Metatarsal bones are part of the group of small tubular bones of the human skeleton. Metatarsal fractures are the most common bone fractures in the foot. Namely, fractures of the base of the fifth metatarsal bone that occur as a result of inversion of the foot. The location of the fracture should be carefully analyzed by a doctor, since the treatment of fractures of different location and nature varies quite a lot.
Types of fractures of the metatarsal bones of the foot
There are two main types of metatarsal fractures:
- Traumatic fractures - due to acute (sudden) injury to the middle and forefoot.
- Stress fractures are due to excessive long-term stress or repeated minor trauma against a background of completely normal metatarsals.
Fractures of the metatarsal bone of the foot are also classified according to location, nature of the fracture and the presence of displacement:
- Fractures of the base, body or subcapitate fractures of the metatarsal bones;
- Fractures of the metatarsal bone with or without displacement;
- Fractures are oblique, transverse, helical, comminuted.
Prevalence
Metatarsal fractures account for 5% to 6% of all skeletal fractures. They are equally common among men and women of the planet.
To understand the mechanism of metatarsal fractures, it is probably best to start with a brief explanation of the anatomy of the foot.
The human foot consists of 26 bones:
- 5 metatarsal bones. These are tubular bones that are located between the tarsal bones and the phalanges of the fingers. Functionally, the metatarsal bones play an important role in movement, acting as a lever during foot movements (steps, running, jumping).
- 14 phalanges of fingers. The first finger consists of two phalanges, the remaining fingers - of three.
- 3 sphenoid bones. Located between the navicular bone and the first three metatarsal bones.
- Cuboid
- Scaphoid
- Talus
- Calcaneus
Together, the bones of the foot form a very complex mechanism that compensates for the enormous loads throughout the day and helps absorb the shock of every step.
Types and symptoms: how to recognize damage?
When crepitus and pain appear, complaints cannot be ignored, since stress fractures take longer to heal and are prone to recurrence.
The main signs of metatarsal bone fractures:
- painful swelling;
- palpable disruption of integrity;
- pain with axial load.
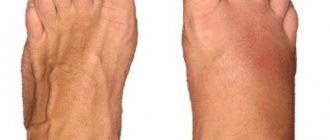
Patients with metatarsal fractures are unable to bear full weight on the affected foot, which becomes swollen and painful. Severe deformations are observed only in complex injuries when bones are displaced.
Depending on the location of the fracture, there are certain signs:
- The center of growth of the first metatarsus is located in the proximal direction in children, so fractures are difficult to detect.
- Fractures of the proximal part of the fifth metatarsal provoke pain in the middle of the foot and at the base of the metatarsus, tenderness of the navicular bone. The patient cannot step on his foot immediately or after 4-5 steps.
- Fractures of the metatarsal head cause swelling, hematoma, and make walking difficult. Initially, pain occurs only during activity. Swelling sometimes makes it difficult to bend the foot. There is pain at the fracture site. Axial load increases pain. This does not happen with soft tissue injury.
- A fracture of the fifth metatarsal bone causes pain along the side of the foot and makes walking difficult. Acute injuries are accompanied by swelling and bruising, while stress injuries are usually associated with a progressive increase in pain, which is complicated by activity.
- Stress fractures result in pain while walking, which goes away with rest. Over time, the symptoms intensify, swelling or pain when touched appears.
A fracture of the base of the 5th metatarsal bone of the foot is more common in athletes, ballet dancers, and physically active people. The first and fourth metatarsal bones are susceptible to injury, but less frequently.
The fifth most often affects young women who wear uncomfortable shoes and high heels, which causes them to twist their ankle.
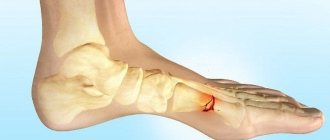
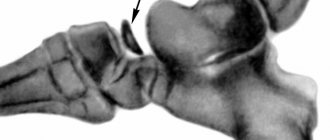
The photo on the right shows a closed fracture of the fifth metatarsal bone - a compaction in the form of a lump, a hematoma.
If there is swelling in the foot, you should consult a doctor.
Doctors divide fractures of the metatarsal bones into 2 types:
- Traumatic, which occurs as a result of injury.
- Stress when bones break due to regular overuse of the feet. In this case, the symptoms are not clearly expressed and are manifested only by periodic pain and slight swelling.
| Type of fracture | Signs |
| Without displacement with the appearance of a crack | Soreness |
| Mild swelling and hematoma | |
| The functionality of the limb is partially preserved | |
| Closed with offset | Strong pain |
| Subcutaneous hemorrhage | |
| Swelling | |
| Unnatural finger position | |
| Movement is difficult due to pain | |
| The integrity of the skin is not compromised | |
| Open offset | Intense sharp pain |
| Extensive swelling and hematoma | |
| Movement and support on the leg is impossible | |
| Local and general increase in temperature | |
| Formation of a wound by bone fragments | |
| Foot deformity | |
| Nausea, dizziness, fainting, as the body’s reaction to pain |
The foot is a mechanism with a complex structure, consisting of many bones, and five of them are tubular metatarsal bones located between the digital phalanges and the tarsus. These bones serve as a kind of lever that moves the foot when moving, jumping, and help maintain balance and stability. Even a slight fracture or crack in one of these bones significantly affects the ability to move.
A fracture of the metatarsal bone of the foot is manifested by the following symptoms:
- crunch at the moment of injury;
- sharp pain, which at first may be muffled by shoes that hold the foot tightly, but then always become more pronounced;
- pain increases with movement and touching the foot;
- difficulty moving, lameness;
- increasing swelling of the foot;
- blue discoloration of tissue at the site of injury.
Signs of a fracture of the metatarsal bone of the foot are not obvious to patients in all cases, and such an injury is often mistaken for a severe bruise or sprain. This is especially true for situations where the fracture is not traumatic, associated with a sharp mechanical impact, but stressful. Stress fractures begin with the formation of a small crack in the bone as a result of regular stress on the feet, often in athletes.
In cases where no displacement of bone fragments is observed during a fracture, the damaged bone maintains its anatomically correct position. Such injuries are less dangerous, easier to treat and heal. Separately, it is worth highlighting a non-displaced fracture of the fifth metatarsal bone of the foot, called a Jones fracture. Because
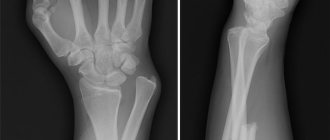
A fracture of the metatarsal bone, accompanied by separation and displacement of bone fragments, can be recognized by a visual change in the structure of the foot, but this is not always noticeable. An accurate picture of the injury can only be obtained through x-ray diagnostics. A fracture of the metatarsal bone of the foot with displacement is dangerous due to the development of bleeding and an increased risk of suppurative processes in the tissues. If you do not consult a doctor in time, the fusion may not occur correctly, and a complex operation will be required.
Symptoms of fractures
- Pain that develops gradually and increases with exercise
- Foot swelling
- Subcutaneous hemorrhage (bruise)
Patients with these symptoms typically experience a sudden onset of sharp, intense pain following an injury. Sometimes the patient may hear a crunching or clicking sound at the time of injury. The pain causes the patient to limp. Patients with a metatarsal fracture are also accompanied by swelling, which increases during the day and decreases at night. In severe displaced metatarsal fractures, obvious deformity may not be noticeable.
Diagnostic measures
To have an accurate idea of what exactly happened to the bones of the foot, it is necessary to take an x-ray in 2-3 projections (frontal, lateral and at an angle). Some fractures of the metatarsal bones are invisible on the initial x-ray; they appear 10-15 days later, when callus begins to form. This is true for nondisplaced stress fractures.
In doubtful cases, it is recommended to do a computer or magnetic resonance imaging scan of the foot. Thanks to a comprehensive study, the doctor will be able to choose the most appropriate treatment method.
Diagnosis of metatarsal fractures
For a more detailed understanding of the problem, the doctor finds out from the patient the mechanism of injury, including the force, location and direction of the blow.
Stress fractures are usually associated with increased intensity or duration of repetitive movements such as running, ballroom dancing, and others.
Examination: Careful examination and examination of the entire foot and ankle is critical in identifying associated injuries. Deformity, swelling and hemorrhage are easily visualized.
X-rays in 2 projections are usually sufficient to diagnose a fracture. But with stress fractures without displacement, sometimes it is impossible to determine them even for a very experienced doctor.
In such cases, control radiographs are prescribed after 10-14 days, when bone tissue resorption occurs at the fracture site. Stress fractures are also difficult to see on x-rays until they begin to heal and callus begins to form. This is exactly what is clearly visible on x-rays. A CT scan or MRI may be necessary to rule out stress fractures and other foot pathologies.
First aid for metatarsal fractures
- Limiting loads and movements. It is important to limit movement and stress on the foot to prevent further damage.
- Cold locally. Using ice will help slow or reduce swelling and provide a numbing sensation that will relieve pain. It makes sense to apply ice to the injury site for the first 48 hours after the injury. Never hold ice for more than 20 minutes at a time to prevent frostbite. A break of 1.5 hours before repeated exposure to ice, this allows the tissues to return to normal temperature and trophism, repeat as necessary. You can wrap any frozen product in a towel and apply it to the damaged area. Ice should be applied as soon as possible after the injury. (Do not place ice directly on your skin. Also, do not leave ice on while you sleep, or leave it on for more than 30 minutes. This may cause frostbite.)
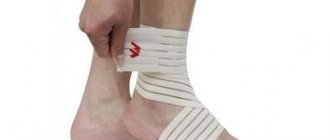
- Elastic bandaging. You need to bandage your leg with an elastic bandage. But bandage it correctly, not too tightly. If your fingers become cold or numb, it means the bandage is too tight. An elastic bandage will limit swelling and limit movement in the joint. You can sleep without a bandage. But be sure to move around with your leg wrapped in an elastic bandage.
- Elevated position. Elevate the injured leg, such as resting your leg on a pillow while lying on a sofa or bed. If you are sitting, you can rest your leg on a chair to reduce swelling and pain.
Avoid: heating the damaged area during the first week, rubbing with alcohol and massage, which can aggravate the swelling. For example, exclude hot baths and saunas. Heat has the opposite effect compared to ice. That is, it stimulates blood flow.
It is important to limit the load when walking (do not rely entirely on the foot) until the injury has been diagnosed by a doctor.
First aid and diagnostics
Foot fractures most often occur due to trauma. They can be caused by bruises or heavy objects falling on the leg. Damage can be caused by road accidents, falls from heights and personal growth. They are often diagnosed in runners and professional football players. If a closed fracture occurs without displacement, a series of sequential actions must be performed:
- ensure maximum fixation of the ankle, place it on a hill;
- apply a cold compress to the injured area - this way you can avoid the appearance of extensive tissue swelling;
- If necessary, give the patient painkillers in tablets.
If the fracture is open, it is necessary to stop the bleeding with a tourniquet. It is important to try not to directly impact the site of injury - if further movement of the fragments occurs, it will be more difficult to compare them. If it is not possible to remove the victim’s shoes (if he is wearing bulky boots), it is better to wait for the doctors to arrive.
The initial diagnosis of injury occurs at the scene of the incident. The injured foot appears swollen and the victim cannot bear weight on it. However, to begin treatment, it is important to determine the type of damage, its location and the presence of complications. The first method of instrumental diagnosis is radiography; bone fragments will be clearly visible in the image. If more serious damage is suspected, an additional study may be needed - an MRI. It shows the condition of soft and hard tissues in different projections.
Treatment of fractures of the metatarsal bones of the foot
Conservative treatment of moldy bone
Treatment tactics will depend on the location of the fracture and its severity.
The goal of any treatment for metatarsal fractures is to help the patient return to a full life. Following your doctor's recommendations will help you quickly restore foot function and prevent further problems in the future.
We are convinced that for non-displaced fractures, adult patients do not need to apply plaster, as this causes a lot of inconvenience, and they are able to understand that it is necessary to limit the load in order for the fracture to heal as quickly as possible. Displacement of bone fragments does not occur without load. But it is difficult to explain to our young patients that they should not step on their feet or walk only with support on their heels. That's why we cast children.
As a rule, in case of traumatic fractures, it is recommended to walk only with support on the heel or without any support at all, moving with crutches.
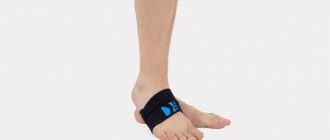
In case of stress fractures, it is recommended to walk with partial weight bearing on the foot, but always in individual orthopedic insoles, which “unload” the damaged area.
If the metatarsal fracture is slightly displaced, an attempt is made to reduce it and fix it with a plaster splint.
If the fracture is accompanied by a significant displacement of bone fragments (more than half the width of the metatarsal bone), the issue of surgery is decided.
Basic therapy methods
What are they? As mentioned earlier in this article, treatment of the metatarsal bones of the foot during a fracture is selected by a specialized specialist on an individual basis, depending on the severity of the injury, the clinical picture and other factors. The duration of therapy largely depends on how quickly after the fracture the person consulted a doctor. If he decides to visit after the bone has begun to heal, then in this case you can’t count on a quick recovery.
Doctors first send patients for a two-projection x-ray, which will provide information about:
- fault lines;
- base of the foot;
- central section of the tubular bone;
- condition of the neck or head;
- the presence or absence of bone displacement.
Based on all the data obtained, the doctor can determine the patient’s condition and select a suitable therapy program for him. In most cases, the following treatment regimen is prescribed:
- Applying a plaster cast to the lower limb.
- Giving the bone the correct position.
- Restoration of bone fragments using surgery and their fixation with special parts.
- Putting a plaster cast on the leg.
Throughout the entire treatment period, the patient is advised to minimize physical activity on the injured limb. He is also prescribed medications containing calcium and vitamin D, which are necessary for rapid bone healing and a speedy recovery. In addition, an orthosis may be installed on the leg. This is a special device made from modern materials with high strength and low weight. It is designed to reduce the load on the leg when moving.
Surgery for a metatarsal fracture
The indication for surgery for a fracture is displacement of metatarsal bone fragments by more than half the width of the bone.
Percutaneous pin fixation
It has been popular for many years and continues to be one of the most popular methods internationally.
First, the doctor closes the displacement of the fragments, then wires are drilled through the fragments in certain (taking into account the nature of the fracture) directions.
Pros: low trauma, speed, ease, low cost, absence of an incision and, as a consequence, a postoperative scar.
Disadvantages: the ends of the wires remain above the skin so that the wire can be removed after the fracture has healed; the risk of wound infection and penetration of infection into the fracture area; long-term wearing of a plaster cast for 1 month; inconveniences in everyday life.
Open fracture reduction
Open reduction for a fracture of the metatarsal bone of the foot, external osteosynthesis with a plate and screws. The operation involves a surgical incision, access to the broken metatarsal bone by carefully retracting the tendons, vessels and nerves, mobilization of bone fragments, elimination of displacement and fixation in the correct position.
Plaster immobilization is not carried out, since the metal structure fixes the fragments.
Walking with support on the heel area is allowed for a month.
ethnoscience
Fractures can be treated not only with the help of modern, but also traditional medicine. However, it is important to understand that decoctions alone cannot do this. It is best if the therapy combines various methods. Qualified experts advise using folk methods that will act as auxiliary measures. To speed up the process of bone fusion and reduce pain, you can take various herbal tinctures and decoctions.
The following recipe is very effective:
- ground comfrey root - 1 tbsp. l.;
- water - 200 ml.
The medicinal plant is poured with boiling water, allowed to cool completely and the decoction is taken one tablespoon three times a day for a month. Some people rub the injured limb with warming ointments and alcohol tinctures, but this is strictly prohibited, as this increases blood flow to the leg and increases pain.
Rehabilitation after a metatarsal fracture
As soon as the fracture of the metatarsal bone heals and the pain decreases, the doctor will allow you to step on the foot in doses and gradually increase the load.
Don't self-medicate!
Only a doctor can determine the diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment. If you have any questions, you can call or ask a question by email.
| Treatment of foot fractures | Price, rub |
| Manual reduction | from 2 500 |
| Applying a plaster cast | from 1 500 |
| Osteosynthesis (excluding metal structures) | from 38 000 |
| Local anesthesia | from 700 |
| Conduction anesthesia | from 3000 |
| Dressing, suture removal | from 500 |
| To the list of articles | Calcaneal fracture |
Possible complications
If you do not seek medical help in a timely manner, an injury can lead to various consequences:
- Bone deformations, which limit movement, complicate the selection of shoes.
- With an intra-articular fracture of the fifth metatarsal, arthrosis may develop in the area of injury over time.
- If the fracture is a fragment, and the bones have not been reset into place, then during healing, an angular deformity of the foot develops.
- Chronic foot pain.
- Rapid leg fatigue.