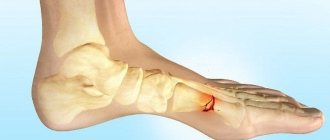
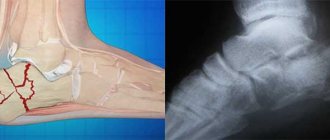
The heel bone in the arch of the foot breaks quite rarely, especially on both sides. The main cause of a fracture is often a strong blow to the heels or a fall on the feet from a height. Often such an injury is combined with a fracture in the thoracic and lumbar spine or ankle joint.
After completion of the recommended treatment, a long period of rehabilitation is required. An orthosis for a fracture of the calcaneus can significantly facilitate and speed up the recovery process.
Mechanism and causes of fracture
The heel bone is rightfully considered the largest bone of the foot. When walking and standing, it bears most of the load and acts as a shock absorber. According to anatomical data, it is customary to distinguish the body and the tubercle located behind it. In front, the bone has a connection with the cuboid bone, and above with the talus.
It is the talus bone that directly connects the heel and shin bones to each other. In the event of a jump to the feet or a high-altitude fall, the weight of the entire body is transferred to the ankle, and through it to the talus. The result is its wedging into the heel bone, followed by splitting the latter into pieces.
The fracture and its type, the nature of the displacement of fragments directly depend on the position of the foot and the height of the fall. Another cause of fractures can be bone compression due to an accident or constant physical activity in professional athletes. A fracture due to a blow to the heel bone with a massive object is much less common.
Anatomy of the foot
Let's start by deciphering some terms.
Tarsals are small bones located between the tibia and metatarsus.
Metatarsus - bones of the foot between the tarsus and phalanges.
So, the foot consists of the bones of the tarsus, metatarsus and phalanges of the toes. There are only 27 bones. The rear supporting point of the foot is located in the tarsus, one of the largest and strongest bones in our body - the heel bone. It is attached to the tendons and muscles of the foot. The joint work of tendons, muscles and the bone itself ensures the normal position of the latter and its correct movements when necessary.
In cases of bone fractures, in addition to its anatomical structure, the balance of forces that act on it also changes. As a result, long-term and possibly lifelong functional impairment occurs.
Classification
All calcaneal fractures are usually divided into two large groups:
- extra-articular fractures: tubercles (horizontal, vertical, separation of the median tubercle, “beak” type), body;
- intra-articular: compression, isolated, marginal, with and without displacement of fragments.
We should not forget that a fracture often leads to damage to surrounding tissues. Based on this feature, fractures are classified into closed and open.
Indications for heel osteosynthesis
Medicine recommends osteosynthesis of the heel in case of displacement of bone fragments and other cases. These may be open fractures, when urgent surgical intervention is required to disinfect the wound and remove particles of soil, dust, etc. that have gotten into it. It is possible that scraps of tissue from the insole, pieces of sole, and stones may get into the wound. All this debris must be removed.
In case of an avulsion fracture, surgery is required as soon as possible. This injury is rare. This happens due to the traction of the Achilles tendon. It is attached to the heel bone and sometimes comes off along with a piece of bone. Only the earliest possible surgical intervention can reduce the risk of skin damage in this area of the limb.
Symptoms
The main complaint with a fracture in the heel is pain. During the examination, pronounced swelling is noticeable, extending all the way to the Achilles tendon. Other symptoms include:
- change in the shape of the foot in the heel area (expands and flattens);
- presence of hemorrhage (occupies the center of the sole);
- pain on palpation;
- preservation of movements in the ankle joint (if it is not broken).
A characteristic sign is the fact that the patient cannot stand on his foot.
Important! Calcaneal fractures often go undetected due to concomitant spinal or ankle injuries. In this regard, all patients whose injury is associated with a fall on the foot should be examined for the presence of this fracture.
Diagnosis and treatment
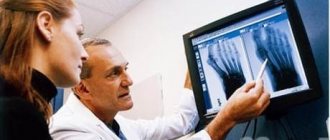
To diagnose a heel fracture, in addition to collecting complaints and the presence of injury, an external examination and additional research methods are important. Radiography in three projections is of key importance. The nature of the damage is judged by the change in the angle of the heel bone (Behler angle).
For a non-displaced fracture, conservative therapy is indicated by immobilizing the affected limb with a plaster cast. It is applied for at least three weeks from the toes to the knee joint. If there is displacement, the treatment tactics change - reposition is performed under local anesthesia.
Particular attention is required to comminuted fractures that accompany damage to the articular surfaces of the talus and calcaneus and significant displacement of bone fragments. If necessary, an Ilizarov apparatus can be used.
When a false joint is formed between bone fragments, a three-joint resection operation with additional excision of the bone plates of each fragment is necessary. Then all parts are connected to each other using a special screw. The next step should be competent rehabilitation.
Important! Regardless of the type of fracture, its severity and method of treatment, resting on the injured leg is strictly prohibited. This will not only worsen the condition and prolong the recovery period, but may also lead to displacement of bone fragments.
Osteosynthesis of the calcaneus
Treatment of the calcaneal bones is carried out mainly by plate osteosynthesis. This method allows you to restore the correct position of bone fragments and securely fix them. Such operations require a great deal of experience because one of the characteristics of this injury is the formation of many small fragments. To treat a fracture, all the fragments must be collected in the right order, restoring the original shape of the heel bone.
Osteosynthesis of the calcaneus refers to operations performed to openly eliminate displacement and secure bone elements using screws or plates for osteosynthesis of the calcaneus . Indications for surgical intervention are the diagnosis of fractures:
- compression;
- comminuted;
- with displacement of fragments;
- with deformation and change in the shape of the joints;
- with unsuccessful double reduction in a closed form;
- secondary displacement.
During surgery, the patient is placed on his side and an external incision is made. The postoperative period lasts 2 weeks, which the patient spends with a plaster cast. Rehabilitation is carried out after removal of the cast; recovery time is from 8 to 12 weeks. Below is a more detailed description of bone and calcaneal joint restoration.
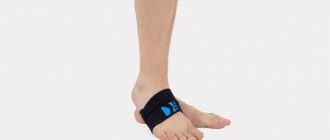
Using an orthosis
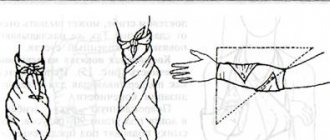
To speed up the recovery period for heel fractures, it is often recommended to use a special ankle joint brace called the 28f10 heel-off-load orthosis. Orthoses are commonly called external therapeutic and prophylactic devices used for injuries to the musculoskeletal system.
The devices can consist of an elastic fabric with additional inserts or special materials (turbocast), which provide the entire structure with the necessary rigidity for maximum fixation. They are often equipped with lacing or straps.
Advantages of using orthoses for heel fractures:
- allow you to support the longitudinal arch of the foot by covering the metatarsal bones and transferring part of the support to the ankle;
- provide reduction of loads on the heel bone;
- allow the foot to roll, similar to the physiological one;
- help reduce pain and shorten rehabilitation time;
- help quickly restore motor activity;
- reduce swelling in the lower limb and minimize muscle atrophy.
When wearing an orthosis, the foot is in almost a physiological position, which is a good prevention of complications in the form of flat feet.
This device allows for active movements that increase blood flow. As a result, the risk of post-traumatic osteomyelitis, arthrosis and osteoporosis is reduced.
Another undeniable advantage is the ability to independently remove the brace from your leg. For example, to wash a limb. The clamps weigh a little and do not cause any inconvenience. In the orthosis, you can walk without crutches and freely apply a variety of ointments. You can walk freely in it and even ride a bike.
Terms of use
Basically, an orthosis for heel fractures is necessary during the period of treatment and rehabilitation measures, which on average last about three months. It is often prescribed after the cast is removed to speed up the recovery process.
Important! All orthoses are sold disassembled; their direct fitting to the leg and assembly must be carried out exclusively by a specialist.
The use of a retainer requires compliance with certain rules:
- used only with the permission of the treating doctor;
- the size is selected individually;
- application is possible only in the absence of plaster, open wounds or swelling;
- Gradually, the load on the leg can be increased, guided by the recommendations of the treating doctor and the instructions for the brace;
- While wearing, you should put a load on the affected limb, but only in the absence of pain.
Materials and manufacturing features
In the production of orthoses, materials are used containing:
- Elastic elements;
- Metals;
- Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA);
- Carbon fiber;
- Textile;
- Thermoplastic.
Models made from a combination of several components are popular.
Traditionally, before making an orthosis, the limb is measured and its contour is created. This ensures maximum efficiency from using the device.
First, a plaster mold can be made. It serves as the basis for the production of the orthosis. Then, using the plaster sample, an orthosis is made from plastic or other materials.
The latest orthopedic production uses devices with various automated systems. The module prepares a special program for computerized production. The devices are equipped with three-dimensional printing and CAx computer-aided design systems (CAD, CNC, CAE/CAD/CAM).
The use of computer technology makes it possible to produce orthoses with maximum compliance with individual shapes. The 3D printing method is combined with different materials. In the production of orthoses, polymer gypsum (USA), low-temperature plastic (Netherlands), and polylactide (Russia) have been used.
Recovery period
The rehabilitation period for a fracture in the heel bone should include a full range of measures:
- massage;
- physiotherapy;
- physiotherapy;
- proper nutrition.
The main objectives of all procedures are to improve blood supply to damaged tissues, quickly eliminate signs of inflammation and accelerate regenerative processes. For this, massage sessions with cedar oil, thermal procedures with ozokerite and regular exercises with rising on your toes and then lowering onto your heels will be useful. Warm baths with sea salt have worked well.
As a balanced diet for a heel fracture, foods high in vitamin D, calcium, phosphorus, silicon, copper and zinc will be useful. These can be dairy and fermented milk products, sea fish, meat broths, legumes, eggs, potatoes and bananas.
Possible complications
If therapy is not started in a timely manner, all doctor’s instructions are not followed, or severe cases of heel fracture, the likelihood of complications increases several times. Possible problems include:
- flat feet of a post-traumatic nature;
- development of arthrosis in the area of the subtalar joint and the joint formed by the talus and navicular bones of the foot (Chopard);
- pain when putting pressure on the foot;
- formation of heel spurs and bone protrusions;
- violation of support.
With chronic fractures, there is a high probability of deformation of the foot, an increase in the transverse dimensions of the heel bone, and the inability to actively move the thumb of the lower limb, and in especially severe cases, all the toes on the foot.
From all of the above, it becomes clear that heel fractures are a serious injury that requires a careful approach and appropriate treatment.
Good to know about this
After observing patients with various heel fractures, orthopedists and surgeons made quite important conclusions:
- With closed simultaneous reduction and in the case of a comminuted fracture, there is a high probability of subsequent disability.
- For a specific and accurate picture, radiography should be performed in five projections and, if possible, in a high-profile specialized institution.
- Skeletal traction should be used only as a preparatory step for a three-joint resection operation.
- Relief from chronic pain and complete restoration of supporting function is possible after surgery for resection of the talocalcaneal and Shopar joints.
Restoring sensation and motor activity to the fingers of the lower limb is possible by cutting the long extensors.
On a note
It must be remembered that after the final restoration of all functions of the lower limb in the foot area after a fracture, there is no need to immediately stand on heels or wear tight and narrow shoes.
For six months, preference should be given to orthopedic shoes with appropriate instep support. In some cases, this period lasts up to a year.
If flat feet or shortening of the foot occurs, it is necessary to make special shoes based on casts of the foot. It will be useful to visit a specialized sanatorium for spa treatment and follow the principles of proper nutrition for at least six months.
The heel bone is quite strong, it is not easy to break it, but if it is broken, serious problems will arise, since movement will simply become impossible. Do not assume that the capabilities of the human body are limitless, exposing the body to excessive stress. Even a broken bone can change your quality of life for the worse. It is worth taking care of your body and directing your strength in the right direction.
Step-by-step plan for using an orthosis
The treatment plan provided is indicative. The step-by-step order was compiled through the processing of many years and numerous statistical data.
This is a brief description of the step-by-step application of a heel orthosis.
- 8 – 12 days. The stitches have been removed, the swelling has gone down, and the orthosis is being adjusted. Loading of the injured limb with the use of crutches is allowed. The patient adapts to walking in a heel orthosis. It is recommended to give up crutches as quickly as possible;
- Week 4. The 1st X-ray control is carried out. Usually the following are examined: the lateral projection of the ankle joint, the same projection at maximum load, specifically the calcaneus;
- Week 6. The 1st load liner is used;
- Week 8. The 2nd x-ray control is carried out. A 2nd load liner is used;
- Week 10 A 3rd load liner is used;
- Week 11 The anatomical and functional state of the feet is studied (plantography, plantogram). If necessary, orthopedic shoes are made (within 4–6 days);
- Week 12. The final stage of treatment. The patient is tested for performance (if there has been a work-related injury).
The decision to start using a heel orthosis is made by the attending physician. In each specific case, the doctor independently decides when to move to the next stage of treatment.