Osteochondrosis in children today is much more common than you think. It is generally accepted that osteochondrosis is a degenerative disease characteristic of people in the older age category. More recently, it was diagnosed in people aged 40–45 years.
At the beginning of this century, osteochondrosis began to be diagnosed in younger people - at the age of 25 - 30 years. And now the trend of “rejuvenation” of degenerative diseases has reached its maximum. Nowadays, juvenile osteochondrosis, which can develop in a child at 5-6 years old, is flourishing quite often. But more often, juvenile osteochondrosis of the spine begins to form at the age of 10–12 years against the background of hormonal changes in the body.
It is quite difficult to recognize spinal osteochondrosis in a child, since the classic symptoms of the disease may be erased or not fully manifest. But clinical manifestations of impaired autonomic nervous function often come to the fore. These are symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia that prevent a teenager from living a full life and studying successfully. And the reason may be hidden in cervical osteochondrosis in children who have not been thoroughly diagnosed.
Meanwhile, parents may suspect osteochondrosis in children and adolescents if they have the necessary information about the clinical manifestations of this disease. You can find them out from this article.
If you are located in Moscow and your child has typical signs, then you can show him to our neurologist. The initial appointment is absolutely free. During the consultation, the doctor will conduct an examination and a series of diagnostic functional tests. Then he will make an accurate diagnosis and tell you what needs to be done to restore the health of the child’s spinal column.
general information
Youthful osteochondrosis of the spine is a dangerous pathological process that dissipates against the background of active growth of the musculoskeletal system. The disease manifests itself as degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs, joints, ligaments, and bones. The lack of comprehensive timely treatment often leads to patient disability.
Osteochondrosis in adolescents is diagnosed in the early stages by chance, since at the first stage the disease practically does not manifest itself at all. Both boys and girls are at risk. The main symptom by which characteristic changes can be suspected is back discomfort and muscle stiffness in the morning. In most patients, the pathological process proceeds safely, causing only minor inconvenience.
Treatment options
Despite the fact that a child’s spine is a fragile structure that can undergo severe deformations under the influence of various factors, treatment in childhood and adolescence is easier with a competent and correct approach. If a child’s cervical osteochondrosis is detected at an early stage, it can be completely cured. If the stage is already running, then the process can be suspended and kept under control in the future.
Therapeutic gymnastics, swimming
In the treatment of childhood cervical osteochondrosis, preference is still given to conservative and non-drug methods. Doctors recommend strengthening the back muscles and spine, and the best way to cope with this is swimming and therapeutic exercises, when a convenient and necessary set of exercises is selected for the child. It is advisable to do therapeutic exercises under the supervision of a specialist.
Massage, acupuncture
Massage, acupuncture and other physiotherapeutic procedures can relieve muscle tension and spasms in the neck, remove or reduce pain, as well as strengthen the immune system and increase the stamina and resistance of the child’s body to external factors. Massage is prescribed only in cases where x-rays have been taken and displacement and instability of the vertebrae have been excluded.
Medications
If taking medications is unavoidable, the child may be prescribed tablets that relieve pain and inflammation, as well as subcutaneous, intravenous or intramuscular injections, gels and ointments.
Causes
Osteochondrosis in a teenager appears during the period of active skeletal growth. But this is far from the only reason for the development of this disease. The following factors can provoke degenerative changes:
- History of injuries.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Metabolic disease.
- Poor nutrition, lack of intake of beneficial vitamins and minerals into the body.
- Infectious, endocrine and autoimmune diseases.
- Lack of physical activity.
- Incorrect physical activity during intense sports activities.
Provoking factors for the development of this disease in a child are carrying a bag on one shoulder, sleeping on a surface that is too soft or uneven, and the habit of sitting in the wrong position at the computer. But the main impetus for the onset of degenerative changes is always internal processes.
The classic form leads to irreversible changes in the spine, and in the absence of comprehensive treatment, the patient can expect a serious decrease in quality of life and limited mobility even at a young age. The pathology affects any part of the ridge (cervical, thoracic, lower back), and although it develops slowly, you should consult a doctor as early as possible, when the first symptoms appear.
Causes of development of juvenile osteochondrosis
There are various reasons for the development of juvenile osteochondrosis of the spine in children and adolescents, but the leading negative factor is considered to be widespread computerization, which leads to a lack of sufficient physical activity on the muscular frame of the back. The problem of a sedentary lifestyle becomes especially relevant during puberty and hormonal changes in the body. The fact is that at this time a real hormonal storm is raging in the child’s body. And only physical activity can remove excess hormones, since with the active work of muscle tissue, most sex hormones disintegrate and are utilized.
If this does not happen, these substances begin to attack the cartilage tissue in the teenager’s body. Rapid degeneration of intervertebral discs begins in all parts of the spinal column without exception. This reaction can only be stopped with the help of a specialist.
Other potential causes include the following aspects of negative influence:
- pronounced negative heredity (if at least one of the parents has problems with the spine, there is a high probability that the children will also suffer from this disease);
- weakness of the muscular frame of the back;
- stooping and other postural disorders associated with a certain lifestyle;
- incorrect foot placement (flat feet or club feet);
- incorrectly selected shoes and clothes (not appropriate for age or size);
- carrying a bag with school supplies and textbooks on one shoulder;
- improperly organized sleeping and working space (it is worth paying attention to the desk at which the teenager learns homework and the appropriate chair height);
- violation of diet and diet;
- deficiency of vitamins and minerals, amino acids and protein;
- lack of habit of drinking clean drinking water;
- increased stress load in an educational institution;
- injuries in the form of blows, bruises, compression fractures of the spinous processes of the vertebral bodies;
- lifting weights, including starting weightlifting before the age of 16.
These are not all the factors that can provoke the development of childhood or juvenile spinal osteochondrosis. Only a consultation with an experienced neurologist will help identify the potential cause in each specific case. Without eliminating the cause, it is impossible to cure juvenile osteochondrosis of the spine. Relapses of the disease will constantly occur.
Characteristic differences
Osteochondrosis in children does not occur in the same way as in adult patients. Pathology has its own characteristic differences, allowing doctors to determine tactics of control and plan treatment. What are the features?
Neck pain in a child
- Changes in the younger generation are most often diagnosed in the cervical and lumbar spine. In the thoracic part it occurs in patients suffering from kyphosis or scoliosis.
- The symptoms are more pronounced, which makes it possible to identify the disease earlier than in an adult patient.
- Neurological disorders are mild and rarely coincide with standard innervation zones.
- In children, the disease almost never leads to loss of sensation or motor impairment.
- No changes in the functioning of the excretory system when diagnosing disorders in the lumbar region.
Diagnosing childhood osteochondrosis is much more difficult, although adolescents more often undergo preventive examinations at school and upon admission. In most cases, characteristic changes in cartilage tissue are discovered by chance.
No ads 1
How does the disease manifest?
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine in children and adolescents develops differently and largely depends on the general state of health, development and growth conditions. Damage to the cervical spine is the most common form of the disease. Symptomatically, osteochondrosis in children in the neck is manifested by the following signs:
- headache;
- fatigue and weakness;
- decreased activity and mobility;
- change in posture;
- etc.
The child may often lose consciousness or appear to be in a state of near fainting, and there may also be loss of coordination. At the initial stage, the disease develops almost asymptomatically. Sometimes a child can become so accustomed to the changes that have appeared that they will consider them the norm. In later stages, he may complain of frequent and intense headaches. If you do not pay attention or do not attach importance to the signs of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine in children and adolescents, this can lead to displacement of the vertebral discs, the formation of intervertebral hernias, growth retardation, disruption of the functioning of internal organs, etc.
Symptoms
Juvenile osteochondrosis of the spine manifests itself in different ways, it all depends on the location of the pathological process. Degenerative changes can provoke headaches, general fatigue, create a constant feeling of tiredness, and back discomfort. These are common signs that parents need to pay attention to. At the initial stage, the disease shows almost nothing about itself. As destructive changes develop, patients experience the following symptoms:
- Cervical region: headache of varying intensity, frequent dizziness, decreased concentration, insomnia, increased fatigue, loss of consciousness, ear pain, ringing or extraneous noise. The patient complains of discomfort in the shoulders, spasms, muscle stiffness, and the inability to rotate the neck freely.
- Thoracic: lump in the throat, pain in the shoulder blades or heart, discomfort in the stomach, difficulty breathing. Symptoms are often mistaken for scoliosis, so it is important to carry out a differential diagnosis.
- Lumbar: sharp pain in the lower abdomen, discomfort when turning, aggravated by moving the limbs or trying to raise the arms and legs up.
The parent should pay attention to the appearance of stooping as the child grows sharply. Poor posture is also a symptom of degenerative changes in the spine. Also, do not ignore a teenager’s complaints of headaches, blurred vision or hearing, or discomfort anywhere in the back.
[node:field_similarlink]
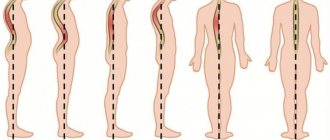
Stages of kyphosis
Advanced thoracic kyphosis can be complicated by osteochondrosis, disc protrusion, and intervertebral hernias.
The occurrence of this type of disease significantly affects the spinal column. The shape changes, muscle tone decreases, and actions can lead to pain.
Blood pressure in the cervical vessels can be hampered by a greatly increased curvature of the spine, which also affects the hemodynamics of the brain organ. As a result, the person begins to experience headaches and tinnitus.
Information from the medical history, tests, laboratory and instrumental methods, complaints of poor health constitute the diagnosis of kyphosis.
Kyphosis is divided into several main stages:
- The first (30-40 degrees) – a person does not feel pain symptoms. The first stage is usually preceded by scoliosis.
- The second (40-50 degrees) - a person feels numbness in the hands, severe fatigue in the forearms and chest pain.
- Late (50-70 degrees) – a person with a late stage of development of scoliosis looks stooped, the shoulders are strongly leaned forward. From the spine, pain spreads to the entire body. The presence of cardiac dysfunction, respiratory failure, and neurological complications. In special advanced cases, the disease leads to forced surgery, where the vertebrae are fixed using high-strength alloys.
Prevention
- Medical massage necessary to relax the muscles of the shoulders and forearms. Treatment with a method called osteopathy involves influencing the body with hand movements to correct defects in the anatomical structure of the body;
- Gymnastics. The first thing you need to do against the disease is to exercise. According to doctors, this is the very first and necessary way to avoid spinal diseases at home;
- Therapeutic physical classes;
Thanks to exercise therapy, you can cope with some difficulties:
- Reduce pain and intervertebral disc tension.
- Increase the tone of the spinal muscles.
- Accelerate the growth of healthy tissue - bone and cartilage - of the spine.
- Practical exercises that increase the speed of blood flow help cleanse the body of toxins and unnecessary waste products during exercise.
Swimming helps improve the condition of your back muscles. It is very important during the course of treatment for kyphosis to be under the supervision of a specialist and do everything in accordance with his advice. It is not recommended to engage in therapeutic swimming on your own. Aquatic physical therapy against kyphosis does not include exercises directly related to swimming. It is necessary to carry out exercises with proper breathing, exercises to relax muscles, exercises with equipment, classes with elements of water polo and more;
Physiotherapy is an integral part of the treatment of kyphosis. The procedures will strengthen muscle tone, relieve muscle dystrophy, remove blocks in the spinal segments, relieve pain, improve blood circulation and lymphatic drainage. During the procedures, the patient is exposed to heat, cold, ultrasound, magnetic field, laser and others;
Stages
Osteochondrosis in adolescents goes unnoticed in the early stages, but it is at this moment that treatment has the best effect. The pathological process develops in several stages. It is determined at the time of diagnosis in order to formulate the most effective treatment tactics. There are three of them in total:
- Latent. The patient does not notice changes in the body, since there are no characteristic signs of the disease. Rare unpleasant sensations in the back after exercise are practically not alarming, as they are attributed to overwork. But pathology can be noticed with a careful examination. The patient is diagnosed with kyphosis, which, although mildly expressed, does not allow him to reach the floor when bending over. This stage is most often observed in children aged 11 to 15 years.
- Early. The patient has neurological abnormalities and characteristic symptoms of the disorder. Pathologists can provoke pain at the localization site due to pinched nerve endings. Curvature of the ridge, displacement of the vertebrae and other destructive changes are observed. Pathology can be diagnosed by a medical examination, during which the doctor determines impaired mobility of the spine and the presence of kyphosis.
- Late. The signs of the disease in patients are already clearly expressed; the problem cannot be ignored. Against the background of severe pain, dysfunction, and limitation of motor activity, patients develop intervertebral hernias in the spine and spondylosis. Most patients develop kyphosis in the form of a hump, while some develop only scoliosis.
Stages of development of the pathological process clearly
The earlier the disease is diagnosed, the more effective the prescribed complex therapy will be. Therefore, it is important for parents not to ignore the first characteristic changes in the child’s health and to consult a doctor in a timely manner.
No ads 2
Treatment
Why should you consult an osteopath with signs of cervical osteochondrosis?
- Firstly, osteopathic therapy is carried out very carefully and carefully, without causing additional discomfort.
- Secondly, osteopaths are people with medical or physiotherapeutic education, they are professionals and are responsible for the safety of the procedures performed, including when it comes to treating children.
- Thirdly, and most importantly, osteopathy focuses not only on unpleasant symptoms, but on the body as a whole.
An osteopath without strong intervention in the body and medications, but with the help of palpation diagnostic and therapeutic techniques, stimulates the body to launch internal processes of self-healing and self-healing. During the session, an experienced osteopath influences the patient’s body through pressure, friction, and vibration. This allows you to tone and strengthen your back muscles, improve blood circulation, relieve stress and reduce muscle tension. Visceral manipulations provide a regenerative effect on the immune system, help normalize metabolism, and improve joint mobility.
It should be emphasized that different osteopathic therapy is prescribed for each patient. The procedure, duration of therapy and range of methods used by the osteopath are selected individually for a particular person.
Diagnostics
Only an experienced specialist can visually detect dystrophic changes in the spine. To make a diagnosis, the patient’s complaints, anamnesis, medical history, and hereditary predisposition are taken into account. The doctor conducts an external examination, assesses the condition of posture and the spine as a whole, determines muscle tone and the presence of unnatural tension. For the purpose of clarification, the following types of examination are prescribed:
- X-ray. The resulting image allows you to assess the general condition of the bone tissue and identify even minor changes in the vertebrae.
- CT scan. Allows you to see the general condition of bones, intervertebral discs, the location of blood vessels and surrounding tissues. Appointed to clarify information obtained using x-rays.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. In particularly difficult cases, an MRI is prescribed to identify neurological disorders.
- Electromyography. This test determines the strength of the back muscles. It is not prescribed to all patients, but only if indicated.
- Ultrasound. It is used when there is suspected damage to blood vessels in the cervical spine or dysfunction of internal organs, to determine their general condition.
- Cardiogram. Allows you to eliminate disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system due to pain in the chest area.
- General analysis of urine and blood. The results obtained determine the presence of an inflammatory process.
After diagnosis, the degree of development of the pathological process is assessed. This allows you to correctly determine the necessary set of measures to restore the patient’s quality of life.
The course of therapy is prescribed after determining the stage of progression and characteristic changes in the body
M42.9 - Osteochondrosis of the spine, unspecified
When a patient comes for an initial consultation, he is given a preliminary diagnosis - spinal osteochondrosis M42; further code is entered only after the examination. Sometimes the medical history contains code M 42.9, which indicates that the localization of the pathology is unspecified.
The code is set when a disease is accidentally detected, when the client is being examined for a different profile. Usually he is additionally prescribed a CT or MRI, after which the type of disease and the localization of degenerative-dystrophic changes are determined.
Treatment of osteochondrosis in children
Treatment of osteochondrosis in children and adolescents is a long process. The main task of the specialist is to relieve acute pain, slow down degeneration, eliminate other signs, and prevent complications or irreversible changes. For this purpose, various methods of therapy are prescribed.
An integrated approach, including medication, therapeutic exercises, physiotherapy and massage, allows you to achieve good results. Self-medication is excluded, since only an experienced specialist can assess the general condition and select an individual treatment regimen. It takes into account age, the presence of contraindications and chronic concomitant diseases.
Drug treatment
Elimination of symptoms is impossible without the use of pharmacological products. The drug group, dosage, and duration of use are always selected by the doctor. The complex includes the following medications:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Ibuprofen). They are aimed at reducing the inflammatory process and eliminating pain.
- Muscle relaxants (Sirdalud, Baclofen). They are prescribed to eliminate muscle spasms. They are used with caution, taking into account the age of the child, as there are a number of serious contraindications.
- Chondroprotectors (“Dona”, “Teraflex”, “Arthra”). The drugs are aimed at starting the process of tissue regeneration, restoring damaged cells of the intervertebral discs. They are always used in courses of several months, as they have a cumulative effect.
- B vitamins (“Milgamma”). They promote the restoration of nerve fibers and damaged tissues, including bones.
Vitamin complexes are also useful for teenagers, promoting general stimulation of the immune system, normalizing blood flow and saturating tissues with useful substances. They are selected individually, taking into account the identified deficiency in the body.
No ads 3
Non-drug treatment
The use of pharmaceutical drugs is not enough to cure juvenile osteochondrosis. The complex effect on the pathological process also includes alternative methods. They are aimed at strengthening muscle tissue, improving their nutrition, and restoring the flexibility of the damaged area. The patient is recommended:
- Swimming lessons. They allow you to eliminate excess tension in muscle tissue, get rid of spasms, blockages in the back, and improve the nutrition of damaged tissues by normalizing the movement of all biological fluids in the body.
- Massage. A visit to a highly qualified specialist allows the patient to get rid of back pain, normalize the mental and physiological state, activate the body’s defenses, and relax stiff muscles. To obtain a lasting result, you will need to complete a course of 10 sessions.
- Acupuncture. Impact on certain biologically active points in the body allows you to start the process of regeneration in tissues, improve their condition, and even relieve attacks of acute pain. All manipulations should be carried out by an experienced specialist, otherwise the patient’s condition may worsen.
- Physiotherapy. Regular exercise and morning exercises, which include techniques developed by doctors, allows you to achieve stable remission of the pathology. Physical education restores spine mobility and functionality.
- Mud therapy. The use of healing mud helps to enhance the effectiveness of drug treatment.
If conservative treatment methods do not give the expected result, the patient is prescribed surgery. Timely intervention eliminates the possibility of disability or irreversible processes in the body that significantly reduce the quality of life. A radical method is prescribed in advanced stages, for herniation or protrusion of the intervertebral disc, or radicular syndrome.
Treatment of osteochondrosis in adolescents is carried out by a doctor after a visual examination and assessment of the patient’s condition
UZ "Bobruisk City Children's Hospital"
Osteochondrosis in children is a lesion of the osteoarticular area due to trauma, metabolic disorders, poor nutrition, and excessive stress. Osteochondrosis of the spine is dystrophy, or in other words, a violation of the nutrition of the tissues of the intervertebral disc with a weakening of its shock-absorbing properties. With osteochondrosis, the fixing ability of the spine, the condition of the paravertebral muscles and ligaments, especially under load, deteriorate, making them inelastic and weak.
First, dehydration of the nucleus pulposus and metabolic disorders in the cartilage occur. As a result, the disc loses its elasticity, dries out, decreases in size and cannot withstand physical activity. The annulus fibrosus of the disc also loses its elasticity, causing it to crack and rupture. The central part, the so-called nucleus pulposus, protrudes into the resulting defects and then falls out (partially or completely). This is a herniated intervertebral disc.
It is now known that the main cause of osteochondrosis is associated with our lifestyle, which leads to changes in the spine. These include sedentary work, emotional and physical overload, poor posture and poor nutrition. In order for the spine to remain healthy, it must be taken care of from a young age. Ancient doctors believed that human health was determined by the health of the spine. Modern medicine confirms the role of the spine in maintaining good health.
Causes
Osteochondrosis in children of congenital form is associated with:
- hereditary predisposition and autoimmune pathologies that lead to disruption of the development of bone and cartilage tissue and metabolic processes;
- congenital malformations of the musculoskeletal system (absence of a vertebra, deformation, weakness of the muscular system) and circulatory system, which leads to insufficient supply of oxygen and nutritional components to the spinal column.
Acquired osteochondrosis in children is associated with the following factors:
- hormonal imbalance and other endocrine pathologies;
- overweight in children and adolescents;
- excessive or insufficient physical activity;
- injuries of various natures, for example, the cervical spine can be damaged during passage through the birth canal;
- poor posture;
- poor diet with insufficient intake of vitamins and minerals.
For diagnosis, you need to consult an orthopedist and neurologist. The appointment begins with an examination and medical history. The basis for diagnosis is poor posture, pain and discomfort when palpating certain areas of the back, and the results of motor tests. To confirm the diagnosis, radiography, magnetic resonance and computed tomography of the back are prescribed. If hormonal imbalances are suspected, a general blood test and hormone testing are required. A detailed blood test allows you to identify infectious processes in the body
4 stages of development of osteochondrosis:
- First: the main symptom of osteochondrosis at this stage is instability, manifested in initial disorders of the vertebral discs. Feeling of malaise and discomfort.
- Second: the main symptom of the second stage of osteochondrosis is disc protrusion. The destruction of the fibrous ring begins, the gaps between the vertebrae decrease, and pinching of nerve endings with pain syndromes is possible.
- Third: at this stage of osteochondrosis, the destruction of the ring occurs with the appearance of intervertebral hernias. The third stage is characterized by significant deformation of the spine.
- Fourth: the last and most severe stage of osteochondrosis. It becomes difficult to move. Any movement leads to acute pain. Periodically, the condition improves and the pain subsides, but this clearly indicates the formation of bone growths. They connect the vertebrae, limiting the ability to move and leading to disability.
Clinical manifestations
In children, osteochondrosis occurs in an asymptomatic form. The first signs of the disease begin to bother you at puberty.
Symptoms of neck osteochondrosis:
- frequent headaches;
- dizziness;
- increased fatigue;
- feeling of discomfort and pain in the neck.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region:
- pain in the area between the shoulder blades and behind the sternum;
- shortness of breath, difficulty breathing;
- numbness in the arms or thoracic back.
Symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis:
- pain in the lower back, radiating to the lower extremities, which intensifies after prolonged standing in an upright position or lifting heavy objects;
- mobility impairment.
The difficulty of diagnosis in childhood lies in the absence of a clear clinical picture. When the first complaints appear in adolescents, there is a high probability of an incorrect diagnosis, since the symptoms are similar to other diseases. Cervical osteochondrosis occurs with similar symptoms characteristic of pathologies of the cardiovascular system. Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis in children are pain, nausea. Pathology of the thoracic region occurs with signs of diseases of the heart muscle or damage to inflammatory nerve fibers.
The diagnosis is made in stages. First, the doctor interviews the child, studying his complaints and feelings. Then he finds out the history of the development of the disease, after which, getting acquainted with the life history, the doctor finds out the factors that provoke osteochondrosis, the presence of heredity and anomalies in the development of the spine.
Examination of the patient is the next step in making a diagnosis. Posture and range of motion in all parts of the spine are assessed, palpation (feeling), percussion (tapping) of the spine is performed, and muscle strength is studied. It is important to diagnose motor stereotype disorders, that is, to identify immobility of some parts of the spine and hypermobility of others. Based on the results of the examination, the doctor may prescribe examination methods.
X-ray examination (spondylography) is an important method for assessing the condition of the spine. Typically, an in-depth diagnosis of osteochondrosis begins with a spondylogram. Radiography allows you to obtain information about the condition of the vertebrae, and indirectly, the intervertebral discs and bone canals.
· Computed tomography (CT) is a hard x-ray that illuminates an object with a narrow beam and is captured by receiving equipment at the output. The received data is processed by a computer, and the image is visible on the display. The patient is placed between the emitter and the receiver, where the entire system rotates around the axis of the patient's body. X-ray absorption is recorded at all stages of rotation. As a result, vertebral bodies, soft tissues, intervertebral discs, ligaments, and blood vessels are visible. CT scans reveal disc contour ruptures, nerve root compression, and dura mater deformations.
Unlike X-rays, where images of entire sections of the spine can be taken, CT scans specifically target one or two segments. A CT scan is usually prescribed after an x-ray if it is necessary to clarify the condition of a specific intervertebral disc. With this type of study, the x-ray dose is significantly higher than with a spondylogram.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is prescribed in diagnostically difficult cases. It is mandatory when consulting a neurosurgeon and is always used during surgery. The method allows you to obtain an image due to the property of tissue hydrogen nuclei (protons) to give the phenomenon of resonance in a strong magnetic field. Constant and alternating magnetic fields are used, which create a signal characteristic of each tissue of the body. These signals are recorded, processed by a computer and produced an image on the screen. An anatomical cross-section of the body is obtained in three projections without the harmful effects of x-ray radiation. Sections are visible in different planes, the image has high contrast. Nerve roots, intervertebral discs and blood vessels are visible. On MRI, the nucleus pulposus, which has less hydrophilicity due to osteochondrosis, does not produce an MRI signal and is clearly visible. · Ultrasound Dopplerography (USDG) is a method for studying the blood supply to the brain, which allows you to study cerebral blood flow in cervical osteochondrosis.
Thus, having correctly diagnosed osteochondrosis using the above methods, treatment should begin. The therapy program is drawn up by the doctor, taking into account all the nuances or features of the manifestation of the disease in a particular person.
Treatment
Based on the data obtained as a result of research, a protocol is drawn up, the observance of which during the development of the musculoskeletal system makes it possible to completely cope with the disease.
Drug therapy
Treatment is comprehensive and includes the use of:
- vitamin and mineral complexes that are rich in B vitamins, vitamin D, calcium, phosphorus and Omega-3 to strengthen the immune system, normalize blood flow, metabolic processes, restore tissue of the spinal column and nerve fibers;
- muscle relaxants to relax muscles and eliminate muscle pain;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to suppress the inflammatory process and relieve pain;
- chondoprotectors with glucosamine and chondroitin, the action of which is aimed at restoring cartilage tissue;
- amino acids for the renewal and restoration of cartilage tissue.
Medicines are prescribed in the form of tablets, intramuscular injections, gels and ointments for external application. The dosage is selected individually, based on the degree of damage.
Non-drug therapy
Treatment of osteochondrosis in the initial stages of development in childhood and adolescence is carried out without the use of drugs and includes:
- Therapeutic exercise. Selection of exercises taking into account the localization of the pathological process. Helps improve general condition, relieve pain and discomfort in the back, restore mobility and performance of the spine, and strengthen the muscular corset of the back.
- Back massage has a general strengthening effect, improves blood flow and lymphatic drainage, tones and relaxes muscles.
- Acupuncture, which involves the use of needles or special rays to activate biologically active points responsible for the restoration of cartilage tissue.
- Swimming, which allows you to cope with muscle tension and spasms, prevents complications: hernias, scoliosis, kyphosis.
- Physiotherapy: electrophoresis, ultrasound, magnetotherapy, vibration and laser treatment, which are aimed at relieving tension, normalizing blood flow and metabolic processes. The use of electrophoresis helps in applying medications topically to the affected area. Detensor therapy is aimed at stretching the spine.
Complications
Cervical and thoracic osteochondrosis in the absence of timely treatment can lead to the following consequences:
- curvature of the spinal column;
- protrusion of intervertebral discs;
- growth slowdown;
- intervertebral hernia;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- risk of stroke.
If complications develop in the form of a hernia or protrusion in complex cases, the child is prescribed surgical treatment.
Prevention
Prevention of osteochondrosis begins in childhood. The most critical period of bone tissue activity is the youthful period of intensive growth, during which calcium consumption in the body increases.
Clinical recommendations from doctors for the prevention of osteochondrosis:
- annual preventive examinations with a neurologist and orthopedist;
- proper nutrition, rich in vitamins and minerals, for normal growth and development of the child;
- posture control and injury prevention;
- regular physical activity (exercise, swimming);
- correct choice of shoes (in size, with orthopedic insoles);
- long walks in the fresh air.
“Peak” bone mass can be increased by eating foods high in calcium and phosphorus. These include dairy products, fish, dried fruits, nuts, seeds, green vegetables and brown bread.
It is believed that physical exercise prevents the development of osteochondrosis. However, excessive physical activity can lead to a decrease in the level of sex hormones estogens, and then to osteoporosis, which is often combined with osteochondrosis.
Such changes in the spine are typical for professional athletes.
Vitamin D levels in the body are closely related to skin exposure to sunlight. Holidays in the south, sunbathing and trips to the sea are a pleasant and necessary measure to prevent osteochondrosis. Eating seafood, mainly red fish, plays an important role in obtaining vitamin D. Maybe someone will remember the “fish oil” that they hated in childhood. It is also an effective measure to prevent bone weakness. Calcium supplements with vitamin D are useful to improve bone health.
Thus, rational nutrition from childhood is an important factor in the prevention of osteochondrosis. Adequate nutrition is especially necessary for a growing body, because in youth a health program is laid for life.
Spinal injury is the second risk factor for osteochondrosis. In recent years, young people with back pain due to the spine have begun to attract the attention of doctors. It was found that the early development of osteochondrosis in them was facilitated by the incorrect position of the cervical vertebrae, which arose in newborn age as a result of birth trauma.
You should pay attention to the fact that during physical activity (physical education class), if you fall sharply on your tailbone after a jump, a cracking sound may appear in the cervical spine. Usually this causes pain that passes quickly, and children do not go to the doctor. However, the resulting traumatic redistribution of axial load on the spine and discs subsequently leads to increased wear and early osteochondrosis.
During an injury, you can stretch your back muscles, ligaments, or dislocate your spinal joints. Such microtraumas instantly aggravate osteochondrosis with sharp back pain.
The early development of osteochondrosis is facilitated by incorrect posture, especially from childhood. Poor posture (static) is a precursor and characteristic symptom of spinal osteochondrosis. The mechanisms of these changes are complex. And we will not delve into professional details, but will focus on the main thing: treatment and prevention of exacerbations of osteochondrosis necessarily includes posture correction to correct the impaired biomechanics of the spine.
Possible consequences
Cervical osteochondrosis is especially dangerous, because any changes in this area disrupt the blood supply to the brain. The patient develops problems with vision, hearing, vestibular apparatus, and blood pressure. In the absence of treatment for osteochondrosis in the thoracic region, problems associated with the intestines, bile, stomach, lungs, and heart gradually develop. Pathology in the lumbar region leads to inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system and the development of paralysis of the lower extremities.
Preventive actions
It is extremely important to prevent the development of osteochondrosis in a child, since treatment does not completely eliminate all changes in the body. To do this, parents are recommended to take the following preventive measures:
- Monitor the child’s posture from early childhood, organize the workplace, and avoid long periods of sitting at the computer in the wrong position.
- Select high-quality orthopedic sleep accessories (mattress and pillow).
- Balance your diet by adding more fresh vegetables, fruits, and dairy products to your menu.
- Control the child’s weight, eliminating the gain of extra pounds.
- Enroll your teenager in a sports section for regular dosed physical activity.
- Organize a regimen of rest, walks and work, encourage the growing body to stay in the fresh air.
- Eliminate the possibility of injury as a result of extreme sports.
Juvenile osteochondrosis is a dangerous pathological process that develops in adolescents during a period of active growth. The main reasons for the appearance of degenerative changes are uneven physical activity, injuries, poor quality nutrition, poor posture and hormonal levels. It is better to identify pathology in the early stages, when it can be successfully treated.
Causes of osteochondrosis
According to experts, the following factors lead to the development of this inflammatory-degenerative disease:
- sitting and standing work;
- regular lifting of weights (during physically demanding work, sports);
- spinal column injuries;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- overweight;
- malnutrition;
- infectious diseases, hypothermia;
- metabolic disorders;
- autoimmune processes;
- hereditary factor;
- stress, bad habits;
- pregnancy;
- natural aging of the body.