Myositis is a disease that brings severe discomfort to a person and a significant deterioration in the quality of life. The essence of the pathological process is inflammation of the skeletal muscles. It may affect one or more groups of muscle fibers.
Alas, a significant part of patients, having felt pain in the muscles of the neck, lower back, upper and lower extremities or other parts of the body for the first time, do not rush to seek help, but begin to self-medicate. This attitude towards one’s own health often leads to a significant deterioration in well-being and/or the disease becoming chronic.
Why is this happening? Because the term “myositis” itself combines several types of diseases with a similar pathological process. Each of them differs in the mechanism of occurrence, degree of prevalence, and symptoms. Moreover, muscle myositis can often be confused with completely different diseases that require a completely different approach to therapy. Only a specialist can differentiate one form of the disease from another and select the most effective treatment for each individual case.
Types of myositis
One of the main criteria for classifying muscle inflammation is etiological.
Depending on the cause that provoked the disease, there are:
- Acute infectious myositis. However, it can be of a viral or bacterial nature. Myositis of the extremities is characterized by weakness in the arms and legs, pain (especially the shoulders and hips). Rapid progression involves the muscles of the neck, chest, and back and leads to partial immobilization, but does not disrupt basic reflexes. Having reached the peak, the process just as unexpectedly begins to decline. Usually recovery occurs after 2-3 days, in severe situations - after 2-3 weeks.
- Inflammation due to the penetration of parasites. Larvae of echinococcus, trichinella, pork and bovine tapeworm can settle in muscle tissue and cause inflammatory processes. Unpleasant sensations bother the patient only when the parasite is active. Weakness and functional impairment are almost never observed.
- Interstitial form. Typically, such changes occur during the migration of tuberculosis or syphilis pathogens. Settled in the interstitium (connective tissue between muscles), they form specific compactions. Over time, inflammation of the interstitium spreads to muscle tissue. The disease has a chronic, slowly progressive form without pronounced periods of exacerbation.
- Typical traumatic myositis. Athletes and people who lead a very active lifestyle suffer most from muscle inflammation after a blow or some other injury.
Depending on the extent of the process, the pathology can be localized (involving one muscle group) or diffuse (spreading over several muscle groups).
The diffuse form is called poliomyositis . It most often occurs in people prone to autoimmune diseases. This type is characterized by pain, which increases significantly with movement, and the development of contractures. Contracted muscles do not relax either during sleep or when exposed to anesthesia drugs.
The main forms of poliomyositis:
- Dermatomyositis. It affects the skin and is accompanied by muscle pain. It begins acutely, with an erythematous rash appearing on the face, chest, neck, and extensor parts of the limbs. A little earlier or simultaneously with it - muscle weakness. This form of myositis must be differentiated from scleroderma, polyneuritis, disseminated lupus erythematosus and periarthritis nodosa.
- Neuromyositis is a disease that affects both muscle and nerve fibers. It is characterized by a change in sensitivity, severe pain, aggravated by palpation. Over time, pain may persist even in a resting position. Symptoms of tension are weakly positive, joint pain or skin lesions are present (rarely). EMG shows elements of denervation changes.
- Polyfibromyositis. The inflammatory process leads to the destruction of typical cells and their replacement with connective tissue cells. The person complains of pain when moving, sharp pain on palpation, thickening of the muscles at the places of their attachment, development of contractures and abnormal muscle contractions.
What is post-isometric muscle relaxation
Any modern person with almost 100% probability has some kind of health problems. Most of us are busy working in offices or studying, which require staying in one position for a long time. This leads to tension, spasms, and immobility of the joints. The spine loses its flexibility.
Postisometric relaxation of the spinal muscles is directly related to manual therapy. But this method is somewhat different. It is more gentle and almost completely painless. The relaxation method was first used in 1906 by Dr. Puusel. He first tried it on his patients and realized that the traction method effectively relieves muscle and ligament tension. Based on the technology invented by Puusel, post-isometric relaxation was developed directly in America.
The procedure is very relaxing and removes tension. As a result, you gain lightness and energy. The body again becomes mobile and resilient.
Common symptoms of myositis that should make you see a doctor
One of the typical signs of any inflammation is pain. This is a kind of cry from the body for help. With myositis, pain is localized in the muscles. It can have a different character. The main symptoms of diagnostic significance are:
- pain syndrome;
- the presence of dense hyper-irritable zones (trigger pain points) in muscle tissue;
- increased muscle weakness and decreased muscle mass
- redness and swelling of the skin over the affected area;
- local (sometimes general) increase in temperature, fever;
- movement disorders.
Any of these symptoms (and especially a combination of several) is a serious reason for immediate contact with a specialist!
Step-by-step technique for post-isometric muscle relaxation
Certain relaxation exercises work on the muscles, loosening them and removing blockages. During the session, the person is on the floor or on a massage table. The specialist performs stretching with short movements. The focus is on blocked muscles. Some types of manipulation require the participation of the patient himself (for example, forcefully resisting a stretch). The intensity with which the master will work depends on the degree of muscle blockage. Of course, your feelings are taken into account. If necessary, the impact is reduced.
But even the most powerful manipulations are completely painless. Postisometric relaxation does not involve severe pain.
The wizard's procedure:
- First, the specialist abducts the joint that will be worked on to limit its movement. This is the first impact on the stressed area.
- As soon as the patient begins to feel pain, the joint is released.
- The contraction of the muscle will increase significantly if you continue to influence it.
- The muscle is stretched, and in the next stage you need to provide resistance without squeezing the muscles.
- The master acts precisely and briefly (within 5–7 seconds).
- Then there is a pause of up to 3 seconds.
- The manipulation is repeated about four times.
A post-isometric muscle relaxation session lasts from 30 to 45 minutes. At the same time, you will immediately feel the stretching of the muscles, and a pleasant lightness will occur. There may be slight pain in some areas. This is the body's natural reaction to stress. Then you will get used to it, and the discomfort will go away. For an effective result, you will need about ten sessions.
Diagnosis of myositis at the Med&Care clinic
As mentioned above, different forms of the disease have their own clinical picture. If myositis is suspected, a neurologist at our clinic will interview and examine the patient and prescribe the necessary tests and studies.
The most informative instrumental diagnostic method for myositis is ultrasound of soft tissues and ultrasound angiography. Our medical center uses modern expert class ultrasound equipment TOSHIBA APLIO CV. It allows you to detect inflammation of muscle tissue (foci of hyperechogenicity), fibrous layers (hypoechoic areas), abscesses and other pathological processes.
To confirm the diagnosis, electromyography is sometimes used to help evaluate the electrical activity of muscles.
The following are a good help to the doctor:
- General blood analysis. It allows you to confirm or exclude infectious myositis (accompanied by an increase in ESR, the number of leukocytes and neutrophils) and a parasitic form of pathology that provokes the growth of eosinophils.
- Blood test for creatine phosphokinase. Exceeding the permissible norms of this enzyme indicates damage to muscle cells.
- Rheumatic tests that help identify local or systemic autoimmune diseases. Of particular diagnostic value is the analysis for myositis-specific autoantibodies (MSA).
- Biopsy. Taking a biopsy allows you to see structural changes in muscle tissue, the vessels that feed it and nearby connective tissue.
Postisometric relaxation for glenohumeral periarthritis and piriformis syndrome
- Periarthritis.
This disease usually follows an injury. It can begin for no apparent reason, and can also be virtually asymptomatic. Periarthritis often occurs with hypothermia, predisposition to osteochondrosis, and congenital pathologies. People over 40 years of age are at risk. An excellent treatment option for the disease is post-isometric muscle relaxation. This is an easy, almost painless effect.
Massage is useful during the treatment of glenohumeral periarthritis. Of course, therapy comes in combination with prescribed medications and physical procedures. In addition, the doctor may recommend doing exercise therapy.
We recommend
What are the SPA treatments for women and men? Read more
- Piriformis syndrome.
Here, pain occurs because the muscle compresses certain nerves. Possible causes are excessive stress in sports, as well as hypothermia.
Postisometric relaxation of the piriformis muscle helps relieve tightness and spasms in a short time. Lightness comes, pain goes away. What the exercise consists of: Lie on your back, bend one leg. Bring this limb beyond the straight line (the one in which pain is observed should be on the other). With the opposite hand you need to stretch the bent leg diagonally upward. Pull until you feel discomfort.
Now tense your leg. At the same time, try to pull it back. You need to be in this tension for five seconds. Then relax for three seconds. Do this exercise four times.
The main set of exercises for post-isometric muscle relaxation
This set of exercises can be done independently. It is used to strengthen and relax specific areas of the spine (for example, post-isometric relaxation of the neck muscles).
But you should be careful with home exercises. If you do not have experience, at first it is better to trust a qualified master. He will follow the technique and will not harm your health.
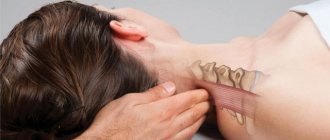
- Neck.
For neck pain, you can do the following exercise. Lie on the table so that your shoulders touch the edge and your hands are behind your head. Now the master should clasp the patient’s head with his hands and pull it back, slightly reducing the pressure when exhaling.
The next exercise will concern post-isometric relaxation of the muscles of the cervical spine. The patient sits on a chair. The professional grabs his head and slowly pulls it up. In the extreme position there is a pause of four seconds. Afterwards there is a rest for a few seconds. The manipulation is repeated the required number of times.
All exercises should be performed smoothly and calmly . During the session, the patient feels a soft, painless effect.
- Breast.
Discomfort in the thoracic spine is a problem that can affect both young and old people. Often it goes in parallel with osteochondrosis of this area. In this case, post-isometric relaxation of the pectoral muscles is a necessary procedure to reduce pain.
During the exercise, the person lies on his side. The specialist holds the joint of the leg close to the floor. The joint of the second limb is pulled to the side. The back is stretched.
Now you need to sit in a comfortable place (for example, on a sofa). Lean your sore side against the armrest. Place one hand behind your head, and hold the abducted limb by the elbow with the other. Press towards your forearm. Hands do not reach to the middle of the back. At the same time, try to move the abducted limb as far as possible. A stretch should be felt in the shoulder area. Once you reach it, wait three seconds, then relax. Repeat the same three times.
We recommend
Body mesotherapy for weight loss: a modern method of body correction Read more
- Small of the back.
The method of post-isometric relaxation of the muscles of the lumbar region has a positive effect on the entire back. At the same time, blood flow to this area increases, the pain goes away. Lie down on the sofa in such a way that you can wrap your arms around it. The master lifts the patient's legs by about 30 cm. Then he pulls them up. If the technique is followed correctly, you should feel relaxed. In some cases, the person is asked to resist the influence, but this practice requires special care.
Causes of tightness in muscles
The main causes of compaction in the muscles are associated with a violation of tissue integrity. Any muscle consists of myocytes. These cells are richly innervated by sensory and motor types of axons. With the help of this nerve fiber the impulse is carried out. Sensory fibers collect information about the impact on muscles and transmit it to brain structures. After analysis and processing, the cerebral motor center transmits a signal through motor axon types to the myocytes about what movement needs to be carried out. This is how all movements of the human body are carried out.
The blood supply to myocytes is carried out using a branched capillary network. Each myocyte has a separate capillary. Myocytes also have a unique ability - they accumulate glycogen and thus participate in the carbohydrate metabolism of the human body. In the case of severe physical activity, glycogen is released from muscle cells and used as an additional source of energy. When blood sugar levels are not high enough, glycogen is released and enters the blood, leveling the glycemic balance.
Potential causes of tightness in muscles can negatively affect not only myocytes, capillaries and nerve endings of axons. The muscle is covered with connective tissue (fascia, which at the ends turns into a tendon. It is responsible for attaching the muscle to the bone tissue. Lesions can occur in the fascia and tendon. It is quite difficult to independently determine the location of the compaction. To do this, you need to have a good knowledge of the anatomy of the human musculoskeletal system.
Causes of tightness and muscle soreness may include:
- disturbance of innervation - if the nerve impulse is carried out incorrectly, some of the myocytes do not have time to respond in time;
- impaired blood supply - against the background of ischemia, an isolated focus of aseptic inflammation occurs;
- accumulation of capillary blood or lymph fluid in a hidden cavity formed against the background of a bruise or tissue rupture;
- formation of scar tissue after injury or inflammatory process;
- helminthiasis;
- a foreign body that has entered the soft tissue during injury.
In some diseases, tightness in the muscles may be signs of increased tension. Thus, osteochondrosis of the spine with exacerbation and infringement of the radicular nerve is always accompanied by muscle fiber tension syndrome. In this way, the body tries to compensate for the insufficient shock-absorbing capacity of damaged intervertebral discs.
Other potential causes of tightness in the muscles may be scar deformations of the surrounding connective tissues (fascia, tendons, ligaments, etc.). For diagnosis, methods of radiographic, ultrasound and magnetic resonance topographic examination are used.
Lumps in the muscles of the arm
A sudden tightening in the muscles of the arm may be a sign of severe overstrain and stretching of individual fibers of the tendon, ligament or fascial tissue. When compaction is located deep in the muscle, as a rule, weakness occurs and the inability to perform certain actions. Doctor's help required.
To diagnose a disease that causes tightness in the muscles of the arm, various approaches are used. An X-ray image allows you to assess the condition of the bone tissue, exclude splintered fractures, bone cracks, deforming osteoarthritis, which are often provoked by excessive tension in nearby muscles. Ultrasound examination of soft tissues allows timely detection of tumor processes, areas of accumulation of lymphatic fluid and capillary blood. To assess the condition of blood vessels, angiography and duplex scanning are performed. The performance of muscle fiber is determined using electromyography.
Compaction in the muscles of the upper limb can be caused by damage to the nerve fiber:
- cervical osteochondrosis with radicular syndrome can provoke pain in any part of the arm;
- brachial plexitis is characterized by damage to one of the branches of innervation;
- cubital tunnel syndrome affects the ulnar nerve;
- Carpal tunnel syndrome or carpal valve syndrome causes pain and impaired mobility in the hand and fingers.
To make a correct diagnosis, you must seek medical help. In Moscow, you can make an appointment for a free appointment with an orthopedist and neurologist at our manual therapy clinic. Here you will be offered an initial examination, an accurate diagnosis and the provision of comprehensive information about the possibilities and prospects of treatment.
Treatment of muscle lumps
It is necessary to begin treatment of compactions in the muscles with a high-quality differential diagnosis. If the lump is a growing tumor, then you definitely need to consult an oncologist. Only with the help of histology can one determine whether this neoplasm is benign or malignant. Then the likelihood of inflammation of the lymph nodes and vasodilation is eliminated.
In case of true damage to muscle, tendon, ligament and fascial tissue, treatment can be carried out using manual therapy and physical therapy. For diseases that are accompanied by muscle fiber tension syndrome, treatment is primarily aimed at eliminating the causes that caused these diseases.
In our manual therapy clinic we use the following methods of influence:
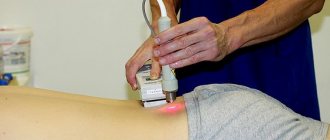
- laser treatment is aimed at eliminating stagnation of lymphatic fluid and blood;
- osteopathy and massage - accelerating microcirculation processes in the lesion;
- reflexology – influence on biologically active points on the human body;
- therapeutic exercises and kinesiotherapy;
- traction traction of the spinal column;
- physiotherapy, etc.
You can schedule a free initial appointment at our manual therapy clinic. During the consultation, the doctor will find out why the tightness in the muscles occurred. Will give recommendations for treating the underlying disease.
Lumps in the back muscles along the spine
Most often, muscle compaction along the spine is a typical clinical symptom of developing degenerative dystrophic disease of the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral discs (osteochondrosis). When it occurs, primary dehydration of the fibrous ring occurs, as a result of which the disc loses its shock-absorbing ability. There is a reduction in the distance between two adjacent vertebral bodies, which provokes compression of the radicular nerves. In order to compensate for this, the body provokes tension in the muscular frame of the back. Constant static tension leads to a tightness in the back muscle and it can be quite painful.
In official medicine, special pharmacological drugs – muscle relaxants – are used to relieve such muscle tension against the background of osteochondrosis. They really effectively relax muscle tissue. But in this case, repeated injury to the nerve fiber occurs.
Lump on the back of the neck muscle
The tightening of the muscle in the neck can be associated with its overstrain, injury, or the development of an internal hematoma. Tension in the back muscles of the neck is also characteristic of some forms of encephalitis and other dangerous infections that affect the structures of the brain.
When diagnosing, the following dangerous diseases should be excluded:
- lymphadenopathy that occurs against the background of oncological and infectious processes in the human body;
- rubella and mumps;
- tumors of muscle tissue and adjacent connective tissue;
- displacement of the vertebral body with its rotation (in this case, the out-of-place spinous process is palpated as a seal;
- comminuted fracture of the arcuate process of the vertebra;
- rupture of muscle tissue with the formation of a cavity hematoma;
- dilation of a blood vessel in the form of an aneurysm
A painful lump on the back of the neck muscle may be a clinical sign of the development of acute myositis. This disease is characterized by short-term ischemia of individual areas of myocytes. Poor blood supply occurs in response to exposure to low temperatures (hypothermia). In areas of ischemia, an inflammatory process is launched in order to eliminate and replace dead myocytes. This lesion may feel like a painful lump for some time.