Therapeutic exercises have long been considered an effective way to combat the symptoms of a hernia at any stage of its manifestation. Surgical intervention is used very rarely, and therefore, the main trump card in the medical tactics of treating a hernia is a set of gymnastic exercises developed and successfully patented by Dr. Bubnovsky.
Spinal hernia has long been a common problem in medicine, and more and more people are faced with such an unpleasant disease. It can affect different parts of the spine, causing not only unpleasant symptoms, but also in advanced form, significantly worsening the quality of life.
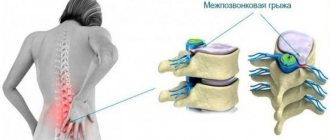
Spinal hernia
The term intervertebral hernia means displacement of the nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral disc, followed by rupture of the fibrous ring. Hernias of discs in the intervertebral space of the sacrolumbar region are more common, approximately 150 cases per 100,000 population per year.
Less commonly, hernias form in the cervical spine, and even less often in the thoracic spine. In 48% of cases, hernias are located at the L5-S1 level of the sacrolumbar region, in 46% of cases - at the L4-L5 level, the remaining 6% at other levels or at several levels of the sacrolumbar region.
Hernias of the spinal column are characterized by very unpleasant symptoms, depending on their location, size and shape.
Types of vertebral hernias are discussed in more detail in the second part of the material.
Causes of pain
The connection between gastrointestinal diseases and back pain can be explained by the following reasons:
- Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum. Most often, stomach pain radiates to the back with a penetrating gastric ulcer. Middle-aged and elderly men are more likely to experience this pathology. Predisposing factors include poor nutrition, frequent exposure to stress factors, and alcohol abuse. Hereditary factors play an important role in the development of gastric ulcers. In addition, long-term use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, reserpine, glucocorticosteroids, acetylsalicylic acid, and caffeine can provoke the development of stomach ulcers. In 80% of cases, stomach ulcers develop under the influence of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, which in the process of its life disrupts the protective mechanisms of the gastric mucosa and makes it vulnerable to an acidic environment. With a gastric ulcer, pain in the back is most often localized in the lumbar or thoracic region. Unlike diseases of the spine, with a gastric ulcer the pain is localized not only in the back, but also directly in the area of the stomach. Painful sensations occur 30-60 minutes after eating, as well as at night, between 23 and 3 am. In addition to back pain, symptoms such as heartburn, belching with a sour taste, nausea, vomiting, and chronic constipation indicate a violation of the functional state of the stomach. The period of exacerbation of gastric ulcer occurs in the off-season.
- Acute cholecystitis. Acute inflammation of the gallbladder often occurs due to stagnation of bile, followed by the formation of gallstones. The secondary causes of acute cholecystitis include bacterial infection (Escherichia coli, staphylococci and streptococci). The main signs of acute cholecystitis include acute pain in the right hypochondrium, as well as pain that spreads to the subclavian region on the right side, shoulder, lower back, scapula, and abdomen. Additional symptoms of this condition include fever, nausea, and general weakness. When the disease is advanced, yellowing of the skin and tension in the abdominal muscles are observed. In laboratory tests, an acceleration of ESR is observed. Treatment of acute cholecystitis in 80% of cases is carried out surgically. If this condition occurs in a gangrenous or purulent form, then the gallbladder is removed.
- Chronic pancreatitis. With a chronic inflammatory process in the pancreas, the process of enzyme production is disrupted, which affects the general condition of a person. Pain in the gastrointestinal tract that radiates to the back and may indicate problems with the pancreas.
Characteristics of pain
A hernia of the lumbar spine is characterized by severe pain. It can be aching or dull in nature. The pain can be so severe that body movements are severely limited, pain intensifies when coughing, standing or sitting. Relief occurs only in a lying position, when there is no load.
When making any movements in the presence of a herniated spine, for example, changing body position or sudden movements, acute shooting pain occurs in the lumbar region.
If the fifth lumbar vertebra is damaged, the pain syndrome is localized in the big toe of the lower limb. If the hernial protrusion is located between the sacral and lumbar vertebrae, then the pain is localized in the sacral region, the back of the leg.
Sacrolumbar hernia is very dangerous for women, since the pelvic organs are located nearby. If a hernia of the lumbar spine occurs, circulatory problems in these organs may begin, which can subsequently lead to disruption of the menstrual cycle, as well as chronic diseases of the uterus.
Due to the pathology of the spine, the smooth muscles of this area are very tense. With prolonged stress, curvature of the spine is possible.
With an intervertebral hernia of the lumbar region, compression of the nerve roots occurs. This leads to loss of skin sensitivity, which is manifested by dry skin.
The pain syndrome increases over time, and the mobility of the torso decreases sharply. Sometimes, the problem is so serious that a person’s knee reflex may temporarily disappear and the sensitivity of the big toe may disappear. In the future, the disease can lead to paralysis of the lower limbs.
Other hernia symptoms
Clinical manifestations of degenerative changes in the intervertebral disc in the lumbosacral spine:
- local pain in the projection area of the affected disc - in the lumbosacral region (lumbodynia), intensifying with exercise;
- pain radiating to the buttock, along the posterior, posterior surface of the thigh and lower leg on the affected side (ischalgia), numbness and tingling in the area of innervation of the affected roots, weakness in the lower limb;
- weakness and loss of sensation in both legs;
- dysfunction of the pelvic organs - urination, defecation and potency, numbness in the perianogenital area.
Clinical manifestations of degenerative changes in the cervical spine:
- pain radiating to the shoulder or arm;
- dizziness;
- rises in blood pressure;
- a combination of headaches with high blood pressure and dizziness;
- numbness of fingers.
Clinical manifestations of degenerative changes in the thoracic spine:
- constant pain in the thoracic region when working in a forced position;
- a combination of pain in the thoracic spine with scoliosis or kyphoscoliosis.
Diagnostics
If you have symptoms that raise suspicion of a lumbar disc hernia, you should consult a neurologist. The doctor collects anamnesis to determine the possible causes of the disease.
An X-ray examination will not provide an accurate picture of the disease, so patients are referred to undergo magnetic resonance imaging.
MRI allows you to determine the size of the hernial protrusion, the width of the intervertebral canal, the presence of protrusions, inflammatory changes and other pathologies of the spinal column.
Making an accurate diagnosis will allow you to determine treatment tactics in the future.
Diagnosis and treatment of hernias
If characteristic symptoms appear, you should consult a neurologist. For a detailed diagnosis, it is recommended to undergo an MRI of the spine. Accurate and timely diagnosis is an important key to proper hernia treatment.
Depending on the stage and level of the disease, treatment can be conservative or surgical . As a rule, both doctors and patients are interested in excluding surgical intervention.
Conservative methods used to treat this disease include the following:
- Motor methods (physical therapy and so on) help strengthen and develop muscle tone and increase immunity. Many exercises involve physical activity, and if done incorrectly, they can cause the condition to worsen. It is important to use this method carefully, under the supervision of a specialist.
- Manual methods. Manual therapy and acupuncture are often used for treatment. Please note that although these methods give good results in terms of reducing pain and pressure on the intervertebral discs, they cannot stop the pathological process that provoked the hernia.
- Physiotherapeutic methods. These are gentle therapeutic procedures: various massages, reflexology, ultrasound, ridge traction, and so on.
Each method has pros and cons. They are usually prescribed in combination. The specialist must create an individual program that will help eliminate the hernia without risk to health and with the maximum probability of getting rid of it.
Typically, a set of activities includes spine stretching, therapeutic exercises, massage and other special procedures. Not all techniques are available at home; for example, a number of physiotherapy procedures must be performed using special equipment. But the exercises are simpler - they can be performed at home. The Bubnovsky method has proven itself well for hernia of the lumbosacral spine. Sergei Mikhailovich Bubnovsky is a famous doctor with extensive experience in treating patients with hernia.
Treatment of lumbar hernia
Depending on the severity of the disease, a conservative or surgical method of treating lumbar hernial protrusion is prescribed.
The surgical method is rarely used, and in order not to resort to it at all, the correct methods of conservative therapy are used:
- Motor technique – strengthening the muscular frame, increasing the overall resistance of the body. Many exercises go in conjunction with training loads. To avoid deterioration of well-being, the motor technique is carried out carefully and under the supervision of a doctor.
- Manual method – undergoing treatment from a chiropractor and using acupuncture. The method is useful in relieving pain and improving overall well-being. But this method cannot stop the disease.
- Physiotherapy methods are gentle therapeutic procedures. These include various massage options, reflexology, and stretching.
As a rule, such methods are used in combination; doctors draw up an individual plan for the treatment and prevention of intervertebral hernias without significant risk to health.
The complex of medical measures includes three methods:
- Spinal stretch.
- Massages and special treatments.
- Physiotherapy.
Many experts recommend an effective and very affordable method - treatment and prevention of intervertebral hernia according to the method of psychotherapist Sergei Mikhailovich Bybnovsky.
However, many treatment methods, for example, physiotherapy, can only be performed in a specialized institution.
Adaptive gymnastics Bubnovsky
The doctor developed and approved a special technique, which is based on the treatment of spinal column pathology using a special device that he himself developed. The device is called the Bubnovsky multifunctional simulator. The treatment method is called kinesiotherapy, which means treatment through movement.
- The gymnastics complex consists of various exercises, which together are aimed at convenience, comfort and efficiency for the patient.
- When performing the exercise, each movement is repeated 10 times. Gradually the number and pace of approaches increase.
- It is important to ensure that when performing the exercise, the tension is concentrated on the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall, and not on the back muscles.
- It is recommended to perform the exercises three to six times a day, distributing the workouts into several groups.
- Also, Dr. Bubnovsky recommends a set of physical activities that can be done at home.
Thanks to statistics, it is known that every fourth person on the planet after thirty years of age suffers from acute pain in the back and joints such as osteochondrosis, lumbago, sciatica, sciatica . This is mainly manifested by rapid fatigue, joint stiffness, discomfort or pain in the back during prolonged sitting/standing, aching back pain at rest, reduced ability to work due to impaired mobility of the spine associated with degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs (protrusion, hernia, etc.). ).
The main causes of back and joint pain are a sedentary and unhealthy lifestyle, as well as prolonged stay of the body in uncomfortable positions from the point of view of physiology and biomechanics of the skeleton. This means that the spine and joints suffer due to the fact that we do not use our body correctly, distribute the load disproportionately, overload some anatomical links without including others. For example, a modern person, starting from the age of six, spends more than 6 hours a day in a sitting position (depending on his profession): we sit at a desk at school, at home watching TV, driving or at work at the computer, etc. Important factors are weight lifting, professional sports, as well as physical labor of a monotonous nature, which also overloads the same areas of the body. The spine or joint wears out and becomes more fragile due to the fact that muscles in a state of overwork cannot perform a protective function, and with increased loads, injuries and deformations of the skeleton can occur, leading to both acute and chronic pain in the back and joints. Therefore, we can conclude that pain in the back and joints is never accidental.
It is also worth noting that in order to prevent back pain, you should not stand bent over for a long time or read while lying in bed, or perform any non-standard actions. It is important to learn how to rationally distribute the load throughout the body, strengthen those areas that are not worked out in everyday life, and unload those areas that are overloaded due to the profession. Local and multifunctional strength and decompression simulators are excellent assistants in this regard. The simulators are designed according to the laws of skeletal biomechanics and, when used correctly, create conditions for high-quality muscle work.
Considering that there are about 700 muscles in the human body, and each of them must work in its own motor mode, you need to correctly navigate how to distribute the load so as not to overload a muscle or relax it if it is in spasm from overwork. Specialists in kinesitherapy have been dealing with these issues for more than 15 years (method of Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. S.M. Bubnovsky) and select individual recovery programs for people of various professions that help not only eliminate pain in the back and joints, but also significantly improve the quality of life. Treatment and health programs are compiled strictly individually, taking into account age, gender and the presence of concomitant diseases. By learning to use exercise equipment as a healing tool with the help of professionals, people free themselves from the need to take painkillers and gain knowledge that will help them further extend the life of their skeleton and gain freedom in movement.
The coordinates of the Centers can be found on the contacts page.
The essence of Bubnovsky's technique
The useful system is focused on the treatment of chronic orthopedic and neurological diseases of the spinal column, small and large joints without medications and the use of special corsets, as well as surgical interventions.
Bubnovsky designed the human body as a “three-story house” and based on this his method works:
- The first is the pelvis, legs and feet.
- The second is the back, chest, stomach.
- The third is the head, shoulders, neck.
By involving in the exercises the work of the muscular apparatus of the “ground floor”, that is, the lower extremities, the circulatory system is stimulated and its circulation improves from bottom to top.
Then, a group of muscles of the thoracic region and back is included in the work to eliminate pain. Afterwards, they begin to activate the muscular system of the cervical spine, shoulder frame and arms.
For a home workout routine, it is important to choose exercises that will help develop the spine and large joints and eliminate pain without the use of medications.
Bubnovsky exercises for hernia of the lumbar spine
The set of exercises is very simple to do independently at home. By performing training, you can eliminate pain, relieve muscle tension, stretch the spinal column, and speed up blood circulation in the affected area of the back. But to consolidate the result, it is important to complete the entire course using Dr. Bubnovsky’s simulator and be under the supervision of a doctor.
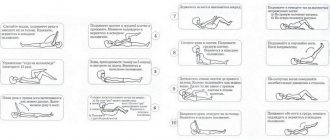
How to do the exercises:
(1) - Cat/Cow
Take a position on all fours. Rest your elbows and knees on the floor. Relax your muscles as much as possible. Take a deep breath and slowly arch your back. Then, slowly exhale and bend your back. Return to starting position. Perform 15-20 repetitions.
If the pain intensifies during movements, then temporarily do not perform this stage of the workout.
(2) - Gluteal bridge
Take a lying position on your back, stretch your arms along your body. Take a deep breath. Exhaling slowly, carefully lift your pelvis off the floor, resting on your feet and shoulders. Try to lift to the maximum height. As you inhale, lower your pelvis. It is recommended to perform at least 15-20 repetitions and then pause.
Gluteal Bridge
(3) — Complex for keeping the body tense
Starting position on your back, arms along your body. Raise your legs up, clasp your knees with your hands. Slowly raise your body. Press your chin to your chest. Then, release your knees without changing position and fix the position for a few seconds. It is not advisable to allow overvoltage. Repeat the exercise until you feel slightly tired.
(4) — Bend forward to hold the body from a position on all fours
Take a position on all fours. Move your body straight, that is, pull it forward, trying not to bend your arms at the elbow joint. At the same time, the shoulders move forward, the knees and palms remain in place. It is necessary to move forward until there is comfortable tension in the lower back. Hold the position for a few seconds and return to the starting position. Repeat the movement 15-20 times.
(5) - Scissors
Exercise "Scissors". Take a horizontal position on your back, arms at your sides, bend your knees slightly. Start with your legs slowly, without making sudden movements. Breathing should be uniform.
Exercise "Scissors"
(6) - Bicycle
Oblique crunches (or “Bicycle” exercise). Lie on your back. Place the left upper limb under the back of the head. Slowly move your right leg, bending it at the knee, to touch the elbow of your left hand. In the same direction, return to the original position. Perform 15 approaches on each side.
Exercise "Bicycle"
(7) - Walking on your buttocks
Take a sitting position on the floor. Place your hands behind the back of your head. Smoothly lift the left and right buttocks in turn, thus moving forward. Move backwards in the same way and take the starting position.
Massage techniques
Classic back massage technique.
The following techniques are used in classical massage:
- stroking - this is how the massage begins and ends, the movements are long and smooth, along and across the spine; such a touch is aimed at raising the temperature, improving the functioning of the circulatory system, calming and relaxing. Stroking also reduces pain and improves superficial circulation.
- rubbing - use your hands or thumb to make circles or spirals on your back, along or across your spine; This massage technique eliminates swelling, inflammatory exudate, hematomas and muscle tension,
- kneading - hands grab a fold of skin and gently lift it up; can only be used in certain places; it causes blood vessels to contract and dilate more intensively, which supports the functioning of the circulatory system and cleanses tissues of metabolic by-products. In addition, kneading allows you to stimulate muscles, increase their endurance and contractility, and speed up regeneration after training. The kneading method can be done with both hands, one or your fingers.
- patting - hands folded crosswise or in a teaspoon, quickly and intensely hit the body, avoiding bone locations (for example, shoulder blades); During a back massage, the kidney area is also avoided; tapping causes better blood supply to tissues and muscle contraction. During the marking process, the temperature increases and the pain decreases.
- vibration - causes the surface and deeper tissues to vibrate, speeds up metabolism, improves flexibility, increases muscle strength. Gentle tapping, in turn, relaxes the muscles, has a calming effect and relieves stress.
Relaxing back massage.
Performing a relaxing massage is not so difficult, just follow the instructions:
- To perform the massage you will need back massage oil. It can also be a regular body lotion or cream. Before applying the drug, warm it between your hands. Oil or lotion will reduce friction and increase pressure. In addition, the beautiful aroma will make your back massage even more relaxing.
- The patient should remove outer clothing, lie on his stomach and place his arms along the body. The body position should be comfortable for both the person being massaged and the massage therapist.
- Start the massage with gentle movements. Remember that slower, less intense movements are calming and relaxing, while faster movements are stimulating.
- Don't forget other parts of the body such as the neck, head, shoulders and buttocks. Massage each part of the body separately. The best technique for the buttocks and shoulders is circular kneading, which intensely relaxes tense muscles.
- Finish the classic massage with stroking - gentle but long-lasting. This will allow the person to relax for a longer period of time.
Exercises for pain with a hernia in the cervical spine
Therapeutic training can help restore circulatory blood flow through the vertebral arteries to the brain. You can have an impact on the back muscles and the vascular system by doing pull-ups.
(1) — Working with rubber
You need to sit on a chair. Perform traction movements using an expander (an exercise machine made of elastic rubber). The row is performed with the arms from side to side, that is, by stretching the machine as much as possible.
(2) - Knee push-ups
Now perform push-ups with emphasis on the knee joint. The torso should remain straight and in contact with the entire plane of the floor. Untrained people do 5 push-ups and a total of 10 approaches with a break of 3 minutes.
Exercises with expander and dumbbells
(1) — Sawing wood
Exercise “sawing wood” with emphasis on the knee joint. The expander is attached down the wall. Place your legs, knee and shin on a high bench, lean your hand against the wall. With the second hand, make movements towards yourself, away from you. This exercise uses the muscles of the cervical spine. Instead of an expander, you can use a dumbbell, lifting it from the floor and lowering it.
(2) - Pullover
Exercise “pullover”. To perform the exercise, you need to lie on a horizontal bench with your back along the bench, put your feet on the floor, and place your head as close to the edge of the bench as possible. At the starting point, the dumbbell is held with outstretched arms above the chest. As you inhale, lower the dumbbell behind your head without bending your arms until your arms hang below the level of the bench. Then, as you exhale, raise the dumbbell to the starting point.
(3) - Straightening the arm from behind the head
You need to sit on a bench, take one dumbbell in your hands, raise it above your head with your hand, bend your arm at the elbow and put the dumbbell behind your head from behind, lift it and put it back again. Repeat the exercise 15 times with each hand. All actions are performed slowly.
Important Exercises for Blood Circulation
Therapeutic exercises from this group help improve blood flow in the pulmonary and systemic circulation, the functioning of the heart muscle, and accelerate the absorption of nutrients into the bone and cartilage tissue of the spine.
Exercise #1 - Squats
Place your feet wider than your shoulders, point your toes to the sides, keep your back straight, stretch your arms forward.
Inhale and squat at an angle of 90 degrees, exhaling forcefully, straighten your legs. This must be repeated 10 times. It is advisable to learn how to perform 4 approaches in 30 days, and 10 approaches in six months.
During the exercise, you must monitor your pulse; a heart rate of no more than 140 beats per minute is acceptable. Check your heart rate zones using the Karvonen formula or mHR (220 - age.)
If after performing the exercise there is pain in the lower extremities, you can take a contrast shower or rub the muscles with a cold wet towel.
This exercise is not recommended for those with arthrosis of the knee joint.
Exercise #2 - Advanced Glute Bridge
Lie on your back, bend your legs and place them on a bench or chair.
Support your head with your hands or you can stretch it along your body. Take a breath.
As you exhale, slowly raise your upper back and reach your elbows towards your knees. It will be enough to lift your shoulder blades off the floor, retracting the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall.
Repeat 10 times.
To stabilize your heartbeat, it is advisable to lie down quietly.
Answers on questions
Bubnovsky S.M.:“First of all, DON’T PANIC!
No one has yet died even from acute back pain that “confines” them to bed. Haste in resorting to medications for acute back pain only masks the treatment process, delaying recovery. And the abuse of painkillers (NSAIDs) ultimately makes a person defenseless against any physical stress (load), turning off the body’s self-regulation function, so I suggest returning to reasonable and logical actions in case of acute pain.
If, as a result of acute back pain, the movement mechanism (musculoskeletal system) has been “turned off,” then this activity can be restored through simple movements.
- Lying on your back, arms extended behind your head, grasping the support. Raising both legs while exhaling (“HA-A” and through the pain) to the stomach. If it is very difficult, then alternately each knee. Next, gradually straighten your legs at the knee joints and move your legs behind your head until they touch the floor behind your head. 20 times or in series of 10-20 per set. This is a very important exercise. Subsequently, it should be performed on the horizontal bar. But the horizontal bar is already a projectile. In this way, we gradually stretch the entire spine - from the lower back to the neck. First with your legs bent at the knees, then with your legs straight until you touch the floor behind your head. I remind you of the rule: “Don’t be afraid of pain, step on it.” Exhaling into the pain with the correct movements will help you. And even if something “clicks” there, continue.
- Lying on your back, legs bent at the knees, feet on the floor, hands clasped behind your head in a “lock”, elbows directed towards your knees. Your legs can be placed with the calf part on the sofa (chair). As you exhale (again, “HA-A,” but sharper), try to touch your knees with your elbows, but it’s not necessary, the main thing is to lift your shoulder blades off the floor and point your elbows toward your knees. 100 times (you can do 6 times 20), or 100-80-60-40-20 (don’t be afraid of these numbers). The chin is constantly pressed to the chest. This exercise can be performed alternately with the previous one. The main task is to unblock the muscles of the thoracic spine. I do not recommend any kind of rotation and twisting for discogenic radiculitis in the acute stage. Only exercises along the body axis from top to bottom and bottom to top are possible. In the future, naturally, their arsenal should expand.
There are situations when these seemingly simple exercises are not possible due to a low pain threshold. In such cases, I recommend folding a wet, cold sheet into a narrow strip and lying with your spine on it, bending your knees. Absorb all the coldness of the sheet and try to complete these exercises. A cold sheet gives the effect of anesthesia, that is, pain relief. For those who find this difficult, let them remember the words of G. Hall cited above about the condition after the operation (if, of course, they want to return to normal life).”
Top
Healthy exercises for the spine
Physical therapy exercises can be used as a preventive measure for diseases of the spinal column, and if they exist.
The exercises are aimed at developing the deep muscular system, expanding the intervertebral space, relieving tension from the joints and intervertebral discs. Also, useful exercises help eliminate spasm of blood vessels and nerve roots, preventing the appearance of hernial tumors.
Complex for acute back pain
Therapeutic exercises will help improve blood circulation in the smooth muscles of the back, relieve tension, expand the intervertebral space, eliminating acute pain.
Exercise #1 - Walking on all fours
Take a pose on all fours, focusing on your knees and palms. Move slowly in this position until the pain subsides, about 10-15 minutes.
When moving, you need to take a deep breath. You should take stretched steps: hand to knee, left leg to right hand and vice versa. Sit on your left limb and simultaneously stretch your right one back. Try to pull your left leg forward as far as possible and lower yourself lower. Exhale at the final stage of the exercise.
When moving, you will probably have to overcome pain. It is recommended to perform 2 sets of 20 repetitions.
Exercise No. 2 - Crunches, knees suspended
Take a lying position on your back, bend your knees, put your hands behind your head. Inhale, and as you exhale, bend your body, lifting your shoulder blades off the floor, if possible. The knees must be pulled towards the elbows.
At the first movements, painful sensations are possible, but you should not be afraid. It is recommended to repeat the training until a burning sensation appears in the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall. When the movements become more synchronized, you can stretch your lower limbs when lowering your head onto the mat.
Exercise #3 - Glute Bridge
Take a lying position on your back, arms parallel to your body. Inhale and, as you exhale, try to lift your pelvis off the floor to create a high half-bridge. As you inhale, slowly lower yourself to the floor. Pause for 2 seconds and repeat the workout 25 times.
Exercise No. 4 - Walking on the buttocks
Take a sitting position on the mat, place your hands in front of your chest. Contracting the gluteal muscles, we begin to “walk” them back and forth for 20 minutes.
Exercise No. 5 - Hanging on the bar
Climb onto the bench, inhale, grab the horizontal bar with your hands, and as you exhale, pull your knees to your chest. Shooting pain may appear in the lumbar region, but do not be alarmed. Slowly lower your feet onto the bench, then onto the floor.
Exercises for back pain at home
Exercises for back pain
This article is especially useful for people who experience pain in the lower back and want to get rid of it as soon as possible. With the help of a full range of special exercises, you will strengthen the muscles of your back and abdomen, which will lead to a speedy recovery of your lower back.
Most often, people who try to get rid of back pain on their own come to different types of solutions, which leads not only to a merciless load on your body, but also to complications that only intensify the already unbearable pain. A set of exercises will help you master such a seemingly difficult task as getting rid of back pain.
The question involuntarily arises: “What are the causes of back pain?”
Let us briefly list the most common causes of this phenomenon:
- Excessive strain on the back and abdominal muscles;
- Lack of straight posture (as a result of the appearance of various diseases);
- Congenital abnormalities in the lumbar region.
The exercises, which are described in detail and illustrated below, can be performed both by people leading an active lifestyle and by those who, due to some circumstances, lead a predominantly sedentary lifestyle.
Let's move on directly to the set of exercises itself. They are divided into 4 blocks:
BLOCK No. 1 includes exercises during which the back muscles are stretched;
BLOCK No. 2 contains a whole set of exercises that are aimed at strengthening your back muscles
BLOCK No. 3 is the final one, its purpose is exercises that help strengthen the abdominal muscles.
BLOCK No. 4 contains exercises aimed at consolidating an existing result
Good advice: It is advisable to perform the exercises in the sequence in which they are presented on the PowerFit96.ru website (gravity boots, cuffs, Bubnovsky technique).
BLOCK No. 1: Stretching the back muscles
1) Stretching the deep back muscles through simple rolls.
This exercise is recommended for people recovering from a back injury. This is necessary to normalize the mobility of vertebrae that are pinched due to injury. If you feel unpleasant pain when rolling, then you should replace this exercise with simple rocking or freezing in a pose with your knees drawn up to your chest.
Directions for implementation: lie on your back, bending your knees and clasping them with your hands, then slightly tense your stomach and do 2-3 rolls back and forth. IMPORTANT: The back should be in the shape of a circle; there should be a complete absence of slaps when rolling. The entire spine should be involved.
Completion time: 30 seconds with 5 approaches and a short rest between completed series.
2) Stretching the deep muscles of the back, pressing the spine to the floor and spreading the legs bent at the knees to the sides.
Directions for implementation: lie on your back, bend your knees, while grabbing your shins with your hands. In this case, you need to point your tailbone down and try to press your back to the floor as tightly as possible.
Execution time: fixation of position for 2 minutes.
3) Stretching the deep back muscles while lying on your back, while leaning your legs along the wall (at a right angle).
How to do it: Lie on your back as close to your back as possible, then lift your legs and stretch them along the wall. Stretch your arms above your head and try to stretch, as shown in the figure below.
Execution time: fixing the current position for 2 minutes.
4) Stretching the deep back muscles in a reclining position.
Directions for execution: Lie on your back, then bend your leg at the knee and, grabbing one leg, try to stretch your forehead to your knee.
Time to perform: fix the position for 2 minutes, then take a short break and repeat the same on the other leg.
5) Stretch the deep back muscles in the “Stretching Cat” pose.
Directions for execution: We squat down, chin directed towards the chest, back arched, as shown in the figure on the left. At the same time, inhale and throw back your head so that your eyes see the ceiling, after which you should bend in the other direction - picture on the right.
Directions for execution: You can repeat the movements for 3 minutes, after which you should perform turns in different directions so that the head and pelvis turn in the same direction.
6) Stretch your back using a regular pillow. For those who find it difficult to perform rolls or other various exercises, a special technique has been invented to remove the disc from the spinal canal.
Directions for implementation: take 2 pillows, put one under the pelvis and the other under the stomach, after which you need to lie down on them.
Execution time: 3 minutes.
Among other things, there are also other types of stretching the back muscles and improving the health of the spine. For example, gravity boots, with which you can quickly and effectively cure a sore back, as well as stretch the spine. We will talk about gravity boots, cuffs, as well as the Bubnovsky technique at the end of this article, but for now we move on!
BLOCK No. 2: Strengthening the back muscles
1) A common exercise that is aimed at strengthening muscle tissue.
Directions for implementation: lie on your stomach and stretch out. Your arms should be extended along your body so that your palms touch the floor.
Number of repetitions: 3 sets of 5 consecutive lifts.
2) Exercise to increase the endurance of the back muscles.
This exercise is considered one of the most effective in the fight against pain in the lower back.
Directions for implementation: lie down with your stomach down, stretch your spine by moving your pelvis back, move your arms forward and raise your legs at the same time, after which you also raise your arms. Look at the picture below
This position must be maintained throughout the entire exercise. Moreover, you need to remember how many breaths you took, gradually increasing the number of breaths with each repetition.
Completion time: For each person individually - you need to look at how you feel.
There are also other options for performing this exercise:
- Hold your bent arms at chest level:
- Extending your arms along your body at the level of your shoulder blades:
Over time, your back muscles will become stronger, and the variations presented above can be performed one by one without interruption.
Proven fact: if you can hold one of the variations for 2 minutes, then back pain will leave you for a very long time! Once you reach this level, you can also try the following exercises:
- Each exercise should be performed in two directions.
3) After the pain has subsided, you should use exercises aimed at consolidating the achieved results:
- Maintaining the established pose with support on the foot of one leg.
This exercise should be performed only after warming up the back muscles.
- Maintaining the established position with support on the palms of both hands:
BLOCK No. 3: Strengthening the abdominal muscles
1) Bend forward from a sitting position. You should slowly lean forward while keeping your back rounded.
Directions for implementation: Sit down, bend your knees, placing them slightly wider than your pelvis. Slowly rounding your back, you should pull in your stomach and bend forward (move as far as possible). Picture below:
After this, without changing the position of your legs, lean back completely and lean your lower back to the floor. Picture below:
Number of approaches: 3 sets of 5 times (no jerks!).
2) Strengthen the longitudinal abdominal muscles. Your legs should be placed slightly wider than your pelvis, your knees bent, your back pressed to the floor. Lock your legs behind your head, then, without breaking the lock, rise (without jerking!) to your knees. Picture below:
Number of repetitions: 3 sets of 5 times.
If this exercise seems a little simple for you, then try to reach your knees from the starting position. Drawing:
Also try another variation: at the final stage, pull your bent knees to your forehead (Fig. 1). When lowering your body down, leave your legs straight and suspended (Fig. 2).
Directions for implementation: 5 approaches 3 times.
BLOCK No. 4: Consolidating the result
To completely relax all the muscles of the back and abdomen, it is recommended to perform fairly simple but very effective exercises:
- Exercise bridge.
Directions for implementation: lie on your back, bend your legs at the knees and lean on them, arch your back towards the ceiling and at the same time grab your ankles with both hands.
Execution time: about 1 minute is enough.
- Simple twists. This category of exercises will help you relax after a short, but very productive work. There are several variations of this exercise:
— Directions for implementation: lie on your back, while stretching your spine. Place the foot of your left foot on the foot of your right foot, and after inhaling, hold your breath. Turn your head and toes in different directions several times in a row. Drawing:
- After which you can safely change the position of your feet to the opposite and do the same, adding at the same time pulling your toes towards you. Drawing:
— We place our feet at a level slightly wider than the pelvis and perform the same twists. Drawing:
— The last exercise is to place your knees to the sides, while performing the same twists. Drawing:
*Each of the exercises presented in Block No. 4 is performed in both directions!
Exercises of this kind can be very useful if you do not have special machines for stretching and treating your back, but if you have such an arsenal, achieving the desired result can be much easier, faster and more effective!
The Powerfit96.ru website provides a full range of products for treatment and back stretching:
- Gravity Boots (Inversion Boots)
- Expanders from professor, as well as doctor of medical sciences Bubnovsky Sergei Mikhailovich
- Arm and leg cuffs
Intervertebral hernia, back pain, osteochondrosis, scoliosis, arthrosis, umbilical hernia, inguinal hernia, Coxarthrosis, gonarthrosis, Osteoarthrosis - all these diseases can be easily cured using our exercise machines at home!
Let's briefly go through each of them:
- Gravity Boots (Inversion)
This product category is innovation in the field of sports. With the help of inversion boots you can easily stretch your spine. If you have any back pain, then gravity boots will help you treat your back, hernia and other diseases.
All that is needed is an ordinary crossbar, which can be a horizontal bar (which, by the way, you can purchase on our website at the best price in the city with home delivery), or a tight joint. With the help of inversion boot hooks, you can hook yourself upside down and perform very simple yet effective exercises.
Several exercises that can be performed using gravity boots (recommendations from Professor Bubnovsky):
— Hands behind the head, raising the torso to the knees;
— Hands behind the head, twisting the torso to the knees;
— Arms along the body, lifting with hands touching the shin;
— Arms along the body, twisting with hands touching the shin;
— Hands at chest level, pull ourselves up to the bar with our knees.
- Expanders
Our website presents several models of expanders, including those from the famous Doctor of Medical Sciences Bubnovsky.
Expanders are designed for exercises on multifunctional exercise machines, horizontal bars, wall bars, or on a regular door at your home. (on the website you can buy: Bubnovsky mini exercise set, Bubnovsky midi exercise set, Bubnovsky maxi exercise set, Gala Sport heavy expander set, Gala Sport medium expander set, Gala Sport light expander set)
Bubnovsky's expanders will help the back muscles recover after an injury, go through the rehabilitation period after recovery, and cure a sore spine, as well as the back.
The most common exercises performed with expanders are swinging your legs forward, backward, left, right.
- Arm and leg cuffs
Surely all people knowledgeable in sports have heard about such a simulator as a crossover. With the help of arm and leg cuffs, you can perform many more exercises on the muscles of the legs, arms, back, and chest.
The cuff is put on the arm or leg, connected with a cable and attached to the exercise machine.
Most often, cuffs are used to swing the legs in different directions and raise the arms from the hip to above the head and back.
You can buy gravity boots, expanders, as well as cuffs for arms and legs in Yekaterinburg, Ozersk, Magnitogorsk, Yaroslavl, Ufa and Kurgan.
We hope this article was useful to you! Play sports and be healthy with Powerfit96.ru!
Preparing for gymnastics at home
In order for therapeutic training to bring the desired effect, you need to follow a number of rules:
- Exercises should be done regularly.
- Start classes no earlier than 2 hours after eating.
- It is necessary to stretch the muscles and joints before starting classes (rubbing, circular movements of the body).
- After completing the workout, take a shower and rest for about half an hour.
- When doing gymnastics, breathe deeply and evenly, without holding your breath for long.
Exercises against night pain
Sometimes the pain syndrome may not bother you throughout the day, but before going to bed, aching pain appears in the lower back.
Bubnovsky exercise with back bending
| Take a lying position on the floor, position your legs so that they are higher than your head, for example, on a chair. Bend your knees and place your hands behind your head. You can put cold under your lower back, for example, wrap ice in a thick cloth. Lifting your chest off the floor, reach forward with your arms and lift your body toward your legs 10 times. |
| Take a position on all fours. Arch your back and round it upward, like a cat. Repeat the movements as long as your health allows. |
Next, for the lesson you will need an expander. Attach an expander to the wall and sit under it. Pull the free end of the exercise machine, securing it to your leg.
Repeat cyclic exercises. With the right leg – lift – bend – straighten – lower. Repeat the same with the other leg. Perform 10 times on each limb.
Prevention for the spine during sedentary work
A sedentary lifestyle, including at work, can cause problems with the spine. Often, in order to relieve pain, a person is forced to take a comfortable position. In such cases, Dr. Bubnovsky advises regularly performing the following set of workouts that help stretch the muscles of the back, buttocks and legs. Exercises can be done both at home and at work.
| Stand straight, feet shoulder-width apart. Tilt your body forward and grab a support with your hands (the back of a chair, a window sill). Look straight ahead. Perform several movements with your torso downwards, stretching the spinal column. Exhaling, release the support, bending lower towards your feet. Try to lower your head as close to your knees as possible, try to stick it and your arms between your legs, but do not bend your limbs. Take the original position. Perform several repetitions. |
| Place your straightened leg on a table or windowsill. Exhaling, bend over to the limb as close as possible, trying to lie with your torso on your thigh and clasp your toe with your hands. Slowly straighten up and repeat the same with the other leg. |
| Lie on your stomach, stretch your arms forward. Raise your torso, pushing off the floor with your hands and, as you exhale, throw your head back. You need to bend as much as possible. Fix the position for 5 seconds and take the original position. Repeat 5-10 times. |
| Take a standing position with one leg forward. Exhaling, bend your torso towards it, trying to reach the sock with your hands. You need to stretch as far as possible for 7 seconds. Legs remain straight. Slowly straighten up, keeping your back and legs straight. Repeat the same with the other leg. |
Regularly performing exercises based on the Bubnovsky technique will strengthen the spinal column and eliminate pain. Before you start exercising on your own, consult your doctor.
Medical opinion
In diseases of the musculoskeletal system, good results can be achieved without the use of medications. For example, with a hernia of the lumbar spine, the prescription of tablets and injections will only give a temporary effect. The main element in the treatment of diseases of the spine and joints is proper gymnastics.
For persons with an existing hernia of the spinal column, training activity should be dosed and correct. You shouldn’t do the wrong exercises on your own and overexert yourself.
To combat the disease, entire complexes of therapeutic exercises have been developed. Doctors unanimously say that exercise therapy is an effective method of treatment, and the result depends on the patient’s desire, effort and discipline. By following the recommendations and performing exercises regularly and correctly, you can achieve lasting improvements in health.
But still, as with any type of treatment, gymnastics has contraindications:
- Exacerbation of the disease, with severe pain.
- Increased body temperature.
- Diseases of internal organs, provided that exercise therapy can lead to aggravation of the condition.
- Metastasis to the spine.
Treatment of vertebral hernias using the Bubnovsky method
Dr. S.M. Bubnovsky created and patented a special method of combating the pathology of the musculoskeletal system using a special device developed by him. This technique is called kinesiotherapy , which means treatment through movement.
Gymnastics for Bubnovsky's spinal hernia includes diverse exercises, the main requirements for which are convenience and comfort for the patient and high efficiency. The movements are repeated up to ten times. First, movement techniques, proper breathing, and concentration are practiced. Over time, the tempo and number of repetitions increase.
During the exercise, the abdominal muscles should tense, not the back muscles. The back muscles should work to stretch.
It is recommended to exercise 3-6 times a day, distributing the exercises into several groups. Bubnovsky also offers exercises that can be performed at home.
Sergei Bubnovsky published the book “Spinal hernia is not a death sentence!”, which will be useful to read for everyone who suffers from this disease.
Therapeutic gymnastics is aimed at activating a person’s internal reserves to combat chronic diseases. And in practice it works very successfully. Each exercise in the complex is specially selected and helps ensure the prevention and treatment of hernia, as well as eliminating pain and improving the general condition of the patient.
Experts are unanimous that Bubnovsky’s gymnastics for lumbar hernias is a very effective method of healing, and its result is largely determined by the desire, effort and discipline of the patient. Those who follow all the recommendations and perform the exercises correctly and regularly always achieve clear progress.
Please note that, despite the benefits of gymnastics, it has contraindications. These include the following:
- Exacerbations of the disease;
- Increased body temperature;
- Diseases of internal organs, if physical therapy can aggravate them.
- Metastases in the spine.
Therapeutic gymnastics activates important biochemical processes in all segments of the spine (in particular in the intervertebral discs), normalizes blood circulation and lymph flow.
Pain-relieving exercises according to Bubnovsky for lower back hernias work out the deep muscles of the spine. Gymnastics helps relieve spasms and relieve pain, improves flexibility and mobility of the spine, reduces salt deposits, and improves blood circulation. Correctly selected movements help to stop the development of a hernia, reduce its size, as a result of which the deformed tissues gradually return to their natural position.
Exercises for Bubnovsky’s lumbar spine hernia involve following the following rules:
- You need to exercise every day, maybe several times a day. If possible, it is recommended to train at the same time.
- Exercises must be performed correctly from a technical point of view. Sudden movements, jumps, jerks, and excessive loads on the spine are not allowed.
- The duration of classes, amplitude and number of repetitions should be increased gradually.
- At the end of the workout, you should feel only slight fatigue, which indicates proper and effective work. Severe fatigue is unacceptable.
- When performing exercise therapy, concentrate on the area where the hernia is located and monitor your well-being. If pain and discomfort in the lower part of the body intensifies, numbness, weakness, or a feeling of “pins and needles” appear, stop exercising and visit your doctor.
Recommendations and rules
Before starting therapeutic training, you must adhere to the rules for their implementation:
- Gymnastics should be done daily, preferably several times a day.
- Perform all movements correctly, avoid sudden movements, jumps and jerks.
- Gradually increase the duration, intensity and number of repetitions during exercise.
- Avoid excessive fatigue during exercise.
- When performing gymnastics, you need to concentrate on the location of the hernia. If pain intensifies during exercise, or a feeling of numbness appears in the lower back, you should stop exercising and consult a doctor.
Types of vertebral hernias
Spinal hernias, like most neoplasms, have their own classification.
The location of hernias depending on the part of the spine, the cause and size of the hernial protrusion
The following groups are distinguished:
Division in relation to the parts of the spinal column in which the hernial protrusions are located:
- lumbar region – 65%;
- ore department -31%;
- cervical region - 4%.
The frequency of a hernia in a specific location is determined by the load carried by a certain segment of the spine, as well as its mobility.
Primary and secondary hernial protrusions:
In this section, the division of hernias is determined by the cause of their occurrence.
- Primary hernias occur due to traumatic injury, as well as excessive physical exertion.
- Secondary hernial protrusions are formed due to degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs and destruction of their structure.
According to the size of the fragment protruding beyond the intervertebral space:
Hernias can protrude beyond the space between the vertebrae.
- Protrusion – disc protrusion up to 1-3 mm.
- Prolapse – disc prolapse up to 3-6 mm.
- Hernia developed up to 15 mm.
It is necessary to take into account that the same size of hernia has a different clinical formulation when it is located in different parts of the spinal column:
- in the cervical region, the hernia is considered small up to 2 mm, in the lumbar region - up to 4 mm.
- medium size - up to 4 mm in the cervical and up to 7 mm in the lumbar.
- large size - up to 6 mm in the cervical and up to 9 mm in the lumbar.
- huge size - up to 8 mm in the cervical and up to 9 mm in the lumbar.
According to anatomical classification:
The anatomical division of hernias is determined by their effect on neighboring organs, spinal tissues or nerve endings.
Free hernia
When part of the contents of the intervertebral disc penetrates the posterior longitudinal ligament, which supports the spinal column in an upright position, but the connection with the disc remains.
Vagal hernia
A deformity in which the connection between the protruding fragment and the intervertebral disc is lost. A hernia is dangerous because if it is present, autoimmune inflammation may develop due to the compressive effect on the spinal cord tissue.
Acute pain in the back and joints (osteochondrosis, lumbago, radiculitis, sciatica)
Thanks to statistics, it is known that every fourth person on the planet after thirty years of age suffers from acute pain in the back and joints such as osteochondrosis, lumbago, sciatica, sciatica . This is mainly manifested by rapid fatigue, joint stiffness, discomfort or pain in the back during prolonged sitting/standing, aching back pain at rest, reduced ability to work due to impaired mobility of the spine associated with degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs (protrusion, hernia, etc.). ).
The main causes of back and joint pain are a sedentary and unhealthy lifestyle, as well as prolonged stay of the body in uncomfortable positions from the point of view of physiology and biomechanics of the skeleton. This means that the spine and joints suffer due to the fact that we do not use our body correctly, distribute the load disproportionately, overload some anatomical links without including others. For example, a modern person, starting from the age of six, spends more than 6 hours a day in a sitting position (depending on his profession): we sit at a desk at school, at home watching TV, driving or at work at the computer, etc. Important factors are weight lifting, professional sports, as well as physical labor of a monotonous nature, which also overloads the same areas of the body. The spine or joint wears out and becomes more fragile due to the fact that muscles in a state of overwork cannot perform a protective function, and with increased loads, injuries and deformations of the skeleton can occur, leading to both acute and chronic pain in the back and joints. Therefore, we can conclude that pain in the back and joints is never accidental.
It is also worth noting that in order to prevent back pain, you should not stand bent over for a long time or read while lying in bed, or perform any non-standard actions. It is important to learn how to rationally distribute the load throughout the body, strengthen those areas that are not worked out in everyday life, and unload those areas that are overloaded due to the profession. Local and multifunctional strength and decompression simulators are excellent assistants in this regard. The simulators are designed according to the laws of skeletal biomechanics and, when used correctly, create conditions for high-quality muscle work.
Considering that there are about 700 muscles in the human body, and each of them must work in its own motor mode, you need to correctly navigate how to distribute the load so as not to overload a muscle or relax it if it is in spasm from overwork. Specialists in kinesitherapy have been dealing with these issues for more than 15 years (method of Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. S.M. Bubnovsky) and select individual recovery programs for people of various professions that help not only eliminate pain in the back and joints, but also significantly improve the quality of life. Treatment and health programs are compiled strictly individually, taking into account age, gender and the presence of concomitant diseases. By learning to use exercise equipment as a healing tool with the help of professionals, people free themselves from the need to take painkillers and gain knowledge that will help them further extend the life of their skeleton and gain freedom in movement.
The coordinates of the Centers can be found on the contacts page.