Foot orthoses are special devices that help prevent joint deformation and relieve tension in muscles and ligaments. Orthosis is the general name for devices that are used in the treatment and restoration of certain parts of the musculoskeletal system. Orthoses are used to treat the lower back, foot, hip, knee and other joints. The device is prescribed by a traumatologist or orthopedist.
When you contact a doctor at the Yusupov Hospital, you can receive qualified advice on the types and purposes of orthoses. After examination and examination, the doctor will be able to select the most suitable product and give advice on where it can be purchased. At the Yusupov Hospital you can undergo rehabilitation after various diseases, injuries, and get advice from a neurologist, orthopedist, surgeon, psychiatrist, and other specialists.
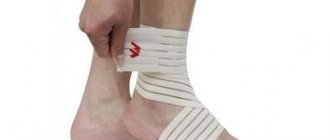
Foot support orthosis for foot drop
Foot drop is a pathological condition in which the foot cannot bend upward or downward. Various diseases lead to this condition: stroke, arthritis, neuritis, myopathies, paralysis of the leg muscles, damage to tendons and muscles, and the development of an inflammatory process in the tissues of the lower limb. An orthosis for foot drop helps the foot to be in the anatomically correct position. An orthosis for a drooping foot fixes the ankle, a rigid fixation immobilizes the foot and ankle joint. The load in this case is compensated on the back of the foot. Conditions are created to restore flexion function and roll of the foot.
An orthosis for fixing the foot is used for chronic instability of the ankle joint, injury during which ligaments are torn or sprained, when performing surgical operations in the area of the ligamentous apparatus, and during ankle replacement. An orthosis for a drop foot consists of a splint that secures the ankle at the back and a support pad. The foot support anatomically follows the curve of the foot, the foot is correctly fixed and secured. The drop foot orthosis can be used for a long time, it is lightweight, and can be worn with regular shoes.
Advantages of orthoses for metatarsal fractures
- Unlike plaster, the retainer is easy to put on and remove when necessary, and does not cause skin itching.
- The product supports the leg structures in an anatomical position, relieving damaged areas from harmful loads.
- The bandage copes not only with the treatment of fractures, but can be successfully used for sprains, bruises, and strokes.
- The orthosis for a metatarsal fracture has a rigid degree of fixation. For convenience, it is equipped with fixing straps, with which you can set the level of pressure on the leg.
- The use of a fixative reduces inflammation and swelling, reduces the intensity of pain, and improves well-being.
- Orthopedic products are made from technologically advanced hypoallergenic materials that do not rub the skin and prevent the formation of diaper rash.
- The orthosis for a metatarsal fracture is simple and easy to use: you can quickly put it on and take it off yourself without assistance.
- Using the product increases confidence when stepping on your foot, and also allows you to experience less discomfort when walking.
- The products do not require special care. If dirt appears, just wash it in warm water and soap and dry it in a dry, dark place.
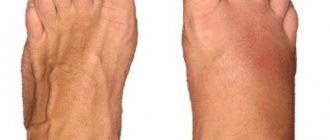
Big Toe Orthosis
A big toe orthosis is required for grade 1 hallux valgus deformity. This allows you to stop the progression of bone deformation. Deformation of the foot leads to deviation of the toe to the side, the appearance of a bump, which changes the shape of the foot, causes discomfort when walking, and brings discomfort while wearing shoes. The orthosis is selected depending on the purpose (treatment, prevention, rehabilitation) and the degree of joint damage. A big toe brace helps to move and support a crooked toe into its normal position. You have to wear an orthosis at the initial stage of finger curvature from two months to a year. With further progression of the disease, wearing a thumb orthosis is ineffective.
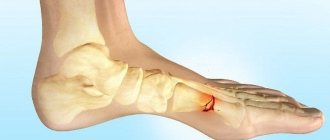
Symptoms of a 5th metatarsal fracture
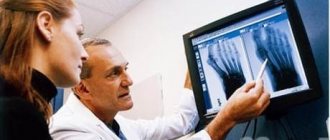
At the moment of fracture, you can hear a crunch and feel a sharp pain. The foot may swell greatly; less often, swelling and pain are located only in the projection of the base of the bone. Stepping on, moving or touching your foot also hurts. Without an x-ray, it can be difficult to distinguish such an injury from a banal ligament tear or a serious bruise.
The symptoms of a stress fracture are often vague. Aching pain and slight swelling along the outer edge of the foot may bother you. When bone strength is reduced to a minimum, a complete fracture may occur with the typical picture of an acute injury: severe pain, swelling, and impaired function of the foot. As in the case of a traumatic fracture, diagnosis cannot be done without radiography.
Treatment Options
The easiest to tolerate is an avulsion fracture of the styloid process. As a rule, the foot is fixed with a plaster cast or a polymer orthopedic boot for a period of 2 to 4 weeks. If the pain syndrome is insignificant and the patient does not engage in heavy physical labor or sports, early exercise in the orthosis is acceptable - walking with support on the injured leg. In athletes, due to increased demands on the condition of the feet, treatment is more strict, sometimes including surgery - osteosynthesis.
Due to poor blood circulation and heavy load when walking, a fracture of the base of the metatarsal bone (Jones fracture) heals extremely poorly. A frequent complication is the formation of a false joint, secondary displacement of fragments. The duration of immobilization varies from 6 to 12 weeks. If during the first month there are no signs of fusion in the orthosis or cast, it is recommended that the fragments be surgically compared with further fixation with a screw, pin or plate.
Foot orthosis for metatarsal fractures
A fracture of the toes or metatarsals of the foot is an indication for the appointment of an orthosis. In case of a fracture of the metatarsal bones, a rigid immobilizing fixator is recommended, which looks like a boot, then a semi-rigid orthosis, the semi-rigid one is replaced with a soft orthosis. Fractures of the metatarsal bones can be non-displaced, displaced, or Jones fracture. They can be open or closed, and vary along the line. Treatment for a fracture depends on its complexity, and in some cases surgery is required.
Most often, when the metatarsal bones are fractured, a plaster cast is applied. In case of a fracture of the 5th metatarsal bone, after removing the plaster cast, an ankle orthosis is worn; after removing the orthosis, a bandage for the metatarsophalangeal joint is used for some time to avoid complications during exercise therapy. When should the plaster cast be removed and replaced with an orthosis, what type of product will be needed, and after what time the orthopedic surgeon decides to change the type of orthosis.
Orthoses for metatarsal fractures
To treat and prevent metatarsal fractures, doctors around the world recommend their patients to use an orthosis.
An orthosis is most often a rigid base that limits the mobility of the foot and fixes it in a stable position - optimal for fusion of bones. The metatarsals are located in the midfoot and connect the toes and tarsals. Injury is often accompanied by painful swelling, severe pain and discomfort when walking. The symptoms are similar to those of a sprain, and a fracture can only be accurately diagnosed with x-rays.
Buy a foot orthosis in Moscow: price
The cost of foot orthoses depends on the manufacturer, the material from which it is made, and the complexity of the design. The cost of an ankle orthosis (made in Germany) is from 3,500 rubles and above, a foot holder for a sagging foot costs 4,000 rubles and above, an orthosis for a sagging foot made of carbon costs over 30,000 rubles.
At the Yusupov Hospital, the patient will be able to undergo diagnosis of foot diseases, examination and treatment for fractures of the metatarsal bones. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital will provide qualified assistance for fractures of the foot bones and select the required orthosis during the recovery period. In the rehabilitation department of the hospital, patients with diseases of the tendons and joints of the foot, after a fracture of the bones of the foot, will be able to undergo rehabilitation therapy. A rehabilitation specialist will draw up an individual program of physical therapy exercises. At the rehabilitation clinic you can undergo various types of physiotherapeutic procedures and massages. You can make an appointment with a doctor by calling the Yusupov Hospital.
Fractures of the foot bones
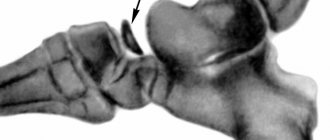
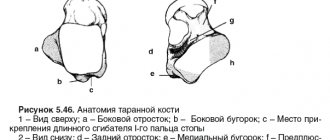
Fractures of the talus
The talus has features that distinguish it from the other bones of the foot.
Firstly, the pressure of the entire weight of the human body is transmitted to the foot through the talus. Secondly, the talus is the only bone of the foot to which no muscle is attached. Thirdly, the talus plays a significant role in the formation of the arches of the feet. Fractures of the talus are rare in traumatology (about 3% of the total number of fractures of the bones of the foot), belong to the group of severe injuries to the bones of the foot and are often combined with other injuries (fractures of the ankles, dislocations of the foot, fractures of other bones of the foot). There are fractures of the body, head, neck, lateral or posterior edge of the talus.
Fractures of the talus are most often the result of indirect trauma (twisting the foot, jumping, falling from a height). Less commonly, the cause of injury is compression of the foot or a direct blow from a heavy object.
Symptoms
The patient complains of sharp pain in the damaged area. The foot and ankle joint are swollen, hemorrhages are visible on the skin, mainly in the area of the inner ankle. When fragments are displaced, deformation is revealed. Movement in the ankle joint is almost impossible due to pain.
Sharp pain is detected when palpated at the level of the joint space, and with neck fractures the pain is more pronounced in the front, and with fractures of the posterior process - along the posterior surface outward from the Achilles tendon.
To confirm a fracture of the talus, determine its location, and identify the nature and degree of displacement of the fragments, radiography is performed in 2 projections.
Treatment
In case of a displaced fracture, urgent reduction of the fragments is indicated. It should be taken into account that as the age of the injury increases, comparison of bone fragments becomes very difficult or even impossible. Failure of closed reduction is an indication for open reduction or skeletal traction.
For fractures of the posterior process, plaster is applied for 2-3 weeks, for other fractures of the talus - for 4-5 weeks. From 3-4 weeks, the patient is recommended to remove the injured leg from the splint and make active movements in the ankle joint.
Subsequently, exercise therapy, massage and physiotherapy are prescribed. Restoration of working capacity occurs after 2.5-3 months. For a year after the injury, patients are recommended to wear arch supports to prevent traumatic flat feet.
Scaphoid fractures
This type of foot fracture usually occurs as a result of direct trauma (a heavy object falling on the back of the foot). Less commonly, the cause of a scaphoid fracture is compression between the sphenoid bones and the head of the talus. Often, scaphoid fractures are combined with other fractures of the bones of the foot.
Symptoms
Support on the leg is limited due to pain. Swelling and hemorrhages are detected on the dorsum of the foot. Palpation of the navicular bone, rotation of the foot inward and outward, as well as abduction and adduction of the foot cause sharp pain in the area of the fracture. To confirm a fracture of the scaphoid, an x-ray of the foot is performed in 2 projections.
Treatment
For fractures of the scaphoid without displacement of bone fragments, the traumatologist applies a circular plaster cast with carefully modeled arches of the foot. For displaced fractures, reduction is performed. If the fragments cannot be reduced or retained, open reduction is performed. Fixation with a plaster cast is carried out within 4-5 weeks.
Fractures of the cuboid and sphenoid bones
The injury is usually caused by a heavy object falling on the back of the foot. The soft tissues in the area of injury are swollen. Pain is detected when palpating, pressing, or turning the foot inward and outward. To confirm this type of fracture of the foot bones, radiography is of great importance. Treatment is a circular plaster cast for a period of 4-5 weeks. For a year after such a fracture of the foot bones, the patient must wear an arch support.