What is osteochondrosis and the causes of its occurrence
Osteochondrosis is a disease that is expressed by degenerative changes in the tissues of the spine. In simple words, this is aging, degeneration and destruction of intervertebral discs, and then vertebrae. It is diagnosed in about 60-80% of people. It occurs due to insufficient nutrition of cartilage tissue and vertebrae or due to hormonal imbalances.
The most important cause of osteochondrosis is uneven distribution of the load on the spine. This could be sleeping on a high pillow or on an overly soft mattress, the manner of carrying a bag on one shoulder or a briefcase in one hand. An uncomfortable office workspace can aggravate the problem. An important factor is wearing low-quality shoes. Let's consider a number of factors that increase the risk of osteochondrosis:
- weak muscle corset;
- curvature of the spine, stooped figure;
- circulatory disorders;
- heavy physical work or, conversely, a sedentary lifestyle;
- damage and injury;
- violation of metabolic processes in the body and non-compliance with nutritional rules;
- uncomfortable body position during sleep, its duration is less than 7-8 hours;
- frequent viral/bacterial infections;
- hereditary factors;
- individual structural features of the cervical spine;
- age-related changes.
Self-massage
You can massage the back and sides of the neck yourself only at the stage of remission. The procedure is indicated for aching, intermittent pain that is not accompanied by limited mobility of the cervical vertebrae. It allows you to prevent exacerbation of chondrosis due to hypothermia, relapse of chronic pathology or heavy lifting. Self-massage should be performed with the pads of your fingers, avoiding excessive pressure on the collar area.
Self-massage of the cervical region.
It is necessary to begin the massage by rubbing the mastoid processes (tubercles behind the ears), shoulders, forearms, and arms. Then the neck is gently massaged and then vigorously rubbed. You need to feel a chain of small bulges in the center of the back area and stroke them with gentle circular movements, pressing lightly.
It is enough to massage once a day for 10 minutes to prevent the spread of the disease to neighboring discs and vertebrae.
Why massage and how to diagnose the problem
Therapeutic massage for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is necessary with an integrated approach to the treatment of the disease. Usually, it is carried out together with physical exercises and physiotherapy.
Back massage for osteochondrosis is carried out for:
- relieving muscle spasms;
- restoration of blood circulation;
- elimination of pain in the neck and shoulder girdle, headaches;
- relieving numbness and tingling sensations in the fingers;
- increasing muscle tone;
- strengthening the muscle corset.
Massage for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is carried out after some diagnostic procedures. It could be:
- X-ray examination of the cervical spine.
- Myelography is a study with a contrast agent and an X-ray apparatus of the spinal cord.
- Examination of reflexes and sensitivity by a neurologist.
Additionally, the doctor may prescribe the patient to undergo a CT, MRI or MRI of the cervical spine. This is aimed at clarifying the diagnosis and determining the stage of the disease.
How is massage of the cervical-collar area beneficial?
Neck pain, pinched nerves, and muscle spasms can lead to such unpleasant consequences as migraines and insomnia. To get rid of these problems, a set of measures will be required. But moderate physical exercise aimed at stretching the neck muscles together with professional massage can give good results.
The correct neck massage technique gives the following effects:
- Relaxes muscles, relieves tension and spasms;
- Reduces pain and stiffness in muscles;
- Normalizes blood pressure;
- Reduces manifestations of osteochondrosis;
- Relieves stoop, straightens posture;
- Normalizes the functioning of the respiratory organs;
- Improves oxygen saturation of brain tissue;
- Removes excess fluid, eliminates swelling in the face;
- Increases performance, relieves fatigue, weakness, drowsiness during the day;
- Improves mood.
Massage of the neck, shoulders, and shoulder girdles has a beneficial effect not only on the muscular, but also on the nervous and circulatory system. Your appearance will also improve: your posture will become straighter, your withers (“widow’s hump”) will disappear, and your neck will become more flexible.
You can do massage not only when osteochondrosis has made itself felt. This is an excellent prevention of various pathologies. Preventing a disease can be easier than treating it.
Due to the fact that blood circulation improves, facial skin rejuvenates. Many beauty treatments begin with relaxing and rubbing the neck area. Over time, the skin of the neck becomes very thin and flabby. Plastic surgery does not always help solve this problem. Massage allows you to increase skin turgor, prevent sagging, and eliminate a double chin. Also, with age, a fatty hump appears in the area of the 7th vertebra. With the help of massage and simple exercises you can completely get rid of it.
Features of the treatment procedure
Massage for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine should be performed by a qualified doctor. This should not be a person without a medical education who has completed courses. Preference should be given to a doctor who has a large knowledge base and experience behind him. It also doesn’t hurt to look on the Internet to find out what patients say about the specialist. The doctor must find out from the client the complaints he is addressing and conduct appropriate research in order to make a correct diagnosis. This procedure can lead to complications in the wrong hands.
Before starting a massage session, the doctor must familiarize the patient with contraindications and features of the procedure. Let's consider the main reasons why a doctor may refuse to treat osteochondrosis with massage:
- The presence of cancer (not necessarily in the cervical spine).
- Deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary thromboembolism.
- High body temperature.
- Hemostasis.
- The presence of a chronic infection or inflammatory process (especially the presence of suppuration).
- Hypertonic disease.
- Trauma or wound to the neck.
The doctor may cancel the procedure if the patient experiences discomfort or pain. Then it is advisable to use other methods of treatment and therapeutic effects.
Contraindications
There is a list of universal contraindications for massage, which includes:
- hypertension;
- fever;
- any infectious processes;
- local skin damage;
- functional organ failure;
- neuropsychiatric disorders;
- intervertebral hernia;
- tumors;
- thrombophlebitis.
The list may be extended, so before going for the procedure, it is better to consult with your doctor. If you feel unwell, it is better to postpone the procedure.
The main stages of massage and their features
Cervical massage is done while lying on your stomach on a couch or in a specialized chair. To ensure comfort, the doctor applies massage oil. The process consists of three stages for high-quality muscle development; the spine should not be touched:
- Smooth rubbing. Using circular movements of the palms from top to bottom, the massage therapist kneads the muscle tissue. A mandatory point is to work on the rhomboid muscle at the base of the 7th vertebra. Then repeat the movements in the opposite direction, returning to the back of the head.
- Active development of the collar area. A smooth increase in force on the same muscles. The direction of movement is from top to bottom and back, from bottom to top. The movements are performed with the fingers or the tissue is pinched with the palm. In the area between the shoulder blades it is possible to grab only the skin. To better work the muscles, the massage therapist makes the same movements with his knuckles or thumbs.
- Relaxation. With all the same circular movements and grips, the force of impact decreases and gradually fades away. At the end of the session, rubbing the area with your palms and gentle tapping with your fingertips is performed again.
When the massage is over, the patient remains lying or sitting in a chair. The skin is wiped with a napkin, the neck and shoulders are covered with a warm towel. This is necessary for recovery. The entire session lasts about half an hour. Each zone must be worked several times with different intensities. In order for a massage to have a therapeutic effect, it must cause some discomfort to the patient. If you carry out the procedure effortlessly, you can only achieve a relaxing effect.
Make an appointment for a massage at our clinic soon.
Technique for massage of the cervical-collar area: types of movements
The main task of a massage therapist is to improve blood flow in the neck and relieve muscle spasms. A massage always begins with preparation. The movements will be light, stroking to warm up the skin and muscles, and then gradually intensify. Before the procedure, it is advisable to take a shower and cleanse the skin of sweat and other contaminants. The specialist must use special gels or creams, oils that will allow the hands to glide over the skin. If the client is allergic to herbal or other components, it is worth informing about this in advance.
Massage of the cervical-collar area includes several types of movements:
- Stroking . The massage session begins and ends with these movements. With the help of stroking, the massage therapist relaxes the muscles and warms the skin. At this stage, you can already feel that the pain in the neck area is gradually decreasing. Strokes can be flat, superficial, deep, intermittent, or continuous, rake-like. The specialist selects their type and intensity for each client separately. It is important that the movements are quite intense, warm up well and prepare the skin and muscles for further manipulation, but they should not cause pain.
- Rubbing . The movements are similar to stroking, but they are more intense, warm up the skin and muscles more, and relieve spasm and pain. Rubbing can be straight, spiral or circular. Typically, types of movements are combined to enhance the warming effect.
- Kneading . This is the longest stage of the massage. The specialist begins to influence the muscles and ligaments. It grabs, lifts, and compresses tissue. There are transverse and longitudinal kneading. Such movements should not be too intense; they are performed at a slow pace and always use gel or oil. With each session, the intensity of kneading will increase.
- Effleurage . These are jerky movements that increase blood flow and improve muscle contractility.
During the massage process, the specialist can also use auxiliary movements, for example, rolling or vibration. Intense vibration is especially useful when you need to increase muscle tone. After vibration, percussive techniques, light tapping with fingers or the edge of the palm are used.
The specialist must well control and regulate the pressure on the skin and muscles so that the massage is quite effective, but does not cause severe pain to the client and does not leave bruises on the skin.
Hardware types of massage
This is one of the most modern and gentle methods of influencing the affected areas. It does not require effort on the part of the massage therapist, and therefore is easier to perform. Hardware massage is usually most effective when there is significant pain. The main types of such massage are hydromassage (water jet massage), as well as pneumatic massage and vibration massage.
Using these techniques allows you to achieve the following results in just a few sessions:
- blood and lymph circulation improves;
- degenerative processes in intervertebral discs are slowed down, the sensitivity of nerve endings is restored;
- after the first session there is a noticeable decrease in inflammation.
Unlike manual massage, hardware procedures are usually more pleasant and “softer”, but they cannot always be recommended in complex cases of osteochondrosis, since the devices cannot “work” the desired areas the way an experienced chiropractor can do.
What is therapeutic massage used for?
Since ancient times, the positive effect of massage on the body has not been in doubt. Impact on active points of the body allows you to relieve the patient from pain, slow down degenerative processes in the body (stop their spread), speed up the healing process, and also prevent relapses of the disease. In addition to massage, hardware procedures similar to massage, as well as therapeutic exercises, are often prescribed.
Massage can be prescribed exclusively by a professional neurologist, who will assess the relevance of the method in each case individually. It is worth noting that therapeutic massage cannot replace full-fledged drug therapy. It is used before treatment, before exercise therapy, first of all, to activate the body’s internal resources, direct them to the healing process, but most importantly, to return comfort to the patient’s life!
Depending on the location of osteochondrosis, there are several main methods of influencing the painful area:
- rubbing;
- stroking;
- tapping;
- vibrations, etc.
The massage technique becomes more complicated with each procedure, which allows you to accelerate the onset of the effect of the sessions and ensures rapid recovery of the patient’s body when receiving complex therapy for osteochondrosis.
Massage technique for osteochondrosis
Massage for osteochondrosis in St. Petersburg
As, unfortunately, many people are well aware, spinal osteochondrosis (a degenerative-dystrophic process in the intervertebral discs) can be accompanied by severe pain. Thus, with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, pain often occurs in various parts of the shoulder region, as well as headaches and dizziness. But that's not all. J. Valnet, a famous French neurologist who has been involved in manual therapy for many years, writes: “Dizziness, tinnitus, lightheadedness, pain in the shoulders, in the back of the head or in the shoulder blades, discomfort or sore throat, impaired memory, hearing or vision - These are all likely symptoms of undiagnosed cervical vertebrae disease. In all the mentioned cases, a hard massage of the cervical spine helps successfully.” Indeed, with osteochondrosis, massage helps improve blood and lymph circulation, relieves pain, and most importantly, promotes the speedy restoration of spinal functions.
Muscle disorders of vertebral etiology. Particular attention to these disorders is justified by the central role played by the spine in the support and movement of the entire body, as well as by the high frequency of manifestations of (mostly painful) disorders of its functions. In addition, one should take into account the complex structure of the articular joints of the spine, which is not easy to understand, and the multi-layered nature of the spinal muscles, which serve both to fix the posture and to carry out movements.
The functional motor unit of the spine is the motor segment. It includes the following anatomical structures involved in the movement of the vertebrae relative to each other:
1) intervertebral discs;
2) paired articular processes
3) ligaments connecting the bodies, arches and processes of the vertebrae.
To perform movements, the unity of actions of all these structures is necessary, each of which has its own specific tasks. Intervertebral discs are elastic and can change their shape due to the fact that the nucleus pulposus of the disc moves inside the fibrous ring. Thanks to this, the vertebral bodies change their location relative to each other, without interfering with the discs performing their function as an elastic pad that transfers the body weight from vertebra to vertebra. The movement occurs in the intervertebral joints, which determine the direction of movement through different orientations of the working planes of the vertebrae and limit the range of movement through the inhibitory role of the bursae and ligaments.
The spinous processes of the vertebrae serve as levers and support the muscles. The back muscles, which perform the task of supporting the torso, consist of several muscles united under the general name “erector trunci”. The spine is moved by the contraction of these muscles. However, as soon as the body leaves the state of labile equilibrium (orthostatic state), gravity begins to force it to further movement. And the execution of movements is undertaken by the muscles that move the motor levers: 1) the lateral trunk of the rectifier spinae (m.longissimus et in.ilioco stalls), originating in the sacrum and on the iliac crest and connecting to the transverse processes of the vertebrae and the posterior surface of the ribs ;
2) abdominal muscles, vertically or obliquely connecting the chest and pelvis.
The body's own mobility is necessary only to perform the function of breathing, in which, however, under normal conditions the spine does not participate. Thus, spinal mobility is necessary in the following cases:
1) to orient the head, primarily the sensory organs located in it (for example, the eyes); 2) to expand the range of movements of the limbs (for example, to perform a tilt of the spine, when you need to reach your feet with your hands without bending your knees); 3) to ensure the transition from a sitting to a standing position and back (remember the patients with ankylosing spondylitis!) and smooth movement (synchronous vibrations of the spine and arms when walking); 4) for gesturing (when a person has a “lumbago”, it is difficult for him to shrug his shoulders).
Diseases of this most important load-bearing organ limit or eliminate the performance of these functions. Therefore, the following diseases should be excluded from the list of indications for massage: tuberculous spondylitis and other inflammations, tumors and metastases. On the contrary, for muscle disorders caused by a violation of the statics and/or mechanics of the spinal column or one of its parts, massage is necessary. These violations are listed below, without, however, claiming to be complete.
All changes in the shape of the spinal column, deviations from physiological curves (increased or weakened kyphosis and lordosis), lateral bending (scoliosis) change the statics of the spine. The reasons for such deviations may be different. They can be divided into the following groups: 1) muscular causes: stoop as a result of weakness of the spinal muscles, lordosis of the sacral spine due to weakness of the abdominal muscles, scoliosis with unilateral muscular paralysis; 2) vertebral causes: existing vertebral deformity (congenital or as a result of a disease, for example, rickets, tuberculous spondylitis), trauma (compression fracture); 3) extravertebral causes: scoliosis as a result of an altered position of the pelvis (for example, due to shortening of one leg after a fracture or inflammation of the hip joint), lordosis of the sacral spine as a compensatory phenomenon for bilateral hip joint rigidity.
Massage can relieve the muscular causes of static spinal disorders completely and eliminate painful overstrain of the back muscles in the presence of other static changes (local metabolic effect, normalization of tone). It is clear that abnormal muscle tension caused by spinal-bone factors will again and again lead the muscles to the above-described state, therefore massage courses should be carried out regularly in order to relieve the patient from renewed pain and prevent further development of degeneration of the load-bearing organ.
Among degenerative changes of this kind, static disorders related to changes in the position of individual vertebrae should also be mentioned: stretching of the spinal ligaments leads to ossification, contact of the edges of the vertebral bodies and their friction against each other (especially on the concave parts of the bends) leads to reactive bone growth (spondylosis), and the incorrect position of limited mobility, but bearing a compressive load, of the vertebral joints leads to cartilage degeneration and spondyloarthrosis.
All types of such local degeneration caused by static disorders can be called disorders of spinal mechanics, since they, like other disorders discussed below, arise in the area of motion segments. In the absence of primary static causes, the anatomical structures of the motor segments undergo inevitable age-related degeneration. These processes can be accelerated by constitutional factors and overload (hard physical labor, irrational training of athletes, ballet dancers, monotonous work, obesity), localized depending on functional conditions. Degenerative changes occur mainly where there is a maximum compressive load, particularly high mobility (cervical, lumbar spine) or a sharp change in the range of movements (transition from a mobile lower part of the cervical spine to a relatively inactive thoracic spine or from a mobile part of the sacral spine to a stationary sacrum ).
The phenomena of advancing wear and tear of the spine can occur without a pronounced clinical picture. However, they are often accompanied by characteristic complaints: local and radiating “rheumatic” pain, limited movement, pain when moving - patients complain about all this quite often. Such patients and their complaints are known to every doctor and every massage therapist.
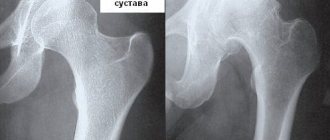
Degeneration begins with the intervertebral discs. They gradually dry out, their nucleus pulposus, as a result of colloidal changes, loses the ability to compress and expand, and radiography shows a narrowing of the intervertebral spaces (chondrosis). Next, the terminal plates of intervertebral cartilage are involved in the process. The decrease in the ability to withstand compressive loads is reflexively compensated by ossification of the vertebral body, which results in x-ray sclerotization of the terminal plates and edges of the vertebral body (osteochondrosis). Loss of water in the disc leads to a decrease in the force pushing the vertebrae apart, and this, in turn, leads to a decrease in the reliability of the motion segment and causes slight shifts of the vertebrae relative to each other. Degenerative destruction and loss of elasticity of the fibrous ring leads to the fact that it is unable to hold the nucleus pulposus in the permissible range of motion and cannot withstand the force developed when two vertebrae are shifted. The outer fibers of the ring are torn. Only the longitudinal ligaments resist the pressure of a disc experiencing a compressive load. The anterior longitudinal ligament, which is closely connected to the vertebrae, reacts to such pathological stress by ossification at the attachment site, which appears on x-rays as outgrowths along the edges of the vertebrae (spondylosis deformans). The posterior longitudinal ligament, closely connected to the discs, bends under the pressure of the core; in extreme cases - especially with a sudden maximum tilt of the body under heavy load - a herniated disc occurs. This can lead to compression of the spinal cord (in the area of 3-5 pairs of nerves of the cauda equina) or nerve roots in the intervertebral foramen and cause pinching of the corresponding nerve.
These degenerative changes also affect the intervertebral joints belonging to the motion segment: a decrease in the height of the intervertebral discs causes their displacement. Displacement of the joints leads to cartilage degeneration, and the vicious circle of arthrosis (in this case, spondyloarthrosis) closes here too. The joints subjected to such a test experience, during movement and load, the action of tensile, literally tearing forces; This is how irritation occurs, closing a vicious circle of articular disorders in the intervertebral joints.
Nervous excitation spreading from irritated intervertebral joints causes a reflex increase in the tone of the monosegmental muscles, the task of which is to fix the posture, as a result of which it keeps the affected motor segment in a painless position, and the polysegmental muscles limit the mobility of the entire affected part of the spine, sending a signal of pain with any attempt to move (check for movement). During palpation examination, oblong pencil-shaped hardenings, painful when pressed (hardening of polysegmental muscles), and more rounded myogeloses, also painful when pressed, are found in the dorsal muscles. The entire musculature of the affected region often becomes rigid. If these phenomena are not treated for a long time, the subcutaneous connective tissue is involved in the process; when loaded, it exhibits gelotic swelling, and when pinched, it gives pain typical of fibrositis. Patients often complain that the pain spreads to both sides of the spine (for example, to the arms, shoulder blades, buttocks and thighs) or radiates to one limb. However, a thorough check of the functions of peripheral muscles, reflexes and sensitivity does not reveal pathological abnormalities, although it does (sometimes) show the presence of connective tissue gelotic changes in the skin of the specified limb (for example, above the deltoid muscle, above the ileotibial tract (“general line”).
These radiating pains can be considered a projection of pain. Rupture of the joint capsules causes local swelling, which depresses the roots of the nerves located in the nearby intervertebral foramina. True radicular symptoms, that is, unilateral motor lesions, sensory excitations and impaired reflexes, occur only with mechanical damage to the spinal nerves as a result of (dorsolateral) prolapse of the intervertebral disc.
We consider the above muscle disorders, pain and reduced mobility to be a violation of spinal etiology, because they are caused by diseases such as chondrosis and osteochondrosis, spondylosis and spondioarthrosis.
In the same way, reflex hardening of the muscles, which is often detected at a considerable distance from the localization of the disorder and is the result of a compensatory reaction, becomes a classic indication for massage after the elimination of the underlying disease. Often this hardening of the muscles persists even after the elimination of the disease itself, and sometimes it itself turns into the main disease. One can recall, for example, the hardening of the pectoralis major muscle after suffering (vasomotor) angina or gelotic changes in the pelvic area, sometimes even affecting the back muscles with improper foot statics.
With the help of massage, you can relieve local rigidity and hardening of muscles (action on muscle fibers), gelosis and muscle pain (local vascular effect). However, before starting the massage, it is necessary to soften the connective tissue gelotic changes in the skin by intensive superficial stroking and kneading.
Peripheral disorders (“general line”) should also be treated. Segmental improvement of blood supply to the tissues of the motor segment promotes the resorption of edema swellings and breaks the vicious circle of articular and arthrosis disorders. Most often, back massage is very painful. To the patient, this pain seems like a wound, superficial pain; With daily massage it goes away in 4-5 days. At the same time, normalization of the palpation test is noted.
Massage should be started in subacute stages (in some cases it can be started earlier, during an exacerbation of the disease, but then the task of massage is to reflexively influence pain localized in the spine, by “treating” healthy areas of the body - on the chest, shoulders, upper part back, shoulder girdle, etc.). The first sessions should be gentle and not cause excessive tension in the muscles, which, when vigorously, harshly performed, contract, causing in this case additional pain.
The optimal position for a massage for a patient with cervical osteochondrosis is lying down. If this is not possible, then massage in a sitting position; for this, a special massage “chair” is used. In both positions, it is necessary to achieve extreme relaxation of the back, neck and the whole body in general - this is the first condition for the patient.
The massage begins from the back: stroking, squeezing, kneading - forceps, with the base of the palm, double ring, ordinary (all techniques - 3-4 times). The upper back, in the area of the shoulder blades, requires special attention. Here, first, stroking is done 6-7 times from the lower corner of the shoulder blades up to the neck - first on one side, then on the other. Then the shoulder girdles are massaged: stroking (6-8 times), squeezing (4-5 times), kneading - ordinary, double circular (3-4 times), stroking and shaking (2-3 times) - first with one, sometimes on the other side. If the patient is sitting, then you can stroke, squeeze and knead the pectoralis major muscles (4-5 times).
Continue the massage with the patient lying on his stomach. The neck is massaged: stroking from the scalp down to the back (8-10 times). If it does not cause pain in the spine, squeeze in three or four lines, along the back and sides of the neck (3-4 times).
On the upper back, near the spinal column, gently squeeze with the pads of four fingers (4-5 times on each side). This is followed by stroking over the entire upper back, after which they begin stroking and squeezing the upper bundles of trapezius muscles, that is, the shoulder girdle (4-5 times).
On the neck muscles, do stroking (6-7 times), squeezing, kneading with the edge of the palm and fingertips, squeezing again (all 3-4 times) and stroking (6-7 times). After repeating the massage of the pectoral muscles: stroking, squeezing, kneading, shaking, stroking (2 times each time), again move to the neck. Performed: stroking (6-7 times), squeezing (4-5 times), stroking (3-4 times), kneading with fingertips (5-6 times), stroking (4-5 times).
Now - rubbing the spinal column: straight with the pads of four fingers (each hand on its side) in the direction from the occipital bone to the back and as close as possible to the spinous processes (4-5 times); circular with pads of one, two, etc. fingers (3-4 times each time). When rubbing in the area of the spinal column, the neck of the person being massaged should be extremely relaxed and the head tilted forward. This will allow the massager to better feel the spinous and lateral processes of the vertebrae and work them deeper (after 5-8 sessions, when the pain subsides, it is useful to slightly turn your head in different directions while rubbing the spine). Rubbing is followed by stroking (6-7 times), squeezing and various kneading (3-4 times). This stage ends with stroking.
In the next part of the session, repeat the massage on the upper back (2-3 times each time) and on the upper bundles of the trapezius muscles (3-4 times each time) and return to the neck again. It is used for stroking (3-4 times), squeezing (4-5 times), kneading (5-6 times), stroking (2-3 times), squeezing (4-5 times) and again the spinal column is thoroughly rubbed. Then the chest: after rubbing, stroking, squeezing, kneading, stroking are carried out here (3-4 times); Using the pads of four fingers, the sternocleidomastoid muscle is massaged (5-6 times), kneading (4-6 times) and stroking (6-8 times).
If the pain radiates to the shoulder joint or upper arm, these parts of the body are also massaged - after carefully working the neck, upper back, and shoulder girdle. In conclusion, a general massage of the neck, back, shoulder girdle is carried out and active and passive movements begin.
After relieving pain in the spine, the technique changes: the number of stroking techniques decreases, and the number of squeezes, kneading and especially rubbing increases. It is rubbing that should become the main technique of the last sessions. We also note that the duration of the first sessions is 5-7 minutes, and subsequent ones - up to 12 minutes.
Massage for lumbosacral osteochondrosis begins after the acute pain subsides. It is always carried out with the patient lying on his stomach, and always on a solid base (table, couch), which would not allow the spine to bend in the lumbar region. For the same purpose, a pillow (rolled blanket, bolster, etc.) is placed under the stomach. The shins should be raised at an angle of 45°, which helps to relax the body and especially the lumbosacral region. The arms are extended down along the body. The head should lie on the right or left cheek, or better if it is slightly lowered below the couch, but rest the forehead on some support (for example, a chair).
The session starts from the back. First, a massage is performed to relieve tension and pain. This purpose is served by combined stroking (8-10 times), light squeezing with the edge of the palm (2-3 times) and double ring (superficial) - it is carried out on both the latissimus and longus muscles (4-5 times each). Having completed this stage with combined stroking (5-6 times), they proceed to massage the gluteal muscles. They are affected by: combined stroking (6-8 times) and double ring stroking (4-6 times), which is accompanied by light shaking in combination with stroking with both hands. Then - thigh massage: combined stroking (6-7 times), long kneading combined with shaking (3-4 times) and combined stroking again (4-5 times).
Now it's the back's turn again. After stroking with both hands (6-8 times), light squeezing (3-4 times), stroking (4-5 times) and kneading on the long muscles - with the base of the palm (4-5 times) and the pads of four fingers (3-4 times) ). Next - stroking (2-4 times) and kneading on the latissimus dorsi muscles (from the iliac crest to the armpit): single (3-4 times), double circular (4-5 times) and stroking with shaking (3-4 times each) times).
Only after all this can you begin to massage the lumbar region. It includes combined stroking from the gluteal mounds to the middle of the back (5-8 times), squeezing with the edge of the palm (3-4 times) and stroking again (5-6 times). After performing various types of squeezing on the gluteal muscles (4-6 times), and then stroking and shaking (3-4 times), we return to the lumbar region. After stroking here (5-8 times) and squeezing (2-3 times), begin rubbing.
Rubbing is a deep technique and is performed with caution so as not to cause pain. If rubbing causes severe pain, you should abstain from it for a day or two. If the pain is tolerable, then rubbing begins with a light transverse (that is, across the spine) edge of the palm. This technique - it is often called “sawing” in everyday life - can be carried out with one or two hands. Next - straight-line rubbing with the pads of your thumbs along the spine (6-8 times), gradually increasing the pressure; spiral rubbing with the pads of the thumbs (4-6 times); again “sawing” - 10-15 s and stroking (4-6 times).
Then apply dotted simultaneous rubbing with the pads of the thumbs along the spinal column. It is performed so that the skin moves 3-4 cm along with the massaging fingers, only in this case will the rubbing be beneficial. The reception is carried out 4-5 times and each time is accompanied by squeezing and stroking (2-3 times).
With each session, the number of repetitions of techniques and the strength of the impact increase.
It is necessary to remember: before massaging the sacral region, the gluteal muscles must be thoroughly worked out. Used: stroking over the entire pelvic area (4-5 times), squeezing (6-7 times), kneading - ordinary (4-5 times), with the base of the palm (3-4 times), shaking (2-3 times), stroking (1-2 times), squeezing (5-6 times), kneading with fists (3-4 times), shaking (2-3 times), kneading with fists, shaking and stroking (3-4 times each).
Sacral massage includes: stroking with both hands (5-7 times), squeezing over the sacral area (6-7 times), rubbing with the palms of both hands (5-6 times), the back of the hands (6-8 times), stroking (3 -4 times), rubbing - straight with the pads of four fingers from the coccyx up to the lower back (6-8 times; after each rubbing, the hands diverge to the sides to the gluteal muscles), circular with the pads of four fingers (5-6 times), straight with the metacarpophalangeal joints (6-7 times), stroking (3-4 times), rubbing with fists (5-6 times) and stroking in all directions.
Having worked the gluteal muscles once again (stroking, squeezing, single and double circular kneading with the pads of four fingers, shaking (all techniques 2-3 times), we again return to the lumbar area, where 3-4 main techniques are performed (repeating each 2-3 times ).
The iliac crest is massaged like this. Stroking from the spinal column to the sides (4-5 times) is followed by squeezing with the base of the palm (the hands are placed on both sides of the spine, with the fingers facing the hip joint; 4-5 times). Next, without changing the position of the hands, knead with the base of the palm along the edge of the ridge and the attachment of the gluteal muscles to the ridge (5-6 times), kneading normally on the gluteal muscles (3-4 times).
After this, they begin to massage the iliac crest itself. Apply: circular rubbing with the pads of four fingers (4-5 times) and phalanges of fingers clenched into a fist (3-4 times), squeezing with the base of the palm (3-4 times), straight and spiral rubbing with ridges formed by the phalangeal joints of four fingers (by 3-4 times), stroking (2-3 times). Repeat the whole complex 2-3 times.
Next, the lumbar region, sacral and gluteal muscles are massaged. All kinds of techniques are used - stroking, squeezing, kneading, shaking and stroking (3-4 times each technique).
The number of repetitions of stroking and kneading and their percentage in a massage session depends on the condition of the person being massaged, progress in the treatment and recovery process, etc. For acute pain, stroking takes up to half the session; as the pain subsides, the massage should become more energetic and deeper (occasionally even to the point of mild pain).
When massaging the lumbar or sacral areas, you need to pay attention to pain points (areas). Particularly careful treatment should be carried out around these places and directly at the painful point. With osteochondrosis of the lumbar region, pain often radiates to the back of the thigh. In this case, special attention is paid to massage on the thigh. They use deep massage - squeezing, kneading (especially double ring, “double bar”, with fists and pads of four fingers).
The massage is performed daily, or twice a day - morning and evening. Session duration is 8-10 minutes if the disease is in the lumbar region. If the sacral region is affected, the session time increases to 15 minutes. And as you recover - up to 18 minutes. The parts of the body being massaged should be extremely relaxed. The massage itself must be combined with active and passive movements in the joints.
Massage for lumbosacral osteochondrosis can be carried out with various warming agents. A good effect is achieved by massage after thermal procedures (sollux, warming with hot sand, baths, etc.).
In conclusion, the description of massage techniques for lumbosacral osteochondrosis and other diseases that are reflexively associated with certain zones located on the palmar surface of the hand (Fig. 1),
Rice. 1. Topography of reflexogenic zones on the human hand: 1 - frontal sinuses; 2 - vision; 3 - hearing; 4 - lungs; 5 — pancreas; 6 - adrenal glands; 7 - heart; 8 - kidney; 9 - shoulder, shoulder joint; 10 - spleen; 11 - large intestine; 12 - small intestine; 13 - rectum; 14 - lumbosacral region; 15 - testicle, ovaries; 16 — penis, ureter, prostate; 17—bladder; 18 - spinal column; 19 - neck; 20 - throat; 21 - pituitary gland
Patients should be recommended to influence these areas in the form of self-massage.
Self-massage is carried out 2-3 times a day for 3-5 minutes. The method of performing self-massage is simple. The following techniques are used: 1) straight, spiral and circular rubbing with the pad of the thumb; 2) straight, spiral and circular rubbing with the pads of three fingers; 3) straight, spiral and circular rubbing with interphalangeal joints (fingers clenched into a fist).
Massage in St. Petersburg
Biryukov A.A. Massotherapy. 2000 “Soviet sport”
Acupressure of the cervical region
This type of massage affects acupuncture points. If you apply this Chinese technique correctly, pain disappears, tension and muscle spasm are relieved. Acupressure treatment has a relaxing effect on them, releasing pinched nerve endings.
The patient usually feels relief at the very beginning of the course of procedures. Blood supply to the cervical spine improves, various seals dissolve faster.
Acupressure for cervical osteochondrosis should be performed exclusively as prescribed by a doctor in order to relieve tension and pain.
Execution technique
Sequence of actions when performing a massage:
- Feng fu point. Acupressure begins with the area under the occipital protuberance. Screwing movements are performed clockwise for 1 minute. After a delay of a few seconds, switch to loosening movements counterclockwise.
- Feng chi point. The point between the sternocleidomastoid muscle and the occipital bone should be impacted for 3-4 minutes with medium force. This will lead to relief of pain and relaxation of the neck muscles.
- Chuntu point. Find a point on the line between the 6th and 7th vertebrae on your back, press it with the pad of your finger for 5 minutes. This will improve venous and lymphatic drainage from the paravertebral tissues and reduce swelling.
- Point da-zhui. This is the 7th cervical vertebra. The impact on this point has a relaxing effect and is the best end to an acupressure session.
To improve the patient’s well-being and increase the effectiveness of treatment, acupressure is best performed after classical massage. For this, several points are usually selected.
Questions and answers
Can massage be harmful for osteochondrosis?
Only massage can cause harm during the acute phase of the disease, up to the deterioration and progression of the disease. In case of exacerbation of the disease, only light stroking without the use of force is allowed. Classic massage should be done in subacute, as well as during rehabilitation and recovery periods, when the pain subsides.
How can hydromassage (underwater) help with osteochondrosis?
One of the first effects is complete relaxation of the body. Since a person, even lying down, may not always completely relax his entire body, in warm water the muscles seem to be in weightlessness and become very relaxed. Hydromassage also increases blood circulation, relieves spasms, improves metabolism, and swelling begins to resolve faster.
Hydromassage
Is it possible to use massage for osteochondrosis while feeding a child?
A nursing girl should know that when treated with massage, there is a possibility of a decrease or complete cessation of lactation. This treatment method is suitable if the feeding period has already ended.
What is the difference between intercostal neuralgia and osteochondrosis?
Both of these diseases have similar symptoms. They differ in the nature of the pain: with neuralgia, pain appears with movements and pressure. And with osteochondrosis, the patient feels nagging pain in the muscles. Patients also note sharp pain in the thoracic region, as if it were pierced by a piercing object. Since the symptoms of the diseases are similar - pain in the chest area or between the shoulder blades, you should contact a knowledgeable specialist for an accurate diagnosis of the disease.
Photo: massage for osteochondrosis step by step
Massage areas for osteochondrosis
Back areas during cupping massage
What is electric massage for osteochondrosis?
Physiotherapy using Bernard current on the back Electric
massage is also called physiotherapy using Bernard current . This is the effect on the body of diadynamic currents with a frequency of 50-100 hertz. This technique brings good results and promotes:
- relieving tension and pinching in nerve endings;
- pain reduction;
- normalization of blood circulation;
- relaxation of body muscles;
- reduces the amount of medications taken.
What neck massagers are there for osteochondrosis?
There is an effective manual massager “Octopus”, which simulates a two-handed massage. It is made of plastic, glass, rubber and wood. It can be used for self-massage or rubbed on another person.
Massager Octopus
There is also such a device as an infrared massager. You just need to plug it into the network and keep it in the problem area for a few minutes. It relieves muscle spasms and increases blood circulation.
The electric massager also uses power from the electrical network and is designed in the form of a long handle and a floating head. There are many attachments for electric massagers for different mechanical effects.
Healing mat - Kuznetsov's Tibetan applicator also helps very well to relax the body and eliminate pain in the cervical area. It looks like a mat with plastic spikes in the shape of a plum blossom. It works on the principle of acupuncture. The Lyapko applicator works on the same principle.
Excellent article on the topic: The healing power of the Kuznetsov applicator for osteochondrosis
There is also a massage pillow - it helps perfectly with constant sedentary work. It can be used lying down or sitting on a chair.
This is a device that will perform a massage using the shiatsu technique at home in any convenient place. A pillow will help relieve stress and tension after a hard day at work. The rollers built into the device imitate the movements of a massage therapist and give an unforgettable experience.
Massage pillow
Roller massagers are designed to perform self-massage for cervical osteochondrosis. Products are made of plastic or wood.
There are professional massagers in the form of chairs. Just five minutes of massage - and back pain begins to decrease.
Be sure to read: TOP 10 methods for straightening your spine at home: exercises, what you can and cannot do?
Is it possible to cure osteochondrosis with massage?
You can completely get rid of symptoms if you combine massage with physical therapy and avoid hypothermia . Manual therapy can help if the doctor knows his job very well. If the pain is severe, then you first need to eliminate the inflammatory processes (rest and warmth), and then begin complex treatment.
What to do if osteochondrosis worsens after a massage?
- To begin with, you should take a stationary position.
- The patient should be placed with a pillow under the spine to ensure a comfortable position.
- You should wrap the patient up and call an ambulance.
- If the pain is not very severe, then take painkillers and ask for a massage with light movements, and then rub in the painkiller cream.
As a rule, the patient feels better after an hour. To eliminate the exacerbation of osteochondrosis, you should temporarily avoid massage sessions, sports or exercise therapy. Massage is permitted only in the form of light stroking with the use of pain-relieving ointments.
In case of an exacerbation, it is allowed to visit the pool, but after it hypothermia should not be allowed. It is important to provide rest and warmth to the painful area. It is not recommended to use heating pads or heat on the back because they can aggravate the pain. It is advisable to use a wool scarf or dog hair belt. An exacerbation can last from 3 to 5 days.
Excellent article in continuation: The whole truth: is it possible to cure osteochondrosis forever? Real reviews and unique techniques
How many minutes does a back massage take?
The average session lasts from 15 to 30 minutes.
How many massage sessions should you do?
A massage course for osteochondrosis is 10-12 procedures
How much does massage cost for the treatment of osteochondrosis?
The price differs depending on the qualifications of the massage therapist and ranges from 700 to 16,000 rubles in Moscow, and from 200-12,000 rubles in St. Petersburg and other regions.
Where to find a qualified massage therapist?
The easiest way to find a massage therapist is to go to a public clinic and make an appointment with him at the reception. If the patient is observed in a private hospital, then there are always massage therapists to whom the attending physician will refer. The cost of a session starts from 200 rubles, duration is at least 14 days. At least 2-3 courses of treatment are required per year.
Cervical osteochondrosis: signs, nuances, massage treatment
It is the cervical spine that reacts to disturbances in a special way - the symptoms of osteochondrosis in this area differ from its other types. This feature is explained by the fact that the cervical vertebrae are located very close and even a slight displacement can lead to serious disorders of the musculoskeletal system, as well as cause acute pain.
Important: In addition to pain, cervical osteochondrosis can manifest itself as weakness and poor sensitivity of the hands (pinched nerve endings), problems with head movements (bone formations, changes in the structure of the intervertebral disc), dizziness (pinched artery) and even impaired vision or hearing (poor circulation) .
The development of this disease occurs in several stages:
- First: the osteochondral tissue of the vertebrae is destroyed, the symptoms are either indistinguishable or absent;
- Second: the height of the intervertebral disc decreases, cracks appear in it, pain and weakness are recorded;
- Third: a herniated disc forms, damage appears in blood vessels and muscles, pain may be accompanied by dizziness;
- Fourth: the bone tissue that protects the vertebrae grows, nerve endings are pinched, movements become constrained, and neighboring joints are certainly damaged.
All this leads to poor nutrition of the brain and disruption of its functioning. A person may lose coordination, his motor activity will be impaired, and pain and spasms will be felt in his arms and legs on a constant basis.
Advanced osteochondrosis can cause ischemia, stroke and other diseases that will cause irreparable harm to the human body, including death.
First of all, treatment of this type of osteochondrosis must be carried out comprehensively - massage procedures are complemented by physical therapy, medications, vitamins, a proper diet, an active lifestyle and traditional medicine. All this should improve blood circulation and eliminate the occurrence of muscle spasms. It is possible to use painkillers and medications that relieve inflammation.
The principle of massage is practically no different from the classical one:
- impact on the surface layers of the skin from the collar area to the chest through stroking;
- working with deeper layers of skin using a grip;
- warming the skin to improve blood supply;
- kneading and subsequent relaxation.
Helpful advice: If the pain is based on only one side, the massage should begin with the healthy part, and then smoothly move to the area of the pain. The main thing is to exercise extreme caution so as not to worsen the situation.