Causes
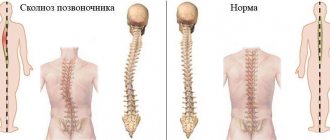
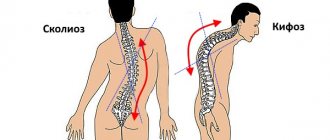
Scoliosis, due to its occurrence, is divided into structural - with changes in the structure of the vertebrae and surrounding tissues, and non-structural - acquired, most often compensatory.
Structural types of scoliosis can cause congenital abnormalities in the structure of the chest or connective tissue pathology, in which the innervation of certain areas of the spinal column changes, osteomyelitis, osteoporosis, tuberculosis, injuries and tumors of the spine.
Non-structural variants of scoliotic changes are most often provoked by injuries to the lower extremities and pelvis, as well as their improper formation during intrauterine development of the fetus. Less commonly, severe inflammation of muscle tissue, burns and scars can be the cause.
Scoliosis is divided into degrees - depending on the angle of deviation of the spine from its axis. Spinal curvature of the 4th degree is characterized by an angle of over 50 degrees.
Correction of kyphoscoliotic spinal deformity
Over the long period of existence of the disease, many methods for correcting scoliosis, both conservative and surgical, have been tested. There have been significant advances in the treatment of this disease in recent years.
Complex conservative treatment is effective only for initial degrees of scoliosis of 1-2 degrees. Conservative therapy includes unloading of the spine, therapeutic corrective gymnastics, massage, physiotherapeutic procedures, and corset therapy.
Surgical treatment is performed for patients with progressive scoliosis of 2 degrees and for all patients with 3-4 degrees of deformity. Currently, a significant number of surgical techniques have been proposed aimed at eliminating curvature and stabilizing the spine. During the operation, the spine is fixed with metal rods.
Indications for surgical treatment:
- deformations of 40º or more (according to Cobb),
- documented progression
- body imbalance,
- cosmetic defect,
- pain syndrome,
- dysfunction of the cardiopulmonary system,
- patient's wishes.
The goals of surgical treatment of scoliosis: feasible correction of deformity in three planes, stopping the progression of curvature, normalizing appearance, achieving body balance in the frontal and sagittal planes.
The generally accepted tactics for adolescent mobile deformities up to 75° is a one-stage dorsal intervention; for severe and rigid scoliosis - two-stage corrections. In a two-stage correction, the first stage involves discectomy at the apex of the deformity; at the second stage - dorsal correction. A technique with simultaneous multi-level discectomy and dorsal correction is also used.
Multilevel discectomy and dorsal correction (one- or two-stage) is accompanied by extensive tissue trauma, heavy blood loss, and a pronounced cosmetic defect of the chest.
At the Center, correction of kyphoscoliotic spinal deformity is carried out using endoscopic technology. This technique was developed in the mid-90s, which led to a reduction in the invasiveness of interventions and made it possible to more thoroughly perform surgical correction. With standard thoracotomy, the apex of the spinal curve is well visualized, but access to the underlying and overlying intervertebral spaces is difficult, which affects the results of operations. The introduction of endoscopic techniques allows us to avoid this drawback.
During thoracoscopic spine surgeries, thoracoscopic release of the anterior parts of the spine and thoracoscopic ventral correction are performed using specialized instruments.
The operation is performed under endobronchial intubation anesthesia, in a position on the side opposite the curvature, with access through 3-4 thoracoports along the middle and posterior axillary lines at the apex of the deformity after marking the skin under image intensifier control. Under direct thoracoscopic assessment with the help of instruments, discectomy is performed at the apex of the deformity (2-4 intervertebral discs). In order to achieve anterior fusion, the interdisk space is filled with a synthetic granular graft using a funnel and an impactor, the specific and constant size of the cells ensures quick and reliable achievement of anterior fusion, and the plasticity of the material prevents it from entering the pleural cavity during dorsal correction.
At the second stage of the operation, with the patient in the prone position, skeletonization of the spine, segmental installation of system elements, deratation maneuver and correction with fixation of the spine using specialized instruments are performed. The installation of systems is complemented by posterolateral spinal fusion, which uses grafts.
Bed rest after surgery is 3-5 days, which is significantly less than when using thoracotomy. Verticalization of patients is carried out on days 4-5. External fixation is not used in the corset. Discharge home - 14 days after surgery.
Examples:
1)
Patient V., born in 1998. She was treated in the children's department of the Federal State Budgetary Institution "FTSTOE" of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia (Cheboksary) with a diagnosis of: Idiopathic right-sided thoracic lordoscoliosis of severe (IV) degree with a lumbar anti-arch. 3c type Lenke.
Treatment was performed: Operation 10/12/2011: Thoracoscopic mobilizing discectomy at the apex of the deformity, anterior spinal fusion. Correction of scoliotic deformity using a two-rod dorsal multi-support CD system. Posterior spinal fusion.
Verticalized on the 4th day. After surgical treatment, a normal sagittal profile was formed, satisfactory correction was achieved (radiologically - correction of the thoracic curve from 68° to 10°, correction of the lumbar curve from 62° to 0°), body balance was normalized, there were no sensory or motor disorders.
BEFORE:
AFTER:
2)
Patient L., born in 1993. She was treated in the children's department of the Federal State Budgetary Institution "FTSTOE" of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia (Cheboksary) with a diagnosis of: Idiopathic right-sided thoracic lordoscoliosis, stage 3. 1a-type Lenke.
Treatment performed: Operation 09.27.2011: Correction of scoliotic deformity with a two-rod dorsal multi-support CD system using the true derotation technique. Posterior spinal fusion.
Verticalized on the 4th day. After surgical treatment, a normal sagittal profile was formed, satisfactory correction was achieved (radiologically - correction of the thoracic arch from 55° to 10° with complete elimination of rotation), body balance was normalized, there were no sensory or motor disorders.
BEFORE:
AFTER:
3)
Patient M. born in 1993. He was treated in the children's department of the Federal State Budgetary Institution "FTSTOE" of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia (Cheboksary) with a diagnosis of Pathological thoracic kyphosis due to Scheuermann-Mau disease.
Treatment was performed: Operation October 17, 2011: Thoracoscopic mobilizing discectomy at the apex of the anterior spinal fusion deformity. Smith-Petersen osteotomy, correction of kyphotic deformity with a two-rod dorsal multi-support CD system. Posterior spinal fusion.
Verticalized for 4 days. After surgical treatment, radiologically, the magnitude of thoracic kyphosis decreased from 85° to 38°, which is the physiological norm; clinically, the correction was satisfactory, sagittal balance was achieved, there were no sensory or motor disorders.
BEFORE:
AFTER:
4)
Patient O., born in 1998. She was treated in the children's department of the Federal State Budgetary Institution "FTSTOE" of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia (Cheboksary) with a diagnosis of Idiopathic juvenile right-sided thoracic lordoscoliosis, stage 4. 1c-type Lenke.
Treatment performed: Operation 05/11/2011. Thoracotomy. Mobilizing discectomy at the apex of the deformity, anterior spinal fusion. Correction of scoliotic deformity using a two-rod dorsal multi-support CD system. Posterior spinal fusion.
Verticalized on the 4th day. After surgical treatment, a normal sagittal profile was formed, satisfactory correction was achieved (radiologically - correction of the thoracic arch from 75° to 15°), body balance was normalized, there were no sensory or motor disorders.
BEFORE:
AFTER:
Symptoms
Severe deformation, characteristic of the last advanced stage of scoliosis, leads to a change in position and compression of internal organs. Such a patient is prone to frequent colds. Due to impaired lung excursion, constant shortness of breath occurs.
Compression of nerve endings leads to sensory disturbances and discomfort in the arms and legs. Prolonged stay in an upright position causes severe back pain.
Impaired blood flow in internal organs with a disease such as scoliosis can cause the development of various pathologies. These include chronic inflammation of the organs located in the pelvis, ulcerative changes in the intestines and stomach, and heart diseases. The complaints that the patient makes in such cases fully correspond to the clinical picture of these diseases.
Treatment of scoliosis without surgery
Treatment
includes: therapeutic exercises and massage for scoliosis, physiotherapy, corsetry and other treatment methods. A diet rich in vitamins and a healthy daily routine are of great importance. Unfortunately, these methods, including therapeutic massage, for scoliosis. They are only of a supportive general therapeutic nature, helping those patients who have not yet completed skeletal growth, and whose spinal curvature is not higher than the 3rd degree. In other cases, general physical exercises and other procedures for scoliosis will be ineffective. Massage for scoliosis is more effective.
In our clinic, at all stages of the disease, we use: autogravity therapy, therapeutic differentiated massage for scoliosis, electrophoresis and electromyostimulation with high-frequency currents of the abdominal and back muscles, paraffin, ozokerite applications, three-dimensional correction of spinal scoliosis using the Schroth method, corsetry with Chenault corsets. Much attention is paid to the development of individual nutrition programs and a healthy daily routine. manual therapy, which has many contraindications, in the treatment of scoliosis , because it is not only ineffective, but can also cause irreparable harm.
For surgical treatment of scoliosis
there should be indications, namely:
- Rapidly increasing curvature of the spine (40 degrees or more) in childhood, when skeletal growth is not yet complete;
- curvature angle of 60 degrees or more;
- deformations that put pressure on internal organs, primarily the heart and lungs, thereby disrupting their function;
- severe pain that cannot be eliminated with conservative methods;
- defect in appearance caused by curvature of the spine.
Of course, operations for scoliosis belong to the category of complex high-tech manipulations and are performed only in specialized clinics.
The choice of one method or another is the exclusive right of the attending physician, and it depends not only on the stage of the disease, but also on the medical history and individual physiological characteristics of the patient.
Treatment and prevention
Conservative treatment is possible in children under 11 years of age.
When prescribing a set of therapeutic exercises, one should take into account the fact that they should begin with a minimal gentle load and then increase it. In this case, monitoring the patient’s well-being is necessary. Hanging on the bar and rotational movements are completely excluded - only passive stretching is shown.
Curing a disease such as grade 4 scoliosis is only possible with complex surgery.
How to treat scoliosis
If you don’t know whether scoliosis in adults can be completely cured, then everything will depend on the degree of manifestation of the disease, as well as on the causes that led to it. As a rule, this is impossible in adulthood, and all that needs to be achieved is to eliminate the unpleasant manifestations associated with scoliosis, eliminate pain, etc. In some difficult cases, surgery is indicated.
Massage
If you ask your doctor how to treat scoliosis, you may be prescribed a course of massages. Massage effects on the back and other areas can reduce the manifestations of scoliosis, improve blood flow in the muscles and the general well-being of the patient.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is not the main method and will not get rid of the disease, but it has a good auxiliary effect. If you are asking the question “How can I get rid of scoliosis?”, you may find the following helpful:
- Magnetotherapy.
- Hydrotherapy.
- Healing mud.
- Exposure to heat.
- Electrical stimulation of tissues.
Also a very effective method is acupuncture, which involves stimulating biologically active points on the human body with needles.
Exercise therapy and exercises
If you recognize your symptoms and need treatment for scoliosis, a neurologist
After confirming the diagnosis, he will prescribe exercises for you. They are all aimed at stretching the muscles, helping to straighten the back and increase muscle tone. Exercises should take into account what type of pathology you have, what causes it, and how serious the disease is.
Pool
If you are interested in the symptoms and treatment of scoliosis in adults, then you or your loved ones are faced with this disease. In such a situation, visiting the pool will be useful. The fact is that swimming allows you to reduce the load on the spine, it strengthens the muscles, while eliminating fatigue and tension.
Surgical intervention
Professionals know how to treat scoliosis in adults. Sometimes the situation is so serious that it is necessary to resort to surgical interventions. As a rule, this is necessary when the condition is accompanied by very severe pain, the person rapidly develops cardiopulmonary failure, and neurological manifestations and other symptoms occur.
Wearing a corset
Specialists can determine the need to wear a corset. Corseting allows the back to take a more natural position, and wearing a corset for a long time will help correct the situation, relieving pain and eliminating the manifestations of scoliosis.
Diagnosis of grade 4 idiopathic scoliosis in children: signs and symptoms of the disease
It is simply impossible not to notice the signs of fourth degree scoliotic spinal deformity in a child or teenager - they are visible at first glance, even without a preliminary thorough examination of the patient. What symptoms indicate that scoliosis has progressed to the fourth degree?
1. The deformation of the spine at this stage of the disease is significant - the angle of scoliotic curvature is more than 60 degrees, according to V.D. Chaklin’s classification.
2. In the vast majority of cases, the fourth degree of scoliosis is characterized by a C-shaped or S-shaped curvature of the spine, when the spinal column has two pathological arches that are directed in different directions.
3. Significantly less frequently, with grade 4 spinal curvature, three pathological curves of the spinal column are observed.
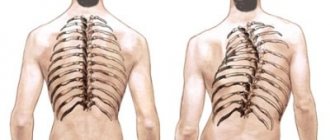
4. Pronounced and very noticeable upon visual examination torsion of the vertebrae, especially at the apex of the curvature arc. Due to the fact that the vertebrae have a pathological rotation around their axis, the child’s ribs are directed incorrectly, and on the one hand they form a rib hump, on the other hand they can be recessed into the chest.
5. The child has very severe back pain that appears after minor exertion, walking, sitting in one position for a short time, and respiratory failure. The pain does not go away even after therapeutic treatments.
6. Pronounced asymmetry of the child’s back, entire torso and chest.
7. In the vast majority of cases of grade 4 scoliosis, the upper pathological arch of the spine is in the thoracic region - the upper part, the lower arch - in the lower part of the thoracic spine or in the lumbar region.
8. A very pronounced rib hump, which is very noticeable even under clothing - it cannot be disguised externally.
To identify all the features of grade 4 idiopathic scoliosis in a particular patient, an X-ray examination of the spine is prescribed. Based on the results of radiography, it is possible to make an accurate diagnosis and assess all the prospects and risks of surgical treatment. To assess the condition of the child’s internal organs, a complete examination and additional consultations with specialists - a pediatrician, cardiologist, nephrologist, surgeon, etc. - are necessary.
When there is a curvature of the spine of the fourth degree, the important and primary task of doctors is to identify all those disorders in the internal organs that were caused by such a serious deformation of the child’s skeleton.
Symptoms of the disease
At the initial stage, scoliosis is noticeable only to a specialist. An experienced orthopedic surgeon can make a diagnosis based on the patient's story and special examination methods.
External signs that suggest the presence of scoliosis in a patient:
- distance between waist and arm;
- asymmetrical arrangement of the blades;
- When bending forward, there is a noticeable curvature of the spine.
Timely contact with an experienced orthopedist and early detection of scoliosis is extremely important and
necessary for the effective treatment of this disease and the prevention of its complications.
Causes of scoliosis
The main cause of scoliosis is congenital deformity of the spine (20%). Other common causes include severe trauma and connective tissue diseases.
The disease can develop as a result of metabolic disorders and against the background of diseases of the muscular system. Scoliosis can be reflexive, when when pain occurs the patient is forced to take a comfortable position, postural, when posture is disturbed, and compensatory due to different lengths of the limbs.
In most cases, the cause of scoliosis cannot be determined.
Scoliosis should not be confused with poor posture, which can be treated with physical therapy, special physical exercises and self-control methods.
Scoliosis requires systematic and complex treatment over many years.
Prevention
Swimming is one of the best means of preventing spinal curvature. Prevention of scoliosis begins with maintaining correct posture. If your job requires you to sit at your desk for long periods of time, try not to hunch over, change your position regularly, and take breaks as often as possible.
During rest, you can walk or do simple physical exercises. It is also important to adjust the chair: it should support your back in the lumbar region and shoulder blades, removing excessive stress from the muscles located in these areas of the body.
To strengthen your spine and back, you should lead an active lifestyle : visit the pool, train on the horizontal bar. Proper organization of night sleep should also be part of the prevention of scoliosis. Avoid too soft mattresses and large pillows.
Place a bolster pillow under your head, supporting the cervical vertebrae, filling the cavity between the shoulder blades and the back of the head and preventing the spine from bending. The optimal position for sleeping is considered to be the fetal position (lying on your right side with your knees slightly bent). Sleeping on your stomach or back is not recommended.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of the disease takes place in several stages.
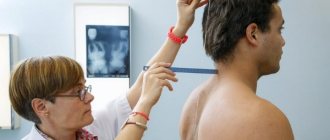
The first stage is a physical examination. During the examination, the orthopedic doctor examines the mobility of the spine, the symmetry of the shoulders, shoulder blades, and examines the chest, abdomen, lower back, and pelvis. The doctor measures the length of the spine, assesses the curvature of the spine, the location of the pelvis in different poses of the limbs, and measures the length of the legs. While lying down, the doctor will determine the level of curvature of the spinal arch and muscle tone.
The second stage of diagnosis is x-ray examination. The images allow you to determine the angle of curvature of the spine. The first x-ray is taken in a standing position, then in different positions, which allows you to determine the level of deformation.
The third stage is instrumental. Ultrasound is used to obtain new data about the patient's condition. In some cases, the patient is prescribed an MRI.