercise seems easy, but few people succeed the first time.
Exercise No. 2
Stand straight with your feet shoulder-width apart. Alternately stand on your toes (transverse arch) and on your heels, making smooth but strong rolls. Please note that you need to press not on your fingers, but on the arch (base of your fingers).
Do not interrupt the procedure for 3-5 minutes until you are completely exhausted.
Exercise No. 3
Stand straight, feet shoulder-width apart. Raise one leg off the floor while maintaining balance. In such a suspended state, rotate your foot first inward, then from the inside. Make 20-30 rotations in each direction and change legs.
Exercise #4
With valgus flat feet, it will be useful to grab the floor with your toes and firmly pinch various small parts or various fabrics (scarf, towel), while straining the muscles of the feet.
Exercise #5
Sitting comfortably on a chair or standing on the floor, roll the ball along the floor with your feet (using the transverse arch), pressing firmly with your feet on the object. Painful sensations should be 6-7 points out of 10. 10 rolls to the left and right are enough to affect this area.
The ball can also be used to train the abductor pollicis muscle.
Keeping the pressure at a low level, we roll the ball lengthwise.
Exercise #6
Insert a pencil or felt-tip pen between the first and second toes; you can try to do this without using your hands, taking a pencil from the floor. If you can't hold a pencil, take a marker; it will be easier to grasp and hold with untrained fingers. Now throw a piece of paper on the floor and write numbers or words on it. During the exercise, you stand and maintain balance on one leg, holding the paper with your fingers, while writing with the other leg. Do the same for each leg.
From all of the above, we understand that flat feet are a problem that cannot be ignored. By performing simple gymnastics daily, you will soon begin to notice changes, but it gives a noticeable effect if you use massage/self-massage.
With the help of massage, we can strengthen the muscles of the foot, reduce muscle fatigue, eliminate pain, and improve blood circulation in the lower leg and foot.
Basic manipulations to prevent flat feet or correct them:
- We begin to stretch the shin. To do this, you need to clasp the shin with the fingers of both hands and stroke the skin from heel to knee with straight movements, gradually increasing the intensity. In this case, while moving up, you need to apply pressure, and when moving down, just stroke the shin.
- We work with the tibialis posterior muscle, as it plays a key role in the formation of the arch of the foot.
It is necessary to apply pressure with the thumbs or the base of the palm along the tibia from the inside from the base of the hip bone to the foot. - We work with the plantar fascia.
Stretch your feet so that your toes are tense, press your fist onto the plantar fascia, rubbing it and making circular movements. - Next, carefully knead each finger from the nail to the base, using these movements to work all the joints. Particular attention can be paid to the thumb (bend, straighten for 5-6 repetitions), then make circular movements with the thumb.
From all of the above, we can conclude that the foot is the part of the body that carries a huge load every day. At the same time, the health of a person as a whole depends on the health of the feet. Of course, in the modern world it is not always possible to maintain a perfect foot structure; flat feet are becoming an extremely common disease. It develops when the muscular-ligamentous mechanism weakens for some reason. However, flat feet can be prevented and sometimes corrected by selecting special exercises that promote the development and strengthening of the muscles of the lower leg, foot and fingers. By performing them daily, it is possible to correct the pathological position of the arches of the feet and record the results obtained.
How does flatfoot occur and manifest?
Early signs of a foot defect in a child are perceived as unpleasant sensations for him, manifested as follows: - when playing football and even during regular walking, he gets tired much faster than other kids; - when under load, swelling appears in the muscles, often leading to short-term cramps in the legs; — the usual shoes turn out to be too narrow and begin to wear out the feet. Naturally, the child will not be able to play to his full potential under such conditions. However, personal sensations alone are, of course, not enough for an accurate diagnosis of flat feet. To be completely sure of your child’s illness, it is advisable to consult an experienced doctor. And only after consultation with a specialist, a parent has the right to judge whether a child with signs of flat feet can be sent to the section.
What to do if you have flat feet?
An orthopedic doctor will be able to select individual orthopedic foot position correctors, taking into account individual characteristics.
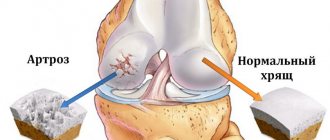
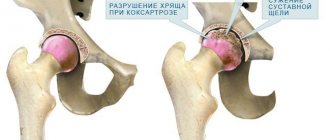
If the degree of flatfoot is third or fourth, then most likely there is pain when walking and arthrosis of the metatarsophalangeal and interphalangeal joints is present. In this case, the orthopedist can recommend orthopedic shoes and exclude model (any other) shoes. And in case of severe pain and severe osteoarthritis and zero effect from conservative treatment (wearing insoles, pharmacotherapy, physiotherapy), surgical intervention is recommended.
Photo: istockphoto.com
Important!
Each case is individual. You should not self-medicate - for timely help, consult a specialist.
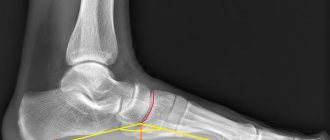
How to determine the degree of flat feet?
Using X-rays, you can determine the relationship of the small joints of the foot and identify osteoarthritis, deformation of the first toe and its degree, and chronic bone damage. The very degree of flatfoot (there are four in total) is determined by calculating the angles and height of the arch of the foot formed by the bone structures. The relationship is as follows: the higher the degree, the lower the height of the foot. This means that the pain syndrome is more pronounced and not only the biomechanics of walking is disturbed, but also the position of the body in space.
Photo: istockphoto.com
Another diagnostic option is plantoscopy. It is performed using a mirror table with lamps (plantoscope). But this type of study will not provide sufficient information to study bone-joint relationships. It is more often used in the early stages of flat feet to confirm or refute the flattening of the arches of the feet in order to select individual insoles.
How to get rid of knee pain? 3 working methods
Develop your foot muscles
Flat feet are associated with weakened foot muscles. Therefore, your task is to train them. Any massage techniques or special exercises are suitable for this. It will also be useful to walk barefoot more often on uneven surfaces (for example, on the ground, sand, pebbles, etc.).
“It is also a prerequisite to complete a complex of exercise therapy,” adds Daria Tretyakova.
Classes in the football section “ABC of SPORTS”
Most experts are confident that playing football with first-degree flat feet is quite acceptable. For a child with this deficiency, the training regimen is usually adjusted according to the maximum duration of the load. In order to attend classes at the children's football school ABC of SPORT, parents will need to obtain a certificate from a medical institution and give it to the coach. Based on a document certified by a doctor and the decision of the general coaching council, the child is given relaxations in the training regime (regardless of the age and group to which he is assigned).